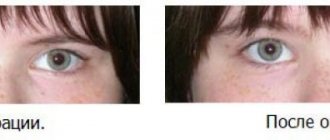
Strabismus is usually called a deviation of the visual axis due to weakness or improper functioning of the muscles of the visual organs, which are responsible for correctly focusing the pupil on an object.
This disease can leave consequences, so any parent will be interested in how to determine strabismus in a child and the ability to do it themselves at home.
For such purposes, there are indeed several tests that can be carried out with children, but none of the tests will show a 100% result that the child has strabismus, because high-quality diagnostics should be carried out exclusively in specialized institutions under the supervision of experienced doctors.
Strabismus in children
How to determine strabismus in a child?
Source: glavvrach.com Another common visual disorder in children is strabismus. However, strabismus itself is extremely rarely an independent disorder. Most often, strabismus is a concomitant phenomenon of diseases such as astigmatism and farsightedness.
And in especially severe cases, divergent strabismus in children is a consequence of myopia. Parents should remember that children's strabismus is not just some kind of cosmetic defect, but a severe disruption of the functioning of the entire visual apparatus.
Normally, the human visual system has a structure in which two different images from the two eyes enter through the visual channels into certain areas of the brain, where they are reunited into a single whole.
And only with the correct, well-coordinated work of the entire visual apparatus, the picture acquires the correct clear outlines, thanks to which a person sees objects from the correct angle, and it is also possible to adequately navigate in space.
A baby who has just come into our world is still, in principle, unable to look and see clear objects. The ability to see with both eyes (binocular vision) develops gradually in a child, finally becoming fully formed only by the age of 4–5 years.
I would like to remind you that at this age all children are also susceptible to physiological myopia, which is directly related to the development of strabismus. Therefore, treatment must be exclusively comprehensive - only in this case is it possible to achieve positive dynamics.
Most often, strabismus is diagnosed in children aged three to five years, however, strabismus in infants is quite common. As a rule, the first to notice symptoms of trouble are parents of children, who spend all their free time with their children.
Many parents ask how to determine strabismus in a child. In fact, if a child does develop strabismus, you will immediately notice it with the naked eye, even without special education.
And if you notice that your child is squinting even a little, rush to seek help from a pediatrician - an ophthalmologist for advice as soon as possible.
You should not be afraid that you will bother the doctor in vain - when it comes to the child’s health, it is much better to be safe than to miss the onset of any disease. Not a single doctor will refuse to help you or blame you.
After all, only an ophthalmologist knows how to treat strabismus in children. Correcting strabismus in children is a labor-intensive process and requires a lot of effort, both from the doctor and from the parents.
How can strabismus be detected in schoolchildren?
The Amsler test is suitable for school-age children. It is a drawn grid with a dot in the center. Swiss ophthalmologist Mark Amsler, the creator of the test, explained how to check for the presence of strabismus in a child in this way. The sheet with the drawn grid should be placed at a distance of at least 30 cm from the child’s eyes. First he must look at the image with both eyes. After this, he needs to do the same, but closing his eyes one by one. During the test, the child must concentrate on the dot and the grid equally.
If in both cases the child describes the same image, he has no deviations in the functioning of the visual apparatus. If he says that the grid seems blurry or uneven to him, then, most likely, strabismus is developing. If the test results are unsatisfactory, parents need to register their child with an ophthalmologist.
Classification
Ophthalmologists offer several classification options for this type of disease. The most common is the division into three main subtypes: imaginary strabismus, esotropia and exotropia.
- Imaginary strabismus
- Esotropia
It is observed in children under one year of age. It is characterized by the anatomical feature of the eyelids, the presence of skin folds in the peripheral zone of the cornea of the eye with a relatively wide bridge of the nose. The fold covers some area of the eye, and a visual effect is created from the side as if the baby’s eyes are looking in different directions.
With age, the child “outgrows” this anatomical defect and not a trace remains of strobism. That is, if a specialist determines that a child has imaginary strabismus, then parents should have no reason to worry, this is not a disease.
The pupil deviates towards the nose. There are two subtypes of esotropia: congenital and accommodative.
- Congenital esotropia is a pronounced heterotopia caused by genetic predisposition. Identified in babies aged 0 to 6 months. A peculiarity of this type is that during periods of deterioration in health or during times of fatigue, the child experiences an increase in the effect of a squinted gaze.
- Accommodative esotropia, detected in children aged eight months to four years, is usually a concomitant disease - childhood ametropia (farsightedness). A child, when examining an object at close range, strains the muscles of the eye, and a deviation occurs. It is at these moments that strabismus most clearly manifests itself. That is, there is a direct relationship: the more often the child examines small objects at close range, the better the disease is expressed. The dynamics of this type of strabismus are varied, from rapid deterioration to a relatively low rate of development.
- Exotropia
The eye deviates towards the temple. As a rule, this type of strabismus begins to appear in children aged one year. It may be temporary or permanent. Unlike the previous case, it occurs when the patient peers into the distance for a long time, but when examining objects close up, it is either barely noticeable or disappears altogether. In this case, the child may experience headaches, the object of observation may split in two, and tearing appears.
What's happening?
There are two forms of strabismus - concomitant and paralytic. In the case of concomitant strabismus, either the left or the right eye squints, while the magnitude of the deviation from the central axis is approximately the same. This type of strabismus is most often associated with the peculiarities of the eye structure, is inherited and manifests itself mainly in children.
