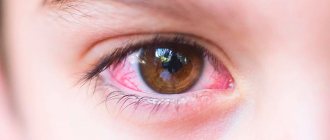
Diagnostics
Diagnosing hemangioma is not difficult; to do this, you only need to correctly assess the appearance of the neoplasm.
To accurately determine the type of pathology, there are various manuals, which consist of numerous images of various forms of tumor processes in the eye. Thanks to such reference books, it is possible to accurately determine the nature of the growths present and the location of the lesion.
When diagnosing an eye hemangioma, the child must be registered at the dispensary, since the doctor must monitor the course of the disease. Adequate treatment is also determined, which can be either conservative or surgical.
Medical practice sometimes encounters difficult cases when the lesion is localized in the deep layers of the orbit. In such situations, a visual examination does not make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, so the specialist prescribes the following additional measures:
- X-ray of the eye.
- CT scan.
- Arteriography.
- Venography.
On this topic
Organs of vision
All about ocular sarcoidosis
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- September 3, 2020
Arteriography and venography make it possible to assess the condition of blood vessels.
During the examination, visual acuity is assessed, the presence of strabismus is determined, as well as the presence of other concomitant diseases. Only after carrying out such measures can the doctor determine the most suitable treatment.
In the presence of superficial lesions that do not affect visual acuity, special therapy is not prescribed, but the child should be constantly monitored by a doctor in order to monitor the progression of the pathology.
More often (in 70% of cases), by the age of 7-8 years of life, the neoplasms disappear on their own; in other situations, the use of steroid medications is required or cosmetic surgery is prescribed.
If the presence of the disease negatively affects visual acuity, then removal of the lesion is required. To eliminate the tumor, laser treatment or liquid nitrogen can be used.
The measure of influence is selected depending on the age category of the patient. Often, after removal of the lesion, the doctor prescribes hormonal medications or radiation exposure (prescribed only as a last resort).
Retinal angioma of the hypertensive type
Angiomas are benign formations that can affect the human epidermis and internal organs.
Retinal angioma is a dangerous disease characterized by the development of cysts and angiomatous formations on the orbit, retina, and membrane of the eye. Untimely treatment can lead to loss of vision, so at the first symptoms you should consult a doctor. The disease has other names - phakomatosis, Hippel-Lindau disease, retinocerebroretinal angiomatosis. Angiomatosis is transmitted as an autosomal dominant type with partial spread outside the organ. The syndrome of birth itself is present in a child, but it begins to develop in people after 30 years of age. The manifestation of the disease indicates a disruption in the functioning of internal organs and chronic diseases. Depending on the pathological abnormalities, doctors distinguish 5 types of retinal angioma.
Return to contents
The development of the disease is a congenital anomaly that manifests itself as a result of exacerbation of other diseases. Among them:
- deviations in intracranial and blood pressure;
- injury to the neck, spine, head;
- osteochondrosis;
- decreased vascular tone in nervous disorders;
- elderly age;
- individual blood diseases;
- abuse of alcohol, cigarettes;
- intoxication of the body in hazardous production.
Often both eyes are affected at once. In the first stages, vision deterioration, flashes in the eyes, and depigmentation of the fundus are observed. Capillary glomeruli form in the fundus and are characterized by slow growth. Angiomas located on the orbits or eyeball reach large sizes, often exceeding 3–4 times the diameter of the optic nerve. As the tumor grows, the eye may become displaced.
At the next stage, the glomeruli move towards the center and can settle on the optic nerve head. The shape, color and size of vascular formations are different: burgundy, blue, green. Under the vessels lie yellow, white foci of the disease. At the last stage, retinal detachment, the development of cataracts, uveitis, and secondary glaucoma are observed. The patient suffers from nosebleeds, sudden changes in blood pressure, and headache. Angioma provokes hemorrhage in the eyeballs and progression of myopia.
An ophthalmologist diagnoses the visual organs after a general examination of the patient. By pressing on the eyeball, the tumor turns pale. To obtain information about the speed of blood flow and vascular tone, the doctor performs an ultrasound. Using an x-ray, an ophthalmologist examines the patency of blood vessels. Thanks to MRI, the ophthalmologist is able to see the structure of the soft tissues to accurately determine the stage of development of retinal angioma. CT scans help identify the disease in its early stages and prevent the disease from getting worse.
