Symptoms
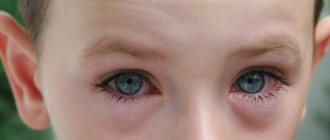
The symptomatic picture depends on the disease that could provoke the pathology. As the infection develops, the skin of the eyelids becomes covered with red spots, and touching causes throbbing pain. Left untreated, bacteria or viruses spread to the eyes, resulting in decreased visual acuity. An allergic reaction is accompanied by severe itching and burning.
Traumatic eye injury is characterized by the appearance of a hematoma - the bruise quickly acquires a purple-blue hue. Often the injury brings severe discomfort: a person feels numbness of the skin around the eyes or an increase in its temperature. In some cases, eyelash loss and watery eyes occur. The eyes become red, visual acuity decreases.
Regardless of the etiology of the disease, general symptoms of inflammation and pain of the eyes are distinguished:
- pain in the affected organ of vision;
- discomfort, foreign body sensation;
- bleeding due to rupture of the capillary vessels of the eyes;
- purulent-inflammatory process;
- photosensitivity;
- redness of the cornea;
- tearing and burning.
IMPORTANT. To determine the cause of the pathological process, the help of an ophthalmologist is needed. Self-medication will worsen the condition.
Symptoms of edema
The visual organ does not have a mucous membrane similar to the one that lines the internal cavities. When talking about swelling of the mucous membrane of the eyeball, we are talking about the cornea, formed by the inner surface of the upper and lower eyelids and the conjunctiva.
When the cornea swells, the state of the organ of vision changes: the tissues thicken, folds and compactions form, which disrupts the normal refraction of light. In this case, the following metamorphoses occur with vision:
- distortion of objects in the field of view;
- decreased vigilance;
- a feeling of fog before the eyes;
- reaction to exposure to bright light;
- feeling of sand or foreign body;
- corneal clouding;
- pain;
- spider veins or redness of the conjunctiva.
With secondary infection, purulent discharge is possible along with swelling. Sometimes there is dryness of the cornea and peeling of the skin of the eyelids.
Note: With swelling, pain in the eyes is not always pronounced, which makes diagnosis difficult. Redness is noticeable on the eyeball and upon careful examination there is a violation of the structure of the cornea.
Common reasons why the eye hurts and the upper eyelid is swollen
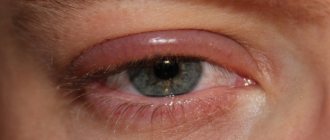
Severe swelling that does not go away on its own within several days is a symptom of the development of a pathological process. The causes of inflammation of the upper eyelid are the following conditions:
- infection of a viral or bacterial nature: barley, cellulitis, blepharitis, conjunctivitis;
- mechanical injury;
- allergy;
- a bite of an insect.
If something gets in your eye
The mucous membranes of the organ of vision are sensitive, therefore, when small particles enter the eye, an acute reaction begins:
- a person feels the presence of a foreign body;
- tear production increases;
- the eye reflexively closes, forced expansion of the eyelids leads to pain and muscle spasm;
- the patient feels sharp pain;
- Redness of the sclera and swelling are observed.
If rinsing the eye with clean water does not produce results, contact a doctor to remove the foreign particle. After eliminating the cause of irritation, you should visit an ophthalmologist to rule out mechanical injury to the eyes and deterioration of vision.
IMPORTANT. When prescribing antibacterial therapy, you should not neglect medical recommendations. Antimicrobial eye drops will help prevent infection.
Impact injury
Blunt injuries from a blow are accompanied by the appearance of hematomas due to rupture of capillary vessels. A special anti-inflammatory eye ointment and a cold compress will help eliminate swelling in the affected area.
Normally, pain and swelling disappear within 3 days. If during this period the pain syndrome remains at the same intensity and inflammation, you should immediately consult a doctor. It will take 1-3 weeks for the skin to recover after hemorrhage, depending on the severity of the injury.
Allergy
Often the eyelids swell due to allergies to pollen, food or metal dust. Irritation of the immune system can be distinguished from other ophthalmological diseases by the following signs:
- severe itching of the eyelids;
- redness;
- swelling of the lower and upper eyelids;
- severe tearing.
Swelling of the mucous membrane of the eyeball – AntiAllergic
The cornea (or cornea) is one of the elements of the visual organs, which performs the functions of refraction of light.
