Method Definition
Enucleation of the eyeball is a procedure for removing the eye. The patient is under anesthesia during the operation; it can be either local or general. The intervention takes place in a specially equipped hospital, where all conditions for the provision of services of this type have been created.
Enucleation of the eyeball – removal of the visual organ, is carried out under anesthesia.
Complications of eye removal surgery
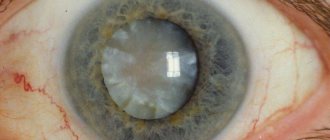
After eye removal, patients often experience anophthalmic syndrome, which is accompanied by: a significant increase in the volume of the conjunctival cavity, drooping of the upper eyelid, inclined position of the prosthesis in the orbit, inactivity or immobility of the ocular prosthesis, recession of the upper eyelid, atony and sagging of the lower eyelid.
Attention! The description of this operation is provided for informational purposes. Our clinic does not currently perform eye removal. You can find a list of available surgical interventions in the “Moscow Eye Clinic” section. You will be able to undergo an examination using the most modern diagnostic equipment, and based on its results, receive individual recommendations from leading specialists on the treatment of identified pathologies.
The clinic is open seven days a week, seven days a week, from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. You can make an appointment and ask the specialists all your questions by calling
8 (800) 777-38-81 and 8 or online using the appropriate form on the website. [anchor href=»mgkl.ru/about/specialists/37"]Mironova Irina Sergeevna
Application area
The procedure is performed for iridocyclitis caused by trauma and there is a high probability of damage to the second eye. In addition to this, there are a number of factors in which enucleation of the eye is considered the only way to save a person’s life:
- Formation of harmful tumors in the eye.
- Atrophy of the eye organ.
- Severe eye damage due to trauma.
- High likelihood of sympathetic ophthalmia.
- Glaucoma, which is in the terminal stage.
- If the eye is completely blind, it is removed for cosmetic purposes.
- A blind eye that has pain and cannot be relieved.
Enucleation of the eye is used only for severe diseases or injuries associated with damage to the visual organ.
Pain relief before surgery
Removal of the eye occurs after the patient has been given an anesthetic. In children - general anesthesia. In adults, local anesthesia is used. Half an hour before surgery, the patient receives 1 ml of 1% morphine solution. Also, adrenaline with novocaine is injected through the thin skin into the lower eyelid. In some cases, the doctor anesthetizes the conjunctival membrane. At the same time, he injects novocaine with adrenaline next to the cornea (under the conjunctiva).
After the patient has received a dose of anesthesia, you must wait 5-7 minutes and you can begin the operation. There are cases when novocaine causes allergies in the patient. Then the doctor replaces this drug with another.
Carrying out the procedure
The operation is indicated for adults and children, but under different conditions.
adults are under local anesthesia, and children are under general anesthesia. 30 minutes before enucleation of the eye, the patient takes etaminal sodium 0.1 g, as well as diphenhydramine 0.05 g orally. 1 ml of Omponone is injected under the skin.
Dicaine is dripped in an amount of 1 ml at a concentration of 1% into the conjunctival sac, the novocaine solution is injected deep behind the eyeball. It is also used for the sclera in the conjunctival area, as well as for muscle tissue.
After the use of medications, surgery begins. The palpebral fissure is opened wide with an eyelid dilatation device. After this, grab the conjunctiva in the area of the sclera of the limbus with tweezers, and use scissors to cut it in a circle. The edge of the muscle is inserted directly into the area of the rectus muscle tendon, cut off not from the sclera itself, but stepping back from it a little in such a way as to preserve the part of the tendon to which the eye is attached.
Now the eye is slightly pulled forward, entering the wound from the inside of the eye using curved Cooper scissors, whose jaws are compressed, the surgeon feels the optic nerve. Next, this instrument is pulled back a little and, moving deeper again, this nerve is cut.
All that remains is to remove the oblique muscles in the area of the sclera and remove the visual organ from the eye orbit.
There is a cosmetic purpose for enucleating the eye. This is done to create mobility of the rounded stump. Having removed the eye in the manner described above, a piece of fat from the gluteal region is inserted into this place. They can also insert an eye-like implant that imitates a human eye.
The procedure for removing the visual organ is quite complicated. It is strongly recommended to follow all doctor's instructions.
Contraindications for surgery
Enucleation, like cataract surgery, has a number of contraindications. The patient should be warned about them before surgery. So, the main contraindication to enucleation is purulent inflammation, which is otherwise called panophthalmitis. Since such an inflammatory process can spread to the orbital area and then to the brain. Enucleation is also contraindicated in cases of general infection of the body.
results
After the eye removal procedure, the patient is under the supervision of a doctor. The essence of this method is to prevent the disease or injury from progressing, as well as to prevent serious complications.
Many specialists have achieved major cosmetic changes. They introduce various materials into the conjunctival area or into the sclera so that no depressing changes occur in the eye muscles.
The specialist will prescribe drops, ointments, and various gels to make your recovery as quick and painless as possible. Sometimes the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics.
As for the implant, it can cause inconvenience, but this happens in extreme cases. If it has been displaced, then repeated surgery is the only way to correct this situation.