Antiography is a new method that allows you to establish objective information about the fundus in the early stages of erased forms of the disease. Shows the source of tumor growth and the size of the tumor.
Getting rid of retinal angioma is possible only with the use of laser therapy or surgery.
Laser photocoagulation is widely used to treat angiomatosis. It is used if the tumor does not exceed one diameter of the optic nerve head. If it exceeds, then additional cryotherapy is used. With hypotonic and hypertensive angiomatosis, it is important to normalize blood pressure and lower the patient’s cholesterol level. A special diet is required for angioma caused by diabetes mellitus. You need to remove foods containing carbohydrates from your diet.
When an angioma is already in an advanced stage, it is difficult to restore vision back even with the help of surgery. Doctors' forecasts are bad: there is a chance of not only losing sight, but also losing life. Therefore, not only a person suffering from angioma, but also his relatives should be systematically examined by an ophthalmologist annually from the age of 5. You should not neglect your health and not treat this disease.
When a neoplasm consisting of blood vessels appears in the visual organs, retinal angioma develops. The disease is accompanied by decreased and distorted vision, and the appearance of plaques. At the first symptoms of visual discomfort, you need to consult a doctor who will conduct a diagnosis, prescribe medications, diet, and perform surgery.
Treatment is effective only in the early stages of the disease; in advanced cases, there is a risk of eye loss or death.
The disease is a congenital disease and is characterized by the appearance of a tumor, which consists of bundles of blood vessels. Most often, the disease manifests itself against the background of other systemic ailments. The main causes of retinal angioma are the following factors:
- increase or decrease in intracranial pressure;
- hypertension or hypotension;
- bad habits;
- impaired blood flow due to osteochondrosis;
- frequent stress;
- traumatic injury to the spinal column or skull.
Return to contents
The pathology has the following symptoms:
- the appearance of fog or a whitish veil before the eyes;
- flashes or lightning when looking at an object;
- significant decrease in vision;
- protrusion of the eyeball;
- persistent increase in intraocular pressure;
- change in fundus color;
- an increase in the size of the angioma relative to the optic nerve.
Return to contents
An ophthalmologist can identify retinal angioma. The doctor listens to complaints, examines the medical history for the presence of provoking factors and prescribes diagnostic procedures, such as:
- angiography using a contrast agent;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- ultrasound examination.
Return to contents
The treatment regimen is determined by the doctor; self-medication is prohibited. To treat retinal angiomatosis, the drugs shown in the table are used:
The following methods are used to treat retinal angioma:
- Laser photocoagulation. It is characterized by the effect on the tumor of laser beams that destroy the vascular tumor.
- Cryotherapy. During this procedure, cold is applied to the formation.
- Radiotherapy. During this procedure, the angioma is irradiated with ionizing radiation, which leads to its destruction.
- X-ray therapy. It is characterized by the use of X-rays, which causes destruction and death of the tumor.
- Diathermocoagulation. When performing this procedure, pathological angioma cells are cauterized with high-frequency current.
Return to contents
To restore the eyes, products containing vitamins A, B, C, E, P are recommended.
To improve the condition of angiomatosis, you should avoid alcohol, spicy, salty, fatty and fried foods. It is recommended to eat liver, egg yolk, apricots, buckwheat, rose hips, black currants, nuts, dairy products, herbs, fresh cucumbers, carrots, fish, onions, garlic.
Retinal capillary hemangioma, originally called retinal angiomatosis, is a benign vascular tumor of varying size located in the retina or along the edge of the optic nerve head.
Diagnosed before the 4th decade of life, it may be the first manifestation of von Hippel-Lindau disease, a familial tumor syndrome.
Capillary hemangioma can be hereditary or occur sporadically. This tumor occurs in 80% of patients with FGL syndrome and is often its first manifestation, diagnosed at an average age of 25 years. FGL syndrome occurs with an incidence of approximately 1:40,000 and appears to occur more frequently in Caucasian people. The syndrome is inherited in a dominant manner; one family may have different phenotypes. The average life expectancy for patients with FGL reaches 41 years.
Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome occurs as a result of a mutation in the VHL gene, a tumor suppressor gene located on chromosome Zp25. The functions of the FGL gene are unknown, but it is believed that it regulates the expression and function of hypoxia-responsive angiogenic factors (for example, vascular endothelial growth factor).
The neoplasm may be accompanied by exudation, accumulation of subretinal fluid and the formation of preretinal fibrosis.
Juxtapanillary capillary hemangioma. Orange-red in color, but with less clear boundaries, often without visible feeding vessels.
• Other tumors: cavernous retinal hemangioma, racemic hemangioma, choroidal melanoma and astrocytic hamartoma. • Vascular diseases: Coats disease, retinal arterial macroaneurysms, familial exudative vitreoretinopathy and exudative macular degeneration.
Modern methods of treatment
Depending on the growth rate of the tumor, its location and other nuances, the child may be prescribed either conservative or surgical treatment. Most often, when indicated, hemangioma is eliminated at the age of 1-3 years.
Surgical
During the operation, under general or local anesthesia, the tumor is partially or completely excised with a scalpel.
Such treatment is not carried out in the first month of life and is often prescribed when the hemangioma is rapidly enlarging or located in an unfavorable location. In this case, the operation should not disrupt the functioning of organs or cause a serious cosmetic defect.
Sclerosing
This treatment helps eliminate cavernous hemangioma. A substance is injected into the tumor, causing it to die due to “sealing” the vessels from the inside.
The disadvantage of this treatment is pain. In addition, sclerosis of large hemangiomas with a large number of vessels is a long process (it lasts 2-4 weeks).
Laser
The tumor is excised with a laser beam. The advantages of this type of coagulation are painlessness and the disappearance of the formation without a trace (no scars or other traces remain).
The disadvantages include the rather high cost and the need in some cases to repeat the procedure.
Radial
This treatment option is used for large flat hemangiomas and cavernous subcutaneous formations. Radiation therapy is also used to eliminate hemangiomas in the brain or eye area.
A child older than 6 months is irradiated several times, performing sessions with a pause of two weeks to six months.
Cryotherapy
Similar treatment is prescribed for small superficial hemangiomas that are not located on the face.
The tumor tissue is exposed to liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide. As a result, frostbite and swelling are caused, after which new skin begins to form at the site of the hemangioma, initially covered with a crust. Sometimes cryotherapy leaves a small scar.
For information on treatment methods for hemangioma, watch the video.
Electrocoagulation
Hemangioma tissue is destroyed by electric current. This treatment is prescribed for tumor diameters less than 3-5 mm. Electrocoagulation is also used in situations where the hemangioma has not been completely removed by other procedures (small parts remain).
Medication
Hormonal therapy using prednisone is used to treat large simple hemangiomas.
Injections are administered into the tissues of the formation according to a specially calculated scheme, supplemented by taking hormones in tablets. The tumor gradually turns pale and subsides, after which it disappears in 80% of cases. Propranolol is also used for drug therapy of hemangiomas.
Treatment
Hemangioma of the eyelid differs from tumors localized in other places in that it more often requires medical intervention. Vascular formations resolve spontaneously in half of children over 5 years of age. But the pathology of the eyelid has to be treated, since its rapid growth poses a danger to vision. In addition, the tumor interferes with the child and is often injured.
Taking into account the growth rate of the hemangioma and the possible risks, the doctor decides whether therapeutic procedures are sufficient or whether surgical intervention is required. It is unlikely to do without radical measures if the tumor has reached a large size and penetrated deep into the tissue.
Doctors have various methods of treating eyelid hemangioma in their arsenal:
- drug therapy;
- ligation of the vessel;
- electrocoagulation;
- sclerosis;
- laser or radiation therapy;
- cryodestruction;
- surgical intervention.
A positive result in treatment is achieved through the use of a set of measures. The doctor decides which methods are best to use in each specific case.
Drug therapy
Taking medications is recommended if a child has a large hemangioma of the eyelid. To treat it, glucocorticosteroids, interferons, propranolol, vincristine are used, which blocks cell division and stops tumor growth.
