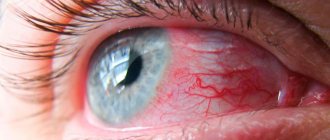
After a blow to the head, there are cases when the white of the eye forms red.
Pain and pain appear in the affected area, and the tissues swell.
Possible internal or external hemorrhage.
This situation becomes dangerous to the life and health of the patient. To prevent complications, it is recommended to consult a traumatologist or ophthalmologist. He will carry out diagnostic measures and determine the cause of the redness. The medicine or procedures will be selected individually, depending on the state of health.
Causes
There are many reasons for a bruise in the eye from an impact:
- Internal bleeding that spreads to the anterior chamber of the eye, causing a red spot visible on the surface of the cornea. The condition does not affect visual acuity. The liquid quickly resolves, so most often no therapeutic measures are used.
- Hemorrhage extending to the vitreous body. Occurs as a result of damage to the walls of blood vessels. Characteristic is a small spot. Decreased visual acuity often occurs. After the impact, spots, dots, and stripes appear before the eyes. For medical treatment, an emergency call to an ambulance is required. In the absence of therapy, retinal detachment and complete disruption of the nutrition of the eyeball will occur.
- Retinal hemorrhage. Symptoms of the condition depend on the degree of damage to the vessel. After the blow, dots appear in front of the eyes, objects appear in double. If the impacts accompanied by damage to the retina are constant, this leads to a decrease in visual acuity, up to its complete loss.
- Hemorrhage into the cornea is accompanied by painful sensations. Blood is located on the surface of the eyes.
- Minor hemorrhages that appear after surgery. If they are small, the fluid will resolve on its own and no treatment is required.
- Increased blood or intraocular pressure. If left untreated, the vascular wall ruptures, causing increased pressure on the retinal area.
- Diabetes. If left untreated, deformation of the capillaries that supply the eyes occurs. The nutrition of tissues is disrupted, which causes their death and decreased function.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms. Capillaries break as the tumor grows.
- Increased physical activity. Lead to rupture of the vessel wall due to high voltage and pressure.
First aid
The skin around the eyes is very delicate, so the impact mark will be noticeable. Disguising an aesthetic defect is quite problematic. If you let the situation take its course, the hematoma can last up to three weeks and will change its shades.
After injury, the following actions should be taken as soon as possible:
- first of all, the patient needs to be calmed down, sat down or laid on the bed;
- apply something cold. This could be ice, a cold water bottle, frozen food from the freezer, or even a cold metal object. Ice must be wrapped in something to prevent tissue frostbite. It is important that the damaged area is cooled for twenty minutes. Cold is applied not only to the hematoma itself, but also to the cheek. Experts recommend doing cold soaks every hour during the first 24 hours after injury;
- for acute pain, give some kind of painkiller, for example, Analgin or Spazmalgon. You should not give Aspirin, as the drug thins the blood. This can lead to the fact that the blood will not clot for a long time, which will lead to an increase in the hematoma in size and the occurrence of edema;
- exclude heat exposure. Warming compresses are allowed on the second day. Excessive heat on the first day may cause increased bruising;
- stop nosebleeds. Do not blow out excess blood, this can lead to the spread of the hematoma to the nose and cheek area;
- In the first hours after a bruise, you should purchase a drug at the pharmacy to reduce swelling and resolve the hematoma.
ATTENTION! Low temperatures constrict blood vessels. As a result, less blood collects under the skin. Cold will help cope not only with swelling, but also with severe pain.
If there are no open wounds, warming up is allowed from the second day. A boiled egg or heated salt wrapped in a bag is suitable for this. Such heating is best performed throughout the entire healing period.
Diagnostics
If the eyes are red, bleeding may occur after the blow. The condition must be diagnosed in order to receive treatment on time:
- general examination of the condition of the mucous membrane, cornea, conjunctiva;
- instillation of agents that eliminate the accommodation of the eyes, which makes it possible to identify the condition of the lens and retina;
- measuring visual acuity using special tables that the patient looks at, identifying letters or pictures;
- measuring visual acuity using special ophthalmological devices;
- measurement of arterial and intraocular pressure;
- the use of MRI, CT to diagnose the condition of the eyeball, blood vessels, and brain.