What helps with stye on the eye?
Read this article about what to do if your eyesight decreases and what diseases we are talking about.
This article will tell you everything about Polinadim eye drops with instructions for use.
The patient is usually under the supervision of a doctor for up to six months. This is due to the fact that this is exactly the time required for the complete formation of the stump and orbital cavity.
The results of enucleation of the eyeball in most cases have a positive effect on the condition of patients. It is important to follow all doctor's recommendations.
Recovery after surgery
Extirpation of the eyeball is an organ-destructive operation. It requires a long recovery, since after it the patient becomes disabled. After the intervention, he is forced to spend a week in an ophthalmology hospital. The bandage is removed after an individual period for each patient - the question of its duration is decided by the attending doctor. After removing the bandage, the patient requires the help of a psychologist. After extirpation, a person has to partially change his life, since he must be doubly careful when crossing the roadway or performing work that requires increased attention.
Enucleation of the eye
For patients with visual impairments, attempts are being made to perform organ-saving surgeries.
Enucleation of the eyeball is done only when there is no other way out, and the developed pathological processes can lead to the spread of infection to the dura mater and cerebral cortex.
Removal of a human eye is performed primarily under general anesthesia, so intolerance to anesthesia will be a contraindication. But if the patient’s condition is critical, they resort to injecting the facial nerves with Novocain.
In wartime, the most common cause of mechanical damage to the organ of vision is mine-shrapnel trauma. The fragments enter the eye, forming numerous capillary ruptures.
What is the essence of this surgical intervention?
Enucleation of the eye is the removal of the eyeball from the orbit along with the optic nerve. Extirpation (complete removal) is performed in case of purulent processes in the orbit, severe destruction of the organ of vision as a result of traumatic, thermal or mechanical influence. It is preceded by specific preparation of the patient.
It includes drug compensation for his condition, stabilization of blood pressure and premedication. There are other ways to partially preserve the organ. These include organ-saving surgical intervention, which is called evisceration. But the function of vision is still lost.
Indications for surgery
The eyeball is removed if the patient has severe destructive changes in the eye orbit. The latter occur after traumatic exposure to the facial region of the skull.
Causes may also include elevated temperature, leading to burns of the cornea and underlying tissues, mechanical damage due to impact with a blunt object or the influence of a shock wave during an explosion.
In case of a total inflammatory process in the orbital area, the visual organ is also recommended to be removed. Extirpation is performed for the following pathologies:
If a patient develops acute choroiditis, surgery is prescribed to remove the eyeball to prevent infection of the cerebral veins.
- Purulent rhinitis or chorioretinitis. With it, acute inflammation of the retina occurs with the death of photoreceptors - rods and cones. The inflammatory process completely eliminates visual function, and the organ becomes unable to recover.
- Acute choroiditis. Here the pathological process involves the choroid plexus. Through the capillaries, the infection spreads to larger and deeper vessels, which leads to the risk of infection of the arteries and veins of the brain.
- Endophthalmitis. Pus in this pathology spreads to the vitreous body and ciliary structure. From here, bacteria are able to migrate into the meninges.
- Panophthalmitis. It causes generalized damage to the eye. Complications of this severe pathology are meningitis and meningoencephalitis.
Procedure behavior
Enucleation of the eye is performed under general anesthesia. Using a scalpel, the surgeon cuts through the soft tissue, retracting the upper and lower eyelids with special holders. Then the conjunctival sac is excised in an arcuate manner and the eyeball is lifted with a special spoon.
At the same time, the surrounding soft tissues of the sclera are separated. Surgeons are especially careful when extracting the optic nerve. The latter directly connects to the brain through the chiasma opticum - the ophthalmic chiasm.
It is removed by carefully cutting it under absolutely sterile conditions. All structures that have been removed are sent for pathological examination and then disposed of. Albucid ointment is placed into the orbit to sterilize the surgical field.
The resulting wound defect is covered with a pressure bandage.
Introduction to anesthesia
The intervention is performed under general anesthesia, and before this the patient is given medications to reduce the allergic reaction.
Eye removal surgery is performed under general anesthesia. Before it, the patient is premedicated with anticholinergics, anticholinergics, narcotic analgesics and antihistamines, which reduce the risk of an allergic reaction.
He also undergoes a special test for sensitivity to anesthetics. Some patients react to the administration of anesthetic drugs in an anaphylactoid manner. If there is a risk of developing anaphylactic shock, the intervention must be abandoned.
Less often they resort to an alternative method - injections of the Novocaine solution, which are given at 4 points, at different angles of the orbit.
Side effects
After removal of the eyeball, patients may develop neurological disorders and infectious complications. The first arise as a result of vision deficiency.
Patients in the postoperative period often experience optical illusions in the form of flickering, luminous geometric shapes or other artifacts. The infection can be caused by a surgeon who does not fully comply with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis.
Infectious infection is dangerous because it can spread through the optic canal to the meninges and cerebral cortex.
At the V. P. Filatov Institute of Eye Diseases and Tissue Therapy of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine, technical means for removing intraocular foreign bodies were developed and introduced into practical ophthalmological surgery. These developments are also widely used in extirpation of the organ of vision.