Ligation of the vessel
This method is used when the hemangioma begins to grow rapidly. Ligation of the vessel that feeds the tumor stops the flow of blood. Thanks to this, the size of the tumor is significantly reduced.
Electrocoagulation
The essence of the method is that the area of the hemangioma is injected with a current of the required strength. This method is used as an independent treatment or additional during surgery. The therapy is long-term, but after it there are no scars.
Sclerosis
To reduce the volume of the hemangioma, the formation itself and the surface around it are injected with ethyl alcohol, a solution of betamethasone or quinine. Injection of corticosteroids into the tumor is also practiced. The procedure requires anesthesia; for this, an anesthetic is first injected.
Laser treatment
Laser tumor removal has no age restrictions. The number of procedures required varies depending on the type and size of the tumor. After treatment there are no scars or crusts left.
Cryodestruction
The procedure involves freezing the hemangioma with liquid nitrogen.
For the treatment of neoplasms on the eyelid, it is used with caution, since small scars remain. The advantage of the method is that a small tumor can be removed in one session
Surgical intervention
In world practice, there is a tendency to refuse operations to remove hemangioma. This is due to the danger of using anesthesia in infants, a long period of rehabilitation and possible tumor relapses.
Surgery is resorted to in extreme cases when the tumor threatens the patient’s health. Hemangiomas can be removed from children no younger than six months old.
Treatment of retinal angiomatosis
Treatment is effective only in the early stages of the disease. The patient is prescribed medications that help strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation. "Trental", "Vazonite". "Calcium dobesilate" is prescribed to patients with fragile blood vessels. The medication thins the blood and normalizes vascular permeability. The doctor performs diathermocoagulation, x-rays and laser therapy. These procedures help to completely restore vision by destroying the antiomatous node and feeding vessels if the formations are small.
Getting rid of retinal angioma is possible only with the use of laser therapy or surgery.
Laser photocoagulation is widely used to treat angiomatosis. It is used if the tumor does not exceed one diameter of the optic nerve head. If it exceeds, then additional cryotherapy is used. With hypotonic and hypertensive angiomatosis, it is important to normalize blood pressure and lower the patient’s cholesterol level. A special diet is required for angioma caused by diabetes mellitus. You need to remove foods containing carbohydrates from your diet.
When an angioma is already in an advanced stage, it is difficult to restore vision back even with the help of surgery. Doctors' forecasts are bad: there is a chance of not only losing sight, but also losing life. Therefore, not only a person suffering from angioma, but also his relatives should be systematically examined by an ophthalmologist annually from the age of 5. You should not neglect your health and not treat this disease.
Symptoms
The formation of eye hemangioma occurs in stages. The initial stages are characterized by small tumor sizes; a slight swelling is observed in the lesion, in which a network of capillaries is clearly visible.
On this topic
Organs of vision
What symptoms can be used to recognize optic nerve glioma?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- September 3, 2020
When mechanical impact is applied to the location of the tumor, painful sensations appear.
Capillary and cavernous neoplasms have some differences between themselves:
- Cavernous form - characterized by the fact that the tumor protrudes above the skin level, the capillary network is clearly visible, and cavities filled with blood are also visible.
- Capillary form - characterized by the appearance of a dark red spot, which consists of thin, intertwined vessels.
In addition, there is an internal form of pathology - this is choroidal hemangioma. Rarely diagnosed in patients, it is a tumor process affecting the orbit of the eye. In the future, if left untreated, it leads to strabismus and vision impairment.
If large hemangiomas are observed, the doctor will prescribe an additional study, which is aimed at diagnosing cardiovascular diseases; also in such situations, a disease such as chondropathy of the upper or lower extremities is often associated.
What is Retinal Angiomatosis
Retinal angiomatosis (Hippsl-Lindau disease, retino-cerebellovisceral angiomatosis, phakomatosis). A rare systemic disease characterized by the development of multiple angiomatous and cystic formations in the retina, central nervous system, as well as in some internal organs and endocrine glands.
What causes retinal angiomatosis?
