Symptoms
Rarely does pain occur exclusively in the eye area. Pain is often accompanied by additional symptoms, which make it possible to accurately diagnose the pathological condition. Additional symptoms in addition to pain may include:
- increased secretion of tear secretion;
- intolerance to bright light;
- decreased clarity and quality of the perceived picture;
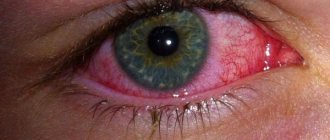
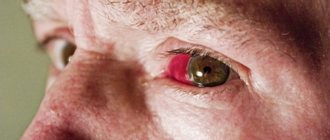
- hyperemia of the eyeball;
- burning;
- itching;
- the appearance of headache;
- swelling of the eyelids or swelling.
Necessary measures
Once the diagnosis is made, the patient is prescribed treatment. This usually involves the use of antimicrobial or antiviral ophthalmic drops or ointments. The most popular ointments are Tetracycline and hydrocortisone. Frequently used drops are sodium sulfacyl, Levomycetin, Oftaquix, Tsiprolet.
If the doctor does not see signs of serious illness in the patient’s condition, then they usually prescribe drops that have a composition close to physiological tear. Drugs such as Artificial tear, Taurine, Quinax, Visomitin are used for eye strain and help fight dry eye syndrome. The pain usually goes away along with it.
At home, you can reduce the intensity of pain when blinking and pressing by using vasoconstrictors, as well as applying cool (not cold) objects to the sore eye.
Causes
Not only diseases, but also other pathological conditions provoke the development of pain. The symptom is not always pronounced and may appear as a result of squinting or pressing. Pain may spread to the corner of the eye and lower eyelid when blinking.
The root causes of pain syndrome are:
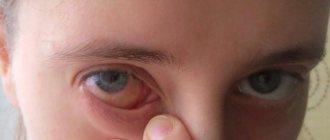
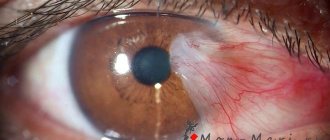
- Conjunctivitis. The condition develops against the background of damage by fungal or infectious microflora. In addition to pain, tearing, photophobia or hyperemia are observed.
- Keratitis. Inflammation of the cornea is caused by damage to pathological microflora. Additional symptoms of the disease include pain when blinking and a feeling of the presence of foreign particles in the organs of vision.
- Myositis. Inflammation of the muscles of the eyeball provokes the development of the disease. The pathology progresses due to mechanical damage, prolonged work at the monitor and hypothermia.
- Graves' disease. The pathology belongs to the autoimmune group. Due to insufficient functionality of the thyroid organ, pain in the visual apparatus is observed. Additional symptoms of the disease include hyperactivity, neurological disorders and increased anxiety.
- Blepharitis. Pathology affects the eyelid regardless of its location. Additionally, swelling of the epithelium, itching and copious secretion of tear secretion develop. Crusts may appear on the eyelid.
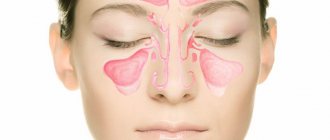
- Sinusitis. The sinuses are located in the nasolacrimal area. Due to a viral infection, inflammation of these areas occurs, which is characterized by soreness of the eyelids and eyes.
- Iridocyclitis. Inflammation occurs in the thin, mobile diaphragm. The symptoms are observed not only when the visual apparatus is calm, but it is also painful to blink.
- Drying of the mucous membrane of the organs of vision. Due to severe drying of the protective surface of the mucous membrane, a feeling of pain may occur.
- Glaucoma. The disease leads to complete blindness. Additional symptoms include double vision, blurred images and decreased visual acuity in low light levels.
- Ulcerative lesion of the cornea. Mechanical or thermal damage to the organs of vision can provoke the formation of ulcers. To eliminate the disease, individual therapy is necessary.
- Barley formation. Before the onset of the disease, an increase in body temperature develops, it is painful to close the eyes, and swelling appears in the lower or upper eyelid.
- Dacryocystitis. Inflammation of the tear ducts occurs against the background of an infectious lesion. Complete blockage of the canal is possible, which requires surgical intervention.
- Inflammation of the nerve of the eye. Damage to the nerve fibers of the organ of vision is accompanied by pain when turning the eyeball. Due to the development of the inflammatory reaction, the transmission of information from the visual apparatus to the brain is disrupted.
- Mechanical damage. Injuries are often accompanied by secondary infection and impaired eye functionality.
