General description of the disease
This is a chronic eye disease that can develop at any age, but is especially common among older people.
Congenital glaucoma occurs in 1 in 20 thousand newborns, by the age of 45 the incidence of glaucoma is approximately 0.1%, among 50-60 year olds this figure reaches 1.5%, and in the age group 70+ more than 3%. Unfortunately, glaucoma is incurable; its severe forms lead to irreversible blindness, which gives the disease a social character.
Types of glaucoma
Glaucoma is classified by age:
- Congenital glaucoma affects newborns. As a rule, the disease is subject to early diagnosis; immediately after birth it is detected in 60% of patients. Congenital glaucoma can manifest itself in the first months of infancy, and in rare cases much later, several years later;
- Juvenile glaucoma is diagnosed in children aged 3 years and up to 35 years;
- Primary adult glaucoma is the most common. It is associated with age-related changes in the organs of vision. Its forms are subject to medical classification, on which the treatment regimen depends. Primary glaucoma can manifest itself in open-angle, closed-angle, mixed forms and glaucoma in which intraocular pressure remains within normal limits;
- Secondary glaucoma in adults develops as a consequence of previous ophthalmological diseases.
Causes of glaucoma
The causes of congenital glaucoma can be a variety of factors, such as genetic predetermination, as well as embryonic and birth injuries. If the mother suffered infections such as mumps, syphilis, rubella, or polio during pregnancy, this can provoke glaucoma in the fetus. Excessive alcohol consumption, poisoning, vitamin deficiency, radiation exposure and abdominal trauma during the embryonic period can also become risk factors.
In adults, the main cause of glaucoma is increased eye pressure, which leads to impaired blood supply to the eyes and deformation of the optic nerve. In addition, the disease provokes high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, diseases of the immune system, severe myopia and hereditary factors [3].
The tendency towards a closed-angle shape is more often manifested among representatives of the fair sex. In this case, the anatomical features of the visual organs are of particular importance: the small size of the eye and the large lens.
Secondary glaucoma can be triggered by long-term use of hormonal drugs indicated for bronchial asthma and autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms of glaucoma
Very often, the disease is asymptomatic and does not cause any discomfort until visual acuity deteriorates significantly. As a rule, the patient turns to an ophthalmologist at a late stage of the disease. The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that in the early stages there is almost no pain or symptoms.
Elderly people should regularly visit an ophthalmologist and measure intraocular pressure, which is the leading symptom of glaucoma. It is impossible to independently detect changes in intraocular pressure, since the increase occurs gradually and the brain adapts to the changes. Only a small group of people have such manifestations as pain in the eyebrows and forehead, deterioration in vision sharpness, and complaints of the appearance of colored circles when looking at light sources.
Another important symptom is a narrowing of the visual field, which begins from the nasal area, as well as a violation of the eye’s rapid adaptation to changes in lighting. A decrease in visual acuity indicates irreversible changes in the morphological structure of the optic nerve, which cannot be restored or treated.
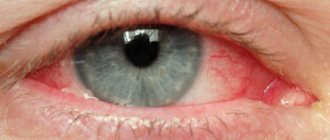
The closed-angle form is quite rare, but is characterized by pronounced symptoms: severe eye pain and headaches, redness of the eye.
Complications of glaucoma
Untimely treatment and diagnosis of glaucoma can provoke acute attacks of the disease, which are fraught with severe visual impairment, including complete blindness. Practical studies show that treatment of glaucoma can only stop and slow down the decline in vision, but cannot restore it.
Prevention of glaucoma
- 1 regular medical examinations with a therapist and endocrinologist for timely detection and prevention of diseases that can provoke the development of glaucoma (hypertension, hypotension, diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid gland);
- 2 systematic visit to the ophthalmologist with mandatory measurement of intraocular pressure;
- 3 timely treatment of ophthalmological diseases to prevent the development of secondary glaucoma;
- 4 expectant mothers should take special care to prevent the risk of developing glaucoma in newborns;
- 5 You should not neglect your own vision test. Self-monitoring is quite simple: close your eyes one by one and compare the sharpness and quality of the picture;
- 6 make it a rule to regularly do morning exercises with mandatory exercises for the cervical spine. Moderate physical activity stimulates blood supply to the organs of vision;
- 7 do not lift heavy objects in order not to provoke an increase in IOP;
- 8 properly formulated diet.
Treatment of glaucoma in official medicine
Unfortunately, it is not yet possible to achieve a complete cure for glaucoma, but it is necessary to monitor and treat it. Having determined the type and stage of glaucoma, the ophthalmologist will prescribe the optimal treatment method, which can be conservative, surgical or laser. Each of these types of treatment is aimed at normalizing intraocular pressure.
Drug treatment tactics involve the use of special anti-glaucoma drops, which not only reduce the level of IOP, but also help improve the blood supply to the internal membranes of the organs of vision. Only an ophthalmologist can select and cancel drops, as well as prescribe an instillation regimen; self-medication for glaucoma can cause irreversible harm to the eyes. In this case, the patient should take into account that antiglaucomatous drugs can have different effects on IOP:
- 1 intraocular pressure decreases immediately after instillation of drops;
- 2 IOP decreases slightly, but with regular instillation of the product, its effect increases over time;
- 3 drops can have the opposite effect and increase IOP levels;
- 4 it is possible that the patient is resistant to antiglaucoma drops, in which case the drug does not affect IOP values.
If conservative treatment does not produce results, the ophthalmologist recommends surgery.
Laser operations for the treatment of glaucoma began to be practiced back in the 70s of the last century. Using laser radiation, intraocular blocks that interfere with the outflow of intraocular fluid are removed. Laser surgery has disadvantages and advantages.
Advantages of laser operations:
- relatively low cost of the operation;
- short rehabilitation period;
- there is no need for general anesthesia, local anesthesia is sufficient;
- laser surgery can be performed on an outpatient basis;
- There are no complications typical for traditional glaucoma surgery.
Disadvantages of laser surgery:
- risk of damage to the lens capsule;
- the possibility of damage to the vessels of the iris;
- In the first few hours after surgery, IOP may increase.
The history of glaucoma surgery goes back more than 150 years. Every year existing ones are improved, new methods of antiglaucomatous operations are developed and introduced. The ophthalmologist decides on the surgical treatment of glaucoma (iridectomy), taking into account the general condition of the patient, IOP indicators and the dynamics of clinical data.
The goal of iridectomy is to normalize IOP levels, improve nutrition and tissue metabolism in the optic nerve. As a result of surgical operations, the pressure in the chambers of the eye is equalized by eliminating the pupillary block.
