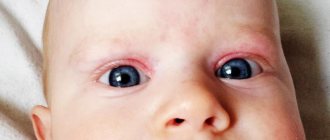
Green snot in a child is a fairly common phenomenon that almost all parents encounter. This unpleasant symptom is caused by the invasion of pathogenic bacterial flora. Discoloration of nasal discharge occurs as a result of the death of bacteria and leukocytes. The shade of the secretion can range from yellow to dark green. The brighter the color of the snot, the more pathogenic bacteria are in the nasal cavity. Sometimes the pathological process can be simultaneously accompanied by coughing and suppuration of the eyes.
This condition should not be ignored, as it can lead to a number of serious complications. In this case, consultation with an otolaryngologist and ophthalmologist will be required. Suitable treatment is prescribed only after identifying the reasons that triggered the development of the disease.
Types of disease
The infection can enter the respiratory tract and cause coughing, or penetrate the mucous membrane of the eyes and cause the appearance of pus. Thus, the child’s body tries to free itself from the bacteria that have penetrated it.
Green snot, which accompanies coughing and purulent discharge from the eyes, is most often found in young children. The reason for this is a rather weak immune system, which finds it difficult to fully fight pathogens. In order for the immune system to learn to fully resist diseases, it needs to endure most of them.
Snot, as a rule, occurs against the background of colds, provoked by the defeat of a particular virus. The green tint of nasal secretions indicates the addition of a bacterial environment. The special color of the discharge is given by dead pathogenic bacteria and leukocytes, which are cells produced by the immune system to fight pathogens.
Conjunctivitis
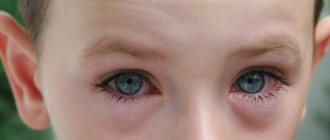
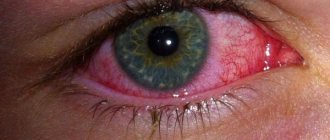
In case of colds, the main cause of suppuration of the eyes is conjunctivitis. Infants may have dacryocystitis, which also leads to the appearance of purulent discharge. With conjunctivitis, there is significant redness of the eyes, increased lacrimation, with further formation of dry crusts. In the absence of timely treatment, symptomatic manifestations will become more intense every day, and there will be more and more pus released.
Inflammation of the lacrimal sac
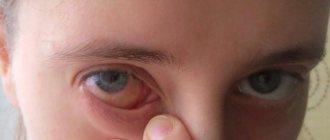
Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac caused by obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct. If dacryocystitis occurs against the background of green snot, the child will experience significant redness of the inner corner of the eye, lacrimation, and discharge of pus.
When green snot is observed, accompanied by a cough and suppuration of the eyes, the child needs to be examined by an ENT doctor and an ophthalmologist.
How to treat
Treatment tactics are determined strictly on an individual basis. Self-therapy, in this case, is unacceptable. The main task is to eliminate the pathogen that provoked the development of the disease.
If the disease is of bacterial origin, antibacterial therapy is recommended. To eliminate green snot, the doctor may prescribe vasoconstrictor drops, which will help the baby get rid of nasal congestion. Such drugs should be used with extreme caution, since they have a fairly large number of side effects. Therefore, they can be used only as prescribed by a specialist who will take into account all the individual characteristics of the child’s body.
Washing
In addition, the doctor may recommend performing procedures for rinsing the nasal passages with saline solutions. Such products are widely available in pharmacies and can be used without fear even in infants, since they contain only microelements and substances from natural sea water.
Microclimate
Medicines that soften the mucous membrane will help eliminate a child’s cough. Also, if green snot accompanies a cough, parents should ensure optimal drinking regimen and monitor air humidity. Excessively dry air in the room contributes to the drying out of the mucous membranes, which is why the cough can be dry.
If pus is released from the eyes due to a cold, emergency care is not required. As a rule, rinsing of the affected eye is prescribed. For this purpose, decoctions of medicinal herbs such as chamomile or sage are used. The product can be prepared as follows: 1 tbsp. a spoonful of dry grass is poured into 1 tbsp. boiling water
Useful video
More information about festering eyes can be found in these videos:
Pus from the eyes is the cause of many inflammatory eye diseases. It can accompany high temperature, cough, runny nose. Washing, lotions, and putting drops in the eyes will help alleviate the baby’s condition. The use of medications is possible only as prescribed by a doctor, because self-medication is harmful.
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Emergency help
If the child produces copious amounts of pus, rinsing with a solution of furatsilin or potassium permanganate may be prescribed. The procedures should be performed several times at a time, and both eyes must be washed at once, even if only one of them is festering. This is necessary to avoid the spread of infection. In addition to the procedures, you can use tetracycline ointment, which should be placed behind the lower eyelid before going to bed.
Green snot, which accompanies coughing and suppuration of the eyes, cannot be ignored, since this condition not only causes a lot of discomfort to the child, but can also lead to the development of unwanted complications.
Problems with a child’s nose are a fairly common situation that many parents face. Congestion and snot can await your baby almost all year round: in autumn, winter and spring. Green discharge requires special attention, and if it is also accompanied by suppuration from the eyes, then it’s time to sound the alarm. You will not be able to determine the origin of the symptoms yourself; only a competent specialist will help.