Using diagnostic tests, the cause of redness and hemorrhage is determined. The doctor prescribes treatment.
Diseases of the eyelids
» Publications » Pharmacotherapy of eye diseases » Diseases of the eyelids
The eyelids protect the front surface of the eye from adverse environmental influences and promote uniform hydration of the cornea and conjunctiva.
In the eyelids, two layers are distinguished: superficial (anterior) - musculocutaneous, consisting of skin and subcutaneous muscle, and deep (posterior) - conjunctival-cartilaginous, consisting of cartilage and conjunctiva, covering the cartilage at the back.
The boundary between these two layers is visible on the free edge of the eyelid as a grayish line located in front of the numerous openings of the meibomian glands (glands of the cartilage of the eyelids).
The anterior layer of the upper and lower eyelids contains eyelashes, near the roots of which there are sebaceous glands. At the edge of the upper and lower eyelids, at the inner corner of the palpebral fissure, there are lacrimal openings, which are the beginning of the lacrimal canaliculi. The skin of the eyelids is thin, the subcutaneous tissue is very loose, as a result of which the skin of the eyelids easily moves, which is widely used in plastic surgery on the eyelids.
The looseness of the subcutaneous tissue explains the easy occurrence of swelling of the eyelids during local inflammatory processes (for example, barley), with disorders of local (especially venous) circulation, angioedema, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus, as well as with some general diseases (kidney disease, heart disease, etc. ).
Under the skin of the eyelid there is a part of the orbicularis oculi muscle, which, by contracting, closes the eyelids. The orbicularis muscle has a small but functionally important part - the lacrimal. With periodic contractions and relaxations in the act of blinking, it ensures alternate narrowing and expansion of the lacrimal sac. The orbicularis oculi muscle is innervated by the facial nerve.
The muscles of the eyelids also include the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid (levator), which, starting in the depths of the orbit near the optic canal, goes under the upper wall of the orbit and ends in the thickness of the upper eyelid in three portions: two of them (anterior, or superficial, and posterior, or deep) are tendon, and the middle one is muscle.
The latter is represented by a thin layer of smooth muscle fibers (Müller's muscle), it is woven into the upper edge of the cartilage and innervated from the cervical part of the sympathetic trunk; the entire remaining muscular part of the levator - striated - is innervated by the oculomotor nerve.
This triple ending of the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid allows the joint movement of the upper eyelid as a whole - cartilage (middle portion of the muscle), skin (anterior portion) and conjunctiva (posterior portion of the muscle).
Sensitive innervation of the upper eyelid is carried out by the first branch of the trigeminal nerve. The lower eyelid receives sensory innervation mainly from the second branch of the trigeminal nerve.
The eyelids have a well-developed arterial network, represented by numerous and richly anastomosing vessels originating from the system of the orbital and facial arteries.
Numerous veins of the eyelids in most cases accompany the arteries and are usually located in two layers: the superficial layer is located under the skin, the deeper one is on the anterior surface of the cartilage. The outflow of venous blood occurs in the system of facial and orbital veins.
Anastomoses between the veins of the face and the orbit are important. The largest anastomosis is the angular vein, located under the skin of the eyelids at the inner corner of the eye.
The lymphatic vessels of the upper eyelid flow into the lymphatic glands located in front of the auricle, therefore, with adenoviral conjunctivitis, this gland is enlarged. The lymphatic vessels of the lower eyelid are directed to the submandibular lymph glands, located at the level of the angle of the lower jaw.
For various diseases of the eyelids, a number of signs have differential diagnostic significance. Swelling of the eyelids is usually a symptom of a disease of the eye or surrounding tissues.
Inflammatory edema is more common (with barley, eyelid abscess, phlegmon of the lacrimal sac, conjunctivitis, iridocyclitis); non-inflammatory edema develops in diseases of the kidneys, heart and may be accompanied by edema in other areas of the body.
Hemorrhages under the skin or in the thickness of the eyelid occur as a result of injury to the eyelids or a fracture of the base of the skull, while the hemorrhage is bilateral and appears after 12-36 hours (so-called blood points).