Paralytic strabismus occurs due to damage to the extraocular muscles, or as a result of disease of the optic nerve. In this case, one (healthy) eye squints. When a person examines an object, his diseased eye moves poorly or does not move at all, while the healthy eye has to deviate to a greater angle. Strabismus can be:
- convergent (often combined with farsightedness), when one of the eyes deviates towards the nose;
- divergent (often combined with myopia), when one of the eyes deviates towards the temple;
- vertical when the eye squints up or down.
Most likely, those around you will be the first to notice strabismus, for example, the child’s parents or peers in kindergarten or school. An adult will be hinted that there is something wrong with his eyes; their position constantly or periodically becomes asymmetrical. At the same time, the patient himself begins to worry about double vision, dizziness and headaches. Instead of a three-dimensional image, he sees a flat one, and notices a decrease in visual acuity in the squinting eye.
Strabismus that develops in childhood can affect the formation of the child’s psyche. Children's perception of the world around them is disrupted, and physical and mental development may slow down. A common complication of strabismus is amblyopia (“lazy eye”) - a sharp drop in vision in the squinting eye as a result of insufficient visual load on the eye muscles.
Is strabismus always noticeable with the naked eye?
Strabismus can be vertical, divergent and convergent, most often with one or both eyes clearly squinting. However, there is also a hidden form of childhood strabismus, which is not outwardly noticeable. It occurs due to muscle imbalance and is dangerous because it causes rapid eye fatigue.
This, in turn, leads to myopia. The disorder develops in the first months of life, and can manifest itself more clearly in the third year of life, when the child is interested in activities that require visual strain - modeling, drawing.
Sometimes strabismus is observed in newborns. This is due to weakness of the eye muscles and is normal. The reason for contacting an ophthalmologist is the presence of obvious strabismus in a child older than six months.
How can strabismus be detected in children?
The first check of a child's vision is carried out in the maternity hospital, in the first days after birth. This examination allows the doctor to determine whether the baby has strabismus or not. If a study confirms that a baby has strabismus, it does not mean that this form of pathology is hereditary. Many newborn babies have strabismus, but it is considered natural. This is due to the fact that in the first months of life the baby is not able to fix both eyes on one object at the same time. The eye apparatus begins to work after birth. Due to the fact that its physiological formation is taking place, and the size of the eyeball is still too small, many children develop heterotropia.
By about three months, the child can already recognize his parents. At this time, the senses try to combine the information received. Vision remains quite low. Usually by five months, ophthalmologists note a decline in strabismus. At this age, the baby can already concentrate his gaze on rattles and other objects of interest to him. A child older than six months begins to develop three-dimensional vision. During this period, the baby’s brain can combine visually received information into a single picture. If the child's strabismus persists at this stage, parents need to take measures to correct this visual disturbance. It is not so easy for parents to determine strabismus at home. For such diagnostics, you need to know the rules for its implementation and basic techniques. It is best to see an ophthalmologist for a vision test. The doctor should analyze the baby’s general health, paying special attention to symptoms such as:
- restlessness, moodiness;
- sudden mood swings;
- formation of a venous network on the head;
- increased head size or rapid growth;
- decreased appetite or refusal to eat.
If these symptoms are present and the examination results are positive, the ophthalmologist can clearly answer the question of whether the child’s strabismus was temporary or permanent.
What should you pay attention to first?
Recently, more and more often, ophthalmologists have to diagnose various visual impairments. Very often, doctors diagnose strabismus in children under one year of age.
This is influenced by a huge number of different factors, including the environmental situation, computers and televisions, which have become firmly established in the life of a modern person, complications during the mother’s pregnancy, and many others.
The factor of genetic predisposition is also important - vision problems often tend to be passed on from generation to generation, from children to parents.
If the baby’s parents have any vision problems, be it myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism or strabismus, there is a fairly serious risk that their child will also have a tendency to the same diseases.
That is why parents with vision problems should treat their baby’s vision as carefully as possible. After the baby reaches three months of age, parents should definitely go to an ophthalmologist to get the first consultation in the baby’s life.
Most often, a referral to an ophthalmologist is given by the pediatrician who is observing the baby. However, if for some reason your pediatrician did not give you a referral to an ophthalmologist, do not hesitate to remind him about it yourself.
An ophthalmologist will carefully examine your baby and conduct the necessary examination, which will help the doctor identify possible visual impairments. If the baby has any problems, the doctor will tell the parents what needs to be done next.
And if the child needs treatment, it is the ophthalmologist who will write out the treatment regimen or refer him for hospitalization to a specialized hospital. If no one in your family has had any problems with vision, the baby’s first visit to the ophthalmologist should be at six months.
After this, if the ophthalmologist does not detect any violations, the next visits will take place as planned, during preventive examinations of the child. In no case, if the doctor says that the child’s vision is fine, do not ignore subsequent visits.
As you know, not all vision problems are congenital - many eye diseases are acquired over time, under the influence of a huge number of adverse effects on the baby’s eyes.
You should also draw the attention of parents to the fact that in no case should you completely rely only on doctors. Firstly, you won't visit an ophthalmologist every week, will you?
And secondly, individual symptoms of some diseases can only be noticed by parents who spend almost all the time with their child. Therefore, mothers and fathers must be extremely attentive and watch the baby.
Ophthalmologists, as a rule, tell parents about which aspects of children's vision need to be paid special attention to. Below we have described the main ones - read carefully and try to remember this information. So:
The baby's reaction is not bright
Almost all young mothers have more than once observed the following picture: the light turns on in the child’s room, and the child immediately reacts to this - he turns his head away, closes his eyes and shows other signs of dissatisfaction. This reaction is the physiological norm.