Causes and mechanisms
Discharge from the nose and eyes that has taken on a greenish tint is a consequence of an inflammatory process of microbial origin. Most often we are talking about bacterial flora, but viruses can also be the causative agent of the disease. The nasal cavity and the conjunctival sac are connected by a system of canals through which tear fluid is drained from the eye. Pathogens also penetrate through them, causing exudative inflammation (accompanied by suppuration). This occurs in the following diseases:
- Acute rhinitis.
- Adenoviral infection.
- Dacryocystitis.
Each condition has its own characteristics, which are taken into account by the pediatrician when carrying out differential diagnosis. And only on the basis of a complete examination can we say why the child has green snot and festering eyes.
To determine the likely cause of changes in the nose and eyes, it is necessary to analyze the clinical symptoms. This means that the doctor interviews parents and older children, finding out complaints, and then conducts an examination. Subjective information is supported by objective signs, and thus the basis for making a preliminary diagnosis is formed.
Any symptom has its own importance, because it speaks of certain disorders - local or general. And all the features of each of them are considered. Even the nature of the snot can tell a lot. To do this, the following points are analyzed:
- Color: transparent, white, yellow-green.
- Consistency: thick or liquid.
- Volume: scanty or abundant.
- Duration: periodic or almost constant.
- Dependence on external factors: time of day, going outside, physical activity.
Discharge from the eyes is also assessed according to a similar principle. It is extremely important to pay attention to all symptoms - both main and additional. If a child has a fever or cough, they should not be left aside. This is the only way to get a more or less complete picture of the pathology at the primary stage.
Each symptom identified in a child is important for making a preliminary diagnosis.
Acute rhinitis
Nasal discharge due to rhinitis is common. They have a different character, depending on the timing of the development of the acute process. The fact is that an infectious runny nose occurs in three stages:
- Irritations.
- Serous discharge.
- Mucopurulent discharge.
At first there is no snot at all - the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity is dry, it is irritated. The patient feels a burning sensation, tickling and itching, and sneezing appears. The inflammatory process is accompanied by a rise in temperature, general weakness and malaise. At the second stage, profuse rhinorrhea appears - clear liquid literally flows from the nose. It becomes increasingly congested, and the swelling makes breathing difficult. Subsequently, the serous discharge becomes mucous and, finally, purulent in nature. When the pathogen spreads through the nasolacrimal ducts, conjunctivitis occurs.
Adenovirus infection
It is not difficult for a doctor to recognize an adenovirus infection. This disease has a fairly characteristic set of clinical signs:
The infection begins acutely, children complain of scratching, sore throat and sore throat, rare cough, nasal congestion and discharge from it (first mucous, and then with a purulent component). The temperature rises, malaise and body aches bother you. At the same time, conjunctivitis appears - in the form of pain in the eyes and a feeling of a foreign body. The eyelids swell and turn red, and a scant yellowish discharge accumulates under them, often sticking the eyelashes together. Enlargement of regional lymph nodes is also characteristic.
On examination, the mucous membrane of the nose, conjunctiva and throat is reddened. Enlarged follicles are often detected on the back wall of the pharynx and the inside of the eyelids. The conjunctiva may become covered with a thin whitish coating. If the process spreads down the respiratory tract, then tracheitis and bronchitis occur. Then the child begins to cough, producing mucous sputum.
Conjunctivitis and rhinitis are typical manifestations of adenovirus infection. In this case, the discharge is often purulent in nature.
Dacryocystitis
If the eyes fester, then a pathology such as dacryocystitis cannot be ruled out. This is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac that occurs due to a violation of the outflow from it. This may occur due to swelling of the mucous membrane against the background of acute rhinitis. Therefore, nasal discharge becomes only a preliminary phenomenon. And then quite characteristic symptoms arise:
- Tearing.
- Painful swelling at the inner edge of the eye socket.
- Redness and swelling of the skin at the site of the lesion.
- Discharge of pus from the lacrimal opening when pressing on the eminence.
Acute bacterial inflammation occurs with fairly intense pain and fever. Swelling can spread to the bridge of the nose, eyelids, cheekbones and cheeks. After the infiltration stage, a fluctuation forms in the center of the lesion, and then pus breaks out. You should be especially careful with young children whose eyes fester due to dacryocystitis. After all, in them the process often becomes widespread, transforming into phlegmon of the orbit or giving rise to intracranial complications.
Causes of swelling
During a cold in both an adult and a child, the inflammatory process can lead to swelling of the eyes. At the same time, they may hurt and tear with a burning sensation. A runny nose can cause sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinuses. When the nasal septum becomes inflamed, the sinuses become clogged. As a result, the free passage of mucus from the sinuses to the nose is disrupted and can put pressure on the forehead and periocular area.
During inflammatory processes, opening of purulent formations is unacceptable. Because of this, the infection can spread to other organs, and serious pathologies such as meningitis and sepsis may develop. If one eye is inflamed, it is necessary to treat both, as the infection quickly spreads to the second. Causes of eye swelling in children and adults:
- sinusitis;
- ARVI, influenza;
- hypothermia;
- conjunctivitis;
- viral infections.
Swelling due to sinusitis
Often this phenomenon accompanies inflammation of the maxillary sinuses.
