Vaginal prolapse is a pathological disease of the inside of the vagina. As a result of abdominal pressure, the muscle tissue weakens and pushes the vaginal walls and organs down towards the genital opening. The disease can be diagnosed at an appointment with a gynecologist. Sometimes a woman can independently observe the pathology visually. Based on your first feeling, you should seek medical help in order to prevent the severity of vaginal prolapse from developing.
This serious disease requires proper diagnosis and treatment. The disease occurs most often in women of Balzac age. As a result of wear and tear of the pelvic muscles or a large number of births. Young girls are also at risk of developing it. An unhealthy lifestyle and the heredity factor spread the pathology to girls during intrauterine life. This is due to improper development of the genitourinary system even before the baby is born.
The muscle tissue of the vagina has a vital function. The internal organs must remain motionless. As a result of impaired muscle contraction, a woman does not receive pleasure during sexual intercourse, and there is no natural stimulation of the uterus. At the first symptoms, immediately contact your gynecologist.
Symptoms of cystitis before menstruation
Many women do not feel their best during their periods. If signs of cystitis appear during menstruation, this can significantly reduce the usual rhythm of life.
Symptoms of cystitis during menstruation:
- urination occurs with a feeling of pain in the perineum;
- urine comes out often, but in small quantities;
- periodic or constant pain in the lower abdomen;
- sometimes body temperature may rise;
- general deterioration of health;
- cloudy urine.
In some women, frequent urination is associated with physiological characteristics. This can happen during menstruation due to an increase in the volume of the genital organs (in particular the uterus), which begin to put pressure on the bladder.
In such cases, frequent urge to go to the toilet is not associated with diseases of the urinary system, but still an examination by a doctor and tests will help determine the true cause.
Postcoital cystitis: what you need to know?
Postcoital cystitis: what you need to know?
Many women know what cystitis is after intimacy. Such an unpleasant consequence of sex poisons life with painful symptoms and difficult thoughts about the sexual partner. Is he always the culprit when his partner develops cystitis after sex? Or are there reasons related to the woman’s health, physiological and anatomical characteristics?
Cystitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. Due to the structure of the genital organs, a woman is more likely than a man to get it after coitus. Among the symptoms suggesting acute or chronic postcoital cystitis:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urination;
- increased body temperature;
- burning in the urethral area;
- a woman has pain in her labia;
- weakness, fatigue.
Symptoms of the disease may not appear immediately after intercourse, but after 24-48 hours. This makes a woman think badly about her partner, prevents her from leading a full life, including sex, and worsens her well-being and mood due to pain, discomfort, and feelings of guilt.
Is cystitis possible due to sex?
A normal intimate life presupposes the physical health of both sexual partners, the absence of sexually transmitted infections, and trust in the couple. However, quite often, especially after prolonged intense sex, the partner begins to feel a frequent urge to urinate. You should not immediately jump to the conclusion that this is due to infection during sexual intercourse. Perhaps the urethra and cervix reacted this way to too active actions of the sexual partner.
We can talk about the inflammatory process due to infection in the genitals and bladder 24 hours after coitus. If by this time the symptoms of cystitis have not disappeared, the woman needs urgent comprehensive diagnosis and examination by a gynecologist or urologist. The sooner the patient begins to treat acute cystitis, the better for the genitourinary and reproductive systems.
Cystitis, age, sex
Cystitis after sex can occur in women of any age. In the old days, when many girls remained virgins until marriage, it was often called the honeymoon disease. Nowadays, doctors do not associate the disease with any specific period of a woman’s life.
After sexual intercourse, a woman may experience symptoms of bladder inflammation:
- due to sexual contact after a long break in intimate relationships;
- coitus with a new partner;
- too active sexual games.
It is difficult to predict or insure against acute cystitis. It occurs in both young and mature women. You should carefully monitor your body’s reaction to intimacy, avoid situations and behavior that can provoke cystitis, and try to minimize their impact on health.