By closing his eyes, the child thus instinctively protects his eyes, helping them adapt to bright light. But if the baby does not react in any way to bright lighting, especially to a light suddenly turned on in a dark room, parents need to be wary.
In this case, there are two acceptable explanations: either you are lucky and you are the parents of an unrealistically calm child, or, what is more likely, your baby has certain vision problems.
To find out if this is so, try to casually direct a beam of light directly into the baby’s eyes and hold it for 1 - 2 seconds. Never let sunbeams into your baby's eyes - this can damage the retina.
If in this case the baby does not react in any way to the bright light, parents should seek help from an ophthalmologist as soon as possible and show the child to him. The doctor will examine the child and accurately diagnose or, on the contrary, dispel your fears and concerns.
Recognizing your toys
Pay attention to whether your baby can independently find his toys - rattles, balls, dolls. If the child’s vision is fine, he will recognize his toys even from a distance. Moreover, the child should see them equally well with both eyes - both right and left.
If your child is old enough, you can try to test your vision yourself - show him an object and ask him to name it. After that, move on to smaller details - for example, ask to tell what color the wheel of the car is or find out if there is a pocket on the doll's skirt.
But even if the baby is not yet big enough and cannot yet maintain a dialogue, attentive parents are able to notice that not everything is in order with the baby’s vision.
For example, some parents whose children suffer from eye diseases say that a situation very often occurs when the child persistently reaches out to an object that interests him. But as soon as you give him the object, the baby throws it and may even cry.
This happens because the baby is disappointed, since the item turned out to be not at all what the baby wanted to receive. If this periodically happens to your baby, be sure to consult an ophthalmologist.
Squinting your eyes
Have you noticed that sometimes, when looking at some objects that are at a great distance from the child, your baby begins to squint his eyes?
Try asking him a few leading questions that will allow you to understand whether the child sees these objects. If the child cannot answer these questions, or complains that he sees poorly, take this into account and show the child to an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Assessing the location of various objects
A very important factor in good vision is the child’s ability to follow a moving object with his eyes without losing it from his field of vision. Even very small babies discover this skill by following their mother, a rattle or a mobile phone with their eyes. If your baby fails to do this, show him to the doctors.
Moreover, please note that you need to consult not only an ophthalmologist, but also a neurologist, since the child’s inability to follow objects with his eyes may also indicate the presence of disturbances in the normal functioning of the central nervous system.
Red eyes, watery eyes
If the child's eyes periodically look inflamed and red, pay attention to whether the child's eyes are overloaded - perhaps he spends too much time in front of the TV or at the computer? Or maybe he cried recently?
If the eyes turn red periodically, and for no apparent reason, this is also an alarm signal for parents - be sure to consult an ophthalmologist, who will help determine the cause of regular eye inflammation.
What is strabismus
Strabismus, or, as it is scientifically called, strabismus, is a violation of the synchronicity of the eyes. This is mainly a childhood disease, but also occurs in adults. The age of the patient plays a huge role in the success of treatment. The longer strabismus is not treated, the worse the recovery of binocular vision, even after surgery.
12 extraocular muscles are involved in the movement of both eyeballs, 6 for each eye. Each muscle is responsible for turning the eye in one direction or another, up or down. At birth they are not synchronized; the child learns to look in the process of acquiring visual experience. Therefore, strabismus up to 6 months is natural and considered normal.
As the brain grows older, it learns to perfectly match the images received from the right and left eyes. Thanks to this, binocular (three-dimensional, three-dimensional) vision is formed. It is binocular vision that is responsible for hundredths of degrees of the ideal location of the eyeballs. This quality is acquired, that is, in the absence of a double visual image during the formation of vision, a person will never learn to see correctly again.
Mild strabismus is hardly noticeable, is usually detected by chance, and is easy to eliminate. Severe advanced strabismus is often associated with disturbances in the optic nerves in the cerebral cortex, which is not always treatable.
If the image quality in one of the eyes is impaired, the brain switches to the second eye, which sees more clearly. In this case, the lagging eye begins to be suppressed, squinted, or completely excluded from the vision process. This is how amblyopia, or “lazy eye,” develops.
With amblyopia, the visually impaired eye completely loses its functions over time, which leads to blindness even after correction. There is no cure for adult amblyopia. The quality of vision can only be fixed, stopping the progression of adult amblyopia at the level at which treatment began.
The video below shows more clearly what strabismus is:
Read more about the features of childhood strabismus here.
How do cross-eyed people see?
In order to clearly see an image with a healthy visual apparatus, the eye needs to fix it in a certain visual zone on the retina. This is called focusing the image.
Ideal focusing is achieved at a certain point where the axes of both eyes intersect, which gives the same, clear, three-dimensional image. We get two images of the same object on both sides. This information is transformed in the brain and gives us an understanding of the thickness, depth, and volume of an object.
The world a person sees with strabismus is flat. The dominant eye is fixed correctly on the object, while the squinting eye gives a completely different picture, from a different angle, without clarity, as if in fog. Therefore, it is suppressed and only one image remains - a two-dimensional one.
In the initial stages of strabismus, with binocular vision still preserved, objects appear double. At first, the borders and outlines become double, and over time, as the angle of strabismus increases, the entire image becomes double. Gradually, double vision is suppressed by the brain and turns into a flat image.
Is strabismus inherited?
Many parents ask: “Can strabismus be inherited from the father or mother?” Definitely not, there may be a genetic predisposition to this disease, for example, weakness of the extraocular muscles or the structure of the eyeball, but the pathology itself is not transmitted.