With sinusitis (frontal sinusitis, sinusitis), the mucous membrane swells and the nasal sinuses become inflamed, as a result of which the anastomosis located between them and the nasal cavity is blocked. As a result, mucus accumulates in the sinuses. Gradually it turns into pus, which is difficult to evacuate from the sinuses. It is able to break into nearby tissues of other structures of the body, for example, into the organs of vision. At the same time, the eyes begin to turn red and swell.
Hypothermia
This can also cause swelling during a runny nose. In this case, the following signs of the disease appear:
- swelling in the periocular area;
- the appearance of an abscess;
- pain on palpation;
- redness and inflammation of the organ of vision;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness.
When a doctor examines swollen eyes, he often finds small lumps under the skin. They may occur due to conjunctivitis. When blood vessels dilate during illness, swelling occurs.
Infectious diseases
Due to a viral infection, a person may suffer from headaches.
The causes of pathological eye conditions in children and adults can be viruses that cause colds. Such infections are quite common. They are contagious and can cause an epidemic. The following symptoms appear:
- pain in the eyes;
- runny nose;
- purulent discharge;
- redness and swelling of the conjunctiva;
- temperature increase;
- eyelid gluing;
- headaches;
- weakness;
- lacrimation;
- insomnia.
Additional diagnostics
Additional methods help to understand why a child’s eyes may fester against the background of green nasal discharge. Therefore, the doctor will refer the small patient to laboratory and instrumental procedures:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Analysis of secretions (cytology, culture, PCR).
- Rhinoscopy.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye.
- Probing of the nasolacrimal duct.
- Dacryocystography.
A consultation is required not only with an ENT doctor, but also with an ophthalmologist. And sometimes it is necessary to involve even a maxillofacial surgeon in the examination. Everything suggests that the situation with purulent discharge from the eyes and nose in a child is quite serious and requires increased attention from parents. At the first symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor to find out the exact cause of the disorders and start treatment on time, thereby getting rid of thoughts about possible complications.
R
Parents of a child under one year old often experience discharge from the eyes and nose of the baby. The sinuses at this age are not yet formed, and a runny nose in infants, called “rhinitis,” is caused by inflammation of the nasal mucosa, which begins to function only half a month after birth. Young children have narrow nasal passages and a very short nasolacrimal duct, which makes it easier for infection to pass from the nose to the eye. The resulting mucus makes breathing difficult, which causes great discomfort to the child. If a runny nose is accompanied by redness, swelling of the eyes, or discharge from them, then this is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Causes Physiologically, the eyes and nose are connected. Through the lacrimal canal, with the blood flow, through adjacent partitions, the infection can be transmitted in both directions. Some microorganisms can simultaneously infect the mucous membranes of the nose and eyes.
Features The provoking agent, when it gets on the mucous membranes, causes symptoms specific to it, which help to distinguish one disease from another and correctly prescribe treatment.
Types of eye and nose diseases in a child can be viral, bacterial, fungal or allergic. To establish a diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo blood tests, urine tests, and microflora smears.
Introduction
R
Parents of a child under one year old often experience discharge from the eyes and nose of the baby. The sinuses at this age are not yet formed, and a runny nose in infants, called “rhinitis,” is caused by inflammation of the nasal mucosa, which begins to function only half a month after birth. Young children have narrow nasal passages and a very short nasolacrimal duct, which makes it easier for infection to pass from the nose to the eye. The resulting mucus makes breathing difficult, which causes great discomfort to the child. If a runny nose is accompanied by redness, swelling of the eyes, or discharge from them, then this is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
CausesPhysiologically, the eyes and nose are connected. Through the lacrimal canal, with the blood flow, through adjacent partitions, the infection can be transmitted in both directions. Some microorganisms can simultaneously infect the mucous membranes of the nose and eyes.
Features The provoking agent, when it gets on the mucous membranes, causes symptoms specific to it, which help to distinguish one disease from another and correctly prescribe treatment.
Types: Diseases of the eyes and nose in a child can be viral, bacterial, fungal or allergic. To establish a diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo blood tests, urine tests, and microflora smears.
Advice
Violation of the outflow of tear fluid in newborns causes inflammation of the lacrimal sac - dacryocystitis. Treatment with medications will not help until the patency of the tear ducts is restored. If probing is not carried out in time, surgical intervention may be required.
- viral
- bacterial
- allergic
Red, swollen eyelids, watery eyes, sneezing, nasal congestion, or clear mucus indicate an allergic reaction.
. If a child, in addition to swelling of the eyelids, redness of the sclera, runny nose, has purulent discharge from the eyes, then most likely a bacterial infection has joined the allergy, or the inflammation has become chronic. Treatment of allergic rhinitis and eye inflammation in children is carried out with the prescription of antihistamines, hormonal drugs, and contact with the allergen is excluded. If, in addition, the eyes fester, then resort to eye ointments or antimicrobial drops.
Allergy is a dangerous systemic disease that requires a serious approach, restrictions in daily routine, and nutrition. If treatment is not started in a timely manner or the doctor’s recommendations are not followed, ordinary snot in children can develop into atopic dermatitis, obstructive bronchitis and even asthma.