Vitamins for glaucoma
The human eyes are an important sensory organ that helps us perceive the world around us and receive information about it.
In ancient times, good eyesight made it possible to preserve life in the aggressive ancient world. However, recently there has been a significant increase in the load on the organs of the optical system, which leads to eye fatigue. All activities that cause strain on the organ of vision (sewing, reading, writing, working with documents, using a computer) lead to eye fatigue, decreased visual acuity, expansion of the vascular network, pain and dryness of the mucous membrane. In modern society, many patients of working age suffer from similar symptoms. Poor nutrition also has a negative impact on the condition of the eyes. Often a modern person, especially those living in a metropolis, eats fast food and consumes a lot of carbonated drinks, sweets, and energy drinks. That is, it deprives the body of essential vitamins and microelements. According to research results, it was found that on average a person living in a city meets no more than 20-40% of the daily requirement of vitamins and other nutrients.
With chronic vitamin deficiency, cataracts, age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma and other pathologies can develop.
Let's first look at what vitamins are essential for eye health.
Essential vitamins for the eyes
For the normal functioning of the organs of the optical system, several groups of microelements and vitamins are required.
Vitamin A
Retinol is a precursor to a substance that is part of the photosensitive layer of the retina. The retinal rods contain the protein rhodopsin, in which retinal plays the role of the active center. With each impact of a light wave on the retina, this substance is gradually destroyed, as a result of which the human body must constantly renew its reserves of vitamin A.
With hypovitaminosis (lack of vitamin A), twilight vision decreases and the clarity and brightness of the image decreases. This component is found in large quantities in blueberries, apricots, carrots, and bell peppers.
Vitamin B2
Riboflavin is a precursor of flavin coenzymes, which take part in redox processes. Together with retinol, vitamin B2 leads to increased image clarity and brightness, and also reduces eye fatigue. A lot of riboflavin is found in dairy products, beef, and eggs.
Vitamin B6
Pyridoxine is responsible for the conduction of nerve impulses and is involved in the synthesis of nucleic acids. There is a lot of this vitamin in meat, liver, eggs, leafy greens, and dairy products.
Vitamin C
Ascorbic acid helps make the vascular wall strong and elastic; it is a powerful antioxidant. With a lack of vitamin C, the nutrition of the eyes decreases, and the risk of developing hemorrhage in the vitreous or retina increases. Long-term hypovitaminosis can provoke the development of glaucoma. There is a lot of ascorbic acid in blueberries, citrus fruits, potatoes, rose hips, and sauerkraut.
Vitamin D
Calciferol helps muscle fibers absorb calcium, meaning it is responsible for muscle contraction. With a lack of vitamin D, the eyes quickly tire and accommodative ability decreases. Vitamin D is found in sea fish, especially in fish oil, and in milk.
Vitamin E
Tocopherol is an antioxidant that protects the eye from the harmful effects of free radicals and active oxygen. With its deficiency, cataracts can develop. There is a lot of vitamin E in liver, vegetable oil, sea buckthorn, liver, and nuts.
Vitamin PP
Niacin takes part in redox processes. With its deficiency, eye nutrition suffers. Vitamin PP is found in large quantities in legumes.
Calcium
This microelement takes part in the contraction of muscle fibers. If few calcium ions enter the body, the accommodation process is disrupted, myopia occurs, fatigue increases and early farsightedness develops.
Zinc is involved in the conversion of vitamin A into the substance retinal. With zinc deficiency, color vision is impaired and cataracts develop. To increase the level of zinc in the blood, you need to eat more fish, brain, liver and pumpkin.
>Selenium
Selenium takes an active part in converting a light signal into a nerve impulse. This microelement also has an antioxidant effect. Low selenium levels may lead to the development of cataracts and decreased visual acuity. There is a lot of selenium in coconut, peanuts, lard and mushrooms. Also, the vitamin complex Complivit Selenium is excellent for eliminating selenium deficiency.
Lutein
Lutein, which is a yellow pigment related to carotenoids, should be included in a separate group. The main function of this substance is to protect the retina from the effects of ultraviolet and intense radiation. There is a lot of lutein in yellow fruits and vegetables, and chicken yolk.
For the optical system to work properly, it is necessary that all of the listed substances be present in sufficient quantities in human food. At the same time, it is not always possible to eat a balanced diet, so multivitamin complexes come to the rescue, which enrich the body with the necessary drugs.
What products are recommended for glaucoma?
Treatment for glaucoma should include a diet consisting of foods rich in antioxidants. Natural antioxidants help not only in the process of combating pathology, they are also effective at the prevention stage.
Where to get vitamins from:
- Vitamin A is found in calf liver, whole milk, egg yolks, carrots, beets, red peppers, broccoli, leafy greens, pink grapefruit, papaya and apricot. Vitamin A improves visual acuity.
- Vitamin B is found in lean fish, chicken eggs, dairy products, cereals and legumes. It helps normalize metabolism in optic nerve cells.
- Vitamin C is found in cauliflower and Brussels sprouts, broccoli, tomatoes, peppers, citrus fruits and berries (rose hips, black currants, sea buckthorn). This vitamin increases defenses and is involved in metabolism and blood circulation of the eye.
- Vitamin E is found in meat, seafood, vegetable and butter, egg yolks, milk fat, grain products (especially wheat), green leafy vegetables, avocados, nuts, and seeds. With a lack of vitamin E, a person with progressive glaucoma often develops cataracts.
A proper diet includes not only a sufficient amount of vitamins, but also a balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Therefore, for glaucoma, vegetable and cereal soups, lean meat and fish, milk porridges, vegetable stews, salads and fresh fruits are preferred.
Foods containing lutein and zeaxanthin:
- pumpkin;
- cucumbers;
- corn;
- Green pepper;
- leaf and Brussels sprouts;
- broccoli;
- spinach;
- parsley;
- lettuce leaves;
- celery;
- greenery;
- peas;
- beans (green);
- olives.
Sources of zinc:
- meat (lean);
- seafood;
- cheese;
- bran;
- eggs;
- green leafy vegetables;
- whole grains;
- soya beans.
For pathologies of the visual system, doctors recommend using curcumin. This is a substance that is part of turmeric, a spice made from the herbaceous plant of the same name. In addition to curcumin, the root of this plant contains iron, phosphorus, iodine, vitamins B and C, as well as essential oils.