When the cornea functions properly, this results in a clear image on the retina .
In certain diseases, the cornea swells , which leads to both disruption of its functions and pathological damage to its tissues, which subsequently makes it difficult to restore this element.
Symptoms of corneal edema
Such pathological changes are accompanied by the following symptoms:
Sometimes such symptoms are absent , and swelling of the eyeball can only be detected during examination.
In some cases, this can be done in advance due to patient complaints of hemorrhages and violations of the integrity of the cornea.
Corneal edema is quite common , and some people do not even suspect that they have suffered such a disorder.
The following disorders and problems usually lead to this pathological condition :
Sometimes this condition occurs as a result of surgery; swelling is often observed with prolonged use of incorrectly selected contact lenses.
Depending on the reasons, this phenomenon is tolerated more or less asymptomatically, but upon examination by an ophthalmologist it is determined quite quickly.
Most often, mild to moderate swelling of the eyeball goes away without consequences .
Another complication may be clouding of the cornea , as a result of which vision deteriorates. If measures are not taken in this case, this effect becomes irreversible.
Treatment based on the causes of swelling
Treatment for edema depends entirely on what caused it .
If this is a sign of an infection , the patient is prescribed antibiotic drops or antibacterial ointments .
In severe cases, several types of drugs are prescribed at once , including in the form of injections.
If the edema process is not caused by an infection, it is necessary to first eliminate the inflammatory processes. This is done using non-hormonal decongestants.
Swelling is most severe due to allergies, and in such cases the swelling extends not only to the cornea, but also to the area around the eyes and eyelids.
In such situations it is necessary to prescribe antihistamines , as well as limit contact with potential or direct allergens.
Subsequently, if it is difficult to determine the causative agent of the allergy, hormonal agents may be additionally prescribed .
a cold compress to the victim’s eyes as first aid .
If the problem occurs due to glaucoma, in most cases surgical intervention is required.
Only an ophthalmologist can accurately determine the necessary treatment methods after a comprehensive examination.
Based on the diagnostic results, appropriate treatment will be prescribed.
It is not recommended to take measures to eliminate such pathology on your own in order to avoid the development of irreversible complications.
Swelling of the cornea after cataract surgery
In most cases, corneal edema occurs cataract surgery .
During this procedure, a large amount of medical solution is passed through the cornea.
As a result, such exposure leads to saturation of the cornea with this liquid, and the longer the lens is washed out, the more pronounced this complication will be.
This is not a critical consequence and does not require special additional treatment..
Such swelling is considered absolutely normal in the first two weeks after surgery.
And if during this time it does not subside, the doctor, who sees the patient for some time after cataract removal, conducts local therapy using injections and instillations of decongestants.
Causes of swelling of the eye mucosa
Let's look at this issue from a biological point of view. There is no such disease as “swelling of the eye mucosa”. They call it that only to simplify perception.
From a biological point of view, the mucosa is a multilayered squamous non-keratinizing epithelium (as in the oral cavity, pharynx). Of course, there is no epithelium in the eye.
In this case, we are talking about formations in the outer shell of the eye (sclera), in its anterior part - the cornea, the inner part of the upper eyelid, the inner part of the lower eyelid, or the conjunctiva.
Symptoms and causes
Swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye - the causes of this condition?
Swelling can be caused by many things, and many of them have different symptoms. Below we present the most common causes of edema. We will also look at their symptoms.
Postoperative injuries
Sometimes operations to improve vision or remove cataracts can have negative side effects. And one of them can be swelling. Decreased vision and a feeling of fogginess are also possible. Often such swelling goes away in the first week after surgery.
Possible consequences
Like any change, neoplasm or disease, swelling of the eye mucosa without the necessary treatment can cause complications and undesirable consequences. Such as blepharitis, keratitis, iritis, corneal ulcer, barley, erysipelas, eyelid abscess, boil.
Due to a frivolous attitude towards the fact that the mucous membrane of the eye is swollen, often (in 20% of the population) there is at least one case of blepharitis.
More severe cases are also possible - a creeping corneal ulcer. This pathology lasts quite a long time and has a lot of symptoms (pain in the eyes, severe photophobia, lacrimation, and others).