Advice
At the age of up to 3 months, a child experiences a physiological runny nose, that is, mucus discharge from the nose for no apparent reason. This is a sign of the readiness of the nasal mucosa for its main function - protection from microbes. This type of runny nose does not require treatment.
Adenovirus infection in children is accompanied by inflammation, sore throat, and fever; herpetic - blisters on the eyelids, photophobia.
Treatment is carried out using systemic antiviral drugs. Antiseptics are used locally to prevent bacterial infections and reduce inflammation.
Conjunctivitis, as an independent disease, can occur due to a cold caused by hypothermia, against the background of reduced immunity.
In advanced cases of inflammation of the lacrimal sac with dacryocystitis, phlegmon can develop, that is, a subcutaneous purulent process accompanied by headaches and high fever.
If a child has festering eyes and fever, then it is necessary to call a doctor at home to rule out serious complications. It is not recommended to bring down a temperature below 38.5 in order to allow the body’s defenses to overcome the infection. The baby should be without a diaper to avoid overheating.
In this case, bacterial conjunctivitis occurs, caused by staphylococci or streptococci, which most often goes away on its own in 5-7 days. To reduce discomfort, it is necessary to rinse the eyes with aseptic solutions, for example, warm chamomile decoction, furatsilin, saline, as pus appears. The use of antibacterial drops helps speed up recovery. Children under one year old are allowed Albucid and Vitabact drops.
In addition to insufficient hand hygiene, visiting a children's group, purulent inflammation of the eyes can provoke:
- improper baby care
- weak immunity
- chronic inflammatory diseases
The child has a runny nose and the eyes are festering, is an allergic reaction possible?
IN
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes is called conjunctivitis. Depending on the reason that caused it, it can be:
Red, swollen eyelids, watery eyes, sneezing, nasal congestion, or clear mucus indicate an allergic reaction.
. If a child, in addition to swelling of the eyelids, redness of the sclera, runny nose, has purulent discharge from the eyes, then most likely a bacterial infection has joined the allergy, or the inflammation has become chronic. Treatment of allergic rhinitis and eye inflammation in children is carried out with the prescription of antihistamines, hormonal drugs, and contact with the allergen is excluded. If, in addition, the eyes fester, then resort to eye ointments or antimicrobial drops.
Allergy is a dangerous systemic disease that requires a serious approach, restrictions in daily routine, and nutrition. If treatment is not started in a timely manner or the doctor’s recommendations are not followed, ordinary snot in children can develop into atopic dermatitis, obstructive bronchitis and even asthma.
How to deal with the disease?
Depending on the nature of the reddish eyeball, it is treated differently, but the first aid for the baby will be to visit a doctor. He will examine your eyes and make the correct diagnosis. Mothers, even the most caring and intelligent ones, will not be able to diagnose the disease on their own. The doctor will determine the cause and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If the redness was caused by concomitant diseases: rhinitis, flu, whooping cough, ARVI, upon recovery from these ailments, the symptom of red eyes will disappear.
If, when the baby is red, green snot flows, it means that the membrane has become infected through the tear duct from the nose. You should inform your doctor about your symptoms and he will prescribe treatment. Self-treatment will not give results. The doctor will prescribe an antibiotic in the nose to treat a purulent runny nose, and antibiotic eye drops in the eyes. The redness will go away when the runny nose disappears.
Non-drug help for redness
In addition to medications, you can use safe traditional methods to relieve symptoms. Among them:
- cold compresses;
- washing;
- lotions.
Cold compresses help relieve symptoms of visual fatigue. This happens when watching TV or computer for a long time. Performed using cotton swabs and ice. You need to take a piece of ice and wrap it in a tampon. Apply to the inflamed eyelid for a couple of minutes. It is recommended to apply such compresses no more than once every few hours.
For rinsing, pharmacies sell special and harmless drops. They are used according to the attached instructions.
Lotions are a favorite remedy for red eyes due to colds among the older generation. They often used chamomile infusions or tea leaves, applying gauze soaked in the infusion to sore eyes.
If you have inflammation from watching TV, you just need to give your eyes a rest, and the whole body should rest.
If the redness is caused by an allergy, the dangerous allergen must be removed, and the eyes will recover without outside help.
The child has a fever and his eyes are purulent. Conjunctivitis?
IN
High temperatures indicate the viral nature of the disease. The causative agent in children can be adenovirus, influenza virus, herpes, Coxsackie virus, enterovirus, chicken pox, measles.
Adenovirus infection in children is accompanied by inflammation, sore throat, and fever; herpetic - blisters on the eyelids, photophobia.
Treatment is carried out using systemic antiviral drugs. Antiseptics are used locally to prevent bacterial infections and reduce inflammation.
Conjunctivitis, as an independent disease, can occur due to a cold caused by hypothermia, against the background of reduced immunity.
In advanced cases of inflammation of the lacrimal sac with dacryocystitis, phlegmon can develop, that is, a subcutaneous purulent process accompanied by headaches and high fever.
If a child has festering eyes and fever, then it is necessary to call a doctor at home to rule out serious complications. It is not recommended to bring down a temperature below 38.5 in order to allow the body’s defenses to overcome the infection. The baby should be without a diaper to avoid overheating.
How to treat swelling of the eyelids?