Glaucoma patients are advised to take fish oil. This is due to the effect of the polyunsaturated fats it contains on the retina: fatty acids help reduce oxidative damage. Fish oil improves blood circulation in the eye, thereby preventing retinal ischemia due to increased intraocular pressure. It is believed that the drug can lower blood pressure to some extent and protect the macula (corpus luteum, the center of the retina).
Multivitamin complexes
Typically, vitamins for eye health include various active components focused on a particular pathology. In particular, there are complexes that were developed specifically for the prevention and treatment of age-related organ degeneration (cataracts, age-related degeneration of the corpus luteum, glaucoma). Another group of medications are vitamins for patients with myopia and twilight vision impairment. You can buy these complexes at almost any pharmacy.
Vitamins that are prescribed by highly specialized specialists stand apart. These include preparations with a high content of B vitamins, which are used by pilots in aviation (flight fatigue).
Below are the most popular multivitamin complexes prescribed for eye health.
Strix Forte
This dietary supplement contains:
- Beta-carotene, aimed at normalizing color and twilight vision and helps maintain vision despite prolonged stress.
- Vitamins C and E help stabilize the capillary membrane and improve blood flow through the vessels of the eye.
- Lutein is a component of the macula because it plays the role of a light filter and protects the retina from the harmful effects of short-wave radiation.
- Seen and zinc are classified as stabilizers of the activity of nerve and muscle fibers.
- Blueberry anthocyanins help reduce the effects of hypoxia, are antioxidant agents and prevent the development of vascular disorders and cataracts.
Region. Applications of Strax Forte include myopia, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, intense eye strain, including long-term driving.
Blueberry Forte
This dietary supplement contains mainly blueberry fruit extract, the pigments of which are powerful anthocyanins. These substances perform angioprotective and antioxidant functions and normalize metabolic processes. For additional protection, the drug contains zinc, rutin and vitamin C. There are also B vitamins that support the functioning of the optic nerve.
Blueberry forte is useful for eye fatigue due to long work and driving. These vitamins are also used in the complex treatment of eye diseases (cataracts and glaucoma), myopia.
Lutein complex
This multivitamin mainly consists of lutein, which provides protection against age-related changes. Lutein is found in the structures of the macula, and with regular replenishment of its reserves by the body, it helps to cope with age-related macular degeneration.
The complex also contains blueberry extract, vitamins C, E and A, zinc, selenium, copper, taurine.
All these substances normalize metabolic processes in the structures of the eye, protect retinal cells from the negative effects of blue radiation and free active radicals. Vitamin A also increases the concentration of photosensitive pigment.
This complex is used for severe eye fatigue, computer syndrome, long-term driving, as well as for the treatment and prevention of age-related changes.
Vitrum Vision
This vitamin complex consists of plant microelements and pigments:
Prohibited foods and drinks
Products that can retain fluid in the body are prohibited, especially before bedtime and in the hot season. The salt concentration in sausages, sausages, smoked meats, and canned food is very high. You should eat white bread, confectionery, sugar, jam, and sweets as little as possible.
Caffeine has a stimulating effect on the nervous system, so strong tea and coffee should be limited. Strong broths and meat by-products are too fatty; for the same reason, you should avoid butter, margarine and lard. Spices, especially industrially produced ones, and smoked fish should also be excluded.
Alcoholic drinks, including beer and wine, champagne, coffee, cocoa, and sweet soft drinks, should be excluded from the diet.
Drop preparations
There are vitamin preparations not only for oral administration, but also for instillation into the eyes. This allows you to quickly deliver the necessary components to the target, that is, their effect occurs faster.
Taufon is used to prevent night blindness and eye fatigue. Vita Yodurol contains nicotinic acid, calcium salts and is designed for the treatment of farsightedness and cataracts. Khrustalin contains nicotinic acid, and Oftan katachrome - redox cytochromes, vitamin PP.
For myopia and glaucoma, use Emoxipin drops with provitamin B6.
Which vitamins to choose?
If symptoms of eye fatigue, decreased visual acuity, or other disturbances in the visual system appear, you need to change your diet and provide the organs of the optical system with proper rest.
To increase the level of vitamins and microelements, you can use multivitamin complexes. To choose the right drug correctly, it is better to consult a doctor, who will be guided by the characteristics of the body and lifestyle. The doctor will select not only the optimal complex of vitamins, but also determine possible malfunctions in the organs of the optical system. At the same time, at an early stage of the disease, the development of serious pathology can still be prevented.
Features of nutrition for older people with glaucoma and cataracts
Eating a diet high in omega-3 fatty acids reduces the risk of developing glaucoma by 35%. Elderly people should fill their diet with this substance to prevent the development of eye disease.
Proper nutrition for cataracts in old age will strengthen vision and maintain intraocular pressure at a normal level. The following foods are sources of omega-3 fatty acids:
- mackerel, salmon, herring;
- nuts, flax seeds;
- beans and soybeans;
- oat and wheat germs;
- cauliflower, spinach, leek;
- raspberries, strawberries, avocado;
- vegetable oils (soybean, nut, flaxseed).
Omega-3 acids are not synthesized in the body, so it is necessary to take care of the systematic consumption of foods rich in these substances
Vitamins for glaucoma
Vitamin supplements are used to reduce symptoms and eliminate diseases of the visual organs. Vitamins for glaucoma help restore vision, relieve fatigue and eye strain, increase performance and prevent the development of the disease. By improving the circulation of eye tissues and affecting the optic nerves, they slow down the deformation of the visual organs in glaucoma and help avoid blindness.
The healing properties of vitamins
Constant tension in the organs of vision contributes to their rapid fatigue and redness. As a result of overexertion, pain appears, vision deteriorates, the mucous membrane dries out and eye diseases develop. Lack of vitamins due to insufficient nutrition also has a negative effect on the organs of the visual system. Vitamins for the eyes contain a special complex of nutrients that normalize metabolic processes in the eye vessels, nerves and inhibit pathological changes in the visual organ system. Taking such necessary and beneficial substances prevents the development of glaucoma and normalizes the functioning of the visual organs.
In case of glaucoma or cataracts, eye vitamins are neuroprotectors and have a beneficial effect on the restoration of ocular functions.
The effect of vitamins on vision
| Name | Action |
| "Mirtilene Forte" | It has a clear therapeutic effect in cases of retinal pathology and damage to the eye muscles, regenerates eye photoreceptors, relieves tension and improves the ability to see clearly. |
| "Blueberry Forte" | Performs angioprotective and antioxidant effects, helps metabolic processes, and has an effective strengthening effect. |
| "Vitrum Vision" | Consists of plant microelements that normalize blood flow and accelerate metabolic processes in the eye vessels. |
| "Complivit Oftalmo" | Includes all B vitamins and a complete set of microelements. Protects the retina from the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays. Eliminates inflammatory processes in glaucoma. |
Return to contents
What is healthy and what foods should you eat?