Emphysema of the eyelids develops as a result of air entering under the skin of the eyelid when the bone walls of any of the paranasal sinuses are damaged as a result of trauma. A typical sign of emphysema is crepitus on palpation of the eyelids. Air resorption occurs on its own within a few days.
Numerous and varied diseases of the eyelids include inflammatory, degenerative and atrophic processes, diseases of the neuromuscular system, developmental abnormalities, circulatory disorders, and tumors. The pathological process can involve the skin, cartilage, muscles of the eyelid, and subsequently the tissue surrounding the eyelid.
B.I. Morozov, A.A. Yakovlev
Source: https://www.glazmed.ru/lib/public30/pharmterap0001.shtml
Treatment
Red eyes due to an impact can be caused by many conditions.
After identifying them, the doctor will prescribe therapeutic measures that can eliminate negative symptoms:
- Use of moisturizing, metabolic, antiseptic, antibacterial drops. They eliminate the disturbance formed on the surface of the eyes.
- The use of agents that help eliminate minor hemorrhages.
- Painkillers that are used as symptomatic therapy to eliminate acute pain.
- Drops that help reduce intraocular pressure by draining fluid from the chambers of the eyes.
- A surgical intervention that eliminates damage to blood vessels, internal structures of the eyes and neighboring tissues.
Medications
Preparations for eliminating bruises are often found in the home medicine cabinet. If they are not available, you can purchase a suitable product at your nearest pharmacy.
Heparin ointment
The active substance - heparin - prevents blood clotting and prevents platelets from sticking together, accelerates the resorption of edema and the inflammatory process. The product also contains anesthesin, a substance that relieves pain. If you apply the ointment twice a day, the result will be obvious within a few days. It dilates blood vessels and increases blood circulation. Heparin accelerates blood flow, enhances metabolism and restores the deep layers of the skin.
Do not forget about some warnings in connection with the use of Heparin ointment:
- regular application to the skin of the face can lead to the appearance of blackheads and clogged pores;
- the risks of rosacea increase, since heparin makes the vascular walls more fragile and increases their permeability;
- there are risks of developing allergies in the form of redness and swelling;
- after using the product, tightness, inflammation, irritation, and urticaria may appear.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the severity of the impact and the cause of the redness of the eyes. If the condition is caused by minor bleeding that will resolve on its own, the prognosis is positive. No therapeutic action is required.
If bleeding is significant, emergency therapeutic measures are required. If they were performed on time, the prognosis is positive, the patient will keep the organ of vision intact. In the absence of therapeutic manipulations, the prognosis is unfavorable. The condition can lead to complete loss of vision or death of a person.
Types and classification of eye hemorrhages
The classification of the disease depends on the location of blood clots in the organs of vision. In addition, the pathological phenomenon is divided based on the intensity of development:
| Severity | Main characteristics |
| Lightweight | There are no painful sensations. The structure of the organ does not change and is restored over time. |
| Average | Minor eye damage. Needs drug therapy. |
| Heavy | Serious and sometimes irreversible impairments, including loss of vision. Treatment is carried out through surgery. |
Prevention
To prevent eye redness after impacts, it is recommended to use the following principles:
- timely consultation with a doctor, diagnostics and treatment procedures;
- state of rest after the impact, it is prohibited to perform any physical activity;
- It is recommended not to use contact lenses until you see a doctor.
A blow to the head is a condition that can cause serious complications, including bleeding into the internal structures of the eyes. It is important to consult a specialist in time and diagnose the patient’s health condition. With immediate treatment, the risk of complications is reduced.
Clinical symptoms
Contusion of the visual organ manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- impaired movement of the eyeball;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- hemorrhage into the white of the eye;
- swelling, pain, pain;
- worsening reaction to light;
- bulging or sinking of the eyeball;
- drooping upper eyelid;
- blurred vision;
- diplopia – double vision;
- the palpebral fissure does not close;
- continuous tearing;
- involuntary closing of the eyelids;
- nausea, dizziness, headache;
- in severe cases, loss of consciousness is possible.