Recovery after surgery
Extirpation of the eyeball is an organ-destructive operation. It requires a long recovery, since after it the patient becomes disabled. After the intervention, he is forced to spend a week in an ophthalmology hospital.
The bandage is removed after an individual period for each patient - the question of its duration is decided by the attending doctor. After removing the bandage, the patient requires the help of a psychologist.
After extirpation, a person has to partially change his life, since he must be doubly careful when crossing the roadway or performing work that requires increased attention.
Source: https://EtoGlaza.ru/hirurgia/enukleatsiya-glaznogo-yabloka.html
Enucleation of the eyeball in humans: indications, implementation
The phrase “enucleation of the eyeball” sounds completely incomprehensible to a person who is far from medicine. But “removing an eye” is much clearer and simpler. But it's the same thing.
What is enucleation
Enucleation of the eyeball is an operation that is performed when it is no longer possible to save the eye, and its very presence in the skull can cause damage to a person. Sometimes the procedure has cosmetic purposes, but more often it is intended to save the body from the effects of inflammation or a malignant tumor.
How is the procedure performed?
Preparation for the operation is standard - do not smoke, do not drink alcohol for two days, do not take medications that can affect blood clotting. On the morning of the operation, do not have breakfast and take a shower.
The patient is usually admitted to the hospital the evening before surgery. In the morning they are taken to the operating room and anesthesia is administered - for children it is always general, for adults it is either general or local. Then they proceed directly to the process:
- remove the eyelashes on the desired eye and cover it with a sterile napkin with a hole in the middle so that the surgeon has access only to the desired part;
- using a special apparatus, the eyelids are fixed in the open position;
- use a scalpel to cut off the eyeball from the bed - to do this, just circle it around the perimeter with a tip;
- a sharp surgical hook is placed behind the apple;
- cut off the muscle fibers and nerve tissue that hold it in place;
- remove the apple from the bed with the same hook;
- stop bleeding with tampons soaked in an antiseptic solution and suturing the wound;
- Instill an antiseptic into the wound and apply a pressure bandage over it.
To create the impression that there is an eye in the socket, a piece of fat taken from the same patient is inserted into it. Or, which is now being practiced much more widely, an artificial eye is inserted into it.
The prosthesis can be made of plastic or glass. It imitates a real eye quite accurately, creating an illusion that is destroyed only if you look closely. The prosthesis is selected individually, according to the patient’s measurements.
Contraindications
Since the operation is a weapon of last chance, there are few contraindications to it and these do not include childhood, pregnancy, or pathologies of internal organs. There are actually only two of them:
- Extensive infectious inflammation. If it is localized in the eye, then the pus can enter the brain and cause encephalitis. If in other organs, then the body simply cannot cope with the consequences of the operation and it will not be possible to avoid complications.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases. The same problem - the body, weakened by the fight against the disease, will not be able to recover normally after surgery.
But both of these contraindications are temporary. The infection is brought down using antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, the exacerbation is stopped, again putting the disease into remission. And then they carry out the operation.
Postoperative period and complications
When the operation is performed, the patient remains in the hospital for at least several days so that doctors can monitor how his recovery period progresses.
During this period, he is prescribed antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and antiseptics, which will prevent possible infection. Meals should be small, food should be light. It is recommended to sleep on your back to avoid damaging the seams.
Additionally, the doctor can, and most often prescribes, painkillers that relieve pain.
Further recovery takes about six months. Active period – up to two months.
At this time, you cannot take baths or go to the sauna, swim in the sea or in the pool - only shower. Do not touch the sore eye with dirty hands, do not bend over sharply and lift heavy objects.
Physical activity is contraindicated - all but minimal, such as walks in the park. Nutrition should be correct, sleep should be at least eight hours.
It is recommended not to overstrain a healthy eye, otherwise it may also get sick.
During recovery, you need to visit a doctor and monitor the process. If something goes wrong, the doctor will notice and be able to adjust the treatment.
Complications are quite rare. Among them:
- inflammation of the tissues in the operated eye socket - fraught with pain and blood poisoning, which can be treated with antibiotics;
- bleeding is normal in the first few days, then it can also be controlled with medication;
- swelling is normal in the first days, then it needs treatment;
- an allergic reaction to a medicine - this is rare because all doctors first ask patients if they are allergic to anything;
- encephalitis - if the inflammation was not stopped in time and managed to reach the brain.
If the patient has been given a prosthesis, it may move relative to the place where it should stand. Then it is corrected during a surgical operation - and then it is fixed more reliably.
If fat was placed in the patient's eye socket, it may be rejected by the body. Then they take it out, let the inflammation go away and try again.
If a patient worries about his appearance, he may become depressed. A psychotherapist and support from loved ones will help here.
In general, the operation is not considered the most dangerous. If a person follows all the doctor’s instructions, takes the recommended medications and does not try to carry weights, the eye socket will heal quickly.
Source: https://oculistic.ru/protsedury/operacii/chto-takoe-enukleatsiya-glaznogo-yabloka-i-kogda-ona-provoditsya