Source: uglaznogo.ru When a patient is referred for treatment, the doctor prescribes vitamins.
Usually this is a course therapy. It provides nutrition to the eyes during glaucoma, but the course usually lasts 10-14 days, and the eyes need constant nutrition with vitamins, which must also enter the body from natural sources. Vitamin A is considered the most important microelement. A lack of this particular vitamin causes vision impairment and various complications. This vitamin is contained in both animal and plant products.
Therefore, to enrich the body with vitamin A, you should eat and use the following products in cooking:
- zucchini,
- carrot,
- rose hip,
- tomatoes,
- sea buckthorn,
- all fruits and vegetables are orange.
Another important element for good vision and eye health is vitamin E. Rich in it:
- cereals,
- legumes,
- broccoli,
- nuts.
There are cases when another serious disease develops with glaucoma - eye cataracts. It is believed that a lack of vitamin E leads to the formation of cataracts.
Vitamin C is involved in all types of metabolism and is therefore considered essential. Lack of this vitamin in the body leads to the formation of blood clots. If you have glaucoma, it is very important to ensure that your food contains vitamin C.
Otherwise, its deficiency in glaucoma can lead to impaired blood supply, swelling, and necrosis of eye tissue.
Rich in vitamin C:
- pepper,
- cabbage,
- dill,
- citrus,
- spinach,
- black currants and other berries.
There are some microelements that can regulate metabolism in our body. These are B vitamins. They stimulate the central nervous system and participate in the production of energy, which the body needs so much for fat and protein metabolism.
Rich in B vitamins:
- cereals,
- nuts,
- greenery,
- garlic,
- horseradish,
- cucumbers,
- potato,
- dairy products,
- eggs.
Unsaturated fatty acids play a major role in reducing oxidative damage to the retina and improving ocular blood flow. You can replenish your body with them by eating seafood, pumpkin seeds, spinach, greens, and flaxseed. IOP can be lowered by eliminating food allergens.
It is important to know!
Nutrition for glaucoma must fully and in the right proportion ensure that the body receives all nutrients: proteins, carbohydrates, fats, trace elements and minerals. It is advisable to eat low-fat meat, boiled fish, vegetable soups and cereals.
If you have eye glaucoma, you should switch to proper nutrition, the components of which are determined by a nutritionist. However, there are general lists of recommended and prohibited foods when dieting. If you follow the recommendations and prepare dishes from these ingredients, the course of the disease will slow down and recovery will come faster.
The daily diet should include the following products:
- ingredients of dairy and fermented milk origin;
- soy products;
- cereals: oatmeal, buckwheat and millet;
- low-fat meat or vegetable broths;
- meat and fish with low fat content;
- weak green or black teas.
- Boiled sausages (“doctor’s”)
- Bread up to 200 g per day
- Vegetables and fruits in moderation
- Legumes
If possible, reduce the presence of sour cream, butter and easily digestible carbohydrates (sugar, honey) in the diet. Drink no more than one and a half liters per day.
Patients should remember that glaucoma is a fairly serious ophthalmological disease that develops due to a disruption in the outflow of intraocular fluid. This disease, like type 2 diabetes, cannot be neglected.
The fact is that the lack of therapy will lead to the death of the optic nerve. Doctors have long established what causes a deficiency in the human body of very important vitamins that are needed for the eyes.
Important!
That is why, in a fairly long process of treating the disease, you should definitely use a special diet, which will be filled with the most beneficial products for the visual organs.
In addition to medications, when treating an illness, the doctor must prescribe vitamin supplements to the patient, which will improve the nutrition of the eyes. But you need to remember that it is not recommended to take synthetic vitamins offered in pharmacies for a long time.
That is why doctors advise patients to diversify their daily diet with glaucoma using natural sources.
To combat the disease, those people who suffer from glaucoma need to receive B vitamins every day, as well as A, C and E. They will improve the functioning of the very important visual organ.
Other Natural Antioxidants to Fight Glaucoma
Among natural compounds and extracts, curcumin, omega-3 fatty acids and ginkgo biloba are of great interest for the treatment and prevention of glaucoma.
- Curcumin
Curcumin, which is a component of the popular spice turmeric, has been shown in recent studies to have high neuroprotective activity in patients with glaucoma, as well as possible positive effects on the development and progression of glaucoma.
- Unsaturated fatty acids
Polyunsaturated fats, present in large quantities in fish oil, play an important role in reducing oxidative damage to the retina, improving ocular blood flow and protecting the retina from ischemia caused by elevated IOP.
It is also suggested that fish oil may reduce intraocular pressure and have a protective effect on the macula.
- Ginkgo biloba extract
Ginkgo biloba extract is believed to be effective in the treatment of various diseases associated with aging, as well as in the treatment of IOP-dependent risk factors for damage to the sensitive structures of the eye in glaucoma.
Ginkgo biloba extract improves central and peripheral blood flow, reduces spasm of blood vessels and has a protective effect against free radicals due to its antioxidant properties.
Ginkgo extract has been shown to be effective in treating Raynaud's disease, which is often associated with something called normal-tension glaucoma.
These and other properties of ginkgo prove that its extract can be used as one of the auxiliary elements in complex therapy and prevention of the consequences of glaucoma.
Vitamin A is very important for glaucoma and diabetes, which is known to be responsible for visual acuity. In order to compensate for its deficiency, the patient should include in the daily diet:
- veal liver;
- sour cream;
- orange fruits;
- butter;
- egg yolk.
The most important vitamins for glaucoma can strengthen the defenses of a weakened body. And vitamin B helps support metabolic processes inside the eyes.
If there is a deficiency of this substance, in people who suffer from glaucoma and type 2 diabetes, the blood supply gradually deteriorates, which leads to the death of eye tissue. In order not to experience a lack of vitamins, you need to include in your diet:
- red pepper;
- rose hip;
- cabbage;
- green pea;
- black currant;
- greenery;
- sea buckthorn
In case of glaucoma and type 2 diabetes, vitamin E is included in the patient’s daily diet. But in medicine it has long been known that its deficiency is the cause of the development of cataracts. In order to fill the body with reserves of this substance, the patient should consume seeds, vegetable oils and nuts.
Choosing eye vitamins for glaucoma
Before starting to take any vitamin complexes for the eyes, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist.