- Foreign particles entering the visual apparatus. The feeling of sand in the organs of vision signals the development of pathological conditions. Due to microtraumas, additional infection or the need for surgical intervention may develop.
- Increased overstrain of the visual apparatus. Staying at a gadget monitor for a long time leads to a decrease in picture clarity. The eyes are susceptible to overstrain, which may impair their functionality.
Why does your eye hurt when you blink?
The most common reason why it hurts to blink one or both eyes is a foreign body in it. When blinking, the result is not sliding, but friction of the upper eyelid against this body, and the nerves passing through it report discomfort and pain. By the way, the frequency of blinking in a person increases, because the body thus tries to produce as much tear fluid as possible and push out the foreign body located under the upper eyelid.
Another common cause of pain when blinking is blepharitis.
With this disease, the edges of the skin folds near the eyes become inflamed. This chronic ophthalmological disease is distinguished by the fact that its therapy does not always have results and after a while a relapse is quite possible.
Another common cause of such discomfort is neuritis - inflammation of the optic nerve. Pain when blinking is the only symptom of this condition. If left untreated, such a patient will experience worsening vision over time.
Damage due to trauma
Injuries, especially if they occur in the head or eye area, almost never go away without leaving a trace. Even if no external manifestations (bruises) appear from a blow, fall or collision, this does not mean that they do not exist. It is likely that hemorrhage occurred in the soft tissues due to rupture of blood vessels. A hematoma (blood clot) can take a long time to resolve. All this time, when making physical contact with the eyes, a person will feel discomfort and pain.
What other symptoms may a person notice:
- slight swelling of the soft tissues in the eyelid area appeared;
- the shape of the eye has changed, they have become asymmetrical relative to each other;
- there is pain “as if behind the eyeballs.”
Headache
Very often, migraine patients note that the pain is most severe in the eye area. It may be concentrated closer to the outer edge (at the temples) or the lower eyelid may hurt. In this case, eye pain is a symptom of another disease that requires treatment. Unfortunately, establishing the true cause of headaches in many patients takes more than one month or even a year. The patient undergoes diagnostics and receives treatment from a number of specialists - a neurologist, orthopedist, rheumatologist, cardiologist and others.
Overwork
Stress and overwork are a common cause of various types of disorders and pain, including in the eye area when pressure is applied. This is especially true for those people whose professional activities involve spending a long time in front of a monitor screen. This kind of work requires attention and effort, especially the eyes. It turns out that the visual muscles are in a state of tension for a long time. In addition to pain, a person may experience “dry eye syndrome” in the eye. This is a very unpleasant condition, which, in fact, is not a disease, but at the same time it belongs to pathologies and can subsequently become a provoking factor for the development of complications.
Infectious process
The most common situation is when sinusitis or sinusitis is the cause of pain in the eye when pressing on it. The maxillary sinuses are located in close proximity to the eyes. The inflammatory process is always characterized by swelling due to an increase in the amount of prostaglandins at the site of inflammation. This is a normal physiological process, because the body thus protects itself from the spread of infection and tries to stop pathogens. It is quite natural that pressure increases at the site of swelling, and slight pressure only increases the compression. Nerves passing nearby are pinched by soft tissues and signal pain.
Another common diagnosis associated with eye infection is conjunctivitis.
In this case, there is an inflammatory process on the upper mucous membrane of the ocular analyzer. In this case, the person feels pain in the eyelid, as well as the sensation of a foreign body getting inside the eye. When you try to scratch or rub your eye, no object is found there, of course. It is believed that the bacterial form is distinguished by the stage of purulent discharge, and the viral form is distinguished by redness of the whites of the eyes. But only a specialist can accurately determine the form of conjunctivitis, and therefore it is unwise to make a diagnosis on your own, much less purchase and take ophthalmic medications without consulting a doctor.
Wrong glasses
Optics that have been selected incorrectly cannot be considered useful to a person, and are more likely to harm his vision. Symptoms of this may include headache, dizziness, increased blood pressure, and eye pain. Any violations of optics (incorrectly selected diopters, incorrect or incorrect focus, poor-quality lens material) lead to the fact that the eyes begin to get tired, and in the future this can lead to even greater visual disturbances.
Even good glasses sometimes require replacement, because use leads to lens defects (cuts, cracks, scratches).
Possible diseases
There are a number of diseases, the clinical picture of which just includes the appearance of pain when pressed:
- Glaucoma. This is nothing more than an increase in intraocular pressure. Long-term condition leads to damage to the optic nerve. Symptoms of some types of glaucoma almost do not appear, and this is their main danger. If timely measures are not taken, the situation may well lead to blindness, and treatment of the primary stage almost always gives a good prognosis for a further active life.