It is caused by chronic diseases of the cornea, which, in turn, develop due to the influence of streptococci.
This disease should be treated only in a hospital setting and under the constant supervision of a doctor.
Principles of treatment of ocular edema
If you notice swelling in the eyeball area in the morning, then try to figure out the reason for its appearance.
Make sure it's not an allergic reaction (the tips above will help). If the cause of swelling of the eye mucosa is an allergy, immediately eliminate the allergen. Rinse your eyes with chamomile infusion or boiled (cooled) water (this will help relieve discomfort). And also take a drug like Suprastin (antihistamines - reduce allergic reactions).
If this is not an allergy, or you have not detected an allergen, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. He will examine you and send you for biological tests for bacteriological examination and isolation of a pure culture. Antibiotic susceptibility testing may be necessary in the future.
Traditional medicine in the fight against edema
And also in the process of treating swelling of the eye mucosa, traditional medicine can be used, such as:
- Treating the eyelids with an infusion of cold black tea, or washing the eyes with a warm infusion (it has antiseptic properties and helps relieve eye puffiness);
- Compresses made from raw grated potatoes, which will also reduce swelling and have an analgesic effect;
- Rinsing the eyes with a warm aqueous solution of propolis or honey will help with defects, injuries or ulcers of the cornea.
- Infusions of chamomile, linden, sage, dill, arnica or cornflower have an anti-inflammatory effect on the mucous membrane of the eye. They need to be used several times a day.
Source: //continentnn.ru/bez-rubriki/otek-slizistoj-glaznogo-yabloka.html
Why does the lower eyelid hurt?
The lower eyelid swells due to fluid retention in the soft tissues. The reason for this phenomenon may be:
- disruption of the heart and kidneys;
- alcohol consumption;
- eating salty foods;
- allergies to cosmetics;
- Drink plenty of fluids before bed.
In most cases, swelling of the lower eyelid is not characterized by pain.
Lots of water before bed
During the night's rest, melatonin is produced, which causes the brain to slow down the functional activity of other internal organs. The kidneys stop intensively processing fluid. Therefore, drinking a large amount of water before bed creates additional stress on paired organs. Their activity is reduced, so fluid begins to leak into the intercellular space of soft tissues.
This is not a pathological reaction, so there is no special treatment. Inflammation of the lower eyelids goes away on its own if you adjust your fluid intake in your diet. To quickly relieve swelling, it is recommended to apply a cold compress or tea bags.
Lots of salty food
Excess salty food in the diet disrupts the water-electrolyte balance of the body. Salt or sodium chloride retains fluid in the soft tissues, causing swelling. There is practically no fatty tissue in the lower eyelid area, so after waking up, a person has noticeable bags under the eyes.
Alcohol
Alcoholic drinks contain ethyl alcohol, which negatively affects the functioning of the liver and kidneys. Due to a strong decrease in their functional activity, swelling of the eyelids is observed. This situation is typical for people who abuse alcohol.
Wrong chosen cosmetics
Low quality cosmetics can cause a severe allergic reaction. Eye shadow, mascara or eyeliner lead to swelling, itching and increased tear production. To eliminate allergies, it is necessary to take antihistamines and replace cosmetics.
Diseases that cause swelling and pain in the eye
If swelling does not go away for a long time, it is necessary to exclude the presence of an ophthalmic disease. The emerging problem may be associated with pathologies of the liver, cardiovascular or urinary system.
Swelling and pain in the eyes can be caused by:
- Conjunctivitis. Characterized by acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes. Inflammation develops against the background of an infectious process, which in parallel causes general intoxication of the body and headaches. Conjunctivitis often disrupts the functioning of the lacrimal glands, which causes dry eyes. In such a situation, they begin to water while blinking, and the skin around them itches and flakes off.
- Ptosis. Accompanied by drooping of the upper eyelid due to severe swelling. The cause of the pathology is diseases such as stroke or encephalitis, so the symptomatic picture, in addition to ptosis, is supplemented by signs of neurological disorders.
- Blepharitis. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. The patient sees a film of tears before his eyes, which prevents him from seeing objects normally. The skin in the eyelash area becomes covered with scales and itches. The eyes quickly get tired and become more sensitive to light. Headache develops against the background of photosensitivity.