Causes of cystitis
Postcoital inflammation of the bladder in women is most often caused by infection. This happens due to the anatomical features of the structure of the female body. Bacteria from the vagina easily penetrate the urethra and bladder if the external opening of the ureter is located too close to it.
Cystitis often occurs as a result of neglect of the rules of intimate hygiene by one or both partners. The combination of vaginal and anal sex in one sexual act also leads to infection of the genitourinary system with Escherihia coli. According to statistics, it causes 9 cases of cystitis out of every 10. Active frictions during sexual intercourse provoke an ascending infection in the urethra and bladder.
STIs (sexually transmitted infections) often cause cystitis in women after sex. A risk factor is considered to be a lack of natural lubrication of the partner's genitals. Any damage to the mucous membrane greatly increases the risk of infection during sexual intercourse. Some positions, such as sex from behind, also cause similar problems. The doctor analyzes the causes and selects treatment individually for each patient. He will also recommend preventive measures to avoid exacerbation of cystitis in the future.
Is it possible to have sex with cystitis?
The recommendations of gynecologists and urologists on this issue agree - if you have inflammation of the bladder, it is better to postpone sex until complete recovery. However, if a woman does not have such an opportunity or desire, she should adhere to rules of behavior that will reduce the risk of complications:
- careful intimate hygiene of both partners;
- do not touch the anus with your penis before beginning vaginal intercourse;
- refuse clitoral stimulation so as not to cause irritation and inflammation in the ureter;
- after coitus, a woman should take a shower with mild, low-alkaline soap;
- You can use folk remedies to treat inflammatory processes in the female genital area.
Sex with cystitis should be protected. Using a condom reduces the risk of unpleasant consequences of sexual intercourse for both partners. The condom protects the female genital organs from additional infection. The mucous membrane of the glans penis will not be irritated upon contact with the vagina, burdened by abnormal acidity and acute inflammatory process.
Partners should refrain from using intimate means to stimulate arousal, or toys that can cause even greater irritation to the already inflamed mucous membranes. Compliance by a couple with these rules reduces the risk of complications and contributes to the woman’s normal well-being.
It should be emphasized that these recommendations relate to the period of a woman’s recovery or remission of chronic cystitis. During the acute stage of the disease, sex is inappropriate, as it will aggravate already unpleasant symptoms and poor health.
Causes of cystitis during menstruation
What is the reason for the occurrence of cystitis during menstrual periods? To find the source of the disease, you need to visit a urologist and gynecologist.
The most common causes of cystitis during menstruation are:
- active growth of pathogenic microorganisms due to poor personal hygiene. Blood clots become a favorable environment for the development of bacteria. When menstrual flow stagnates in the perineum, pathogenic microorganisms quickly enter the urethra;
- inflammatory processes in the genital organs. Often, inflammatory processes in the appendages or in the uterus do not bother a woman for a long time (and are detected only at an appointment with a gynecologist); during menstruation, pathogens of inflammation in the genitals can easily enter the bladder;
- changes in intestinal microflora. If a woman is diagnosed with thrush, which is provoked by fungi of the genus Candida, then during menstruation these protozoan microorganisms multiply in large numbers and can enter the urethra;
- allergies to personal hygiene products. The variety of products for individual use during menstrual periods is amazing. But there are often cases when a woman experiences allergic reactions from pads in the form of irritation of the bladder (allergens act on the organ through the urethra).
During menstruation, the decisive factors for such rapid and active growth of bacteria, viruses or yeast-like fungi are: decreased immune strength, hormonal fluctuations in the woman’s body and lack of personal hygiene during menstruation.
Classification and degree of development of the disease
There are three degrees of development of the pathology of vaginal prolapse. They differ in the stage of prolapse and severity of symptoms:
1. in the first degree, the cervix is 2-3 centimeters from the perineum. The gap is widened, but with muscle contraction it can be closed. Accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen that occurs after physical activity. Frequent urination is not accompanied by pain. During sex, there is discomfort during insertion of the penis.