Congenital malformation of capillaries in different organs is important. Cystic formations originate from angioblastic tumors - capillary angiomas that arise as a result of anomalies in the development of the mesoderm, and are typical angiomas; Due to reactive changes, glial tissue grows. The disease is hereditary and is transmitted in a dominant manner.
Symptoms of Retinal Angiomatosis
Usually both eyes are affected. The process begins at a young age, between 10 and 30 years. The first visual disturbances are photopsia. Subsequently, there is a slow progressive decrease in visual acuity. In the fundus, a characteristic appearance of capillary angiomas is determined - vascular glomeruli, usually forming first at the periphery. The dilated and tortuous artery and vein go from the optic disc to the red spherical tumor and enter it. The size of the tumor is often 2-5 times the diameter of the optic nerve head.
Later, such glomeruli form centrally and even on the optic nerve head. They are varied in size, shape and color. The vessels of the retina are sharply dilated and tortuous, with aneurysmal dilatations. The terminal branches of vessels can form loops, networks, and anastomoses. Newly formed vessels appear in different parts of the fundus of the eye.
Under the vessels there are large lesions - yellow, bright white, matte. There are whitish-yellow plaques located in the form of a star around the macula. The macular area remains intact for a long time. In later stages, retinal detachment and hemorrhages are possible - sub- and supraretinal, as well as into the vitreous body. Sometimes secondary glaucoma develops. Changes in the optic nerve are in the nature of congestive discs or secondary atrophy. Neurological symptoms indicate intracranial hypertension and cerebellar-vestibular disorders. Cerebellar angioma with retinal angiomatosis is observed in 25% of patients.
Diagnosis of retinal angiomatosis
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture ; in the early stages it does not present any difficulties. The tumor becomes pale when pressure is applied to the eyeball. In an advanced stage, in the presence of complications, it is differentiated from Coats disease, which affects one eye.
Treatment of retinal angiomatosis
Treatment can be effective only in the early stages of the disease , with single tumors. Deep (subscleral) diathermocoagulation of the sclera, x-ray and radiotherapy, photo and laser coagulation are performed. It is necessary to achieve complete coagulation of the angioma and obliteration of the vessels feeding it. In advanced stages of the disease in the presence of complications (proliferating retinitis, retinal detachment, secondary absolute glaucoma), treatment is ineffective.
The prognosis is always serious regarding not only the organ of vision, but also the life of the patient. In an advanced stage, secondary changes can lead to complete loss of vision.
Diagnostics
If parents suspect such a formation, then they should show the baby to the doctor.
If a hemangioma is detected, it is necessary to show the newborn to a pediatrician or dermatologist. The doctor examines the affected area. To determine the extent and danger of a tumor, the following basic examinations are used:
- General blood analysis. Shows the state of the body and the hematopoietic system as a whole.
- Coagulogram is a study of blood clotting.
- Dermatoscopy is an examination of the tumor structure with a device that provides multiple magnification.
- Thermometry is the measurement of the temperature difference between healthy skin and the surface of the hemangioma.
- Thermography is the recording of thermal radiation from the skin, which determines the depth and boundaries of the tumor.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) is a study of the size, structure, size and depth of a neoplasm.
- Angiography - determination of blood circulation rate, size of hemangioma and spread to neighboring tissues using an injected contrast agent.
- Computed tomography (CT) is a cross-sectional scan of the affected area.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - detailed layer-by-layer visualization of the hemangioma and surrounding tissues.
- Biopsy is the removal of a sample of tumor tissue for microscopic examination.
- Histology - examination of the cells and structure of the tumor.
Treatment methods
If a hemangioma begins to form on the upper eyelid, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately. The tumor grows in size very quickly, and if it is not eliminated in a timely manner using conservative methods, the tumor will have to be removed surgically. Only in 2% of all cases the tumor goes away on its own.
Treatment of pathology includes three main methods:
- medicinal;
- surgical;
- physical.
The drug method has been applied to the treatment of hemangiomas relatively recently. Taking certain drugs reduces the growth of tumor formations and also contributes to their reverse development. But using this method alone is ineffective. With the help of medications, it is possible to get rid of a hemangiosal tumor only in 2% of cases.
Treatment should only be prescribed by the attending physician.