All congenital types of strabismus are intrauterine problems with the development of the fetus, under the influence of some external factors. In its pure form, strabismus is not formed and is not transmitted.
Also, the second option for predisposition to strabismus may be inherited eye diseases, which in the future will cause the development of strabismus. The only thing worth paying attention to if parents suffer from strabismus is early prevention and regular examination of the child by an ophthalmologist.
Can the disease appear in adulthood?
You can acquire strabismus at any age, as it is a complication of many eye diseases, visual strain, injuries, and general systemic diseases of the body.
Binocular vision is formed before the age of 14. If strabismus is not treated during this period, there is nothing that can be done to help it at an older age. The quality of vision is not corrected in any way, and the operation will only help temporarily eliminate the defect of deviation of the eyes from the point of fixation.
If strabismus develops in an adult against the background of normal vision formation in childhood, then timely treatment will restore the sharpness and external aesthetics of the visual apparatus.
Can the disease go away on its own?
Depends on the reason that provokes it. Eliminate the cause and strabismus goes away. There are different cases, there is hidden strabismus, which, due to binocular vision, is not distinguished by a clear violation of the visual axes. Wearing corrective optics in the early stages completely eliminates the external defect.
The development of strabismus is not an independent disease; most often it is a consequence of another disease. Therefore, people with strabismus treat asynchrony of the eyeballs only as one of the stages of the general treatment of another “main” disease. Strabismus does not appear or go away on its own.
Causes of the disease
- Microphthalmos (shrinkage of the eyeball);
- corneal opacities;
- cataract (clouding of the lens);
- iris coloboma (congenital absence of part of the eye shell);
- uveitis (disease of the uvea);
- above average astigmatism (impaired shape of the lens or cornea), myopia and farsightedness;
- dysarthria or paresis (partial disconnection of muscles from the nervous system);
- paralysis;
- traumatic brain injury;
- infectious disease (influenza, diphtheria, scarlet fever, measles, etc.);
- abnormal development of the eye muscles and other eye diseases;
- stress;
- severe fear;
- somatic diseases (asthenia, neuroses, affective disorders, etc.).
Can strabismus be inherited?
If one of the parents or one of the child’s immediate relatives suffers from strabismus (heterotropia), then there is a possibility that the child will develop this disease. That is why children prone to developing strabismus need to be regularly observed by a pediatric ophthalmologist for timely detection of pathology.
This is because some vision defects, such as abnormalities of the eye muscles or improper attachment of the eye muscles, can be inherited.
What are the causes of strabismus in children?
The causes of strabismus in children can be different - genetic, a consequence of birth trauma or even mental disorders. We will look at the main ones. In addition to genetic factors, the most common cause of strabismus in a child is pathology of pregnancy and childbirth.
Due to fetal hypoxia, as well as due to birth trauma to the cervical spine or brain, innervation is disrupted and the extraocular muscles are deviated from the visual axis. At the same time, myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism can provoke the development of strabismus in a child.
Head injuries, eye surgeries, mental disorders and brain diseases can also cause strabismus in children. There are cases when this pathology occurs in a child after he has had the flu, measles, diphtheria or scarlet fever.
Apparent strabismus
Often, when parents go to the doctor, they complain about their child’s strabismus, but after examination the doctor does not detect it. This happens, as a rule, due to the congenital epicanthus, the structure of the skull or the wide bridge of the nose.
Apparent strabismus is more likely to disappear with age as soon as the skeleton begins to change. To determine hidden strabismus, you can try a cover test.
In this case, when the child has both eyes open, strabismus is not observed, but as soon as one of them is closed, the other begins to move to the side, and when opened, returns to its place. The main condition for this method is this: the child must look at the object that is being shown to him.
At 3 years of age, in addition to the above methods, visual acuity is tested using a table with or without glass correction. The state of binocular vision can be determined using a color test.
Color test technique
The study is carried out using a special disk with luminous circles of different colors located on it (1 red, 1 white and 2 green). The child wears glasses specially designed for this purpose with red glass on the right and green on the left.
Thus, the eyes see the color that is in front of them, that is, the right one is red and the left one is green. The white ball appears as one of two colors due to the filters placed in front of the eyes.
If the baby does not have any visual impairments, he will see 4 circles (either 2 red and 2 green, or red and 3 green). If one eye of a child turns off, he sees 3 green or 2 red circles (monocular vision). If the baby has alternating strabismus, he will see either 3 green or 2 red.
Determining the amount of phoria
An assistant will most likely be needed to perform this test. The chair is installed so that the distance between the eyes and the glass surface is a multiple of one meter (for example, 1, 2, 3 or even 4 or 5 meters) - the greater the distance, the more accurate the study. Then you need to do everything as when determining the direction of the phoria.
Be sure to mark on the glass the points at which images of the object appear when you open your right and left eyes alternately. This will be done by the assistant, who will be shown the position of these points using a laser pointer. Afterwards, it is necessary to measure the distance between these points in order to calculate the numerical value of phoria (r). This is done in the equation r = l/L, where l is the distance between the points, measured in cm, L is the distance between the eyes and the glass surface in meters.
For example, the study was carried out from a distance of 3 meters, that is, L = 3 m. The distance obtained between the points is 30 cm, that is, l = 30 cm. We substitute the data into the equation and get r = 30/3, that is, 10. The phoria value is 10 prism dioptres.
Since one prism diopter is approximately 0.5 degrees, the phoria value, measured in degrees, will be 5 degrees (10 x 0.5).
If you discover a deviation in the correct position of your eyes, contact a professional: this will allow you to quickly identify the cause of strabismus and cure the disease, avoiding the development of serious complications!