- Barley . Purulent-inflammatory diseases of the eyelids. If left untreated, the swelling quickly increases in size, and pain occurs when blinking.
- Uveitis. The pathological process spreads to the choroid of the organ of vision, which causes swelling and redness. The patient feels pain inside the eye and sees dark spots.
- Phlegmon. A purulent process develops in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the eyelids. A bacterial infection causes an increase in temperature to +39...+40°C, muscle weakness, fever and cephalalgia.
Often, swelling of the eyelids is a sign of kidney dysfunction. Neoplasms, inflammation or dystrophy reduce the functional activity of the organs of the urinary system. The kidneys become unable to fully remove water from the body. There is fluid retention in soft tissues.
Expert opinion
Slonimsky Mikhail Germanovich
Ophthalmologist of the highest qualification category. Has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating eye diseases in adults and children. More than 20 years of experience.
Pain to the touch and swelling can be caused by arterial hypertension or heart failure. If the cause of the development of the pathology is associated with a disruption of the circulatory system, blood pressure rises and jumps in heart rate are observed. The patient suffers from dizziness, ringing in the ears and decreased visual acuity.
Swelling of the eyes, not accompanied by pain, can be the cause of liver damage - cirrhosis, fatty degeneration, hepatitis. In this case, general intoxication of the body develops. The liver loses its ability to process and neutralize toxic substances.
IMPORTANT. With liver damage, in addition to swelling of the eyelids, jaundice of the sclera may be observed.
Swelling of the white of the eye, what to do, how to treat it
You can often see such a request in search engines.
From the point of view of the anatomy of the eye, this is somewhat incorrect, since there is no mucous membrane in the usual sense (stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium, as in the oral cavity, pharynx, rectum) in the human eye. So what is meant when they say that “the mucous membrane of the eye is swollen”?
In this case, we can talk about three formations that touch the outer shell of the eyeball - the sclera in its front, transparent part, which is called the cornea:
- inner part of the upper eyelid;
- inner part of the lower eyelid;
- connecting transitional fold between each eyelid, which is called the conjunctiva.
Symptoms of edema
Despite the abundance of reasons that can lead to edema, it is necessary to distinguish between unilateral lesions and bilateral disorders.
Most often, unilateral edema is characteristic of trauma to the eyeball, dry conjunctivitis, and the consequences of ophthalmological and neurosurgical interventions.
Symmetrical (or bilateral) damage can occur with a hypertensive crisis, a fracture of the base of the skull, as well as bilateral allergic (angioneurotic) Quincke's edema.
Swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye is characterized by the following symptoms:
- redness of the eyes;
- injection of blood vessels of the sclera and conjunctiva;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- pronounced edema is possible - swelling of the eyelids;
- the addition of a secondary infection is manifested by the discharge of purulent discharge;
- with a pronounced protein content, exudative inflammation occurs. It is the protein that is to blame for the fact that in the morning it is impossible to “unstick” your eyes, as the eyelashes stick together;
- later symptoms are excessive dryness and flaking of the skin of the eyelids.
About the causes of edema
Acute allergic edema occurs symmetrically, develops very quickly, sometimes in a matter of hours, and there is no pus. The swelling and itching are so pronounced that it is simply impossible to open the eyes - they turn into small “slits”.
Bacterial and viral infections often affect one eye. The most common and contagious forms that are transmitted by contact and airborne droplets are acute epidemic, meningococcal, pneumococcal conjunctivitis.
The greatest danger is herpetic viral conjunctivitis. It can cause ulceration of the cornea, and also spread the virus through the perineural spaces into the brain, with the development of herpetic encephalitis. This complication is characterized by high rates of mortality and disability.
Also common is adenoviral conjunctivitis, which is similar to the common “cold” with fever, sore throat at the beginning and conjunctivitis appearing later.
Thus, swelling of the eye mucosa, the causes mentioned above, has a polyetiological nature.
Principles of treatment of edema
It is very important to examine the patient by an ophthalmologist, as well as to take the discharge for bacteriological examination, isolate a pure culture, and then determine sensitivity to antibiotics. The principles of emergency treatment include the administration of the following drugs:
- antihistamines and desensitizers (they are the main ones for the treatment of allergic edema): Claritin, Suprastin, Cetrin, Tavegil, Erius;
- antiseptic and disinfectants: solution of furacillin, potassium permarganate, hydrogen peroxide;
- antibiotics: sulfacyl - sodium (albucid), chloramphenicol ophthalmic ointment;
- antiviral drugs, including forms for topical ophthalmic use (acyclovir, Zovirax, famciclovir) for the treatment of ophthalmoherpes.