2. the second degree is recognized at a doctor’s appointment. The prolapse of the walls and cervix reaches the entrance to the vagina. When pushing, the throat of the cervix comes out, and comes back after relaxation. The pain intensifies and spreads throughout the abdominal cavity and perineal area. It does not stop at rest, but intensifies with load. The process of sexual intercourse becomes impossible or very painful. The penis enters the vagina tightly. Urination becomes involuntary. Jogging or jumping is accompanied by severe pain.
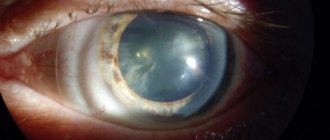
3. in the third degree, the vaginal walls weaken completely and lose the ability to hold the cervix and the organ itself inside. Uterine prolapse is observed visually. This leads to inflammatory processes and the development of microorganisms; due to the influence of the external environment, microcracks are formed in the vaginal mucosa. Failure of the hormonal cycle leads to menstrual irregularities. The pain syndrome is progressive. The woman is completely limited in her ability to move independently and visit the toilet.
4. The fourth stage means complete prolapse of the uterus and vaginal walls from the perineum.
In gynecological practice, prolapse of the vaginal walls is divided into 2 types:
- Cystocele is the process of prolapse of the anterior vaginal wall. Accompanied by a change in the position of the bladder towards the vaginal outlet;
- Rectocele is a pathological process of prolapse of the posterior wall, as a result of which a bend is formed in the rectum in which feces collect. Chronic constipation appears.
Prolapse of the vaginal walls develops gradually. The smooth development of the process is accompanied by the appearance of a hernia. The patient's condition is deteriorating. The disease can progress over 15 years. The exception is childbirth, after which the pathology is diagnosed immediately.
Cystitis during menstruation treatment
Like any other serious disease, cystitis should be treated only after consultation with a specialist. To select the necessary medications, you need to visit a urologist, and to diagnose diseases of the reproductive system, you need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
To treat cystitis during menstruation, the following drugs are most often prescribed:
- "Furagin";
- "Furamag";
- "Nolitsin";
- "Tsiprolet";
- "Amoxiclav";
- "Monural".
Description of all drugs for the treatment of cystitis cystitis here
These medications relieve inflammation in the bladder and destroy most pathogens.
Painful sensations from cystitis, which appear together with menstruation, can significantly “knock out” for some time. To reduce pain, antispasmodics are excellent: “No-shpa”, “Papaverine”.
In addition to the main treatment, medications containing herbal composition are prescribed:
- "Phytolysin";
- "Canephron N".
They have anti-inflammatory, diuretic and analgesic effects.
To prevent cystitis during menstruation you need:
- change gaskets as often as possible;
- wash yourself correctly (from the pubis to the anus);
- promptly treat gynecological diseases;
- It is advisable not to use tampons during menstruation;
- don't get too cold.
When cystitis worsens, you should drink a lot of water (to flush the urinary tract) and ensure maximum rest. It is recommended to take a course of vitamin complexes to increase the body's defenses.
Candidal cystitis and thrush
Candidal cystitis: symptoms and causes of the disease
Frequent urge to urinate, reduction in portions of urine excreted, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder - these are all manifestations of canida cystitis. The clinical picture also includes changes in the urine - it becomes cloudy, acquires a pungent odor, and may contain blood. [16, 39]
When cystitis worsens, patients experience sharp pain in the lower abdomen and fever. During the act of urination, itching and burning are felt in the perineum. [16, 39]
The causative agent of the inflammatory process in candidal cystitis is the fungus Candida Albicans. The infection can enter the bladder through an ascending or descending route. In the first case, a fungal infection enters the urethra from the external genitalia, after which it penetrates the bladder and causes inflammation. Sometimes infection occurs during catheterization, but the external genitalia are not affected. [38, 40]
The descending path is realized when the skin, stomach and other organs are affected by the fungus. After this, the pathogen penetrates the bloodstream, spreads throughout the body and penetrates the bladder. Typically, Candida fungus becomes especially active during a period of decline in immune function. [38, 40]
How to choose a treatment regimen for candidal cystitis?