Drug therapy
If swelling occurs, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist. If the eyelids are swollen due to colds, they are treated at home, and the patient must adhere to bed rest. If the swelling is caused by sinusitis, first it is necessary to treat the underlying ailment, that is, eliminate the inflammatory process that occurs in the sinuses. After you manage to get rid of this pathological condition, the swelling should disappear.
Signs of sinusitis will go away faster when using special drops.
The following medications are used to treat sinusitis:
- local medications - vasoconstrictor drops, inhalers, sprays;
- antibacterial agents;
- antiseptics;
- antihistamines.
When a secondary infectious disease develops, that is, when pathogens spread from the sinuses to the visual organs, antimicrobial drops are used. The drug "Sulfacyl" is effective. This medication is used to treat eye infections with existing swelling and for preventive purposes.
If a stye has formed on the eyelid due to a cold, dry heat must be applied to the swollen, painful area as it matures. You can also spot-apply a solution containing iodine or alcohol. After the abscess has matured and is opened, tetracycline ointment should be applied to the affected area, and Albucid drops should be applied to the mucous membranes of the visual organs. Conjunctivitis is treated with antiviral medications.
Traditional medicine
To eliminate swelling of the eyelids due to colds, it is necessary to wash the eyes with infusions of sage or chamomile and make compresses from them. For these purposes, 2 teaspoons of medicinal herbs must be poured into 50 ml of boiling water. It is useful to smear your eyelids with calendula ointment at night. A good effect is also observed when using freshly squeezed aloe juice. It should be diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10 and instilled. Rosehip infusion is useful to relieve swelling. You need to pour 2 teaspoons of fruit with a glass of water, hold on low heat for 5 minutes and leave for half an hour.
In the morning, the child’s eyelids are stuck together with pus, bacterial conjunctivitis
AND
Sometimes children have eye problems without other symptoms. After a night's sleep, the eyelids are stuck together with pus. Most often, the eyes fester in the morning if the day before the child walked in windy weather, or after visiting playgrounds and playrooms. If street dust gets into the eyes, or the baby rubs them while playing with other children, then bacteria enter the already irritated mucous membrane and cause inflammation faster.
In this case, bacterial conjunctivitis occurs, caused by staphylococci or streptococci, which most often goes away on its own in 5-7 days. To reduce discomfort, it is necessary to rinse the eyes with aseptic solutions, for example, warm chamomile decoction, furatsilin, saline, as pus appears. The use of antibacterial drops helps speed up recovery. Children under one year old are allowed Albucid and Vitabact drops.
In addition to insufficient hand hygiene, visiting a children's group, purulent inflammation of the eyes can provoke:
- improper baby care
- weak immunity
- chronic inflammatory diseases
Viral diseases: cough and festering eyes
P
The appearance of a cough in a child indicates a systemic disease of the body. In this case, the cause of the cough should be identified and the disease that caused it should be treated.
Viral diseases accompanied by cough and suppuration of the eyes in children are:
- adenovirus infection
- flu
- coxsackie virus
- measles
- viral pneumonia due to chickenpox
A sick baby is contagious and requires isolation in the initial stages of the disease. Bed rest and medical supervision every 2-3 days are required.
Viral conjunctivitis is characterized by a small amount of pus or its absence, with a predominance of symptoms characteristic of a particular virus, for example, measles, in addition to a rash, is distinguished by a “barking” cough.
The eyes also fester and the child suffers from a cough due to an advanced viral infection or a bacterial complication with a transition to the lower respiratory organs: bronchitis, pneumonia.
Coughing and eye soreness may be a sign of an allergy.
In rare cases, this combination of symptoms in children is characteristic of a fungal infection.
Green snot in a child and pus in the eyes, bacterial infection
E
If only the eyes fester, then conjunctivitis is called primary; such an infection requires local treatment with antibacterial drugs. The presence of purulent nasal discharge in a child indicates a bacterial infection of the body. If conjunctivitis appeared first, and then green snot was added, this indicates the spread of bacteria to the nasal mucosa, including:
- staphylococcus
- streptococcus
- gonococcus
- hemophilus influenzae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Pneumococcus
- coli
- Koch's wand
Secondary conjunctivitis in children occurs as a bacterial complication of diseases of the respiratory system: tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis; viral diseases such as adenovirus, measles, influenza. In this case, first green snot appears, then purulent inflammation of the conjunctiva.
In both cases, the disease is dangerous due to its consequences:
- Bacterial conjunctivitis leads to deeper eye lesions - keratitis and corneal ulcers, and can cause decreased vision and even blindness.
- Bacterial rhinitis can cause meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, often fatal in children.
For treatment, a systemic antibiotic is prescribed.
If during a cold a child’s eyes fester and runny nose, this is because the tear duct is located very close to the nasal passages. And as soon as an infection starts in the nose, it very easily gets into the baby’s eyes.
Causes of purulent discharge
If a child's eyes become infected and a runny nose appears, the mother should visit two doctors - a pediatrician and an ophthalmologist. It is necessary to pay special attention to the eyes and find out the exact reason for the appearance of pus in them. They can be different, for example:
- Most often, the mucous membrane of the eye becomes inflamed and conjunctivitis occurs.
- Newborns often experience obstruction of the lacrimal duct - dacryocystitis. This is a congenital pathology that goes away over time.