Other drugs are used either in the form of tablets or injections. These include antibiotics, agents that enhance immunity (interferon, ridostin, various interferon inducers).
Swelling of the eye mucosa, the treatment of which is difficult, can be tried (with caution) to be treated with hormonal corticosteroid drugs, but for a short time and taking into account concomitant diseases and contraindications.
Traditional medicines that are used to treat eye swelling are as follows:
- treatment of the sclera and eyelids with cold infusion of tea;
- compresses with raw grated potatoes, which relieves signs of swelling and reduces pain;
- washing the eyes with a warm aqueous solution of honey, propolis and mumiyo. Helps with defects, injuries and ulcers of the cornea, as well as during the recovery stage of keratitis and ophthalmic herpes;
- An aqueous infusion of chamomile has a gentle effect on the mucous membrane of the eye. You need to wash your eyes several times a day.
Postoperative swelling
Swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye after blepharoplasty is the most common type of iatrogenic (that is, caused by medical intervention) edema. Blepharoplasty is a cosmetic surgery that removes bags under the eyes.
After surgery, swelling may bother you for some time, so to reduce its severity and quickly eliminate it, you can use the following methods:
- During sleep, the head should be significantly higher than the legs, this ensures the outflow of blood;
- cold lotions should be placed on the eyes;
- no need to strain your eyes by reading, blinking, being in bright places, or working on a computer;
- wear sunglasses and avoid dusty places until you recover;
- Bend over work, gymnastics, swimming, visiting the bathhouse and other types of physical activity are prohibited.
These simple tips will help you quickly get rid of swelling after surgery, and if it occurs while you are fully healthy, you will know which specialists you should contact.
Source: //ushib-lechenie.ru/otek-belka-glaza-chto-delat-chem-lechit.html
What does swollen eyes mean in a child?
Swollen eyes accompanied by increased tearing and viscous discharge from the eyes may indicate the onset of an infectious process. The most common condition is conjunctivitis. In this case, redness, pus production, and itching are observed.
In most cases, children who touch their eyes with dirty hands develop a fungal infection of the mucous membranes of the organ of vision. To treat conjunctivitis, drug therapy with antibiotics, antifungal or antiviral drugs is carried out. Treatment depends on the type of disease.
REFERENCE. When a new product is suddenly introduced into a child’s diet, an allergic reaction may occur. In such a situation, therapy with antihistamines is necessary under the strict supervision of a physician.
Swelling of the eyelids can develop due to increased intracranial pressure or against the background of congenital pathologies of the cardiovascular system. In such a situation, you must immediately consult a doctor and undergo a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Doctors and diagnostics
An ophthalmologist, who relies on the data obtained during the tests, helps to identify the cause of the development of swelling. If there are concomitant diseases, it is necessary to consult with other specialists: a cardiologist, a surgeon, a gastroenterologist.
To determine the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a number of instrumental and laboratory tests:
- allergy tests;
- exclude demodicosis in the eyelash area;
- get tested for bacteria;
- undergo biomicroscopy;
- dacryocystography;
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- tubular test.
Depending on the established diagnosis, further treatment will depend. To relieve swelling, anti-inflammatory eye drops may be prescribed as part of symptomatic therapy.
Treatment
Treatment is not carried out if swelling of the eyelids appears due to poor diet or drinking too much water. To speed up the recovery process, apply a cold compress to the affected area.
Antihistamines help get rid of allergic reactions and inflammation after an insect bite:
- Suprastin;
- Claritin;
- Tavegil;
- Loratadine.
Drugs from this group suppress the synthesis of histamine, which leads to the development of edema. As a result of proper medication use, you can get rid of the symptoms of allergies, headaches, coughs and inflammation of the mucous membranes.
In the presence of concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system, leading to swelling of the eyelids, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed to normalize blood pressure. If the kidneys are damaged, excess fluid is removed by taking diuretics.