The choice of treatment tactics is based on the results of complex diagnostics. The patient needs to consult with a urologist and therapist, and undergo an examination. Usually, after examination by specialists, a general urinalysis, serological (PCR, ELISA, RNGA), as well as microscopic examinations are carried out, which allow identifying the pathogen. [40]
A clearer clinical picture can be obtained by performing an ultrasound of the bladder. The study helps detect signs of the inflammatory process. For candidal cystitis in women, treatment is prescribed only by a doctor. The treatment regimen depends on the nature of the pathogen. [40]
The fact is that not all antifungal drugs can destroy it, and the use of antibiotics can only worsen the situation. With the simultaneous development of candidiasis and cystitis, patients must follow a drinking regimen, diet, and sexual abstinence. It is important to understand that both partners need treatment. [16, 40]
Thrush with cystitis: how to avoid?
To prevent infection of the bladder with Candida fungi, you must maintain a regimen of sexual abstinence until the end of therapy. Even when using a condom, the urethra can become infected, leading to the development of candidal cystitis. [16, 40]
This pathology, in turn, can cause infection of the external genitalia. To avoid this, you need to take special medications that maintain normal vaginal flora. [40]
Thrush and candidal cystitis often “act” in tandem. Therefore, patients must understand the importance of preventive measures and comply with them. [40] Herbal medicine in the treatment of cystitis in women
In the complex therapy of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract, herbal remedies, for example, Fitolysin® paste, can be used. The herbal diuretic contains 4 essential oils (orange, pine, sage, mint), as well as 9 medicinal extracts (goldenrod, lovage, birch leaves, etc.). [1, 6, 26]
The drug for the treatment of cystitis Fitolysin® is available in the form of a paste for the preparation of an oral suspension. This form ensures faster absorption of the active components. They are delivered directly to the site of inflammation faster than in the case of taking tablets. [2]
The herbal diuretic has diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic effects. [6] The drug is produced in Europe. Its production meets international GMP standards [3]. It helps eliminate inflammation and pain, normalize urination, flush sand from the urinary tract and reduce the crystallization of urine minerals [1,6].
Folk remedies for treating cystitis during menstruation
One of the popular folk methods of treating cystitis is taking baths with the addition of medicinal herbs. But during menstruation, this method is not suitable, because when exposed to hot water, the amount of discharge can increase sharply.
The most rational treatment would be to use herbs with antimicrobial and antispasmodic effects.
Parsley infusion:
- 1 tsp. chopped parsley;
- 200 ml hot water.
How to prepare: pour boiling water over the herb, close the lid, leave for 2 hours. Drink 1/3 glass before meals.
Cranberry decoction:
- 0.5 tbsp. cranberries;
- 0.5 l of water;
- 2 tbsp. l. honey
How to prepare: Grind the berries in a blender. After squeezing the berries, the resulting juice should be stored in the refrigerator. Place the squeezed berries in an enamel bowl and add water, place on the stove and boil for 7 minutes. Cool the resulting broth to room temperature and mix with juice from the refrigerator. Add honey. This drink will not only have an anti-inflammatory effect, but will also help boost your immunity. Another great way to get rid of cystitis is treatment with bay leaves.
Cystitis is a disease that occurs not only due to the fact that a woman dresses lightly in the cold season. In fact, there are a number of factors that can cause your bladder to become inflamed. Quite often, cystitis provokes the onset of menstruation.
Cystitis before menstruation, treatment
Almost every woman knows that menstruation directly depends on hormonal levels. The causes of cystitis before menstruation lie precisely in this fact. Plus, other factors also influence the occurrence of the disease.
These include:
- Changed microflora. The vagina becomes most susceptible to various kinds of bacteria, which during this time period easily penetrate the tissues of the organ;
- weakened immune system. During menstruation, the body directs all its reserve forces to renew the uterine mucosa;
- use of hygiene products. Changed microflora can give a negative reaction even to the usual components included in the product;
- failure to maintain intimate hygiene. The inflammatory process of the genital organs is transferred to the urinary system.
All of the above factors give an idea of why the disease occurs and why cystitis worsens before menstruation. During this period of time, a woman is least protected. This is due to a reduced level of immunity.