- Neoplasm in the immediate vicinity of the eyeball. Even a slight change in the structure of tissues near the eyes can significantly affect the organs of vision. In the vast majority of cases, the neoplasm is malignant and aggressive. Pressure on the eye area leads to irritation of the tissues of the neoplasm, as a result of which it is further irritated and activated. This is a very serious situation that requires an individual approach to therapy.
- Allergy. Very often, allergic reactions manifest themselves as irritation or inflammation. Adults usually know about the possible manifestations of allergies, and therefore try to avoid contact with objects that may cause their body to react incorrectly to this irritant. In children, everything is somewhat more complicated, and usually an allergy is suspected in the absence of other reasons for the appearance of irritation and pain in the eyes when pressed.
- Myositis. Inflammation of the eye muscles usually manifests itself as redness of the skin of the eyelids and whites of the eyes, lacrimation, and pain when pressing. This condition can cause prolonged hypothermia, strain or mechanical damage to the eyes.
Eye hurts when blinking
To determine the causes of pain when blinking, it is necessary to determine the severity of symptoms, the period of pain, and establish the temporary onset of the syndrome. The presence of a symptom when closing your eyes indicates a pathological state of the visual apparatus:
- violation of the integrity of the eyeball;
- eye injuries;
- formation of areas with hemorrhages;
- staying at the computer for a long time;
- foreign particles entering the mucous membrane of the visual apparatus;
- eye nerve overstrain;
- allergic reaction;
- weather dependence;
- mechanical damage to the eyelid;
- infectious lesion.
If there is discomfort during blinking, you should contact an ophthalmologist, who will prescribe diagnostic measures and prescribe individually selected therapy.
What to do if there is pain under the eye socket?
To determine the cause of a symptom, a person should see an ENT specialist.
When pain appears under the eye when pressed, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist, neurologist, infectious disease specialist, cardiologist, or ENT specialist. Depending on the cause of the pain, treatment is prescribed individually. For sinusitis, antibiotics should be used - Flemoklav, Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Sulbacin, Ampisid, Unazin. You should also rinse your nose with saline solution. For osteomyelitis, antibiotic therapy, drainage and sanitation of the affected area of the jaw are also prescribed. Retinal angiopathy can be cured with medications that improve blood circulation (Actovegin, Cavinton, Trental), thrombolytics (Lospirin, Magnicor, Trombonet).
If an unpleasant sensation or pain under the eye is caused by an injury, it is recommended to apply a cold compress and be sure to consult a doctor to exclude deep damage to the tissues of the visual organ and orbit. For a runny nose during ARVI, antiviral drugs (Viferon, Lavomax, Amizon, Amiksin) and nasal drops (Oxymetazoline, Tizin, Pinosol, Farmazolin) are recommended. It should be remembered that the treatment regimen is determined by the doctor; self-medication is prohibited.
Eye hurts when pressed
When you close your eyes or press, pain in the visual organs of varying intensity may occur. With weak pressure, the appearance of pain signals pathological conditions:
- visual fatigue;
- incorrectly selected optical means;
- prolonged stay in a contact device;
- chronic glaucoma;
- presence of tumor formations.
If there is constant pain, it is necessary to visit a medical facility to prevent the development of complications due to the root causes of the pain syndrome.
Prevention
Preventive measures to eliminate pain in the visual organs:
- it is necessary to check the visual apparatus annually for the presence of diseases or abnormalities;
- pain syndrome in the organs of vision develops against the background of neurological disorders;
- eliminate the impact of negative conditions on the visual apparatus;
- increase physical activity to moderate exercise;
- strengthen immunity;
- in the presence of chronic diseases, it is necessary to carry out therapy to eliminate them;
- adhere to visual hygiene;
- in case of active drying of the mucous membrane, it is necessary to instill medications identical to human tears;
- symptoms after injuries are eliminated with painkillers;
- optics to correct the clarity of the perceived image must be used according to the instructions or prescriptions of the ophthalmologist.
Useful video
Pain when pressing or blinking indicates the presence of pathological conditions and fatigue of the visual apparatus. Regardless of the severity of the symptom, it is necessary to seek qualified help in a timely manner, since the progression of the disease leads to a clouding of the picture. Diseases such as keratitis or glaucoma can lead to complete loss of vision. Pain allows you to timely identify pathology and stop its further development.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 ratings, average: 1.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.