To fully restore vision, it is recommended to strengthen the immune system and replenish the balance of essential nutrients in the body. To prevent the development of serious pathologies with glaucoma, it is necessary to take a course of vitamin supplements and adhere to a proper diet. For this disease, it is recommended to use eye medicinal drops. The best vitamin remedies for combating glaucoma are drops, which contain B vitamins and a complete complex of microelements. Their therapeutic effect is aimed at reducing intraocular pressure and improving the condition of the optic nerve. After completing a course of vitamin therapy, the clarity and acuity of vision improves, eye fatigue during prolonged exercise decreases, and the vitality of the body as a whole increases.
Alternative treatments for glaucoma
Alternative treatments for glaucoma are always on the rise, with people constantly inquiring about these methods. The question arises: can only fashion or advertising be “blamed” for this, or are unconventional therapeutic approaches actually effective?
What do alternative treatments for glaucoma include? First of all, this is nutrition and vitamins for the eyes with glaucoma. The right food choices can have a beneficial effect on many diseases, and glaucoma is no exception. How should you eat, what is recommended to eat to alleviate the symptoms of the disease?
- Vitamin A – has antioxidant properties, its deficiency causes night blindness. Expert studies are currently being conducted to study its effect on intraocular pressure and glaucoma.
- Vitamin B1 or thiamine - has a number of group B and has a positive effect on the treatment of glaucoma.
- Vitamin C or ascorbic acid - some amount of this vitamin is found in the intraocular fluid. Therefore, it is effective in lowering intraocular pressure (do not take it in very high doses - this can have unpleasant side effects!).
- Vitamin E - we are talking about a powerful antioxidant (as well as vitamins A and C), which should contain nutrition for eye glaucoma.
- Ginkgo biloba is also a powerful antioxidant and is known to have beneficial effects on the nervous system. To date, controlled studies are being conducted to confirm its positive effect in the treatment of glaucoma.
- Blueberries - some experts claim that this berry maintains good condition of the optic nerve.
Vitamin B3 could be a cure for glaucoma
Glaucoma is one of the most common eye diseases, affecting tens of millions of people. With this pathology, against the background of increased intraocular pressure, which creates unfavorable conditions for the functioning of eye tissues (blood supply is disrupted, some structures are mechanically compressed), the death of retinal ganglion neurons occurs. Progressive atrophy of the optic nerve develops, through which visual information enters the brain - the nerve is formed by the axons of dying ganglion neurons. First, a person begins to see worse, the field of vision is limited, then blindness occurs. Recently, especially in foreign literature, glaucoma has been classified as a neurodegenerative disease.
The risk of developing glaucoma increases with age. Scientists from The Jackson Laboratory (USA), studying the pathogenesis of glaucoma, draw an analogy with an old motorcycle that seems to ride well, but one day it is not possible to ride it up a hill - some parts have worn out. Thus, a number of age-related changes, on the one hand, contribute to an increase in intraocular pressure, and on the other, to an increase in the vulnerability of neurons to damage caused by high pressure.
Scientists, working with mice that were bred as a model of glaucoma (genetically predisposed to developing it), examined their genome and metabolome - metabolic intermediates - in search of factors that contribute to the development of glaucoma with age. It turned out that in the retina of mice prone to glaucoma, compared with normal animals, the level of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), necessary for energy metabolism, decreases with age. NAD and its phosphorylated form, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), accept and transfer protons in redox reactions that produce energy in the form of ATP molecules. A decrease in NAD levels worsens the energy metabolism of neurons, promoting pathological changes in them.
NAD and NADP are formed in the body from nicotinic acid; more precisely, this substance exists both in the form of nicotinic acid and in the amide form - in the form of nicotinamide. Scientists decided to add nicotinamide (aka vitamin B3 or vitamin PP) to the drinking bowls of young mice predisposed to the development of glaucoma. To their pleasant surprise, nicotinamide prevented optic atrophy in these mice in 93% of cases, apparently increasing the metabolic resilience of aging retinal ganglion neurons and preserving their ability to resist the adverse conditions of high intraocular pressure.
Nicotinamide in foreign literature is more often called vitamin B3, and in Russian - vitamin PP, from Pellagra Prevention - preventing pellagra (Italian pelle agra - “rough skin”), a disease caused by deficiency of vitamin PP. Clinically, pellagra is characterized by damage to the skin and mucous membranes, and in severe cases, mental disorders, including dementia. Nicotinamide is found in large quantities in liver, meat, fish, legumes, buckwheat, black bread, and is synthesized in the body from tryptophan, an essential amino acid, which must also be supplied to the body with food. Nicotinamide is used in addition to the prevention and treatment of pellagra in chronic inflammatory diseases of the digestive system, infectious diseases, and atherosclerosis. Nicotinic acid (which is converted into nicotinamide in the body) is sometimes used in complex therapy of glaucoma as a vasodilator to improve blood supply to the eyes, but it is recommended to do this with caution and under blood pressure control.
The study results open new prospects for the development of inexpensive and safe treatments for glaucoma using nicotinamide. Another option is gene therapy for glaucoma. When scientists using genetic engineering methods increased the expression of the Nmnat1 enzyme, responsible for the last stage of NAD synthesis, in the eye tissues of mice predisposed to glaucoma, glaucoma did not develop in approximately 70% of cases. Scientists believe that gene therapy will be relevant for older patients who may have difficulty taking medications regularly.
In the future, the researchers plan to begin clinical trials of nicotinamide for glaucoma and are exploring the possibility of using it to treat other neurodegenerative diseases.
The role of diet in the prevention and development of glaucoma
Glaucoma is caused by increased intraocular pressure, which leads to damage to the optic nerve. It is known that proper nutrition is closely related to the normal functioning of the optic nerve. This is confirmed by the facts of the development of optic nerve atrophy with deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid.
Available data show that a healthy diet balanced with vitamins and minerals is closely associated with a reduced risk of developing glaucoma, as well as its complications.
No product has yet been discovered that can effectively reduce intraocular pressure. However, dietary changes can help reduce the risk of damage to the retina and optic nerve and prevent or significantly slow down vision loss.
Therefore, the diet for glaucoma should be aimed mainly at protecting nerve cells and fibers from damage under the influence of high intraocular pressure. To do this, it is necessary to pay special attention to antioxidant substances and foods that are rich in them.
For example, spinach contains high levels of antioxidants - lutein and zeaxanthin - nutrients that are present in the retina of the eye. These two substances are believed to be important in protecting eye tissue from the effects of free oxygen radicals, which play a major role in the mechanism of cell damage.