To restore liver function, hepatoprotectors are taken. Symptomatic treatment of swelling and pain in the eyes is carried out using drops or ointments from a number of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
IMPORTANT. The medications should be taken under the supervision of the attending physician. Consultation with a specialist is necessary for swelling of the eyes that does not go away within 3-4 days.
Before using alternative medicine, you should consult a specialist. Folk remedies can only be used with the permission of the attending physician in parallel with drug therapy.
Causes and treatment of eyeball swelling
Due to some external influences or pathologies, swelling of the cornea occurs, which leads to unpleasant and painful symptoms.
By finding out the causes and coordinating the treatment of swelling of the eye mucosa, there is a chance to get rid of the problem and restore vision. Treatment is not easy, especially if it occurs against the background of glaucoma.
And if a person values one of his senses, he should visit an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Symptoms of edema
In the visual organ there is no mucous membrane similar to the one that lines the internal cavities. When talking about swelling of the mucous membrane of the eyeball, we are talking about the cornea, formed by the inner surface of the upper and lower eyelids and conjunctiva.
When the cornea edema, the state of the organ of vision changes: the tissue thickens, folds and compactions form, which disrupts the normal refraction of light. During this process, the following metamorphoses occur:
- distortion of objects in the field of view;
- decreased vigilance;
- a feeling of fog before the eyes;
- reaction to exposure to bright light;
- feeling of sand or foreign body;
- corneal clouding;
- pain;
- spider veins or redness of the conjunctiva.
With secondary infection, purulent discharge is possible along with swelling. Sometimes there is dryness of the cornea and peeling of the skin of the eyelids.
Note: With swelling, pain in the eyes is not always pronounced, which makes diagnosis difficult. Redness is noticeable on the eyeball and upon careful examination there is a violation of the structure of the cornea.
Causes of swelling in the eyeball
The causes of swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye are different. Unilateral swelling is possible as a result of injury to the eyeball, the development of dry conjunctivitis, and manifests itself as a consequence of surgical interventions. Bilateral edema occurs after a hypertensive crisis or a fracture at the base of the skull.
Infections of various kinds
Inflammatory diseases of the eyeball can cause microorganisms that settle on the conjunctiva, capturing the cornea area and causing swelling.
Bacteria or viruses quickly infect both eyes and are easily transmitted from person to person.
Swelling of the white of the eye occurs under the influence of streptococci, staphylococci, chlamydia, viruses, fungi, and the normal microflora of the cornea is replaced by pathogenic ones.
Inflammation and swelling of the conjunctival mucosa is manifested by the following symptoms:
- the eyeball visibly swells due to inflammation;
- irritation from bright light is expressed;
- white or yellowish discharge from the eyes is observed;
- blurred vision, poor visibility.
The main symptoms of conjunctival irritation are a feeling of pain and the discharge of pus, which causes the eyelids to stick together in the morning. The infection is accompanied by redness due to dilated vessels of the eyeball.
The following can cause conjunctivitis and edema:
- microtrauma of the eyeball;
- violation of eye care rules;
- low immune defense;
- infectious lesions of the nasopharynx.
Violation of hygiene rules when wearing contact lenses can also provoke infectious swelling of the eyeball. But the most unpleasant thing is that the infection manifests itself through purulent discharge, which can be quite copious.
Principles of treatment of edema
Treatment of swelling of the eye mucosa begins with finding out the cause of the development of the pathology. Even knowing the nature of the disease, be sure to consult with an ophthalmologist. The disease is diagnosed, as well as the removal of the discharged contents of the eyeball (tear fluid, purulent discharge, film on the surface of the cornea).
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor draws up a treatment plan:
- In case of infection, antibiotic drops or antibacterial ointments are administered: Albucid, chloramphenicol ointment. For viral infections, Acyclovir and Zovirax are prescribed. If purulent discharge appears, the eyes are washed with a solution of potassium permanganate and furacillin.
- If the inflammation is not caused by an infection, then treatment involves eliminating the inflammation itself and relieving swelling. In this case, non-hormonal decongestants are used: Indanazoline, Xylometazoline, Tetrizoline, Naphazoline. They cause vasoconstriction and reduce swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose, throat and eyeball.