How to identify strabismus and what signs does it have? These questions concern thousands of people. Adults and children experience strabismus. With this disorder, there is a deviation from the visual axis, as a result of which eye movements become uncoordinated. You can suspect signs of a disorder and identify the first symptoms of pathology at home. We will tell you how to do this further.
According to statistics, strabismus is quite rare in adults. More often it appears in childhood and begins to progress as one gets older.
Determining strabismus at home is quite simple. For this test, you need to sit in a comfortable chair with your head on the back or headrest. It is important to ensure that it does not roll when the muscles relax, otherwise the test results will be distorted.
It is best to use a chair with a headrest, but if you don’t have one, then a regular model that has a stable back will do.
After this, you need to close each eye in turn with your palm. The break should be only 3 seconds, during which time you can look at the object with both eyes. Try to keep your hands away from your face. If you do everything correctly, it will seem that the selected sign is seen by a person as if through a phantom palm. This effect is achieved thanks to binocular vision. In the presence of strabismus, it will be impossible to achieve such a result.
What will the patient's reaction be?
Before determining strabismus, you should familiarize yourself in advance with the reaction that occurs in sick people. If this disease is present, symptoms such as:
- The object selected for observation can change its position. It will give the false impression that it is moving or deviating when viewed with different eyes. In this case, the ophthalmologist will most likely diagnose hidden horizontal strabismus.
- Similar phenomena also indicate the presence of a latent form of strabismus. In such a situation, the picture will shift to the right if the right eye is closed and vice versa.
- Converging strabismus also results in image displacement. So, when you close your left eye, the image will shift greatly to the right.
- An option with deviations in different directions is also possible. They indicate vertical strabismus.
The determination of the disorder also occurs due to the accompanying symptoms. There will be severe visual discomfort, decreased visual acuity and headaches.
How to determine strabismus in a child at home?
Source: zdorovyeglaza.ru
The most effective way to determine all visual impairments is an ophthalmological examination, but strabismus can be detected at home. To do this you will need a flashlight and a camera with flash.
Home diagnostic method
Of course, congenital strabismus is diagnosed already in the first days of our birth. But with acquired things the situation is different: small deviations are not always noticeable immediately, and medical examinations are not so frequent.
And I would like to determine the tendency to strabismus before visible symptoms appear: deviations of one or both eyes towards the nose or to the side, as well as “floating eyes” syndrome (when it is difficult to “catch” the patient’s gaze).
You can take a test for signs of hidden strabismus (or ask your child to do it) now, it only takes a few minutes.
Rules for performing the test
Lean back in a chair so that your head does not move and look out the window at some small immovable object (for example, a store sign or a satellite dish) and try to focus your gaze on this object for two seconds.
Then close your palm, first one, then the other eye, looking at the object for 1-2 minutes. If the object of fixation remains in place and does not jump from side to side when you open each eye, you can be calm.
Well, or almost calm... After all, only modern diagnostic equipment and professional examination can give a 100% result.
What symptoms indicate the presence of hidden strabismus and how to determine it yourself?
If congenital strabismus in a child under one year old can be detected from the first days of life, then with a hidden handicap of pathology, things are a little more complicated. The presence of small deviations can sometimes simply not be noticed, especially in cases where ophthalmological examinations are carried out less than twice a year.
How to detect strabismus before visible symptoms appear in the form of deviation of the eyes in different directions? Hidden strabismus in a child under one year old can be detected at home after performing a simple test that will take a few minutes. The sequence of its execution is as follows:
- You need to sit the child in a chair and control that he does not move his head.
- He should look out the window at some small object (billboard, antenna, etc.) and fix his gaze on it for 2-3 seconds.
- Next, it is necessary for the baby to alternately cover his right and left eyes with his palm, while peering at the selected object for 1-2 minutes. If it does not change its location (there is no vibration or jumping) when each organ of vision is opened, then the child most likely does not have strabismus.
In a similar way, you can test for the presence of strabismus in adults at home. Of course, such a test does not give the complete picture.
The most accurate result can be obtained after undergoing a full ophthalmological examination, during which special diagnostic equipment is used.
Read on the topic: Review of the most popular programs for the treatment of strabismus
Self-check procedure
In order to independently test for heterotropy at home, it is enough to sit comfortably in a chair, resting your head on the back so that it does not roll when relaxing.
Having sat comfortably, you need to focus your gaze on a static, distant object with high contrast. This could be a bright sign, inscription, etc.
Focusing on the selected object, you need to cover each eye in turn with your palm for a couple of seconds. Breaks should be no longer than 3 seconds of gaze by both organs of visual perception. You cannot let your hand touch your face.
In such conditions, if performed correctly, the object will be seen as if through a phantom palm. In healthy people, a similar phenomenon occurs due to binocular vision, which is impossible with strabismus.
Features of an unhealthy reaction to the test
People with heterotropia have a special reaction to this test, which has the following manifestations:
- If, during such a kind of verification test, the object is not in one position, but there is a deceptive feeling that it is moving or slightly deviating when moving the palm, this is evidence of the presence of hidden horizontal strabismus.
- When the left eye is closed, you will likely notice a shift of the image to the right, and when the right eye is closed and the left one is open, the effect will be the opposite. This means that you have hidden convergent strabismus.
- If, when the left organ of vision is open, the picture shifts to the right, and the right one to the left, then this is a hidden divergent strabismus.
- If a static object on which the gaze is focused during the test shifts in different directions, then this indicates the presence of a vertical deviation.
Strabismus in adults. How to determine?