In order to reduce the growth of pathological formations, the following medications are used:
- Propranolol has a vasoconstrictor effect, activates the process of destruction of capillaries in the affected area and replaces them with scar tissue;
- Prednisolone is a hormonal drug that promotes tissue scarring and compression of capillaries, due to which blood circulation in them decreases, due to which the growth of hemangioma stops;
- Vincristine blocks the process of cell division, which leads to the cessation of tumor development.
Each of the listed drugs has side effects and contraindications, so the dosage and duration of therapy should be prescribed only by the attending physician.
Physical methods act directly on hemangioma tissue, destroy them and help eliminate tumor formation. The most popular methods in this group include:
- irradiation with laser beams;
- electrocoagulation;
- sclerosing therapy;
- X-ray therapy;
- treatment with drops if the internal tissues of the eye are affected.
The laser can remove tumor formations no larger than 2 cm. Tissues exposed to irradiation become charred and evaporate. A crust forms in the area where the treatment was carried out, which disappears after three weeks.
Hemangioma can be removed with a laser.
The electrocoagulation method is based on the action of high frequency electric current on problem areas. The current chars and destroys tissue, which subsequently heals itself.
Large hemangiomas are eliminated using sclerotherapy. The effect in this case is aimed at cauterizing the chemical elements that make up the hemangioma, leading to the destruction of capillaries and cavities. The procedure must be carried out more than once. In treatment, 70% alcohol is used, it is injected into the hemangioma.
The tumor can be exposed to X-rays; this method also leads to tissue destruction. Most often, this procedure is used during preparation for surgery to reduce the affected tissue in order to reduce the volume of the tumor being operated on.
Surgical intervention is used extremely rarely, only when the disease progresses rapidly and carries a risk of complications. This option is not suitable for newborns.
Consequences
An incorrect approach to the treatment of eyelid hemangioma or its absence leads to complications, some of which lead to a threat to human life. Serious complications include:
- destruction of tissues and nearby organs may be affected, including the choroid;
- addition of infection;
- transition to malignant formation;
- development of anemia.
If the disease was diagnosed in a timely manner, the treatment tactics were chosen correctly, the prognosis for a favorable outcome is high.
Hemangioma in most cases is a benign formation. The tumor is unpredictable: it can begin to actively develop, but it can also regress until it disappears completely. To get rid of the disease, you should consult a doctor in time and follow all his recommendations.
Aug 28, 2017Anastasia Tabalina
A child has a growing hemangioma - what to do?
As noted earlier, tumor growth in the first 6 to 12 months after appearance is the norm. Watchful waiting is not used if the hemangioma is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Excessive and prolonged growth. Parents can monitor this parameter themselves by periodically photographing the tumor and measuring its size. The indication for treatment is tumor growth after the child is two years old.
- Development of hemangioma on the eyelids, near physiological openings, in traumatic places.
- Formation of hemangioma on internal organs and bones. Such a tumor does not allow the child’s organs to develop normally.
- Large tumor sizes, creating a significant cosmetic defect.
Capillary hemangioma on the face requiring surgical treatment
Examination of the child
Hemangioma can quickly increase in size, so if this particular pathology is suspected, or if there is slight redness on the eyelid, a consultation with an ophthalmologist is prescribed. Only a specialist can determine the type of tumor and what to do with it in the future. There are other diseases with similar symptoms - vascular malformation, nevus, cyst.
Without an examination, treatment cannot be started, since some forms of pathology go away on their own and only require constant monitoring. For example, capillary hemangiomas disappear on their own without intervention. But in some cases, the tumor grows and interferes with the child; after the examination, it is removed, as a complication in the form of strabismus may arise. But when the pathology does not affect vision or interfere, it is usually not touched, and at a later age, at about 4–5 years, cosmetic surgery is performed.
The ophthalmologist will determine whether the hemangioma is located only on the eyelid or has spread deep into the orbit, or maybe it is located in the orbit. The location of pathological changes is clarified using echo and radiography of blood vessels, computed tomography.
Treatment of hemangiomas in children
First of all, a complete examination of the child is carried out, the purpose of which is to determine the type of tumor, its structure, size and potential dangers during its further development. For this purpose, a set of laboratory and instrumental studies is prescribed:
- A general blood test to check for a decrease in the level of platelets and hemoglobin in the blood circulating through the vessels of the tumor
- Ultrasound - to determine the type of hemangioma
- CT, MRI, thermography - to establish the true size of the hemangioma
- Angiography is a study using a contrast agent injected into the vessels, which determines the degree of involvement of tissues of other organs in the growth of hemangioma; used in complex cases when surgery is required, for example, on the bones of the skull.
Multiple liver hemangiomas (ultrasound)
Cavernous hemangioma of the left frontal lobe of the brain (MRI)
Based on the research results, the doctor chooses wait-and-see or surgical treatment tactics. In modern medicine, the following methods are used to combat hemangiomas in children:
- Cryodestruction is the freezing of a tumor with liquid nitrogen.
- Laser exposure - destruction of tumor vessels with a laser.
- Electrocoagulation is cauterization using electric current. Can be used for any type of superficial hemangioma.
- Sclerosis is the administration of injections with a special composition that clogs blood vessels.
- Radiation therapy is the removal of a tumor using targeted X-rays. It is used in the case of hemangiomas of internal organs, bones, or when it is impossible to use another method (for example, if the tumor is located in the orbit).
- The operation is an ineffective and traumatic method, in which the development of hemangiomas in neighboring areas is often observed. Used only in extreme cases.
- Drug therapy - treatment with drugs containing timolol, propranolol, hormones.
Causes
It is difficult to unambiguously determine the reasons that provoke the formation of hemangioma. Only certain factors are identified that cause such a disorder in the blood vessels.
On this topic
Organs of vision
How to get rid of wen on the eyelid
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- February 27, 2020
Most often, the following conditions contribute to the development of hemangiomas in young children:
- Diseases of the mother during pregnancy.
- Premature birth.
- "Late" pregnancy.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Development or exacerbation of a chronic form of the disease associated with the thyroid gland in the expectant mother.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions during pregnancy.
- Transferred viral pathology in the initial stages of pregnancy (immediately at the time when the circulatory system of the fetus is formed).
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- Hormonal disturbances during pregnancy.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Incompatibility of mother and child by Rh factor.
- Abuse of alcohol and tobacco products while pregnant.
The exclusion of all provoking factors can be considered preventive measures against the manifestation of pathology in the unborn child.
We must not forget that an adult is also not immune from the manifestation of the disease. In such phenomena, the provoking factor is often various eye injuries or thrombus formation processes.
Medical scientists put forward several theories describing the mechanisms of disease formation, but even this does not fully explain all aspects of the development of the disease.
Causes of pathology
It is difficult to name clear reasons for the occurrence of this disease. But there are grounds for creating favorable conditions for the development of such a blood vessel defect.
The culprits in the development of hemangioma may be:
- hormonal disorders in the body of the mother and fetus;
- hereditary predisposition;
- viral diseases during pregnancy, especially at 3–6 weeks, since at this time the child’s vascular system is formed;
- taking strong medications by the expectant mother;
- severe pregnancy, for example, the mother’s age is over 38 years, constant high blood pressure, carrying more than one child;
- low birth weight or prematurity;
- Rhesus – conflict between mother and fetus;
- bad habits of the mother (smoking, drinking alcohol).
Knowing the causes of this pathology, it is necessary to take preventive measures so that such diseases appear less frequently in newborns.
In children
A tumor on the eye of a newborn has the ability to grow quickly, which is why such children are under constant medical supervision. Even the smallest formations should be observed. Pediatricians believe that parents should remain calm in this situation. The main thing is to contact a doctor in a timely manner to eliminate the problem and possible complications.
In almost 90% of small children, the formation on the eye is not treated, since it has the ability to disappear with age, but not always.
According to statistics, education disappears between the ages of 5 and 9 years.
In a situation where rapid tumor growth is noted, it is necessary to begin emergency treatment, since in addition to a cosmetic defect, this can lead to loss of vision. Surgical intervention is performed as a last resort and only after the child reaches 4 months of age.