That's why many doctors tell their patients about the great benefits of spinach and other green leafy vegetables, and also recommend taking dietary supplements rich in antioxidants as additional help for all types of vision problems, including glaucoma.
There are other nutrients that scientists believe may be good for protecting the eyes from the effects of glaucoma due to their antioxidant abilities. These include vitamins A, E, C and zinc.
Important food sources of microelements include fruits, green vegetables, cereals, meat, and fish. A properly selected and formed diet has a positive effect on the optic nerve. This, in turn, helps improve metabolism and slows down the development of glaucoma.
It is especially important to follow a diet if you have cataracts. This is due to the high probability of transition to glaucoma. The diet is selected by a nutritionist based on the patient’s condition.
It is not recommended to switch to a different diet on your own. This is due to the importance of correctly calculating the amount of microelements and substances for the daily diet.
Important rules for treatment and prevention
To become an active physician assistant in the treatment of glaucoma, you must be well informed about your disease. To achieve good functional results, treatment of glaucoma should be started early in the development of the disease, before irreversible changes have occurred in the eye.
People over 40 years old need to be careful about the condition of their eyes. If you experience visual discomfort, fatigue or unpleasant sensations in the eyes, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
Important!
If a family member is diagnosed with glaucoma or the diagnosis has been established in one of the immediate family, periodic examination of all family members is necessary, without adhering to age criteria.
With glaucoma (especially in the case of open-angle form), the patient usually does not worry about anything, and it may seem to him that he is healthy. However, glaucoma is insidious - it is a chronic disease characterized by pathological changes in the eye over time, over a certain (sometimes quite significant) period of time.
Therefore, for follow-up examinations, you should visit a doctor once every 3-6 months. Even if you are taking medications or have undergone laser or surgical treatment, constant monitoring is necessary.
If you experience any unpleasant sensations in the eye (a feeling of fullness, especially in the morning, pain in the eyebrow area, periodic blurred vision or rainbow circles when looking at a light source), you must immediately contact your doctor for an emergency examination.
It is necessary to strictly follow the regimen recommended by your doctor and not try to change it at your own discretion. You should not refuse examination and treatment, or postpone it for a long time.
When leaving the country for a long period of time or changing place of residence, you need to take a detailed extract from the medical history with information about the course and characteristics of the disease, surgical interventions performed, and conservative treatment.
Equally important for successful treatment of glaucoma is the correct lifestyle and daily routine.
Due to impaired vascular regulation, patients with glaucoma do not tolerate changes in ambient temperature, especially low temperatures. Therefore, usually in winter, intraocular pressure (IOP) fluctuations often occur in the direction of its increase.
Patients with glaucoma are advised to avoid hypothermia, not to go outside at very low temperatures, and not to take cold water or air procedures.
During the winter period, it is recommended to visit your doctor more often and monitor intraocular pressure (IOP) and conduct maintenance courses of conservative treatment.
Walking in the fresh air, light exercise, breathing exercises, and general hardening of the body have a positive effect on the course of the glaucomatous process.
In the summer, in bright sunshine, it is necessary to use green glasses produced by the medical industry for patients with glaucoma. Special light filters provide visual comfort and good protection from ultraviolet radiation harmful to the retina.
The use of dark sunglasses is less recommended because they obscure the surroundings, impair the patient's orientation, and may increase intraocular pressure (IOP).
When staying in the sun for a long time, be sure to wear a hat; sunbathing is preferable before 10 a.m. and after 5 p.m.
At home, a patient with glaucoma should, if possible, avoid situations that cause a rush of blood to the head:
- physical labor associated with bending the head and torso
- washing floors
- weeding work on a personal plot
- washing clothes
- picking mushrooms and berries
- lifting weights
- pose “upside down” when doing gymnastics or yoga
- some sports (for example, weightlifting)
If you drive a car, here are a few precautions:
- use glasses when driving;
- in bright sunshine, wear special protective green glasses for patients with glaucoma;
- try not to drive a car at dusk or at night;
- be alert, watch the road in front of you and to the sides.
Diet is considered an important factor in the treatment of glaucoma. Proper nutrition, as well as additional intake of a complex of vitamins and minerals, have a beneficial effect on the condition of the optic nerve and improve metabolic processes in it.
The diet should preferably be dairy-vegetable, rich in vitamins and microelements.
Diet for glaucoma
One of the main places in the prevention and treatment of eye diseases is a healthy lifestyle and balanced nutrition (diet). Doctors recommend that patients with glaucoma use not only medications for treatment, but also take various vitamin complexes, as well as follow a diet to better supply the cornea, optic nerve and retina with the necessary nutrients.
Essential vitamins and minerals for glaucoma
For eye health, especially with glaucoma, you need:
Antioxidants
To revive and preserve the tissues and cells of the eye, you need to adhere to a diet that is based primarily on vitamins rich in antioxidants. These antioxidants include:
- Vitamin C contained in ascorbic acid. It strengthens the walls of blood vessels, normalizes the movement of fluid inside the eye, and reduces pressure in the eye. The glaucoma diet recommends a daily intake of about 90 mg for men and about 70 mg for women.
- Vitamin E (tocopherol and tocotrienol). It accelerates the formation of intercellular substance and bundles of collagen fibers that form connective tissue (which in turn forms the sclera of the eye). Consumption per day for men - 10 mg, for women - 8 mg.
- Vitamin A is needed for the proper functioning of the retina, as it is part of the visual pigment and affects light sensitivity. If there is a deficiency in retinol, the fluid within the eye moves poorly, leading to dry eye and profound changes in the shape of the cornea, ultimately leading to blindness. Nutritionists recommend vitamin A intake for men is 1000 mcg. per day, and for women - 800 mcg.
- Lutein is an important antioxidant and carotenoid that protects the pupil from harmful rays and substances. It comes to us with food, but the carotonoid zeaxanthin is formed in the eye from lutein, accumulates in the eye tissue and helps the retina cope with age-related changes. The daily norm is approximately 10 mg.
- Another vitamin that is needed to protect the eyes from fatigue is vitamin P (rutin). It has a good effect on the quality of vision, increasing the light sensitivity of the retina. Its daily dose has not yet been determined.
- Zeaxanthin;
- Lycopene (in tomatoes).
Vitamins B
In addition to antioxidants, patients with glaucoma should include vitamins belonging to category B (B1, B2, B6, B12) in their intake. Since they manage redox processes, coordinate cell development and carbohydrate metabolism.
- B1 affects metabolism, the proper functionality of nerve cells, and intraocular pressure.
- B2 is needed to maintain the visual apparatus in good shape.
- B12 is necessary for the smooth functioning of the optic nerve, especially in the early stages of glaucoma.
Trace element zinc
With a pathology such as glaucoma, not only vitamins are important, but also various microelements that participate in the vital processes of cells located in the retina and optic nerve. The health and maintenance of these components of vision are vital to a healthy eye. These microelements include, for example, zinc.
Omega-3
To normalize intraocular pressure, nutritionists insist on increasing the consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as omega-3. These acids are necessary for the proper functioning of the macula of the eye, in which rays of light from objects are focused, and on which a clear perception of the environment depends.
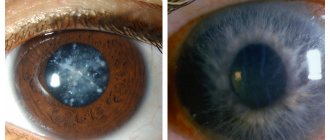
Why do cataracts and glaucoma occur?
Cataract is an irreversible clouding of the lens and capsule. Often the disease is a consequence of the aging of the body. The following pathologies that provoke cataracts are also significant:
- metabolic disorders;
- diabetes.
The chemical composition in the tissues of the lens changes as natural aging occurs, which is accompanied by the formation of free radicals. They lead to the accumulation of toxic compounds.
Over time, the eye's antioxidant protection weakens. This increases the risk of developing cataracts. Gradually, adverse effects on the tissues of toxins are observed. Irreversible changes occur in the lens of the eye. If treatment, which also includes taking vitamins, is not started promptly, cataracts may occur. Pathology significantly worsens the quality of life.
The causes of cataracts include:
- unfavorable heredity;
- deformation of the lens due to injury;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- eye diseases (glaucoma, myopia);
- severe infectious processes;
- Down syndrome;
- burns of the organs of vision;
- eczema, neurodermatitis and other skin diseases;
- prolonged insolation;
- long-term corticosteroid therapy;
- exposure to radiation;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- poisoning with heavy metals and toxic substances;
- bad habits (excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking);
- insufficient sleep.
Sometimes cataracts are congenital. Pathology occurs as a result of previous diseases, which include rubella. Lens abnormality and cataracts may develop if a pregnant woman takes certain medications or has been exposed to radiation.
Attention! Symptoms of cataracts include double vision, blurred vision, increased sensitivity to light, the appearance of a non-existent halo around the light source, impaired color vision, and a feeling of haze.
Glaucoma causes increased pressure in the eyes, which leads to atrophy of the optic nerve. The pathology can progress asymptomatically for a long time. Often, a visit to a doctor is noted when there is a loss of visual acuity.
Glaucoma is considered a dangerous disease that causes blindness if left untreated. Timely therapy can stop the process of optic nerve atrophy. It is not possible to cure the disease completely.
In most cases, glaucoma is bilateral and is associated with a genetic predisposition. If there is a family history, intraocular pressure should be constantly monitored.
Increased pressure in the eyes and the development of cataracts are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- blurred vision;
- narrowing of fields;
- severe pain.
The reasons for the development of glaucoma are due to its varieties:
- congenital;
- secondary;
- open angle;
- closed angle.
Typically, an increase in pressure is associated with a violation of the drainage system of the eyes, leading to a change in the outflow of chamber fluid. Atrophy is caused by stress on the optic nerve. Among the factors that provoke glaucoma are:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- sclerotic changes in blood vessels;
- lowering blood pressure.
These factors cause insufficient blood supply to the brain. Gradually, visual functions are impaired due to changes in metabolism in the tissues of the optic nerve and eye, and cataracts and glaucoma develop.
Necessary products and proper nutrition for eye glaucoma
So, we found out what vitamins, microelements and acids are necessary to support the treatment and prevention of glaucoma. Now let's look at what products these substances can enter our body. This will help you establish the right diet for yourself if you have glaucoma, as well as generally understand what foods are best to eat to maintain the quality of your vision.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is excreted by the body, so it needs to be replenished daily. Sources can be fruits, vegetables, herbs and berries.
Fruits containing vitamin C per 100 grams of product:
- Orange - 60 mg.
- Lemon - 40 mg.
- Mandarin - 38 mg.
- Quince - 23 mg.
- Apple, banana - 10 mg.
- Pear - 5 mg.
- Red bell pepper - 250 mg.
- Yellow bell pepper - 150 mg.
- Brussels sprouts - 120 mg.
- Broccoli - 89 mg.
- Cauliflower - 75 mg.
- Radish - 29 mg.
- Peas, radishes - 25 mg.
- Beans - 20 mg.
- Zucchini - 15 mg.
- Beets, cucumbers, onions - 10 mg.
- Parsley - 150 mg.
- Dill - 100 mg.
- Spinach - 55 mg.
- Sorrel - 43 mg.
- Celery - 38 mg.
- Rosehip - 470 mg.
- Sea buckthorn, black currant - 200 mg.
- Kiwi - 92 mg.
- Rowan - 70 mg.
- Strawberries, wild strawberries - 60 mg.
- Gooseberry - 30 mg.
- Raspberry, melon, pineapple - 20 mg.
- Cranberries, cherries - 15 mg.
It is important to remember that during heat treatment and even upon contact with cold water, ascorbic acid is destroyed.
Tocopherol
It is contained in:
- vegetable oils;
- greenery;
- salad;
- sea fish;
- nuts;
- grains of rye;
- wheat;
- raspberries (half the required dose of vitamin per day can be obtained by eating a glass of raspberries);
- wheat germ oil (more than 215 mg per 100 grams of product).
Adviсe
- If you steam food, it will retain 90% of vitamin E.
- When frying and grilling, the vitamin completely disappears.
- It goes well with foods high in vitamins A and C.
Retinol or pure vitamin A
It is formed from beta-carotene and can accumulate in the body and remain there for more than a year. Large amounts of this substance are found in red and orange vegetables and fruits.
Beta-carotene is found in various plant foods, including:
- Carrot.
- Spinach.
- Pumpkin.
- Apricots, and more in dried varieties.
- Parsley.
In addition, it is also found in products of animal origin, especially such as:
- liver, especially beef;
- fish fat;
- fish roe;
- egg yolks;
- butter;
- cheeses;
- milk;
- cream.
When you cook products containing retinol, they lose 10% of it. In addition, vitamin A is lost if food is exposed to air for a long time or if it is defrosted for a long time.
Products with B vitamins
The list of foods that contain B vitamins should be noted:
- Various yeasts, more in breweries.
- Dairy products, more in cheese and cottage cheese.
- Sunflower seeds, nuts.