- For allergic eye swelling, antihistamines are prescribed and allergy tests are performed, identifying a compound that can cause a negative physiological reaction. It is important not to come into contact with the allergen during treatment. Antihistamine and desensitizing drugs include: Claritin, Cetrin, Tavegil, Suprastin.
First aid for edema of various etiologies
If there is sudden and rapid bleeding of the eyes, the likely cause is an allergy. A cold compress is applied to the eyelids, the patient is given an antihistamine and as much fluid as possible. Useful activated carbon to remove the allergen from the body. With allergies to the eyes, Quincke's edema often develops, which is especially dangerous.
How to relieve swelling of the eyes due to a bruise? Any cold substance is applied to the wound site, for example, ice wrapped in a cloth or a bottle of cold water. This leads to rapid blood clotting and the formation of a smaller hematoma. They use badyaga (water moss), which quickly relieves swelling from the eyeball. The product can be used for bruises and bruises under the eyes.
Note: If the cause of swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye is stress, insomnia, tears, or a cold, then cosmetic procedures will help solve the problem of dull eyes: massage, masks, compresses.
Traditional medicine in the fight against edema
How to remove swelling and swelling, how to relieve corneal irritation? If the eyeball is slightly damaged, but swelling causes unpleasant symptoms, use folk remedies:
- eyes and eyelids are washed with an infusion of black, cold tea, which is a good antiseptic;
- a compress of grated, raw potato gruel is applied to the eyelids, which can alleviate the condition and alleviate the pain of swelling;
- washed with warm infusion of propolis or honey if the cornea is injured;
- apply lotions to the eye socket area from infusions of chamomile, linden, and sage; lotions provide relief from inflammatory processes caused by conjunctivitis.
You can try infusions of agrimony, cornflower, dill seeds, and aloe juice for swelling on the eyeball. The number of “grandmother’s” recipes is simply huge, but this is not a panacea for all ills. An examination by an ophthalmologist is required to determine the stage of the disease and its course.
Postoperative period
After eye surgery, the mucous membrane of the eye remains swollen for some time. This condition causes certain inconveniences. To make eye swelling go away faster, you should listen to some tips:
- During sleep, the head should be higher than the level of the legs so that blood flows away from the organs of vision.
- Reduce the number of television viewings, reducing eye strain.
- Use dark glasses in the sun to avoid causing inflammation of the cornea.
- You should not visit saunas, steam baths, or swimming pools, as this can cause additional infection.
- Limit any physical activity while the recovery period is underway.
Sometimes in the postoperative period swelling of the fundus occurs. At the same time, fluid accumulates in the organs of vision and image clarity is lost. Treatment is prescribed, which is aimed at restoring blood microcirculation and outflow of ocular fluid.
Prevention against swelling
To avoid swelling, it is important to follow some rules:
- choose hypoallergenic cosmetics from reliable manufacturers;
- use protective equipment in the sun and during work hazardous to eyesight;
- after forty years, undergo regular examination by an ophthalmologist due to age-related changes;
- choose the right contact lenses based on the recommendations of specialists.
Massage and a set of exercises help relieve swelling caused by an irrational lifestyle. But for serious pathologies, these measures are ineffective. In some cases, hospitalization and drug treatment are necessary.
Conclusion
If swelling of the eye mucosa occurs, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist. The consequences of self-medication or inaction will affect the quality and acuity of vision. Do not underestimate the disease, which can lead to subsequent complications. And then there is a chance to maintain sharp vision and observe the world around us in bright colors.
Causes and treatment of eyeball swelling Link to main publication
Source: //OtekOff.ru/otek/otek-litsa/otek-glaznogo-yabloka
Prevention
To prevent eye swelling, you should follow some recommendations:
- You need to sleep at least 8 hours a day. You should not overstrain your visual organs during the day.
- After 18:00 you need to reduce your fluid intake, especially sweet and carbonated drinks.
- Do not dine on smoked, pickled, spicy or salty foods. Salt, sugar, spices and preservatives cause fluid retention in the body.
- In summer you should wear sunglasses. Ultraviolet rays can harm the structures of the eyeball: cornea, lens, retina. Damage to the organ of vision can cause swelling.
It is necessary to undergo preventive tests once a year to assess the functioning of internal organs. Timely diagnosis of diseases helps reduce the risk of complications.
Useful video
What to do if the eye is red, hurts and watery?