In order to begin treating the disease as early as possible, you need to carefully study the signs of cystitis before menstruation:
- Constant desire to go to the toilet. This is especially true at night;
- A strong tingling sensation in the lower abdomen;
- Pain very similar to contractions;
- When urinating, a woman feels an unpleasant burning and stinging sensation.
Sick women complain of severe fatigue. In this case, physical labor is not necessary at all.
In addition to all of the above, one of the signs of the disease is a change in the color of urine. It becomes dark, and you can also see foreign secretions and even flake-like particles in it.
If you see traces of blood or pus in your urine, contact a specialist immediately!
Important! An aggravated disease can cause involuntary urination. This fact, of course, cannot but affect the usual way of life.
Cystitis after menstruation
There are quite common cases when signs of cystitis and the disease itself manifest themselves after menstruation. Women do not understand what is happening because the body is completely renewed and is not as susceptible to the appearance of bacteria as during menstrual periods. The discharge may not stop, but may already have a dull white color.
Why do I have cystitis after menstruation? There are several reasons for this, and they have characteristic differences than in other periods of the menstrual cycle:
- discharge can enter the bladder and cause an inflammatory process;
- irritation caused by intimate hygiene products. It is worth saying here that an allergic reaction can occur instantly;
- venereal infections. Viruses and bacteria, along with secretions, very quickly enter the bladder;
- thrush.
Cystitis causes a delay in menstruation
The thing is that a regular cycle is directly related to the normal functioning of the ovaries. If an inflammatory process occurs in the bladder, then this will certainly affect the ovaries.
Note! A delay is possible not only at the moment when the disease was detected, but even after complete recovery. This is due not only to the fact that cystitis may subside for a while, but also to the effect of drugs on the female body.
If the disease is chronic or occurs in an acute form, then changes in the endometrium are possible. Disturbed hormonal levels affect the process of cell separation, excretion and renewal.
Delayed menstruation and cystitis require immediate treatment. The woman will have to take a blood test and undergo an ultrasound examination. The result of the examination will most likely be the identification of disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries. Thus, your period may be late by one week or even a month.
Diagnostic procedures
If timely treatment was carried out and the degree was not advanced, doctors predict a favorable recovery. The walls of the vagina and the body of the uterus return to their normal position and continue to function. The opportunity to become pregnant and bear a child is not lost. In the third degree, complications and a more severe course of treatment and rehabilitation are possible. The functioning of the genital organs may be partially or completely lost. Observation by a gynecologist and muscle strengthening are constantly required to avoid relapse.
Pathology can be diagnosed during a routine examination in a gynecological chair. Also, discomfort can lead a woman to a forced appointment. The gynecologist determines the anatomical structure of the organs and assesses the level of development of cystocele or rectocele. The condition of the pelvic floor muscle tissue is checked.
The woman is sent for an ultrasound. Transvaginal ultrasound involves directing sound waves using a transducer to internal organs. It is inserted through the vaginal opening and illuminates the uterus, cervix and ovaries. The specialist assesses their condition based on the image on the screen.
In addition to the gynecological examination, the patient is sent to the urologist's office. The functioning of the bladder is checked using a urodynamic procedure.
After conducting all the necessary studies, the doctor establishes the diagnosis and its degree. Depending on the severity of the disease, urgent treatment is prescribed.
Delayed menstruation after cystitis
Cystitis affects menstruation and this is a fact. Sometimes after complete recovery, menstruation does not begin again. What is this connected with?
Irregularity of the cycle should alert a woman and force her to see a doctor. Do not forget that if you have or have had sexually transmitted diseases and the treatment was not carried out properly, the pathogens of the virus will not disappear from the body. In simple terms, they will simply subside for a while, and then they will make themselves felt again, but in a more severe form. It is for this reason that measures need to be taken in time.
Cystitis poses a danger not only to the urinary system, but also to the genitals. They are in close proximity to each other and, therefore, inflammation can move from one organ to another. Even after getting rid of cystitis, a woman may be diagnosed with other equally dangerous and unpleasant diseases.