- Bacteria of the coccus group, influenza viruses, herpes, measles, chlamydia.
- Allergic reaction to exposure to dust, pollen, pet hair.
- Poorly treated sore throat or sinusitis.
- Infection acquired during childbirth from the mother or through unsterile instruments. This is the cause of symptoms in every second case of purulent eyes in newborns.
- A foreign body entering the eye, such as an eyelash.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
- Internal inflammation of the mucous membrane, which threatens complete loss of vision.
- Unwashed hands that children constantly rub their eyes with.
- Barley.
- Weakening of the immune system.
A cold is always accompanied by viral or bacterial infections - they are the cause of such symptoms. Such problems can arise at any age and must be dealt with in order to avoid dangerous complications.
The viral or bacterial course of the disease makes the child contagious to others. He needs to be isolated from other children during his illness. If a child goes to kindergarten, he must be left on sick leave until the signs of the disease pass.
At the first stage, eye disease may not manifest itself in any way. Only later may alarming symptoms appear that cannot be ignored, and you should immediately go to the doctor.
In rare cases, parents find out that a child has problems with his eyes when one morning he cannot open them. The eyelids on one or both eyes become stuck together. It happens that without lotions this problem cannot be solved.
But more often, before pus appears in the eyes, other symptoms are observed. If you notice them in time, you can get rid of the disease more easily. It can be:
- redness of the eyeball;
- burning and itching in the eye;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- discharge.
If a child has dacryocystitis, it will be noticeable some time after birth, at the first cold, even the mildest one. But if the child is more than three years old, then we can say with confidence that conjunctivitis occurs, which occurs most often.
You shouldn’t guess where the pus in your child’s eyes came from. The diagnosis must be made by an ophthalmologist. It may well be that the child has some kind of chronic eye disease, and it has worsened with a cold.
Why did the child have green discharge from the nose and pus from the eyes?
If your baby has green snot and his eyes are festering, this indicates that the cause of his illness is an infection. The green color of snot appears when leukocytes and bacteria die. The more of them collect in the nasal cavity, the darker the color will be. It can range from light yellow to dark green.
The baby’s sick body tries to resist the invasion of infection on its own, which is why such discharge is observed.
You cannot ignore such symptoms; you need to go to a doctor, undergo an examination and take treatment. We need to help the little body; it may not be able to cope on its own, and complications will arise.
Prevention
To prevent your baby's eyes from turning red, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- First, teach children to wash their faces and hands frequently. Provide two towels for use: one for hands, one for face.
- Secondly, harden the baby’s body to strengthen the immune system. Eat a lot of healthy foods, fruits, vegetables.
- Thirdly, do not allow your child to watch TV or play computer games for a long time.
- Fourthly, as a preventive measure, wipe the baby’s eyes with chamomile decoction. She disinfects and cleanses them of bacteria.
- Fifthly, promptly consult a doctor for help if you detect the slightest symptoms of the disease.
Timely measures will protect your child from red eyes and snot, and you will be protected from unnecessary worries.
What are the dangers of purulent discharge from the eyes and what complications may arise?
If a child has snot and his eyes are purulent, but there are no other symptoms, this indicates a mild cold. Perhaps the child took a walk down the street in windy weather and just got a little windy. In this case, eye drops will help, and if you use them in time, everything will go away quickly.
But if a child has green snot and conjunctivitis, this is more serious and indicates an infection. If left unattended or poorly treated, dangerous eye complications can occur. These include:
- Blepharitis is an infectious inflammatory process that occurs under the eyelids. It is very difficult to treat and often becomes chronic.
- Keratitis is an inflammatory process in the cornea. Chronic course leads to the formation of a cataract in the eye and partial loss of vision.
- Entropion - can be congenital or acquired. It is characterized by the edges of the eyelids and eyelashes turned inward. In this position, the eyes become vulnerable to infections and viruses.
- Hypopyon – there is an accumulation of pus in the eye. It is difficult to treat and often requires surgery.
- Dry eye – with advanced infection, the lacrimal gland may be damaged and it ceases to perform its functions. The eyes are not moisturized and become inflamed.
To avoid such complications, you need to be attentive to your eyes. This applies to both children and adults. If your eyes fester in the morning, this is no longer a good sign. If it does not go away for a long time or often recurs, you need to sound the alarm and run to the doctor.
Treatment of conjunctivitis and runny nose
If a child or adult’s eyes start to turn sour in the morning, it’s easy to fix. To do this, just rinse your eyelids several times with a decoction of chamomile or calendula. A runny nose that occurs can also be treated by rinsing the nose with these decoctions.
But if such measures do not produce results, and the disease progresses, you need to urgently go to the doctor. Only he can determine the exact cause of the disease. To do this, you may have to take microflora tests to find out what pathogen has settled in your eyes.
To treat such diseases use:
- medicines in the form of drops and ointments;
- lotions;
- washing.
All these activities are carried out after consultation with a doctor.
Medication measures
Of the medications, the best are drops that can be dripped into both the nose and eyes at the same time. This is convenient and saves money. These drops include Albucid. An ophthalmologist should tell you when and how to use them.
Using medications on your own is dangerous. If you choose the wrong dosage, the disease can be classified as chronic, or you can overdose.