How to remove bruises under the eyes
If you find out that the cause of dark circles is not diseases of the internal organs, but external factors or physiological characteristics, then you can eliminate them depending on their origin.
If bruises under the eyes are caused by age-related thinning of the subcutaneous fatty retina, as well as physiological characteristics such as rosacea, then you can get rid of them with the help of cosmetology. You may be prescribed, for example, lipolifting (injection of fat cells under the lower eyelid), lymphatic drainage, which activates blood flow and accelerates lymph circulation, and mesotherapy. Laser peeling also shows good results, radically eliminating dark circles. At home, when you need to quickly deal with a problem, we recommend using a concealer with reflective particles.
Why does this happen
There are several factors for the appearance of a bruise on the eyelid for no reason:
- With age, the elasticity of the skin decreases, and blood vessels lose their elasticity. A hematoma on the eyelid can also appear from slight pressure.
- Hormonal imbalances are a common cause of dark circles under the eyes in women.
- Stressful situations accompanied by problems in blood circulation can lead to bruises on the face.
- Often, a bluish tint under the eyes can appear due to capillaries that are located close to the skin. This feature in the structure of blood vessels can be inherited.
- The formation of swelling and bruising in the eyelid area is caused by prolonged work at the computer, chronic lack of sleep and bad habits such as alcohol abuse and smoking.
- The lower eyelids may swell and turn blue due to problems with the kidneys and urinary system.
- Venous congestion in the eyelid area is often associated with disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- The problem is caused by many eye diseases and pathologies caused by viruses and infections.
- A bruise under the eyes also forms in cases of cancer, when blood clotting is impaired.
Important information: How to treat a severe subcutaneous hematoma on the face after a blow and how to quickly remove (get rid of) a bruise from a bruise
What to do
If a bruise appears above the eye for no reason (or under it), self-medication is not recommended. The doctor selects treatment methods individually in each case. If the cause is a disease, then first of all drug treatment will be required. Traditional recipes can serve as a supplement, especially when the problem is not related to illness.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine will help improve skin color in the eyelid area; masks and compresses are used for this. Tea leaves in bags work well for a compress. They are brewed with boiling water, allowed to cool slightly, squeezed lightly and applied to closed eyelids below the eyebrow. After 15 minutes, the bags are removed.
A paste of aloe leaves is suitable for a compress; it is wrapped in gauze napkins and applied to bruises. This compress can be kept for 2 hours. If the bruise is small, then you can attach a fresh aloe leaf to it with a band-aid.
To prepare the mask, a paste of grated raw potatoes and cucumber, taken in equal proportions, is suitable. The mixture is applied to a gauze pad and applied to the eyelids for half an hour. At least 4 such procedures will help get rid of the bruise.
Medicines
Badyaga helps get rid of bruises; this product is irritating to the skin. Under its action, the flow of blood to the affected area increases, metabolism is normalized and the hematoma quickly passes.
Heparin ointment and Troxevasin are effective. These medications increase blood circulation in the skin, improve their nutrition and restore the walls of blood vessels. The doctor prescribes the dosage and course of drug therapy individually for each patient; if necessary, vitamins for the eyes are also prescribed.
Important information: What ointment (cream) to treat bruises in children and what product to apply to a baby’s hematoma
Major damage to the organs of vision
A blow to the orbital area causes damage to the eyeball. In addition, there is a so-called contusion of the orbit, which is not accompanied by damage to the integrity of the skin. The eye turns red and visual acuity decreases. The eyeball becomes limited in movement.
If the injury has damaged the skin, then it is very likely that there is damage to adjacent structures:
- Muscle fibers;
- Lacrimal gland;
- Tear canal.
The first thing you need to do is get tested! For any eye injury, you must see an ophthalmologist. Only after this the doctor will be able to carry out the necessary treatment.
If the eye is red as a result of an impact, the diagnostic examination includes the following techniques:
- Visual inspection;
- Determination of visual acuity;
- Study of corneal sensitivity;
- Tonometry to clarify the level of intraocular pressure.
These methods are basic and mandatory, however, at the request of the doctor, other types of examination can be performed. All this depends on the data received. In addition, the patient often has to consult with other specialists: