Glaucoma is a disease characterized by high pressure in the eyes. The disease is accompanied by severe eye pain and headache. The consequences of improper treatment of glaucoma are very dire - complete loss of vision. The disease should be treated by an experienced ophthalmologist, especially for those people who have a predisposition. The pain with this disease varies: burning, boring or throbbing. This condition is difficult for a person to tolerate, and most often the unpleasant sensations spread to the head. Feeling unbearable pain, the patient sees a cloudy image and rainbow circles around him.
In this article we will talk about glaucoma, symptoms, causes of pain in the eye and how to deal with this unpleasant disease.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma Source: dvaglaza.ru Glaucoma is a disease of the visual organs, which is manifested by increased intraocular pressure.
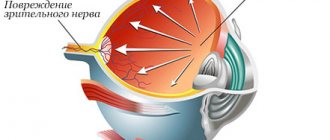
Pain with glaucoma is a common occurrence, affecting not only the eyes, but also the areas near them. The pain is acute and difficult to bear. The seriousness of glaucoma lies precisely in the fact that it inevitably leads to blindness if not intervened in time. If treatment of the disease is started in a timely manner, the likelihood that the process of nerve atrophy will be stopped increases.
Glaucoma is one of a number of eye diseases that cannot be completely cured. As already noted, it is associated with increased intraocular pressure, which primarily affects the optic nerve and disrupts the visual field, and untimely medical intervention leads to loss of vision.
Often, glaucoma is a bilateral process, and one of its occurrence factors is hereditary predisposition. Thus, if a person’s parents were susceptible to glaucoma, then in this case, the pressure inside the eyes must be constantly monitored.
At the first stage of glaucoma development, the patient is found to have high eye pressure, which affects the optic nerve and leads to its atrophy. The patient usually complains of poor vision and narrowing of its fields.
Glaucoma invariably leads to blindness. If vision in one eye has already been lost, this does not mean that the disease has stopped its development. It will continue to affect the other eye. With glaucoma, the patient experiences severe headaches and eye pain. Sometimes it is necessary to remove the eye to relieve pain symptoms.
Eye pain is a characteristic symptom of glaucoma. In this case, the pain syndrome often spreads to the head. However, glaucoma does not always cause pain in the eyeball, which can make diagnosing the disease difficult.
There are cases when, instead of an ophthalmologist, a patient turns to a neurologist with complaints of migraine. As a result of a long examination, it is not always possible to establish the cause. The diagnosis of glaucoma is made after visual acuity begins to decline.
List of medications
The second name of Pyrazidol is Pirlindol. The drug is produced in Russia. It is a reversible inhibitor of MAO type A, like Moclobemide. This drug is used to prevent and treat depression of the inhibited type, as well as depressive disorders with pronounced anxiety manifestations. The advantages of the drug are that it can be taken for glaucoma, prostatitis and heart pathologies.
Another powerful drug created as a result of the synthesis and introduction of a chlorine atom into the imipramine molecule is Anafranil. It is used to treat resistant depression and to relieve the affective phases of severe depression.
Maprotiline, or Ludiomil, is an antidepressant with a tetracyclic structure. It has a fairly powerful thymoanaleptic effect when interacting with anxiolytic and sedative components. It can be used for circular depression in combination with ideas of self-blame. The drug is used for involutional melancholia. Maprotiline is produced in the form of oral medications and injections.
First and second choice drugs are used in treatment. The following antiglaucomatous drugs exist:
- selective sympathomimetics - Clonidine, Clonidine;
- miotics - “Pilocarpine”, “Oftanpilocarpine”;
- sympathomimetics - “Epiphrine”, “Glaucon”;
- beta-blockers “Oftan timolol”, “Timohexal”;
- prostaglandins - “Travatan”, “Xalatan”;
- carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - Azopt, Trusopt;
- combination drugs - “Fotil”, “Cosopt”, “Proxofelin”.
The general rule is that if people receiving psychotropic drugs - hypnotics, tranquilizers, antidepressants or antipsychotics - become unwell, the first action should be to reduce the dose or stop taking the drug, rather than adding another drug to the treatment regimen.
Tranquilizers
In a discussion about the use of tranquilizers and sleeping pills, experts from the World Health Organization (WHO) state the following: “Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress and drug therapy should only be started in cases of excessive anxiety that makes normal functioning impossible. Long-term use. ineffective and should be avoided.
Short-term use (less than two weeks) minimizes the risk of developing drug dependence.” They also concluded: “A basic discussion of the causes of insomnia and anxiety, as well as informing the patient about the disadvantages of drug therapy, can often help patients without resorting to prescribing medications.”
Two studies of alternative treatments have shown conclusively that in the vast majority of cases, the use of tranquilizers and sleeping pills is unnecessary. 90 patients suffering primarily from anxiety were randomly divided into two groups. The first group received the usual dose of a benzodiazepine tranquilizer.
MORE ABOUT: Vitamins for dark circles under the eyes
In the second study, patients with chronic anxiety were given one of three tranquilizers or a placebo (sugar pills). Anxiety assessments were carried out weekly by patients and professional assessors, and at the end of the month the results showed that “all four treatments were similar in their therapeutic effectiveness in cases of severe anxiety.” Therefore, placebos are as effective as tranquilizers.
Faced with declining sales of sibazone (Valium) in the early 1980s, Roche (and other manufacturers of the drug) began aggressive advertising to target its use in older patients. A series of beautifully illustrated brochures entitled “Roche Seminars on Aging” were sent to doctors in 1982. Roche recommended Sibazone as a suitable remedy for older people with “limited” abilities who suffer “not only from their limited physical abilities, but also from social conditions and habitats."
The fact that more than 1.7 million people 65 years of age and older used tranquilizers daily for at least a year is the best evidence of the abuse of these drugs. Considering that the effectiveness of using such drugs for more than four months is questionable, the number of older people using tranquilizers for longer periods is staggering - the average number of tablets (160) for each of the 10 million tranquilizer users at 60 years of age and older buys a year, enough to take daily for more than 5 months.
Sleeping pills
Overprescription or misprescription of sleeping pills results in about half a million people taking such drugs every day for at least a month. Since such remedies have not been proven to be effective for this period or longer, all these patients are putting their health at risk without any justification.
The amount of benzodiazepine sleeping pills prescribed to patients per year on average is sufficient for five months, which is 5 to 10 times longer than their proven effectiveness. Consequently, sleeping pills are misprescribed in 80 to 90% of cases.
The increasing frequency of use of such drugs was the subject of conclusions and recommendations in an extensive study by the Institute of Medicine of the National Academy of Sciences in 1979. Regarding the use of such drugs, the researchers concluded: “Hypnotics may have only limited use in ordinary medical practice: it is difficult to scientifically justify most prescriptions of sleeping pills.
Commenting on the specifics of the use of sleeping pills in older people, the authors
Although older people are more likely than younger people to report sleep disturbances, studies have shown that time to fall asleep does not increase with age, and total sleep time decreases very little, if at all. Insomnia most often occurs in older people who go to bed early and also sleep frequently during the day. Thus, the researchers conclude that "daytime naps should be eliminated rather than treated for nighttime insomnia caused by them."
Dr. Marshall Folstein, a psychiatrist at Johns Hopkins Hospital and an expert on Alzheimer's disease, says it's "extremely rare to find older people who actually need them."
Another danger is excessive dosages. A study of dosages of sleeping pills found that the majority (almost 80%) of people 65 years of age and older took an “overdose” of flurazepam (30 mg), although a dose of 15 mg was recommended for older people. (In this book, we include flurazepam in the "Do Not Use" category.) Given the National Academy of Sciences' recommendations that sleep medications should be used only on a limited basis, these medications are increasingly being prescribed to older adults—especially in the elderly. long periods of time - poses a serious threat to their health.
What are the main dangers of using sleeping pills and tranquilizers?
Drug dependence, daytime sleepiness, amnesia, increased risk of car accidents, poor coordination leading to falls and hip fractures, impaired learning ability, slurred speech and even death are side effects of these drugs. This is especially likely when these drugs are taken with alcohol or other CNS depressants. This can happen to anyone at any age.
Older people's bodies cannot eliminate these drugs as quickly as younger people. Older people are also more sensitive to the side effects of medications. Despite the obviousness of this fact, older people, firstly, are more often prescribed tranquilizers and sleeping pills, secondly, they usually receive a standard rather than a reduced dose, which could reduce the risk of side effects, and thirdly, they are prescribed these drugs for longer periods of time than younger people.
Therefore, it is not surprising that older people are more at risk of experiencing negative effects, and when such effects do occur, they tend to be more pronounced. One of the biggest obstacles to detecting and eliminating these problems is that problems that arise are attributed to the aging process rather than to medications.
Deterioration of thinking processes, amnesia, learning impairment or loss of coordination in younger people when taking the drug is perceived as an alarm signal. If the same symptoms appear in older people, especially if they develop slowly enough, the doctor's reaction often boils down to the remark: “well, he (she) is already old, what did you expect?” This approach leads to worsening negative effects, since the doctor continues the previously started drug therapy.
A study of older adults with hip fracture found that 14% of these injuries were associated with the use of psychotropic medications, including hypnotics, tranquilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants, especially drugs such as sibazone, chlozepid, and flurazepam.
Types and forms of the disease
Source: glazaexpert.ru There are several forms of glaucoma:
- closed angle,
- open angle
- secondary.
Open-angle glaucoma is manifested by an open angle of the anterior chamber, through which chamber humor flows. Open-angle glaucoma accounts for more than 90% of all cases of this disease. In this course of the disease, the iridocorneal angle is open, hence the name - open angle.
There is a disturbance in the outflow of intraocular fluid (the reasons for this have not yet been fully identified), which contributes to the accumulation of fluid and a gradual but constant increase in pressure inside the eye. Ultimately, this process can lead to destruction of the optic nerve and complete loss of vision.
Angle-closure glaucoma is characterized by a closed or extremely narrow angle of the anterior chamber of the eye through which ocular fluid slowly drains. The outflow of fluid leads to increased intraocular pressure. Angle-closure glaucoma is a less common form of this disease.
It occurs mainly in people over 30 years of age who suffer from farsightedness. With this form of the disease, a rapid rise in intraocular pressure occurs. All factors that cause the pupil to dilate can cause the patient's iris to block the outflow of intraocular fluid.
Secondary glaucoma occurs as a side effect of intraocular surgery, intraocular changes, medications, or injury to the eye.
Primary glaucoma is the most common type. As mentioned above, people over forty are most susceptible to it.
Congenital glaucoma is formed as a result of an abnormal development of the eye in the embryo (the so-called dysgenesis of the anterior chamber angle) or as a result of some other eye disease suffered before or during childbirth (this could be trauma, tumors, inflammation or something else ).
Who is more likely to get sick?
Like any other disorder, glaucoma has a risk group. Being in it increases the likelihood of becoming the owner of this unpleasant “gift” significantly. People who should be especially careful about this disease include:
- relatives of patients with glaucoma, the closer the patient is in the blood line, the greater the likelihood that it will be inherited;
- people over 40, at this age health weakens, in particular, eye health;
- specialists who, as part of their profession, have to strain their eyes every day, for example, programmers, welders, accountants, etc.;
- owners of farsightedness, myopia and astigmatism;
- victims of eye injuries, especially from inflammatory processes and infections of various kinds;
- patients who, for various reasons, have undergone or are undergoing treatment with hormonal drugs;
- people with high or low intraocular pressure;
- those who have undergone eye surgeries, whether they were successful or not.
Just don’t be scared, because being in a risk group is not a death sentence, but a warning and an incentive to visit the eye doctor more often.
Symptoms of glaucoma
20 percent of all patients diagnosed with glaucoma suffer from closed glaucoma. In most cases, it develops in farsighted people, who are initially predisposed to the formation of a closed angle of the chamber of the eye. The disease begins to manifest itself, most often, in people after forty years of age.
People who have crossed the age of forty are also susceptible to open-angle glaucoma. In its early stages, there are no symptoms, but intraocular pressure makes itself known, and patients begin to experience severe headaches, a kind of fog in the eyes, as well as irises around light sources.
The clinical picture intensifies from time to time, and then a drop in visual acuity is observed, as well as a narrowing of its fields.
- A person begins to see worse in the dark.
- There is pain in the eye.
- There is a feeling of heaviness.
- The field of view is narrowing.
- Vision becomes weakened and foggy.
- Dizziness.
- In acute forms, pain is felt in the head.
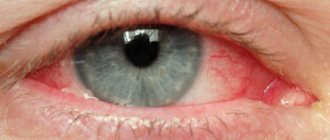
Eye pain due to glaucoma is pain in the eye, which is accompanied by the appearance of fog and iridescent circles. On examination, there is a slight congestive injection, corneal edema, and the pupil is wider than the pupil of the other eye.
Visual acuity is significantly reduced, specific changes in the visual field occur (expansion of the blind spot, annular scotomas, narrowing of the boundaries).
Eye pain can also occur with a sharp increase in intraocular pressure in cases of decompensated glaucoma - the so-called acute attack of glaucoma. It can appear suddenly, first in the form of an acute attack, or it can occur against the background of an exacerbation of the chronic course of the disease.
Symptoms of an acute attack of glaucoma are as follows:
- sharp pain in the eye, which spreads to the temple, occipital region, along the trigeminal nerve
- nausea
- vomit
- general weakness of the body.
Upon examination, swelling of the eyelids, redness of the eye, congestive injection of the eyeball, swelling of the cornea, the pupil is wide, and there is no reaction to light. Vision is sharply reduced. The eyeball is painful and hard on palpation. Intraocular pressure reaches 50-60 mm Hg. Art.
It should be noted that often an acute attack of glaucoma is mistaken for a migraine, hypertensive crisis, or poisoning, which leads to serious consequences, since the patient in this case must be helped immediately and consult a specialist for urgent treatment.
Glaucoma - symptoms and signs of an impending threat
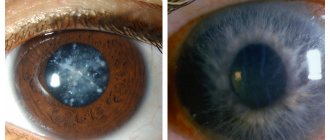
In the popular lexicon, glaucoma is called quite sweetly - “green water”, all due to the fact that when this disorder worsens, the pupil becomes yellow-green. Even though it looks attractive, this disease can lead to irreparable consequences, the most severe of which is complete loss of vision. In order to know the enemy by sight, we suggest you familiarize yourself with his symptoms:
- discomfort in the eye area: burning, squeezing, feeling of heaviness, tension, etc.;
- blurred vision and possible dizziness;
- “clogging” of the review, i.e. the appearance of dots, floating spots, “rainbow” halos, etc.;
- decreased ability to see in low light conditions;
- periodic headaches.
Have you found these symptoms? Even if so, timely contact with a specialist, in most cases, can completely eradicate the disease. A specialist who suspects a patient has glaucoma pays attention to the following signs:
- increase or decrease in pressure inside the eyeball;
- changes in the structure of the optic nerve;
- narrowing of the field of view.
Eye pain
Pain in the eye with glaucoma manifests itself in different ways: throbbing, cutting, drilling, and is often felt as a burning sensation. It can be strong and difficult to bear, manifests itself first in one eye, and gradually takes over the head.
Sometimes there is pressure on the eye and sensitivity to light. A person sees the reflection of rainbow circles from any light sources.
However, in most cases the disease is accompanied by pain in the affected eye. In this case, the nature of the sensations can be sharp, dull or aching - this depends on the stage of the disease and the level of intraocular pressure. At the same time, pain brings with it other unpleasant symptoms:
- blurred image;
- rainbow circles;
- photophobia;
- decreased visual acuity.
An acute attack of glaucoma is accompanied by sudden pain in the eye, which radiates to the temporal lobe of the brain, the occipital part and sometimes spreads to the trigeminal nerve. This may cause nausea and dizziness. Changes are noticeable even upon visual examination: the eyelids are swollen, the cornea is thickened, the pupil is dilated.
With glaucoma, the eyes hurt even when the disease progresses gradually. At the same time, along with unpleasant sensations, a feeling of dilation of the eyes appears.
Symptoms periodically appear and disappear, depending on the level of IOP. One of the problems is that the pain does not go away under the influence of analgesics. Relief occurs only after the pressure in the eye is reduced.
Pain in the eye during glaucoma is associated with increased intraocular pressure; it is observed in some patients with open-angle glaucoma, although it is not a mandatory symptom of this disease.
On examination, there is a slight congestive injection, corneal edema, the pupil is wider than the pupil of the other eye. The anterior chamber is smaller than usual. With the systematic use of miotics, the clinical picture is blurred.
A special study reveals an increase in intraocular pressure to 35-50 mm Hg. Art. often decreased visual acuity, specific changes in the visual field (expansion of the blind spot, annular scotomas, narrowing of the boundaries).
Urgent Care
Instillation of 1-2 drops of 1% or 2% polycarpine solution 2-3 times a day. In some cases, pilocarpine installations reduce pain due to a decrease in intraocular pressure.
Hospitalization is not indicated. However, in all cases suspected of glaucoma, it is necessary to refer the patient to an ophthalmologist for a detailed examination and selection of an individual mystical regimen.
If drug treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention is recommended, which gives the best results in the initial stages of the disease.
But still, most often glaucoma is accompanied by pain in the eye. The sensations can be aching and dull, but sometimes acute pain occurs. The clinical picture of the disease depends on the level of intraocular pressure and the stage of glaucoma.
Usually the pain is accompanied by other typical symptoms:
- The appearance of rainbow circles;
- Photophobia;
- Blurred vision;
- Decreased visual acuity.
In an acute attack of intraocular hypertension, pain in the eyeball appears suddenly. It can spread to the innervation zone of the trigeminal nerve, the temporal and occipital lobes of the brain. In addition, nausea and dizziness occur.
In the chronic course of glaucoma, the pain syndrome is accompanied by a feeling of dilation of the eye. These signs are persistent and depend on the level of intraocular pressure.
A distinctive feature is that the pain does not disappear when taking non-steroidal analgesics. True relief comes only from normalizing blood pressure.
Causes of eye pain
Pain in the eye occurs due to increased pressure in the organ of vision. Intraocular pressure depends on the balance of secretion (excretion) and outflow of eye fluid. When the indicator rises, pain occurs, since the fluid does not leave and puts pressure on the structural units of the eye.
The occurrence and progression of the primary form of glaucoma can be influenced by two types of factors: local and general. Local factors include changes in the ocular drainage system, as well as changes in microvessels.
Common factors include heredity, as well as neuroendocrine and hemodynamic disorders. The mentioned changes lead to disruption of the ocular drainage system, resulting in poor outflow of chamber fluid from the eye, which leads to increased ocular pressure.
In addition, pressure occurs on the optic nerve, which leads to its atrophy. Middle-aged and elderly patients suffer mainly from open-angle glaucoma. Its occurrence is due to a number of changes in the body that are characteristic of this age.
A number of negative factors have been established that influence the development of open primary glaucoma, namely:
- cervical osteochondrosis,
- low blood pressure,
- sclerotic changes in the cervical vessels.
All of the factors mentioned cause poor blood supply to the brain, which disrupts visual functions, as well as disrupts metabolism in the tissues of the eye and optic nerve.
There are certain risk factors that influence the occurrence of glaucoma and its progression. These factors are usually divided into local and general. A local factor is myopic refraction, better known as myopia.
And common factors may include poor heredity, diseases of the thyroid gland or central nervous system, and diabetes mellitus. In addition, common factors include advanced age - over 60-65 years.
That is why regular medical examination is necessary in order to detect the disease at an early stage and prescribe appropriate drug treatment.
An acute attack of glaucoma occurs as a result of a sharp increase in intraocular pressure, which leads to impaired blood circulation in the eye and can lead to irreversible blindness.
How to relieve pain?
The main task is to reduce intraocular pressure. To do this, you need to ensure the outflow of fluid from the eyeball. This can be done with special drops prescribed by your doctor.
Important
Self-medication is highly discouraged, because the selection of medications is made individually depending on the stage and characteristics of the disease. At the same time, vasodilator drugs are prescribed.
Analgesics, as a rule, do not help and do not bring relief - another coincidence with migraines. You shouldn’t endure pain, hoping that it will go away on its own. During attacks, adhesions form in the tissues of the eye. A protracted process leads to irreversible changes.
If the pain appears suddenly and is characterized by sharpness, fog in the eyes and other symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Most likely, this is acute-angle glaucoma, for which only emergency therapy will help.
If the disease causes pain in the eyes, urgent therapy is necessary, which consists of instilling drops of a 1-2% solution of Polycarpine. This therapy reduces the pressure in the inside of the eye. The patient is not hospitalized, but the patient must be referred for examination to an ophthalmologist.
The doctor will examine and select individual therapy. In an acute attack of glaucoma, pain occurs due to a sharp jump in eye pressure.
In this case, urgent help is needed and the introduction of the necessary drugs aimed at urgently lowering eye pressure. Miotics and a medicinal compress with Polycarpine are used, which will help relieve pressure.
Glaucoma and its treatment
There is no cure for glaucoma, you can only stop the progression of the disease. Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor.
- prostaglandin derivatives (increase the outflow of intraocular fluid) - Travatan, Xalatan - instill 1 drop into each eye before bedtime
- β-blockers - reduce the production of aqueous humor - (non-selective (do not have side effects on the heart and bronchi, contraindicated for people with bronchospasm) and selective) - Timolol (Arutimol, Kusimolol 0.25% or 0.5%), Betoptik and Betoptik S. Instilled every 12 hours.
- miotics - pilocarpine 1% - used for angle-closure glaucoma (the pupil is narrowed, the root of the iris extends from the angle of the anterior chamber, thereby opening it) - 1 drop up to 3 times a day.
— carbonic anhydrase inhibitors reduce the production of intraocular fluid (Azopt, Trusopt) - 1 drop 2 times a day.
First, 1 drug is prescribed (usually prostaglandin derivatives). If there is no effect, add other drops, for example β-blockers. Treatment is selected only by a doctor, because Some drugs are toxic and have many contraindications.
Antihypertensive drops are used continuously to slow the progression of glaucoma.
2. Neuroprotectors are necessary, because Glaucoma affects nervous tissue.
There are direct and indirect (they improve microcirculation and indirectly affect neurons). Direct vitamins include vitamins C, A, group B, emoxipine, mexidol, histochrome, neuropeptides (retinalamine, cortexin), indirect - theophylline, vinpocetine, pentoxifylline, nootropics, hypocholesterolemic drugs.
The patient undergoes a course of drug therapy in the hospital 1-2 times a year.
3. Physiotherapeutic treatment includes the use of methods such as electrical stimulation of the optic nerve, magnetic therapy, laser therapy.
4. If drug therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment (laser or traditional) is indicated.
The main types of laser treatment: laser iridectomy (they form a hole in the iris), trabeculoplasty (they improve the permeability of the trabeculae).
Iridectomy
There are many methods of microsurgical treatment. The most widely used method is sinustrabeculectomy.
in which a new path for the outflow of aqueous humor is formed under the conjunctiva, and from there the liquid is absorbed into the surrounding tissues. Other operations are also possible - iridocycloretraction (expanding the angle of the anterior chamber), sinusotomy (improving outflow), cyclocoagulation (reducing the production of aqueous humor).
Folk remedies are ineffective. Patients only waste valuable time on their treatment while the disease progresses.
Glaucoma is a pathology of the visual system, characterized by increased intraocular pressure. The cause of the disease is a violation of the circulation of intraocular fluid in the eyeball.
In a healthy human visual system, the eyeball is provided with the necessary amount of useful and nutrients by supplying blood under a certain pressure through the capillaries. A number of factors, such as aging of the body, heredity, cause increased fragility of blood vessels, decreased elasticity, which leads to an imbalance between the inflow and outflow of intraocular fluid.
This is the reason for the increase in pressure. Please note that this can be either short-term or permanent.
So, there is glaucoma, and how to treat it is our concern in this article...
With this constant phenomenon, less and less blood flows to the eyes, and the eyeball does not receive the necessary beneficial elements. There is a deficiency in nutrition of the iris, retina, and optic nerve.
A lack of essential elements and vitamins and increased intraocular pressure are accompanied by decreased lateral vision, headache, and blurred vision. In severe cases, without treatment, glaucoma can result in complete loss of vision and blindness.
Today, unfortunately, medicine cannot offer a complete cure for glaucoma.
The world-famous ophthalmologist professor William Horatio Bates, who wrote the scientific work “Glaucoma,” made disappointing conclusions: “... good methods of treating glaucoma in medicine do not yet exist today.
Good ones would include those that would completely cure a person. There are only satisfactory methods of therapy, those that stop the development of the disease, nourish the eye and reduce intraocular pressure.”
The main goal of glaucoma therapy is to reduce the pressure inside the eyeball. Equally important are actions aimed at improving metabolic processes in the eyeball and stimulating blood circulation.
In general, methods of treating glaucoma can be divided into those offered by traditional medicine and traditional medicine recipes. But all treatment options for glaucoma are aimed at normalizing intraocular pressure.
An ophthalmologist will help you choose the most effective type of treatment after an examination and consideration of the individual characteristics of the patient.
In the early stages of development, when glaucoma causes a short-term increase in eye pressure, the most optimal method of therapy is special eye drops. In more complex cases, the only solution to the pathology problem may be laser or surgical intervention. It should be noted that both correction methods do not require a long hospital stay for the patient.
The treatment methods offered by traditional medicine are also effective, but in some cases they can only be used as accompanying therapy.
- short-term or permanent impairment of visual acuity;
- narrowing of view;
- optic nerve deformation;
- a feeling of pressure or tension in the eyeball.
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- open-angle glaucoma;
- mixed glaucoma.
- decrease in intraocular pressure;
- improving blood supply to the structures of the eye and optic nerve;
- normalization of metabolism, inhibition of degenerative processes.
Attention! Before describing in detail all the effective and efficient treatment methods, we note that self-medication can lead to a deterioration in the functions of the visual system. All types of treatment for this pathology should be carried out under the supervision of an ophthalmologist.
At the initial stage of glaucoma treatment, drug therapy is the most effective treatment. The use of medications allows you to control intraocular pressure and stimulate blood supply to the eyeball at the desired level. Treatment methods with drugs vary depending on the type of initial stage of the pathology.
Content
SYMPTOMS INDICATING THE DEVELOPMENT OF GLAUCOMA
A patient with an eye disease should understand that traditional medicine. in areas of care such as glaucoma treatment. is his only savior.
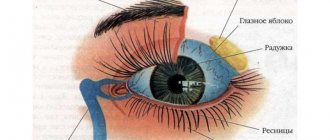
Blood is supplied to the eyes through vessels under a certain pressure. In the eye cavity, normally there is usually no more than two drops of blood, which is quite enough for nutrition and metabolism in all tissues of the eye and maintaining full vision.
But in our body, due to the inevitable aging processes, the walls of blood vessels by the age of 40 become less elastic, fragile, and narrowed. This aging process, leading to an imbalance between the inflow and outflow of intraocular fluid, is the main cause of increased intraocular pressure.
At the same time, glaucoma, as a disease, most often begins asymptomatically: the eyes do not water or redden. With a prolonged increase in intraocular pressure, less and less blood flows to the tissues of the eye through narrowed vessels, which leads to a deficiency in nutrition of the very delicate retina, iris and optic nerve.
At this time, the patient notices that the border of the visual field is narrowing. But the peculiarity of our Russian character is that, in the hope that everything will pass, we try not to pay attention to it.
Self-medication can lead to worsening of glaucoma. Therefore, before using folk remedies, you need to consult an ophthalmologist, and the use of medications without a doctor’s recommendation is strictly prohibited. It is necessary to strictly follow the treatment plan prescribed by the ophthalmologist.
Are you familiar with the problem of glaucoma? Which recommendations do you follow? Tell us about your personal experience in the comments to this material.
Currently, there is no absolutely effective means to combat glaucoma. The best methods are those that can cure or stop the development of glaucoma without structural changes in the organs of vision.
Glaucoma is treated with medication or with surgery or laser surgery. The choice should be made by the doctor, taking into account the type of glaucoma. Traditional medicine can be used, but only with the approval of the attending physician. It is very important to check all contraindications and evaluate the advisability of such an addition to therapy.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H6wqavwqy4g
Proper treatment for primary glaucoma includes:
The main goal of therapy is to reduce eye pressure. Other therapeutic measures are considered auxiliary, including traditional medicine recipes. Glaucoma medications are divided into two groups: those that improve fluid outflow, and those that inhibit the secretion of aqueous humor.
The use of folk remedies during an acute attack of glaucoma is dangerous. In this case, emergency assistance is required. If intraocular pressure is not reduced on the first day of the attack, the prognosis is unfavorable.
Medical assistance during an acute attack:
- Miotics. Pilocarpine solution drops every 15 minutes for the first two hours, another two hours every half hour, another two hours every hour. Then Pilocarpine is instilled 3-6 times a day.
- Timolol solution drop by drop twice a day.
- Acetazolamide (Diacarb) 0.25-0.5 g three times a day. Dorzolamide solution three times a day or Brinzolamide suspension twice.
- Osmotic diuretics. Glycerin solution (1.5-2 g per kilogram of weight).
- Loop diuretics. Furosemide at a dose of 20-40 mg if other drugs are ineffective.
The success of glaucoma therapy is determined by your daily routine. Patients should get a good night's sleep for 7-8 hours on high pillows (a low position contributes to stagnation of intraocular fluid and blood), balance their diet and diet. A few hours before bedtime, you should not eat food, and in the morning it is better to get out of bed immediately. It is easier to control intraocular pressure if you follow a daily routine.
Patients with increased intraocular pressure should not bend over or overexert themselves (cleaning, gardening, washing, lifting heavy objects). You cannot engage in certain sports and do postures upside down when doing gymnastics and yoga. Intraocular pressure may jump due to strong feelings and excitement.
Since vascular regulation is disrupted in glaucoma, patients do not tolerate temperature changes, especially decreases. Increases in pressure occur more frequently in the cold season.
It is important for patients with glaucoma to avoid hypothermia, not take cold treatments, and not walk in the cold. In winter, it is worth visiting the ophthalmologist more often and monitoring intraocular pressure.
Maintenance medications may be prescribed. It is strictly forbidden to overheat your head.
To prevent your visual organs from being overstrained, you can work with small details only in good lighting. Intraocular pressure increases when there is insufficient lighting. Patients should not wear tinted glasses, stay in the dark for a long time, or draw curtains while sleeping. For glaucoma, it is recommended to wear glasses with light green lenses.
Rules for driving with glaucoma
- use of glasses;
- protect your eyes from the bright sun with glasses with green lenses;
- refusal to drive at dusk and at night;
- increased attention.
In summer you need to wear glasses with green lenses. They are produced specifically for patients with glaucoma. Thanks to light filters, visual comfort is ensured; the eyes will be protected from ultraviolet radiation. Glasses with dark lenses darken the environment, complicate spatial orientation and often only increase eye pressure.
Patients with glaucoma can sunbathe only from 10 a.m. to 5 p.m. It is mandatory to wear a hat. The positive effect is noticeable after walking in warm weather, breathing exercises, and proper hardening.
Gymnastics for the eyes for glaucoma
- Slowly move your gaze up and down, from right to left. You need to deviate your eyes as much as possible, but do not turn your head.
- Make circular movements with maximum coverage.
It is very important to eat right. Smoked meats, pickles, spicy foods and seasonings, tea and coffee should be excluded from the diet. It is recommended to cook food in vegetable oil or boil it. Lean varieties of meat and fish will be beneficial. With glaucoma, it is necessary to increase the consumption of vegetables and fruits, as well as dairy. Patients with glaucoma should not abuse alcohol or smoke.
When leaving the country for a long period of time, patients with glaucoma need to take an extract from their medical history. The characteristics of the patient’s condition and information about the course of the disease will help the new doctor navigate when prescribing therapy.
Headache
Source: estet-portal.com As a rule, it appears simultaneously with pain in the eye.
Many people mistakenly associate it with a migraine, not even paying attention to the accompanying symptoms: flickering spots before the eyes, blurring. As a rule, the pain is characterized by monotony. It appears on the side of the head on which the affected eye is located. The discomfort is usually localized in the front part of the head: the temples, the eyebrows, the frontal part. Sometimes it reaches the back of the head and even the cervical area.
Pain occurs as a result of overirritation of the orbital nerve and its endings. In addition, due to constant pressure from the inside, the muscles are toned and tense. This causes spasms that do not go away on their own.
Along the chain, neighboring ligaments also suffer. Thus, the pain spreads much further than the disease itself. It goes away almost immediately after the main cause of the disease is eliminated: increased pressure in the eye.
Pain with glaucoma is often paroxysmal in nature, which is very similar to migraine. However, it can manifest itself differently each time. Various factors can provoke this feeling:
- long exposure to poor lighting, when the eyes are forced to overstrain;
- taking a large amount of liquid, which invariably leads to an increase in blood pressure;
- exposure to bright sunlight;
- emotional tension or stress;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- improper use of medications leading to increased IOP;
- excessive physical activity.
Head pain in patients with glaucoma can lead to misdiagnosis of the disease. Often, patients believe that their problems are related to migraines, and not to high levels of intraocular pressure. It is important to pay attention to possible accompanying phenomena.
Pain in the head is often located on the side of the affected eye, is monotonous and localized in the temporal, superciliary and frontal areas. Sometimes the pain spreads to the occipital and cervical regions.
Cause of headache
The cause of headaches in glaucoma is irritation of the receptors of the orbital nerve. In addition, these symptoms are caused by constant tension in the muscle fibers due to high levels of intraocular pressure.
Spasms do not go away on their own and spread to neighboring ligaments and muscles. After reducing intraocular pressure, the headache quickly disappears.
Development mechanism
Headaches resulting from glaucoma appear as a result of excessive irritation of the optic nerve and its endings located in the muscles of the organ of vision. Due to a disruption in the functioning of the visual system, neurons are constantly tense, overwork occurs, which results in a signal in the form of pain.
The muscles located in the forehead and temples are also in a tense state, which is why cephalgia appears (a condition in which the head hurts). Often, cephalalgia begins to spread from the frontal area, covering the temples.
In severe cases, glaucoma headaches spread to the back of the head and neck. The nature of the pain can be aching, dull, throbbing. Most often, cephalalgia begins in the frontal areas, then covers the temples, and in especially severe cases can reach the back of the head and even the neck. The nature of the pain is aching, throbbing, dull.
Strong headache
In fact, a headache of ocular origin occurs due to overirritation of the orbital nerve (the upper branch of the trigeminal nerve) and its endings, which are located in the muscles of the eye.
Due to the pathology of the visual analyzer, the muscles are in constant tone and tension, they gradually get tired and signal this with pain. The muscles of the temporo-frontal region are also in constant tension, they also get tired, pain receptors are irritated and cephalgia occurs.
In addition, increased intraocular pressure contributes to pain. Persistent aching pain in the orbit can gradually expand its boundaries and move to the forehead and along the entire length of the trigeminal nerve - to the entire front of the head.
With glaucoma, headaches can be:
- very intense
- paroxysmal,
- practically unresponsive to analgesics, may worsen at night with a low head of the bed.
In addition, cephalalgia can be caused by increased drinking, prolonged exposure to a darkened room, heavy lifting, or improper instillation of eye drops.
Favorite places for its localization are the fronto-orbital, temporal and parietal zones; most often it predominates on the side of the affected eye, but if the process is bilateral, it covers the entire front part of the head. In the absence of attacks, the pain stops or is insignificant.
Contrary to popular belief, not all structures of the head can feel pain. For example, the bones of the skull are not susceptible to pain - they do not have the corresponding receptors. The brain parenchyma and pia mater are also deprived of sensitive innervation.
But arteries, veins, venous sinuses, dura mater, skin, muscles and periosteum are very susceptible to painful stimuli, which is why they are the sources of headaches.
How to get rid of a headache?
It is necessary to clearly understand that a headache with glaucoma signals an increase in intraocular pressure. Therefore, by normalizing the pressure in the eye, the patient will automatically get rid of cephalgia.
Headache most often occurs with closed-angle glaucoma, when there is excessive accumulation of moisture in the anterior chamber of the eye, but can also occur with open-angle glaucoma.
In addition, a sharp headache can be caused by the onset of an attack of acute-angle glaucoma and then, in addition to this, there will be a sharp pain in the eyes, weakness, sweating, nausea, and vomiting. In some cases, pain can radiate to the chest and even the abdomen. Without emergency treatment, a person may lose his sight forever.
Do you know what you absolutely can’t do with glaucoma, and what you can?
Glaucoma is an insidious disease. Proceeding with almost no symptoms, it can one day lead to complete blindness .
In the article, we will look at what you should not do with glaucoma - what medications you should not take if you have high intraocular pressure, how much sleep you need, why you should not work at night with glaucoma, and other restrictions. We’ll also talk about what is quite possible.
Why is this disease so dangerous?
There is always a small amount of fluid inside the eyeball that provides nutrition to the eye. It constantly circulates, that is, it is formed and flows freely from the eye chambers. With glaucomatous changes, the outflow of fluid is disrupted. It accumulates and puts pressure on the eye from the inside, increasing intraocular pressure (IOP).
Excessive pressure inside the eyeball negatively affects vision. Over time, it leads to optic nerve atrophy. For a person, this threatens a gradual, subtle decrease in vision, up to its complete disappearance.
A feature of decreased vision in glaucoma is its decrease on the sides.
Due to the fact that central vision is the last to be lost, the person himself does not feel the problem. Therefore, it is important after 40 years to regularly measure intraocular pressure .
The outcome of elevated IOP in an unfavorable case is irreversible blindness and disability.
Restrictions for increased intraocular pressure
Glaucoma is a chronic pathology and lasts for many years. It cannot be cured completely, but blindness must be prevented . A person has to live with increased pressure inside the eyeball.
In order to avoid pressure surges and decreased vision, glaucoma patients must follow some simple lifestyle rules.
Medications
Every person who has glaucoma trains himself to always study the instructions for use of the medicine. Some medications increase IOP and are therefore contraindicated for use :
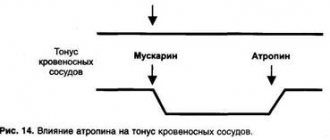
- atropine;
- some antihypertensive drugs;
- oral contraceptives;
- vasodilators;
- nitrates;
- antihistamines – suprastin, diphenhydramine;
- some analgesics.
IMPORTANT ! One of the popular painkillers, aspirin, causes swelling of the lens. In this case, the outflow of fluid worsens, which provokes deterioration of vision.
It is worth mentioning separately about nasal drops for a runny nose. The most common of them are not recommended for glaucoma patients, as they cause a short-term increase in IOP. Therefore, you should not use when you have a runny nose :
- xylometazoline (Rinostop, Rinorus);
- naphazoline (Naphthyzin);
- phenylephrine (Vibrocil);
- oxymetazoline (Nazivin, Afrin).
They can be replaced by other means . Rinsing with warm sea water is effective - it moisturizes the mucous membrane and washes away mucus.
Of the permitted drops and sprays, drugs with an antihistamine component, as well as local hormonal agents, are usually used. They do not help as quickly as classic vasoconstrictors, but they are safe for the eyes of glaucoma patients :
- Allergodil;
- Nasonex;
- Aldecin.
Some drugs used during anesthesia also have the ability to increase IOP. Therefore, if surgery is planned, you should inform the anesthesiologist about existing glaucoma. The doctor will select the type of pain relief that will not cause harm to the eyes.
Among sleeping pills there are drugs that are undesirable for people with glaucoma. They block the flow of fluid, increasing intraocular pressure.
It is better not to use Yunisom and Donormil for sound sleep - they contain doxylamine, which is prohibited in patients with glaucoma. But you can use modern sleeping pills - Ivadal or Sanval.
They contain zolpidem, which is safe for high IOP.
Exercise stress
Excessive physical stress and hard work contribute to increased blood pressure, so they are not recommended for diagnosed glaucoma. You should especially limit those activities that lead to blood flow to the head :
- washing floors;
- carpet cleaning;
- weeding;
- picking mushrooms and berries;
- planting seedlings.
Working in the garden, in addition to the unfavorable situation, is also dangerous due to the hot weather. Under these conditions, the head quickly overheats, which will cause an influx of intraocular fluid and a surge in pressure.
Therefore, gardening work in hot weather is limited to 20 minutes a day, and in cool weather to a couple of hours . Be sure to take regular breaks from work, which are necessary for the outflow of blood. During them, you should sit with your head higher than your body.
HELP : When working outdoors, it is recommended to always wear a hat - it will reduce the risk of overheating.
Moderate exercise will not harm your eyes. They will improve the condition of blood vessels and blood flow in general. You can play sports based on aerobic exercise . Swimming in the pool, athletics, cycling, etc. are useful. . When performing them, it is worth monitoring the general condition. Any symptoms of increased IOP serve as a warning to stop exercising.
It is undesirable to engage in scuba diving and deep diving - this causes an increase in pressure. It is worth completely excluding traumatic sports that easily lead to injuries and injuries to the head and eyes. Examples of sports you should not do:
- weightlifting;
- boxing;
- football, hockey, rugby.
Solar and electric light
Periodic exposure to bright light is not harmful to a person with glaucoma. But when working for a long time in an overly lit room , with a computer or tablet screen, EDV increases . Therefore, it is not recommended to work with electronic equipment for a long time without breaks.
Special unusual glasses provide protection from sunlight to eyes with high blood pressure. ideal - they protect from light and do not obscure .
Through classic dark sunglasses, everything appears in twilight, which provokes attacks of glaucoma.
Night shift work is contraindicated for glaucoma patients . At dusk, the pupil dilates, which prevents the outflow of fluid from the chambers of the eye. In such a situation, there is a threat of a jump in intraocular pressure. Therefore, if the work previously involved night shifts, it should be abandoned after diagnosis.
Sauna
Steam and high temperatures inside a sauna or bathhouse can slightly and briefly increase pressure. Therefore, staying in a sauna for a long time is undesirable.
You can safely steam in a bathhouse/sauna for no more than 15 minutes . But sudden changes in temperature are even more dangerous: jumping into the snow or dousing yourself with cold water after a bath.
These activities cause strong jumps in intraocular pressure, so this should not be done at all.
IMPORTANT ! Contrast showers and rubdowns are also undesirable. They are replaced with more gentle contrasting hand baths, if well tolerated.
Work and sleep
A person with glaucoma can work in the same way as others. But be a little more attentive to your well-being: take breaks more often and allow less nervous tension.
The workplace should be in a bright room, but away from direct light sources that irritate vision.
Sleep is recommended to be the same full, eight hours, as for healthy people.
Lack of sleep puts excessive stress on the nervous system, which can cause headaches and increased IOP in a patient with glaucoma.
It is better if the head end of the bed is higher than the foot end - this facilitates the outflow of blood from the head. If a headache appears after waking up, then the head edge is raised even higher.
Car driving
Many people ask: is it possible to continue driving? Driving with glaucoma is not contraindicated unless vision is completely impaired . In the most advanced stages, if a person has not received treatment and has lost most of their vision, they will not be allowed to drive when examined.
It is undesirable to spend a lot of time driving at dusk and at night - at this time the vision of glaucoma patients is significantly reduced.
In addition, the factor of a wide pupil and a possible jump in intraocular pressure is added. When driving, it is worth considering the possible worse vision in the periphery.
Therefore, you should be extremely careful while driving, watching the road not only in front of you, but also to the side.
Air travel
People with glaucoma usually tolerate flights well . Episodes of takeoff and landing that are associated with pressure changes may cause slight discomfort.
But these are short-term moments, after which the pressure quickly returns to normal.
To be sure, before flying, you should definitely visit an ophthalmologist - after the examination, the doctor will either allow you to fly on an airplane or advise you to abstain.
Food
The diet for glaucoma is similar to the usual diet of a healthy person. It is not recommended to frequently eat spicy and salty foods.
Preference is given to dairy and plant foods with gentle heat treatment. It is prohibited to consume foods that increase intraocular pressure: strong tea and coffee, energy drinks.
All features are discussed in a separate article about nutrition for glaucoma.
HELP : A complete abstinence from coffee and tea is not required - you just need to use no more than 1-2 cups of the drink per day. Drink in small sips, slowly.
Liquid
The total amount of fluid that a glaucoma patient should drink does not differ from standard recommendations. It’s good if you drink about 2 liters of clean water. With glaucoma, it is not advisable to drink more than 200 ml or one glass of liquid at a time . If more than 200 ml or a glass of liquid enters the body at a time, the pressure threatens to increase.
Smoking and alcohol
Cigarettes and alcoholic beverages are harmful even to a healthy person. In the case of glaucoma, if you drink alcohol, the water balance in the body is sharply disturbed.
This leads to changes in the pressure of the intraocular fluid, which complicates the course of the disease and contributes to rapid loss of vision. Smoking sharply constricts blood vessels, which also interferes with the normal circulation of intraocular fluid and impairs vision.
Contact lenses
Wearing lenses for glaucoma is not contraindicated . Therapeutic drops accumulate in the contact lens in small quantities, like in a depot, and are gradually released from it to the eye. This has a positive effect on the condition of the eyes and allows you to reduce the dosage of the medication.
Some medications prescribed for glaucoma can cause dry eyes. In order to cope with this condition, moisturizing drops and solutions are recommended. If dry eye syndrome is severe, which often happens among those who work at a computer, it is better to replace contact lenses with glasses.
Detection of increased intraocular pressure should not cause panic . Today, medications and minor surgical interventions help slow the progression of glaucoma and avoid blindness. Regular visits to the ophthalmologist, tonometry and simple lifestyle changes will help maintain clear vision for many years.
RATE THIS ARTICLE: ( 16 4.38 out of 5) Loading…
Source: https://glaza.guru/bolezni-glaz/zabolevaniya/glaukoma/kak-zhit-s-glk/chto-nelzya-pri-glk.html
Diagnostics
Source: medicinemoscow.ru The diagnosis of glaucoma is made by an ophthalmologist.
Diagnosis occurs in several stages. First, the doctor measures the pressure inside the eye. This is done using a pneumotonograph - special equipment that records pressure using compressed air, or using special weights inserted by eye. The pressure should not exceed 24-25 millimeters of mercury. The ophthalmological examination also includes examination of the fundus and optic nerve using a slit lamp, as well as tomography of the optic nerve with a special eye tomograph.
In addition, it is considered important to determine the sensitivity of the nerve, examine the patient’s visual fields, conduct an ultrasound examination of the eye, and conduct gonioscopy (study of the angle of the eye chamber) in order to determine the degree of destruction of the drainage system.
Important
Early detection of glaucoma (which requires an ophthalmological examination) is important because successful treatment is only possible at the very beginning of the disease. It should be noted that changes in the early stages of the disease are sometimes difficult to distinguish from normal variants that do not pose a particular threat.
When diagnosing glaucoma, it is customary to take into account the presence of five leading symptoms, such as:
- difficulty and deterioration in the outflow of moisture from the eye
- instability of intraocular pressure (daily fluctuations are normally no more than 5 mm Hg, they are detected during loading and unloading tests using elastotonometry)
- increased intraocular pressure
- glaucomatous excavation
- decreased visual function.
Determination of the level and regulation of intraocular pressure using the following methods is of leading importance in the diagnosis of glaucoma:
- measurement of intraocular pressure: tonometry, elastotonometry
- study of indicators of the outflow of intraocular fluid: tonography
- visual field examination: various perimetry techniques.
If glaucoma is suspected, repeated measurements of intraocular pressure at different times of the day are of great importance.
It should be noted that for a long time, a patient with glaucoma may not notice any changes in vision, and during the initial examination, the ophthalmologist may already detect large changes.
And in rare cases, an acute attack of glaucoma forces the patient to go straight to the clinic when, with a sudden increase in intraocular pressure, headaches, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, and redness of the eyes appear.
First aid for green water headaches
If a patient is diagnosed with glaucoma during an attack, the first step is to reduce intraocular pressure. This is done by draining excess fluid from the eyeballs (the doctor prescribes special eye drops, the effect of which is aimed at reducing symptoms).
Patients are advised to avoid self-medication, since incorrectly selected medications can aggravate the situation and lead to complete loss of vision. Painkillers will not be effective during a headache - they will not be able to relieve other manifestations of glaucoma.
Doctors also do not advise trying to endure the pain syndrome, since during an attack adhesions form in the tissues of the organ of vision. Prolonged pain can cause irreversible, deplorable changes. If the sensations arise suddenly and there is a haze when looking, then you should immediately visit an ophthalmologist. These symptoms indicate an acute-angle form, which should be treated quickly and comprehensively.
The disease can be diagnosed using several examination methods: tonometry, refraction measurements, gonioscopy, ultrasound diagnostics, and ophthalmoscopy. The field of view is also examined (for this the doctor uses a computer perimeter), the depth of the anterior chamber and the thickness of the lens are determined. Anamnesis must be studied.
Treatment of the disease
There are 3 ways to treat glaucoma and eliminate symptoms. The first of them is therapy with drops that relieve symptoms. The selection of medications and instillation regimen are prescribed individually based on the results of the examination. There is also a method of laser therapy that is used if medications are ineffective. And the last method is surgery.
Glaucoma therapy addresses the main factor causing nerve atrophy, namely: reducing intraocular pressure.
Today there are three ways to treat glaucoma:
- medicinal,
- laser
- microsurgical.
If the diagnosis of glaucoma is confirmed, the patient is prescribed eye drops for regular use. If they have an effective effect, which is to lower intraocular pressure, then the patient should not stop using the drops and undergo regular examination by an ophthalmologist.
The examination consists of a complete ophthalmological examination, during which intraocular pressure is also measured. The point of regular examinations is to ensure that the ophthalmologist is able to intensify drug treatment in a timely manner if the development of glaucoma begins to progress.
During drug therapy for glaucoma, the following drugs are often used:
- dorzolamide,
- latanoprost,
- maleatepilocarpine,
- timolol,
- betaxalol,
- combination drugs.
In the event that the desired effect is not achieved using drug treatment, or the diagnosis of “closed glaucoma” is determined, then laser therapy is used. It is performed on an outpatient basis.
When carrying out such treatment, a small hole is made in the patient inside the eye, as a result of which the outflow of chamber fluid improves and intraocular pressure decreases. There are cases when laser therapy does not bring the desired effect or is contraindicated, and in this case microsurgery is prescribed.
Low pressure inside the eye is the key to ensuring that the fibers of the optic nerves are preserved. In any case, a patient suffering from glaucoma must be constantly monitored by a doctor who will examine his visual function and prescribe medications that improve blood supply to the brain.
What tranquilizers are available for glaucoma?
Modern medications that are used to reduce intraocular pressure can be divided according to their principles of action into two groups:
- medications that improve the outflow of aqueous humor from the eye;
- medications that reduce the level of intraocular fluid production.
Drugs that improve the outflow of aqueous humor
Medicines that improve fluid outflow include: prostaglandins F-2a, cholinomimetics and sympathomimetics.
Medicines that reduce the production of aqueous humor
This group of medications includes B-blockers, central agonists, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
Sedatives for adults
Stress, mild and short-term, is useful for a person, it activates the immune system and forces you to improve your life qualitatively. However, if the psychological stress is excessive, you need to take a time out, calm down, so that you can quickly and correctly solve your problems. This is why sedatives have been developed.
Why are they needed and how do they work?
Persen
An ordinary nervous breakdown may be the beginning of a serious mental disorder, and irritability may be a consequence of hormonal imbalance or a symptom of a serious illness of the internal organs.
But more often, the person himself realizes the need for help and resorts to sedatives. They reduce tension and the threshold of sensitivity, normalize the balance of excitation and inhibition processes, therefore they are indicated even for mild and neurotic depression that lasts up to 3 weeks.
They are used once, in a stressful situation, and in courses not exceeding 1-3 months.
Tablets for the treatment of glaucoma
Glaucoma affects more than 60 million people worldwide.
Filtration device EX-PRESS®.
This device is specially designed to reduce increased intraocular pressure due to glaucoma.
In the process of treating glaucoma in Minsk, the patient goes through several stages - from eye drops to surgery. There are different methods of surgical treatment of glaucoma, the effectiveness of which is individual for each patient. Today, a new highly effective method of surgical treatment of glaucoma has emerged that is suitable for most patients.
An alternative that helps control glaucoma symptoms is the EX-PRESS® Glaucoma Filtration Device, which is specifically designed to reduce elevated intraocular pressure.
To date, world statistics total more than 60,000 successful EX-PRESS® implantations.
Glaucoma filtration device EX-PRESS®
EX-PRESS® is a tiny implant, smaller than a grain of rice, that is placed under a scleral flap during surgery. The device replaces the function of the drainage system of the eye, which is damaged due to glaucoma.
Thus, it creates an alternative pathway through which excess intraocular fluid is successfully removed from the eye. The result is clear control of intraocular pressure and maintaining it at the target (healthy) level.
- Reduced intraocular pressure
- Reduced or eliminated dependence on anti-glaucoma medications in the long term
- Better restoration of visual functions
- In the operating room, the patient is given pain-relieving eye drops.
- The eye is then washed and the face and body are covered with a sterile surgical drape, leaving one eye uncovered, which is secured to prevent blinking.
- Intravenous sedatives may be given for comfort.
This procedure can be performed at the same time as cataract surgery.
Before surgery
After operation
As a rule, acute attacks of glaucoma occur in the evening and at night, so it is worth knowing about possible pre-medical care measures for the patient.
Anaprilin
This type of tablet belongs to synthetic drugs. Produced in the form of tablets of 0.01 and 0.04 g.
Medicinal properties. Anaprilin reduces the level of vascular pressure, improves heart rhythm and reduces the level of intraocular pressure.
Prozerin
Prozerin is also a synthetic drug. It is produced in the form of tablets, weighing 0.015 g each.
The medicine affects various functions of the human body. This drug helps reduce IOP levels, increase the functionality of the muscles of the bladder and uterus, and provides increased muscle tone in general.
Clonidine
Clonidine is a synthetic drug that is produced in the form of tablets of 0.075 mg and 0.15 mg.
The drug lowers blood pressure, reduces heart rate, and lowers IOP levels. Clonidine lowers blood pressure, lowers heart rate, lowers intraocular pressure and causes a general calming effect.
Cavinton
This drug is produced in tablets that contain 0.005 g of Cavintone.
Cavinton helps to dilate blood vessels in the brain. The drug increases the level of blood circulation in these vessels, which increases the amount of oxygen received by the brain. Does not affect blood pressure or heart function.
Hypothiazide
Synthetic drug. Produced in the form of tablets weighing 0.025 and 0.1 g.
Hypothiazide is a strong diuretic medicine. Used to remove fluid and sodium ions from the body. The effect begins to appear an hour and a half after taking the tablet. Due to the decrease in fluid volume, vascular pressure and IOP levels decrease.
Material on the topic: Modern methods of treating glaucoma
Source: https://mir-ua.ru/kakie-trankvilizatory-mozhno-pri-glaukome/
Folk remedies for treating eye pain
Source: happiness-and-beauty.ru As mentioned above, you can successfully cure such a serious disease as glaucoma, and thereby avoid loss of vision, by starting treatment at an early stage of the disease. And in this case, not only the methods of official medicine, but also some folk remedies can help:
- In folk medicine, in order to relieve eye pain in glaucoma, juice and tinctures from plants such as aloe, duckweed (swamp grass), woodlice grass and many other plants that help reduce pressure inside the eye are often used. Infusions are taken orally in small doses.
- To relieve eye pain with glaucoma you need to: cook celandine juice with honey over low heat until it releases all the foam and thickens to the consistency of honey. Then, using the resulting ointment, you need to apply lotions to the affected eyes. It is said to be the best remedy for treating glaucoma.
- To prevent glaucoma, before going to bed, rub your upper eyelids with bee honey diluted 1:1 with water.
- Also, to reduce eye pain with glaucoma, you can pour 1 tablespoon of cleanly washed and crushed duckweed grass with 1 glass of vodka, leave for 4 days, then strain. Take tincture 20 drops with 2-3 tablespoons of water 2-3 times a day.
- You can completely get rid of eye pain due to glaucoma using the following remedy: 1/2 tbsp. spoons of nettle and 1 teaspoon of lily of the valley petals, collected in May, mixed with 1 tbsp. spoon of water, let it brew in a dark place for 9 hours, then add 1/2 teaspoon of baking soda. Make eye lotions from the resulting mass twice a day.
- Another way to treat eye pain with glaucoma is as follows: you need to take 2 parts of blood-red hawthorn fruit, 1 part each of periwinkle herb, mistletoe herb, yarrow herb, horsetail herb. Take 0.5 cups 2-3 times a day.
Home remedy to help relieve eye pain due to glaucoma: Dissolve 0.2 g of mumiyo in 1 glass of water. Drink 2 times a day on an empty stomach, before lunch and before bed. The course of treatment for glaucoma is 20 days.
However, we should not forget that glaucoma cannot be cured with folk methods and remedies alone - you need to consult a specialist.
Sedatives for adults
Stress, mild and short-term, is useful for a person, it activates the immune system and forces you to improve your life qualitatively. However, if the psychological stress is excessive, you need to take a time out, calm down, so that you can quickly and correctly solve your problems. This is why sedatives have been developed.
Why are they needed and how do they work?
Persen
An ordinary nervous breakdown may be the beginning of a serious mental disorder, and irritability may be a consequence of hormonal imbalance or a symptom of a serious illness of the internal organs.
But more often, the person himself realizes the need for help and resorts to sedatives. They reduce tension and the threshold of sensitivity, normalize the balance of excitation and inhibition processes, therefore they are indicated even for mild and neurotic depression that lasts up to 3 weeks.
They are used once, in a stressful situation, and in courses not exceeding 1-3 months.
Drugs
Source: glaukoma.info They reduce the level of moisture formation and increase its outflow, thereby having a protective effect.
Miotics - increase the outflow of moisture from the eye chambers. Pilocarpine is effective. Beta blockers - Timolol, Niolol, Maleate. These medications reduce the level of moisture formation and increase its outflow; the medications have a protective effect on the optic nerve.
Combination of drugs "Pilocarpine" and "Adrenaline" or "Timolol". Effective when emergency assistance is needed.
Among the drugs that are used to treat glaucoma, the main place is occupied by drugs that normalize intraocular pressure.
Miotics - improve the outflow of moisture from the chambers of the eye. These include pilocarpine in drops, membranes or films.
Beta blockers - timolol, betaxalol, maleate, proxodolol, niolol, etc. These drugs reduce the formation of aqueous humor and improve its outflow from the eye; some drugs have a protective effect on the optic nerve. Drugs in this group are convenient because they can be instilled only a few times a day.
Adrenergic drugs - inhibit the production of intraocular fluid and improve the drainage function of the eye. This group includes adrenaline, oftan-dipivefrin.
Diuretics, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - diacarb. Its ability to reduce the production of intraocular fluid and reduce pressure in the eye has found application in acute attacks of glaucoma. Diacarb is able to reduce intraocular pressure within half an hour and exert its effect for almost 12 hours.
For a faster effect, a combination of pilocarpine and adrenaline (adrenopilocarpine) or pilocarpine with timolol (Fotil, Fotil-Forte) is used.
These drugs can serve as emergency drugs during an attack of acute glaucoma, when the headache is at its peak and urgent measures are required within the next few hours.
Types of medications
Eye drops for glaucoma are distinguished according to the principle of their effect on the body.
They are prescribed for angle-closure glaucoma. Medicines with prostaglandins that suppress the production of intraocular fluid are often used to reduce intraocular pressure - these are carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cholinomimetics, beta-blockers, alpha-2-adrenergic receptor antagonists in the form of eye drops. The doctor will also advise the use of miotics, diuretics (tablets, injections), and adrenergic agonists. There is a certain list of medications to treat the disease.
Since “Atropine” increases intraocular pressure, it cannot treat this disease; the medicine can significantly worsen the patient’s condition; “Aspirin” is also strictly contraindicated. Vitamin eye drops are often prescribed as a preventive measure for the disease. For normal blood pressure, vasodilators (nicotinic acid) are used. Eye drops for glaucoma
| A drug | Operating principle |
| Cholinomimetic | Reduce blood pressure and normalize fluid circulation by constricting the pupil of the eye |
| Sympathomimetic | Affects the nervous system, in particular the optic nerve |
| Suppressing fluid generation | Reduce moisture production |
| Prostaglandin | Prescribed for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma |
| Diuretic | Diuretic, removes fluid from the body |
There are several options for classifying antidepressants. One of them is based on exactly what clinical effect the drugs have on the nervous system. There are three types of such actions:
- Sedative
- Balanced
- Activating
Sedative antidepressants have a calming effect on the psyche, relieving anxiety and increasing the activity of nervous processes. Activating drugs fight well against such manifestations of depression as apathy and lethargy. Balanced drugs have a universal effect. As a rule, the sedative or stimulating effect of drugs begins to be felt from the very beginning of administration.
This classification is considered traditional. It is based on what chemicals are included in the drug and how they affect the biochemical processes in the nervous system.
A large and diverse group of drugs. TCAs have long been used in the treatment of depression and have a solid evidence base. The effectiveness of some drugs in the group allows them to be considered a standard for antidepressants.
Tricyclic drugs can increase the activity of neurotransmitters - norepinephrine and serotonin, thereby reducing the causes of depression. The name of the group was given by biochemists. It is associated with the appearance of the molecules of substances of this group, consisting of three carbon rings connected together.
TCAs are effective drugs, but have many side effects. They are observed in approximately 30% of patients.
The main drugs of the group include:
- Amitriptyline
- Imipramine
- Maprotiline
- Clomipramine
- Mianserin
AmitriptylineTricyclic antidepressant. Has both antidepressant and mild analgesic effects Composition: 10 or 25 mg amitriptyline hydrochloride Dosage form: dragees or tablets Indications: depression, sleep disorders, behavioral disorders, mixed emotional disorders, chronic pain syndrome, migraine, enuresis. Side effects: agitation, hallucinations, visual disturbances, tachycardia, blood pressure fluctuations, tachycardia, stomach upset Contraindications: heart attack, individual intolerance, lactation, intoxication with alcohol and psychotropic drugs, cardiac muscle conduction disorders. Application: immediately after meals. The initial dose is 25-50 mg at night. Gradually the daily dose is increased to 200 mg in three doses. |
These are first generation antidepressants.
Monoamine oxidase is an enzyme that destroys various hormones, including neurotransmitters. MAO inhibitors interfere with this process, due to which the amount of neurotransmitters in the nervous system increases, which in turn leads to the activation of mental processes.
MAO inhibitors are quite effective and cheap antidepressants, but have a large number of side effects. These include:
- Hypotension
- Hallucinations
- Rave
- Insomnia
- Agitation
- Constipation
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Sexual dysfunction
- Visual impairment
When taking certain medications, you must also follow a special diet to avoid introducing potentially dangerous enzymes into your body that are metabolized by MAO.
The most modern antidepressants of this class have the ability to inhibit only one of two types of enzyme - MAO-A or MAO-B. These antidepressants have fewer side effects and are called selective inhibitors. Non-selective inhibitors are currently rarely used. Their main advantage is their low price.
Main selective MAO inhibitors:
- Moclobemide
- Pirlindol (pyrazidol)
- Bethol
- Metrolindole
- Garmaline
- Selegilin
- Rasagiline
MoclobemideAntidepressant, selective MAO inhibitor. It mainly affects MAO type A, has an antidepressant and immunostimulating effect. Indications: schizophrenia, sociophobia, manic-depressive psychosis, alcoholism, reactive, senile, neurotic depression Contraindications: exacerbations of mental illness, agitation, confusion, agitation, pregnancy and lactation. Side effects: headaches, dizziness, stomach and intestinal disorders Application: after meals. Daily dosage – 300-600 mg, three doses per day. The dosage is gradually increased. |
These drugs belong to the third generation of antidepressants. They are relatively easily tolerated by patients and have fewer contraindications and side effects compared to TCAs and MAO inhibitors. Their overdose is not as dangerous as compared to other groups of drugs. The main indication for drug treatment is major depressive disorder.
The principle of operation of the drugs is based on the fact that the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is used to transmit impulses between neuron contacts, when exposed to SSRIs, does not return back to the cell transmitting the nerve impulse, but is transferred to another cell. Thus, antidepressants such as SSRIs increase the activity of serotonin in the nerve circuit, which has a beneficial effect on brain cells affected by depression.
As a rule, drugs in this group are especially effective for severe depression. For depressive disorders of minor and moderate severity, the effect of the drugs is not so noticeable. However, a number of doctors have a different opinion, which is that for severe forms of depression it is preferable to use proven TCAs.
The therapeutic effect of SSRIs does not appear immediately, usually after 2-5 weeks of use.
The class includes substances such as:
- Fluoxetine
- Paroxetine
- Citalopram
- Sertraline
- Fluvoxamine
- Escitalopram
FluoxetineAntidepressant, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Has an antidepressant effect, relieves feelings of depression Release form: Tablets 10 mg Indications: depression of various origins, obsessive-compulsive disorder, bulimia nervosa Contraindications: epilepsy, tendency to seizures, severe renal or liver failure, glaucoma, adenoma, suicidal tendencies, taking MAO inhibitors Side effects: hyperhidrosis, chills, serotonin intoxication, stomach upset Application: regardless of food intake. The usual regimen is 20 mg once a day, in the morning. After three weeks, the dose can be doubled. Fluoxetine analogues: Deprex, Prodep, Prozac |
MORE ABOUT: Open-angle and closed-angle glaucoma: treatment and symptoms
There are also other groups of drugs, for example, norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, noradrenergic and specific serotonergic drugs, melatonergic antidepressants. Among such drugs are Bupropion (Zyban), Maprotiline, Reboxetine, Mirtazapine, Trazadone, Agomelatine. All of these are good antidepressants, proven in practice.
Bupropion (Zyban)Antidepressant, selective norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitor. An antagonist of nicotinic receptors, due to which it is widely used in the treatment of nicotine addiction. Release form: Tablets 150 and 300 mg. Indications: depression, social phobia, nicotine addiction, seasonal affective disorder. Contraindications: allergy to components, age under 18 years, concomitant use with MAO inhibitors, anorexia nervosa, convulsive disorders. Side effects: an overdose of the drug is extremely dangerous, which can cause epileptic seizures (2% of patients at a dose of 600 mg). Urticaria, anorexia or lack of appetite, tremor, and tachycardia are also observed. Application: the medicine should be taken once a day, in the morning. The typical dose is 150 mg, the maximum daily dose is 300 mg. |
Laser surgery
Source: glaza.guru Laser surgery has its pros and cons.
The advantages of this treatment method include the absence of the need for general anesthesia, low risk of complications, and treatment of the natural pathways through which fluid outflows. The disadvantages of this therapy include: the effect is temporary (1-5 years), neighboring tissues are often damaged. There are 2 main types of laser therapy available.
Laser iridectomy
The outflow of fluid from the chamber of the eye occurs through a hole in the iris. To normalize the process, another one is done in the thinnest places on the periphery of the iris.
Trabeculoplasty
The trabecular diaphragm is located between the anterior and posterior chambers. The laser burns the top layer of the diaphragm, resulting in an increase in its tension and transmittance. The fluid circulates faster, the pressure decreases.
Surgery
Iridectomy. The operation involves removing a block in the pupil through which fluid flows between the chambers of the eye. For angle-closure glaucoma, iridocycloretraction is performed, during which the angle of the anterior chamber of the visual organ is opened and widened.
Fistulating operations. This method is aimed at forming new outlets for the outflow of moisture from the eye. Stabilizes intraocular pressure in 85% of patients. Traeculectomy is considered the most effective - the formation of a channel in the trabecular diaphragm. It is performed under local anesthesia.
Non-penetrating operations. These operations are performed in conjunction with laser surgery. The eye is not opened; an incision is made and cauterization is applied in the trabecula, which facilitates the outflow of moisture.
Surgery is prescribed when laser therapy and drug treatment do not produce results. Before the operation, patients are prescribed sedatives, since the patient needs good sleep and a stable mental state.
Medicines are taken until the time of surgery, since intraocular pressure should decrease as much as possible.
In addition to drug therapy, proprietary methods and traditional methods of combating both headaches and the entire complex of manifestations of glaucoma have been developed. Various surgical methods for correcting intraocular pressure have been developed and are quite successfully used.
The following operations have proven themselves to be effective: peripheral iridectomy, iridocycloretraction, as well as many variations of non-penetrating and penetrating surgical interventions, for example using a laser.
Can you buy antidepressants without a prescription?
Get a good night's sleep without visiting a doctor
MORE ABOUT: Pregnancy with glaucoma
A person should spend a third of his life sleeping – quite a lot. After a full sleep, the charge of vigor and performance lasts for a long time. At the same time, intermittent, superficial sleep and poor sleep can become a real torment, especially on the eve of an important day.
The most powerful sleeping pills are limited-release drugs and require a prescription to purchase. Such drugs, for example, include old and well-known barbiturates: etaminal - sodium, barbamyl, phenobarbital. To purchase such modern and mildly active drugs as Imovan (zopiclone) and zolpidem, you also need a prescription.
At the same time, there is a large group of over-the-counter drugs that have a hypnotic effect. They are commercially available because their psychoactive inhibitory effect on the central nervous system is much lower, and an overdose does not cause serious side effects. However, they can help you fall asleep in most cases of mild sleep disorders.
We present these drugs in descending order of hypnotic effect.
According to the rules for the dispensing of medicines in Russia, in order to obtain psychotropic drugs in pharmacies, a doctor’s prescription is required, that is, a prescription. And antidepressants are no exception. Therefore, theoretically, strong antidepressants cannot be purchased without prescriptions. In practice, of course, pharmacists may sometimes turn a blind eye to the rules in the pursuit of profit, but this phenomenon cannot be taken for granted. And if you are given a medicine without a prescription in one pharmacy, this does not mean that the same situation will happen in another.
You can only buy drugs for the treatment of mild depressive disorders such as Afobazole, “daytime” tranquilizers and herbal-based drugs without a doctor’s prescription. But in most cases it is difficult to classify them as real antidepressants. It would be more correct to classify them as sedatives.
AfobazoleRussian-made anti-anxiety, anxiolytic and mild antidepressant without side effects. Over-the-counter drug. Release forms: Tablets 5 and 10 mg Indications: anxiety disorders and conditions of various origins, sleep disorders, neurocirculatory dystonia, alcohol withdrawal. Side effects: Side effects while taking the drug are extremely rare. These may be allergic reactions, gastrointestinal disorders, headaches. Application: it is advisable to take the drug after meals. The single dose is 10 mg, the daily dose is 30 mg. The course of treatment is 2-4 weeks. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the tablets, age under 18 years, pregnancy and lactation |
If you believe that you are depressed, it is recommended that you consult a psychotherapist or neurologist. Only he can carefully examine your symptoms and prescribe the drug that is appropriate for your case.
The most popular herbal preparations today to lift your mood contain extracts of mint, chamomile, valerian, and motherwort. But preparations containing St. John's wort have demonstrated the greatest effectiveness in treating depression.
The mechanism of the therapeutic effect of St. John's wort has not yet been precisely clarified, but scientists believe that the enzyme hypericin contained in it is capable of accelerating the synthesis of norepinephrine from dopamine. St. John's wort also contains other substances that have a beneficial effect on the nervous system and other body systems - flavonoids, tannins, essential oils.
St. John's wort preparations are mild antidepressants. They will not help with all depression, especially with its severe forms. However, the effectiveness of St. John's wort for mild and moderate depression has been proven by serious clinical studies, in which it has shown to be no worse, and in some respects even better, than popular tricyclic drugs for depression and SSRIs.
In addition, St. John's wort preparations have a relatively small number of side effects. They can be taken by children from 12 years of age. Among the negative effects of taking St. John's wort, the phenomenon of photosensitivity should be noted, which means that when the skin is exposed to sunlight during the course of treatment with the drug, rashes and burns may appear on it.
Medicines based on St. John's wort are sold without a prescription. So if you're looking for depression medications that you can take without a prescription, this class of drugs may be your best choice.
Some preparations based on St. John's wort:
- Negrustin
- Deprim
- Gelarium Hypericum
- Neuroplant
NegrustinAntidepressant and anti-anxiety agent based on St. John's wort extract Release form: there are two release forms - capsules containing 425 mg of St. John's wort extract and a solution for internal use, bottled in 50 and 100 ml bottles. Indications: mild and moderate depression, hypochondriacal depression, anxiety, manic-depressive states, chronic fatigue syndrome. Contraindications: photodermatitis, endogenous depression, pregnancy and lactation, simultaneous use of MAO inhibitors, cyclosporine, digoxin and some other drugs. Side effects: eczema, urticaria, increased allergic reactions, gastrointestinal disorders, headaches, iron deficiency anemia. Application: take Negrustin capsule or 1 ml of solution three times a day. Children under 16 are prescribed 1-2 capsules per day. The maximum daily dose is 6 capsules or 6 ml of solution. |
Prevention
It is possible to avoid the development of glaucoma by undergoing regular examinations by an ophthalmologist. It is necessary to constantly monitor eye pressure, preventing it from exceeding the permissible level.
If your immediate family has suffered from glaucoma, you need to be more careful: keep eye pressure under control, undergo regular examination of the optic nerve, and also conduct tomography. There are drops against glaucoma, which are often prescribed by a doctor.
With such an appointment, it is imperative to follow the schedule for taking them and not miss a single day. Only with such a careful approach can the occurrence and development of the disease be avoided, thereby maintaining vision and a high level of visual function.
Complications
As noted earlier, it is impossible to completely cure glaucoma, and its development inevitably leads to blindness. Some patients with glaucoma have experienced severe degeneration of the ocular cornea, resulting in tearing, pain, and the patient's inability to open their eyes.
With increased eye pressure, the pain can become so severe that strong medications are required to relieve pain. If they are also powerless, then removal of the eye cannot be avoided.
Eye pain due to glaucoma
Exercise stress
"Encyclopedia of Pain"
IRITIS, IRIDOCYCLITIS
Oddly enough, the situation in the case of glaucoma can be improved with proper nutrition and a proper lifestyle.
If you have high eye pressure, you just need to move as much as possible. Swimming, badminton, and tennis will have the most beneficial effect.
Simple evening walks on foot are also suitable, but they must be long - at least half an hour. But when playing sports, be careful not to overexert your body.
The therapeutic effect of moderate physical activity is that blood circulation in the body improves, the eyes receive much more blood, and this simple action lowers eye pressure.
Neck massage will be of great benefit for this disease. You also need to adjust your diet. Eat more foods rich in vitamins A, C, D, E, PP and calcium. Limit your time on the computer. Do eye exercises regularly.
Limit the amount of salt in your diet and do not drink more than six glasses of liquid per day. Try to forget about coffee, strong tea, alcohol and smoking. Following these rules will benefit not only your eyes, but also your body as a whole.
Don’t forget to eat more watermelons, grapes, dill, rowan, pumpkin, currants - these delicious foods will not only please you, but will also benefit your health, in particular your eyes. Also use birch sap.