You can also use eye ointments that are placed behind the inflamed eyelid. At the same time, put drops into your nose for a runny nose.
Washings and lotions
You can treat suppuration in the eyes by washing with chamomile, calendula, and tea. You need to rinse your eyes with a cotton swab using movements from the corner to the center. The tampon must be changed after each movement.
If there is so much pus that it has glued the eyelids together, under no circumstances should you force them open. You need to place a cotton swab soaked in some solution on your closed eyelids. For example, furatsilin or potassium permanganate . If you don't have them on hand, you can use regular warm water.
During illness, one must carefully observe hygiene and try not to expose already sore eyes to drafts and dust.
If pus appears in the eyes and a runny nose during a cold, this indicates that an inflammatory process has begun, simultaneously affecting the lacrimal canal and the nasal cavity. The reasons for this may be different, and to understand them, you need a competent specialist.
If a child has festering eyes and a severe runny nose, it is imperative to undergo an examination. It will allow you to identify the cause of the disease and begin treatment correctly. The nasal cavity and the conjunctival sac are connected by channels. Therefore, infection from one organ easily penetrates another. The main causes of such symptoms are: acute bacterial rhinitis, adenoviral infection and dacryocystitis.
Treatment methods for runny nose and conjunctivitis
Treatment should be supervised by an experienced specialist
You will need to consult an ENT doctor and an ophthalmologist. They will prescribe complex therapy for the disease. To determine what infection has struck the baby, it is necessary to have the pus analyzed for bacterial culture. After this, the specialist will be able to prescribe effective treatment with oral and topical medications.
The treatment regimen and dosage of each drug is selected individually depending on the age, diagnosis and characteristics of the child.
It is important to maintain bed rest at elevated temperatures and drink plenty of fluids. Typically, colds in children are more severe than in adults, so it is important for parents to closely monitor the condition of their sick child.
Pharmacy drugs
The doctor will decide what exactly is right for your child. It is better not to self-medicate and follow the recommendations of a specialist. Then the risk of complications is much lower.
Bacterial rhinitis is treated:
- washing the mucous membrane with a solution of sea water, drops (Aqua Maris, Aqualor Baby, Otrivin Baby), saline or saline solution;
- vasoconstrictor drops to eliminate swelling of the mucous membrane (Nazivin, Nazol baby);
- if necessary, antibiotics for internal use (Flemoxin Solutab, Amoxiclav, Augmentin) and local action (Bioparox, Polydexa, Isofra);
- To cleanse the nose, special aspirators are used in newborns and children up to one year old.
To treat suppuration of the eyes in children, the following are usually used:
- Tetracycline ointment;
- Levomycetin drops;
- Albucid;
- Eubital;
- Vitabact;
- Colbiocin;
- Furacilin solution - used topically 2-3 times a day for 5-7 days.
When performing eye procedures, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Even if one eye is affected, both need to be treated;
- do not use one cotton pad for both eyes;
- wipe from the outer edge of the eye to the inner.
If the body temperature is elevated (from 38°C), you need to give the child an antipyretic drug (Nurofen, Paracetamol for children). It relieves headaches and other symptoms of intoxication.
When a high temperature persists for a long time, and there is no reaction after taking an antipyretic, you need to urgently call a doctor.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine recipes are often used, but not always justified. The fact is that any inflammation in the head is dangerous with complications. It happens that it goes to the brain and in this case already threatens the baby’s life. That is why folk remedies can only be used as concomitant therapy and in consultation with the attending physician.
For a runny nose, traditional healers recommend:
- bury your nose with drops based on water and baking soda;
- instillation of a decoction of calendula and yarrow, a squeeze of parsley roots.
For conjunctivitis:
- instilling black tea into the eyes, a few drops in each eye (it has a good antibacterial effect);
- washing with a decoction of calendula, chamomile, string, celandine.
For conjunctivitis, it is very effective to use a decoction of chamomile and calendula.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
If pus flows from the eyes and green snot from the nose, the condition indicates a bacterial infection. A change in the color of nasal discharge occurs as a result of the death of pathogenic microbes and leukocytes. The shade of the secreted secretion can be different, from yellow to brown. The brighter the color, the more pathogenic bacteria have entered the body.
Acute rhinitis in children occurs in several stages. Each stage is characterized by certain symptoms:
- At the beginning of the disease, there is no snot. There is dryness in the nasal cavity, burning, tingling. The child sneezes frequently. A rise in temperature and weakness in the body may occur.
- At the second stage of the disease, nasal congestion increases. The mucous membrane swells, copious, clear discharge is observed, breathing through the nose is impaired, and a cough may occur.
- At the third stage of inflammation development, viscous snot of a purulent nature is observed. If the infection penetrates the nasolacrimal duct, conjunctivitis develops.
Conjunctivitis can be caused by both viruses and bacteria. The disease is accompanied by yellow, brown or even greenish suppuration:
- Viral conjunctivitis is more common in newborns. In adult children, it may be the result of decreased immunity or a severe cold. Body temperature rises, tears flow from the eyes. The child is bothered by a feeling of pain in the eyes and photophobia. The eyelids become swollen, red and inflamed. Lymph nodes may become enlarged.