Strabismus develops much less frequently in adults than in children. Typically, this visual disturbance is caused by pathologies such as:
- refractive errors;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- high intracranial pressure;
- brain inflammation;
- retinal tumors;
- cataract.
In adults, determining strabismus is quite simple. This can be done at home. To test your vision, you should sit in a comfortable chair so that your head is on the back of it. The chair should be located near the window. It is important to maintain the original position and ensure that the head does not fall lower when relaxing the muscles. This will help you get reliable results. When checking, you should concentrate your gaze on an object that is located in the distance. After this, you need to close your eyes one by one. The break between this should not exceed 3 seconds. At this time, you are allowed to look at the object with both eyes. It is important that at this moment your hands are free and do not touch your face.
If you follow the rules of the vision test, it will begin to seem that the selected image is seen as if through the image of the palm. This result suggests that binocular vision in humans is normally developed. With strabismus, it is impossible to achieve such a result. If the test person says that the location of the object changes, it moves or deviates when trying to examine it, this indicates a hidden form of horizontal strabismus. If, when closing the left eye, the image shifts to the opposite side, the person develops convergent strabismus. Deviation of the image in different directions indicates a vertical type of heterotropia.
How to determine strabismus in a newborn and one-year-old child?
By the end of the first week of a baby’s life, you can independently diagnose the pathology in question. To do this, you need to take a rattle and remove it from the child’s eyes at different distances, moving it from side to side.
Carefully monitor the reaction of the child's eyes when observing a moving object and draw a conclusion about how mobile the baby's pupils are. In newborns, the gaze may be discoordinated until 3-4 months; after this age, both eyes become aligned.
In some cases, in children with a wide bridge of the nose, strabismus may be apparent. You should consult a doctor and sound the alarm only if, after 4 months of life, the child’s eyes do not look at the same point most of the time.
Strabismus in one-year-old children can be recognized by the following signs:
- the child cannot direct his eyes simultaneously to one point in space;
- eyes do not move together;
- one eye squints or closes in bright sun;
- the child tilts or turns his head to look at the object;
- the baby bumps into objects (squint impairs the perception of depth in space).
Let us recall once again that true strabismus is characterized by the deviation of only one eye from the joint point of fixation. At the same time, for a newborn child, a slight defocus of the eyes is considered a completely normal phenomenon, which is observed in all babies.
Moreover, the absence of slight strabismus in a small child is rather an exception to the rule. Firstly, the eye muscles of children are very weak, so they need training. Secondly, the child has not yet learned to use these muscles, so sometimes it is not possible to look in different directions.
That is why small eyes, not listening to their owner, either converge to the bridge of the nose, or scatter in different directions. As soon as the baby learns to control the movements of his eyeballs, the squint will go away.
This pathology in infants is inextricably linked with weakness of the eye muscle. The most common causes of strabismus in newborns are:
- injuries and infectious diseases of the brain;
- changes in the eye muscles of an inflammatory, vascular and tumor nature;
- untimely treatment of myopia, astigmatism, farsightedness;
- congenital diseases and birth injuries;
- increased physical and mental stress;
- placing children's toys too close to the baby's face.
Heredity also quite often causes the development of strabismus in newborns. If one of the parents has this pathology, then there is a high probability that their child will inherit the disease.
Sometimes strabismus manifests itself as a symptom of other congenital diseases or as a result of illnesses suffered by the baby’s mother during pregnancy.
Types of strabismus: where the eyes look
In fact, there are many types of strabismus, and it can be difficult to accurately determine them “by eye” without professional methods of examination and vision correction. Considering the whole range of possible causes, not only ophthalmologists, but also neuropathologists, neurosurgeons and other specialists are busy making a diagnosis. And yet, the reason to consult a doctor is the very fact that the eyes suddenly began to look “in the wrong direction,” even if this is not immediately noticeable. In general, strabismus can be divided into two main types: friendly and unfriendly.
Concomitant strabismus
Eyes with this type of strabismus can squint in all nine directions with the same degree of deviation, but they do this in turn. Most often this happens when the accommodative muscle relaxes and the focus of the eye does not fall on the retina. The good news is that some subtypes of congenital congenital strabismus can resolve over time without intervention. Usually, for minor deviations, treatment does not begin until the patient is ten years old.
Questions from readers on
Krasutsky Viktor Iosifovich
ophthalmology
My son (7 months old) was diagnosed with strabismus (+2.5 in one eye, +4.5 in the other)
18 Oct 2013
My son (7 months old) was diagnosed with strabismus (+2.5 in one eye, +4.5 in the other). They suggested a second consultation at 9 months with atropine instillation (the name may be inaccurate, I can’t make out the doctor’s handwriting). What will this burying give us? What could be the causes of strabismus, other than hereditary? What treatment methods are there? As far as I understand, it is important not to waste time
View answer ?Ask a question
Unfriendly strabismus
This type of strabismus characterizes impaired mobility of one eye. The defect develops when muscle functions are impaired and the eye is limited in movement or completely frozen in one position (restrictive strabismus) or individual nerves are affected, changing the position of the eye (paralytic). Restrictive strabismus in most cases is congenital and is characteristic of various syndromes (Stilling-Türk-Down, etc.) and requires surgical intervention in the early stages. As for paralytic strabismus, neurologists are involved in its treatment and accurate diagnosis, since the cause may lie in the brain, and not just in the orbital nerves of the eye. It is not always possible to completely cure unfriendly strabismus, but a cosmetic effect can be achieved.