The disease affects not only your overall health, but also your usual lifestyle. The woman experiences pain and discomfort and, of course, suffers stress due to the current situation. There may be a delay in menstruation or, on the contrary, more abundant discharge.
If you have cystitis, then you do not need to self-medicate - this will only worsen the situation. The tests and testimony of a specialist will help you choose the right treatment and improve your health.
Cystitis before each menstruation or a periodic disease is a very serious problem that undoubtedly needs to be dealt with.
Prevention
- prevent hypothermia;
- replacing gaskets at high intervals;
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. It is also necessary to exclude spicy foods and fast food from the diet;
- do not use tampons. These hygiene products trap bacteria and provoke an inflammatory process.
Cystitis is far from a safe disease that goes away on its own. If it is started, it can cause infertility. Therefore, if you understand that all the symptoms point to this disease, immediately seek medical help.
As for pregnant women, they should be extremely careful. During the process of bearing a child, cystitis can cause not only discomfort, but also harm the fetus. You also need to understand what exactly triggered the inflammatory process.
Of course, it is best to overcome the disease before conception. If cystitis occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, women are prescribed medications that are safe for both the expectant mother and the baby. Before taking any medications, you must consult your doctor.
On a note
Very often, after the symptoms of the disease are relieved, women stop treatment, which is a wrong and, most importantly, a dangerous decision.
Cystitis often becomes chronic and, with each exacerbation, begins to increasingly affect the bladder mucosa, which can seriously affect health in the future.
To avoid complications of cystitis, do not delay visiting a doctor. It is the doctor who will be able to find the cause of frequent inflammation in the bladder and select the correct treatment.
Elena Mikhailovna Frolova
Urologist of the highest category. Proficient in the full range of outpatient diagnostics and treatment of diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems in men, and the urinary system in women.
More about the author. It is also important to know:
- Non-infectious cystitis.
- What is bullous cystitis?
- Hemorrhagic cystitis: what are the symptoms and how to treat.
- Cystitis in old age.
- Symptoms and treatment of cystitis in children.
- Treatment of cystitis in men.
- Cystitis after childbirth treatment.
- Viral cystitis.
- How to relieve the symptoms of cystitis at home.
Signs and causes of the disease
The first signs of vaginal prolapse are pain. Disorders of the menstrual cycle, the appearance of discharge of varying consistency and color indicate the development of pathology. Symptoms of cystitis can be caused by a prolapsed bladder. Disorder of sexual life, lack of fullness of sensations. A woman feels the presence of a foreign object inside the vagina. At the first signs, you should visit a gynecological examination room.
The following are the causes of prolapse of the vaginal walls:
- age-related atrophy of the pelvic floor muscles occurs in women over the age of 50 years. Loss of muscle elasticity occurs under the weight of internal organs;
- physical inactivity and low levels of physical activity lead to weakening of muscles even in young girls. Staying at rest for a long time and lack of mobility reduces the tone of the vaginal muscles;
- dysplasia, a disease of connective tissue deficiency, including vaginal tissue;
- congenital changes in tissues and organs;
- excessive physical activity;
- disruption of hormone secretion;
- vaginal trauma;
- difficult childbirth associated with bearing a large fetus;
- two or more births, after childbirth the body needs time to rest and normalize blood pressure, tissue healing and restoration of muscle tone;
- numerous abortions;
- surgical operations on the genital organs;
- disorders of the central nervous system. After a stroke, a woman cannot control the movement of her limbs and muscle contraction.
- excess body weight. Fat accumulation puts pressure on the pelvic organs, resulting in stretching of the muscle frame. Alternate or simultaneous prolapse of the walls occurs;
- chronic constipation or intestinal diseases, constant straining while visiting the toilet;
- stressful, sudden weight loss;
- intra-abdominal pressure caused by chronic asthma, bronchitis. They cause frequent coughing and cramping in the lower abdomen;
- long absence of sexual activity;
- frequent and rough intercourse, as a result of which cracks appear on the vaginal wall.