- Bacterial conjunctivitis affects both eyes. The child develops green snot and festering eyes. After sleep, the eyelashes stick together and yellowish, dry crusts form.
Adenoviral disease often begins with pain and discomfort in the throat. At the same time, coughing appears and nasal discharge is bothersome. The snot is initially mucous in nature, and then acquires a yellow-brown or greenish tint. When the infection spreads, the eyes fester.
A baby's eyes may become watery as a result of a disease such as dacryocystitis. Inflammation of the lacrimal sac often occurs against the background of acute rhinitis. Initially, a severe runny nose appears, and only then lacrimation, pain and swelling of the inner corner of the eye occurs, and purulent fluid is released when pressure is applied.
Another reason that a child has green snot is an allergy. Dust, animal hair, plant pollen, chemicals, and food can act as irritants. The eyelids turn red and swell, there is lacrimation, the nose is very stuffy, itching, burning, the snot is initially clear. If the eyes begin to fester, and the color of the mucus in the nose has changed, the condition indicates the addition of a bacterial infection.
Less commonly, the appearance of rhinitis and conjunctivitis is caused by herpes. Small blisters appear around the eyes and nose. When the blisters begin to burst, fluid flows into the eyes, causing purulent discharge.
What types of conjunctivitis are there?
Doctors distinguish three main types that cause the eyeballs to turn red:
- Bacterial infection.
- Viral infection.
- Allergic reaction.
- Bruises or debris.
With a bacterial infection, the eyes are inflamed throughout the day, not just in the morning. The baby is bothered by itching and burning in the eyelid area. At the same time, white, yellow or green discharge constantly appears from the corners. This is the main indicator of the presence of bacterial conjunctivitis.
A viral infection is reflected in the form of redness when you have the flu or a cold. Typically, the eyes become inflamed after the onset of cough and nasal discharge, which is accompanied by clear discharge. Another indicator is burning and stinging.
If you are allergic to plant pollen, animal hair, indoor dust or strong odors, a person experiences redness of the whites, burning and stinging. But there is no purulent discharge. They are usually clear and tear-like. Another symptom of allergic conjunctivitis is itching. The eyelids are very itchy. If a child is allergic to food or external irritants, and the whites turn red, then allergic conjunctivitis can be assumed.
The whites may turn red due to a speck of dirt caught under the eyelid or a blow. Often, children develop redness due to scratches on the eyeballs, which the child inflicts mechanically.
Therapeutic measures
Often a child develops a runny nose and purulent eyes due to a cold. To avoid complications, you need to start treatment on time and correctly. It begins after an examination, which may include rhinoscopy, eye biomicroscopy, and analysis of secretions (bacterial culture, PCR). Based on the results, the doctor makes a diagnosis. Therapy:
- Polidex and Isofra nasal drops are considered effective. Among systemic antibiotics, Azithromycin and Flemoxin are often prescribed.
- For a runny nose and severe swelling, the use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops is indicated: Nazivin, Otrivin, Nazol Baby.
- Salt solutions help clean and moisturize the nasal cavity: Aquamaris, Aqualor.
- If your eyes are festering, you must follow hygiene procedures using a solution of Furacilin or Potassium permanganate. Each eye is wiped with a separate cotton pad.
- To increase immunity, the child is prescribed multivitamin complexes and immunomodulators (Anafern, Grippferon).
- Chamomile or green tea infusions can be used as an antiseptic. They can be used to wipe your eyes or rinse your nose.
- Drops of Albucid, Floxal, Levomycetin, Vitabact will help cope with suppuration of the eyes. The eyelids can be smeared with Tetracycline ointment.
- If symptoms appear as a result of allergies, then antihistamines are prescribed: Suprastin, Loratadine. Allergy symptoms can be relieved by nasal drops Beconase, Avamis, Allergodil.
- For herpes infection, it is advisable to prescribe Acyclovir, Zovirax.
How to treat conjunctivitis and otitis media
Treatment of conjunctivitis that occurs against the background of otitis media is prescribed taking into account the causative agent of the disease. Based on a series of tests, the doctor writes recommendations to the patient and establishes an accurate diagnosis. Self-medication is strictly prohibited! Taking the drugs provides a certain effect on the foci of inflammation, which cannot be independently determined.
Interferon is a drug that is classified as an immunostimulant; it increases immunity, reduces the risk of complications, and is used as a general tonic.
To treat the bacterial form, we use antibiotic drops or ointment at night. Drops based on miramistin are very popular; (Okomistin) eliminates fungi and bacteria and improves immunity. Drops are suitable for the treatment of external otitis and runny nose.
Allergic conjunctivitis is treated by eliminating the source of the allergen. Antihistamines cope well with the symptoms of this disease.
- Suprastin;
- Erius;
- Eden;
- Loratadine.
The treatment process depends on the degree of the disease and the age of the child. The younger he is, the more carefully it is necessary to treat even the initial stage of ear inflammation. At the first stage, the doctor prescribes antiseptic nasal drops and painkillers to the young patient. If there is no temperature, you can use compresses and warm up. In case of a deep inflammatory process, a specialist prescribes a course of antibiotics and medical procedures. This could be piercing the eardrum, using all kinds of solutions. In case of severe illness, hospital treatment is necessary.