Medical definition of strabismus
An ophthalmologist determines the presence of strabismus based on the following examinations:
- An examination by an ophthalmologist will help you most accurately determine visual impairment.
- Checking visual acuity.
- Determination of range of motion, squint angle, eye position.
- Examination of the conducting media of the eyes, the anterior segment.
- Refraction of the eyes in a child with narrow and wide pupils.
- Study of binocular vision.
Strabismus can be completely cured in 2-3 years. In this case, it is good to combine medical recommendations with special gymnastics for the eyes. Do not delay your visit to the doctor, since children suffering from strabismus often develop disorders of the nervous system and psychological problems.
Ways to get rid of the disease
Medication alone cannot cure strabismus, however, they can speed up the healing process. These include drops to improve vision, drugs that relax the muscles of the eye and prevent pupillary constriction.
And the main methods of treating strabismus include non-hardware procedures (sets of exercises, glasses and lenses), hardware treatment and surgery. Acquired strabismus in adults is more difficult to correct, since their vision has already been fully developed.
In such cases, often with the help of optical methods, a new model of stereoscopic vision is formed (that is, with the help of lenses a person sees better, but the problem is not solved).
Surgical intervention is necessary in cases where a person is not content with a partial improvement in appearance: after all, the surgeon will not restore binocular vision, but he can “put the eyes back in place” by removing or weakening the eye muscles.
And only modern hardware procedures can “teach” the eyes to see correctly. Here are some popular hardware techniques that your doctor may suggest to eliminate strabismus.
Treatment of strabismus
Correction of strabismus should begin as early as possible, especially since modern medicine has all the necessary techniques for this.
Correction with glasses or lenses
Optical vision correction, which regulates the ratio of accommodation and convergence, becomes an option for non-drug treatment. Patients are prescribed long-term use of lenses or glasses.
There are several types of glasses to get rid of strabismus:
- Sidorenko vacuum glasses;
- glasses with Fresnel prisms;
- glasses with prismatic lenses;
- glasses with red and blue filters.
As for lenses, the following types are prescribed for strabismus:
- Prismatic (non-contact) - otherwise they are called Fresnel lenses;
- Colored (contact) - they “imitate” the eye; the iris and pupil are drawn on their surface.
It is important to remember that when using lenses and wearing glasses, the patient must independently develop his eyes using gymnastic therapy to obtain the desired effect.
Hardware treatment
To stimulate eyes with pathology, hardware treatment is used and these methods are prescribed:
- Amblyocor;
- Computer therapy;
- Vacuum eye massage;
- Accommodation training;
- Laser stimulation.
Computer programs are indicated at the orthoptic stage of treatment and their goal is to restore binocular vision.
To make a diagnosis and further procedures, precise equipment is needed. The Elite Plus ophthalmology clinic uses the best methods of hardware treatment, using highly effective devices: “Rucheek”, “Visotronic”, Pankov glasses.
A course of 10-15 procedures every 6 months can achieve tangible results that will bring the patient a happy and healthy life.
Wearing an occlusive dressing
Another method is eye occlusion, the essence of which is to cover both the squinting eye and the healthy eye with a bandage. This option is indicated for children, and its duration is 4 months.
During occlusive therapy, it is very important that both eyes do not look at the same time, and daily wearing of a bandage is a prerequisite.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of strabismus makes it possible to eliminate pathology in an adult that was not cured in childhood or an acquired disease. For these purposes, there are two methods of operation: increasing muscle traction and weakening it. The indication for surgical intervention is paralytic and non-accommodative strabismus.
The augmentation method aims to shorten the muscle towards which the eye deviates, which as a result strengthens the opposite weak muscle.
The weakening method involves reducing the pull of the eye muscle by moving it further from the cornea, that is, the side in which the eye squints is weakened.
Top-class specialists working at the Elite Plus vision restoration clinic provide non-surgical treatment and diagnostics using modern equipment, which gives a complete picture of the patient’s vision condition and helps to choose a personal path to recovery.
Treatment
Source: glavvrach.com
Treatment of strabismus in children should be comprehensive and started in a timely manner. Firstly, it is very important to begin treatment of the underlying disease - myopia, farsightedness or astigmatism.
It is very important to choose the right glasses for a child - this should also be done by an ophthalmologist, but not by employees of optical salons. Often, properly selected glasses can significantly reduce the degree of strabismus, reducing it to almost zero.
However, such treatment is very often not enough. In this case, ophthalmologists provide complex hardware treatment to the children. The treatment program for each child is selected exclusively individually, taking into account the visual characteristics of each child.
In some cases, if the doctor considers it necessary and sees strong indications for this, he will place the child in the ophthalmology department of the hospital for subsequent surgical intervention.
The purpose of this operation is to correct the eye muscles, as a result of which an almost complete cure of strabismus is achieved. With this treatment, doctors achieve almost complete rehabilitation of the child’s visual function.
After doctors restore normal movement of the eyeball through surgery, the child will receive complex conservative treatment for a certain time.
Also, using certain training methods, doctors fully restore the baby’s ability to stereoscopic vision. And once again I would like to remind you that strabismus in children has a variety of causes - therefore it is very important to establish the true one.
Below we have outlined the most common of them, but remember that you should never try to make diagnoses yourself - this can lead to the most unpredictable consequences.
Hardware treatment method
The monobinoscope device is used in the treatment of amblyopia and double vision. In such cases, the retina of the eye is exposed to light rays. The choice of this method depends on the age of the patient and the stage of development of strabismus.
A set of computer programs for restoring binocular vision (both eyes see the same picture) allows you to correct strabismus defects in 70% of cases. Infrared laser therapy.