- Cereals and grains.
- Fish.
- Various meats, more in the liver.
- Legumes.
- Mushrooms.
Vitamin P
It predominates in fruits, berries and vegetables:
- Blackberries, currants (black), raspberries, blueberries, rowan, rose hips, cherries.
- Citrus fruits, grapes, apples, apricots.
- Cabbage, tomatoes, spinach, lettuce (Chinese or iceberg), capsicum, greens (green onions, parsley, dill).
If these foods are frozen, vitamin P will be destroyed. Therefore, if possible, eat them fresh.
Antioxidant lutein
Present in fruits, vegetables and yolks. There is especially a lot of it in dark green vegetables, such as:
- spinach;
- cabbage - leafy cabbage and broccoli;
- green pea;
- turnip tops;
- dandelion and mustard leaves.
Notes
- Nutritionists advise putting such vegetables in a light broth, salad, or simply stewing them, adding onions and garlic, and also seasoning them with olive oil.
- Also, good sources of lutein are fruits, vegetables and berries that are orange and bright red. You can consume these products to get lutein for the body, frozen and canned, but without sugar.
- There is also a lot of it in natural juices, for example, tomato juice contains its daily requirement of 6 mg.
- The orange color of the yolk also means that lutein is present there.
- A serving of oatmeal contains about 0.43 mg of this antioxidant.
Microelement zinc for glaucoma
We know that microelements play an important role; they can be obtained by consuming vegetables, legumes, bran, nuts, liver, fish, cereals, cheese and so on. For example, let’s give the content of such an important trace element as zinc per 100 grams of foods rich in it:
- Oysters - 60 mg.
- Fried beef liver, wheat bran - 16 mg.
- Fish - 12 mg.
- Beef stew – 9.5 mg.
- Poppy seeds - 8 mg.
- Cedar nut - 6.5 mg.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
They are present in sufficient quantities in fish oil, vegetable oil, cod liver, black caviar, nuts, and cheese. Since they are very high in calories, they should be consumed strictly limited, in small doses.
Nutrition for the prevention and treatment of eye diseases
Treatment and prevention with diet can reduce the risk of complications and improve overall health. Glaucoma and cataracts, like many other diseases, require proper nutrition. By following certain rules and principles, you can achieve significant improvement in your condition.
The patient's diet should be nutritious and balanced. Nutrition for glaucoma and cataracts must include the following products:
- cabbage, spinach, turnips;
- corn, green peas;
- persimmons, tangerines;
- bell pepper;
- black currant and sea buckthorn;
- rose hips and greens;
- eggs.
People suffering from ophthalmological diseases are prescribed vitamins with blueberries. This berry contains a large amount of antioxidants and nutrients, which allows you to provide sufficient nutrition to the retina and strengthen the muscular system of the eyes.
The most common treatment for cataracts involves surgery. During the rehabilitation period, a person needs to follow special nutritional rules, so this issue must be approached with special attention.
It is worth following a diet after cataract removal to prevent swelling, hemorrhage and other negative consequences. To do this, it is necessary to exclude difficult-to-digest foods, fatty and salty foods from the diet. It is better to divide all daily food into four or five meals. In this way, you can achieve optimal nutritional conditions and reduce the risk of complications after surgery.
Ophthalmologist's advice
To summarize, if you suffer from glaucoma, you need to adhere to a balanced diet, which should combine foods of plant origin (vegetables, fruits, berries, blueberries and blueberries are especially important for the eyes), various dairy products (low in fat), and products of animal origin ( meat, fish, also low-fat).
- Nutritionists also advise not to fry this food, but to consume it boiled or steam it.
- In addition, for patients with glaucoma, it would be a good idea to add eggs to your diet (but they should not be consumed more than four times a week, preferably every other day).
- Liquids should be consumed no more than one and a half liters per day, including all drinks and soup, so as not to provoke intraocular pressure.
- It is not recommended for those suffering from glaucoma to starve or sit on any one product; it is better to eat every day, in small portions and more often.
Prohibited foods for glaucoma
We have found out which foods are useful for patients with glaucoma and how to eat them, now we will consider which foods should be avoided:
- Fried, smoked.
- Canned food and semi-finished products.
- Very salty.
- Meat and fish broths of strong concentration.
- Sweet and floury.
- Tea and coffee, if they are very strong.
- Alcoholic drinks.
Diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma
At the Vision Restoration Center you can undergo examination using modern equipment. Our clinic is equipped with the latest technology. We use the latest developments to thoroughly diagnose and make the most accurate diagnoses. The effectiveness of treatment often depends on proper identification of the causes of the disease. Modern equipment allows you to effectively cope with this task. Diagnostics within the walls of the Vision Restoration Center will be the first step towards successful treatment of glaucoma.
At the Vision Restoration Center, your treatment will be handled by an experienced specialist. Our doctors have personal awards - diplomas and certificates. We work for you 7 days a week, from 8:00 to 20:00.
Don't put off treatment until tomorrow! Make an appointment right now using the feedback form on the website. It's simple: just leave your contact information and select the center you plan to visit.
Presumptive menu for glaucoma
Let's consider a sample menu for patients with glaucoma:
- Breakfast: oatmeal cooked with low-fat milk, or cottage cheese (preferably low-fat, no more than 5%), you can also eat one apple or orange, for the third green tea or herbal decoction.
- Lunch: yogurt, soft cottage cheese.
- Lunch: chicken soup with vegetables (or just chicken broth, but then prepare another salad), a piece of steamed chicken or veal.
- Afternoon snack: berries, preferably fresh.
- Dinner: stewed vegetables and a piece of veal or chicken, freshly squeezed juice, preferably carrot juice.
- At night: kefir or yogurt, you can add a little honey if you wish.
The main recommendations on the diet you need will be given by your attending physician, who will take into account the stage of glaucoma, concomitant diseases and the individual characteristics of your body.
Sample menu
The best breakfast option is cottage cheese with fruit.
When compiling a diet, it is recommended to focus on the following regimen:
- First breakfast: cottage cheese with pieces of apples or pears;
- a glass of juice.
- homemade yogurt with berries.
- lean borscht;
- green salad with olive oil.
- baked hake;
- a glass of kefir.
Portion sizes are calculated based on physiological parameters, so it is better to consult a nutritionist. Individual intolerance to a certain ingredient is possible, manifested by gastrointestinal upset, redness of the skin and itching. In this case, the dish is excluded from the menu. Drinking fresh juices for breakfast is healthy, but not on an empty stomach. People with high acidity should prefer fruit drinks.