This method of laser vision correction can help the eyes focus correctly; infrared radiation restores the muscles of the eye, improves tissue nutrition and eliminates spasms.
Benefits of magnetic therapy
Magnetotherapy (ATOS). This device affects the eyes using a magnetic field. It is usually used for inflammation of the eyes, but in combination with a special attachment, magnetic therapy is effective for treating the problem of the “lazy eye” - amblyopia.
The Forbis device is used for diagnosis and treatment using the diploptic method (a procedure for consolidating restored binocular vision). Synoptophore “Sinf-1” is suitable for complex treatment of strabismus and helps restore a single image, training general eye mobility.
How to treat strabismus
Whether strabismus can be cured depends on the cause of the disease. Initially, you need to identify and eliminate the cause, and only then deal with the consequences in the form of strabismus. The most common cause is a difference in visual acuity in both eyes.
Treatment of strabismus depends 90% on timely consultation with an ophthalmologist. The more advanced the pathology, the less effective the effect of therapy will be. Getting rid of strabismus in the later stages is very difficult. It is possible to surgically restore the correct position of the eyeballs, but visual acuity cannot be restored.
In the early stages, spectacle correction is sufficient for adults; in children, contact lenses are preferable to completely correct the defect of asynchrony of the eyeballs. With the same visual acuity, the squinting eye will be controlled by binocular vision.
When the process is advanced, when the squinting eye becomes amblyopic, surgical treatment can be used to correct the correct position of the eyeball. The duration of the effect will depend on the specific case. Over time, strabismus may return and the operation may be repeated.
The surgical method is successfully replaced using Botox for treatment. Injections of this drug into the eye muscles temporarily relax and paralyze them. What specific type of strabismus you have, whether it can be treated in adults or not, is best told by your doctor. Do not neglect preventive examinations; it is better to prevent a disease than to treat it.
After correction and (if necessary) surgical intervention, the stage of pleoptic treatment begins. This is an increase in visual load on the squinting eye while the other eye is closed. Or instilling drops into the dominant eye to reduce visual acuity. This method helps to force the brain to work with a weak eye.
The next stage is orthoptic treatment. This is hardware treatment using computer programs that teach binocular vision to both eyes. The field of view is divided and a partially incomplete picture is sent to both eyes, joining the pictures together to give the correct image. The results are consolidated with physiotherapeutic procedures.
How to correct strabismus quickly
The surgical method is to restore the balance between weak and strong extraocular muscles. The operation is performed under local anesthesia for 30-40 minutes. A weak muscle is strengthened, and a strong one, on the contrary, is cut off and weakened. The first couple of hours after the operation there will be no vision, but by the end of the day everything will be restored.
Surgery to eliminate strabismus is not a panacea; it only removes an external cosmetic defect. Wearing glasses after surgery continues, and cases of repeated surgery are also common.
How to hide squint and live with it
Strabismus is a noticeable cosmetic defect on the face. Attracts quite a lot of attention and is a source of complexes and irritation. If the opportunity for full treatment is not missed, get rid of the problem using traditional medicine and the methods described above.
Otherwise, surgery can restore the correct position of the eyeballs, even if vision cannot be restored. If for some reason surgery is not possible, you can hide the defect behind photochromic glasses with dark lenses, avoiding looking directly at the person.
Exercises
Excellent eye exercises in the form of simple gymnastics can be performed at home. Exercises will bring greater effect with accommodative strabismus. Do them with us every day, to do this, save the article in your bookmarks.
Read more about treating strabismus at home here.
Physiotherapy
To prevent strabismus, you need to regularly train the eye muscles, and physical activity will also help correct vision in the earliest stages of this disease.
- Exercise 1. All you need to do is extend your arm in front of you and focus on your index finger, closing one eye. Then slowly move your finger ten centimeters closer to your nose, without taking your eyes off.
- Exercise 2. Closing one eye, move the other from side to side until you feel a slight tension.
- Exercise 3. Take any object that is contrasting in color with respect to the background, and move it in front of your eyes without taking your eyes off.
- Exercise 4. Before going to bed, when the lights are already turned off, try to at least roughly examine the contours of surrounding objects.
Forecast
If a child has only one eye squinting, the prognosis is unfavorable. Such strabismus in a child signals a functional inequality of the visual organs and threatens with low vision.
However, the parents of those children who had only one eye squinting before treatment are much more concerned about the situation when, during therapeutic correction, both eyes alternately begin to deviate.
In fact, the transition from monocular to alternating strabismus indicates that the functions of both eyes have become equal and now they work equally.
Experts say that accommodative heterotropia is much easier to treat with hardware than non-accommodative heterotropia, which is often eliminated surgically.
Recovery criteria:
- Sustained binocular vision.
- Symmetrical eye position.
- High visual acuity.
Possible complications
First of all, untreated strabismus will bother the child as a serious cosmetic defect and can lead to the development of an inferiority complex. At the same time, a squinting eye will gradually lose vision, and with such a disease a person will not be able to choose a profession that requires binocular vision.
Duration of treatment
In order to completely recover from strabismus, it will take 2-3 years, regardless of the cause of strabismus in children. If the disease was identified in preschool age, then by the time the child goes to school, experts recommend eliminating the pathology.
Of course, it is difficult to force restless children to perform special tasks on the devices, but it is quite possible to put goggles on them with adhesive.
And in conclusion, I would like to draw the attention of parents to the fact that only by strictly following all medical prescriptions and recommendations can they achieve the maximum effect from the treatment of strabismus and save their child from a serious medical and social problem.