Hemangioma in a child: signs and causes
To correctly diagnose hemangioma, a combination of all characteristic signs is necessary:
- At first, the tumor develops quite quickly and increases in size, thanks to which it is possible to distinguish a hemangioma from, for example, a birthmark.
- Due to the large flow of blood in the vessels of the hemangioma, it is hotter than the surrounding tissue.
- When pressed, the tumor turns pale, and after cessation of exposure it quickly restores its original color.
Combined hemangioma in the breast area
Most often, hemangiomas are located:
- on the scalp (eyelids, cheeks, nose, scalp, back of the head)
- on the skin of the extremities (hands, soles of feet, buttocks)
- on the body (stomach, back)
- on mucous membranes (nasal passages, oral cavity, genitals)
- on internal organs (liver, spleen)
- on the organs of the musculoskeletal system (pelvic bones, skull).
Since in the vast majority of cases, hemangioma appears in a child from birth or in infancy up to one year, it is generally accepted that the main cause is abnormalities in the development of the vascular system in the embryonic period. At the same time, experts also note a dependence on the sex of the baby, since in 80% of cases hemangiomas occur in girls.
Multiple hemangiomas on the leg and body of a newborn
Other probable causes that increase the risk of developing hemangioma in children:
- viral diseases suffered during pregnancy
- heredity
- unfavorable environmental situation
- mature age of mother
- alcohol abuse, smoking
Causes
The number of newborns with congenital pathology is increasing every year. According to statistics, every 10th baby has at least one small tumor. Why do they appear?
Scientists cannot yet give a definite answer about the reasons for the appearance of neoplasms. Most experts agree that their formation is associated with viral-infectious diseases suffered during the period of intrauterine development. Underweight babies and premature babies are at greater risk of getting such a tumor. There are 4 times more cases of the disease in girls than in boys.
According to experts, hemangiomas are the body’s reaction to problems in intrauterine development
Also among the reasons are the following factors:
- mother's use of medications during pregnancy;
- viral diseases suffered by the mother in the 1st and 2nd trimester;
- development of diseases of the endocrine system or their exacerbation during pregnancy;
- poor ecology in the mother’s place of residence;
- diseases that prevent the birth of a full-term baby;
- multiple pregnancy;
- various types of pathologies (placenta previa, preeclampsia);
- mature age of the woman in labor (over 35 years).
Hemangioma can also appear in adolescence. What is this connected with? In most cases, there is a hormonal imbalance, as well as liver disease, against which a tumor subsequently develops.
The appearance of hemangioma in adolescence and adulthood is most often associated with changes in hormonal levels
In the first weeks, the newborn develops a small red spot that rises slightly above the skin. During the first three months, the tumor increases significantly in diameter. A characteristic sign is that when you press on the hemangioma, it turns pale, but then turns red again. This is due to the outflow of blood. In a crying or coughing child, the tumor becomes more saturated and larger, which is due to active blood flow.
Sometimes with hemangioma there is a difference in temperature between the formation and the tissues nearby, i.e. hemangioma is hotter. About 80% of all cases in infants end safely. They do not develop into malignant tumors and most often they regress on their own, i.e. disappear without a trace within 3-5 years. This outcome is most typical for simple hemangiomas that are small in size.
Depending on how the vessels in the hemangioma are built, there will be differences in the appearance of the tumor. You can see a photo of what each form looks like on the Internet:
- Capillary hemangioma. It looks and feels flat or lumpy. It is characterized by the presence of clear boundaries, as well as a reddish or bluish tint. You can distinguish the capillary shape by pressing: after pressing on the spot, it turns pale, after which it regains its previous color. It can be on the lips, on the nose, on the back of the head, on the fontanelle, on the butt, on the shoulder and on other parts of the body.
- Cavernous hemangioma. To the touch, the neoplasm has a soft surface, covered with bluish skin on top. This form of tumor increases in size when crying or coughing. When pressed, the swelling disappears and the skin becomes pale.
Cavernous hemangioma turns red and fills when the child is active
- Combined hemangioma includes the characteristics of the first two types.
- A mixed hemangioma will have a different appearance, depending on the type of tissue included in the tumor process.
- As bone hemangioma grows, it is characterized by bone pain associated with compression of nerve endings and blood vessels.
Causes of the disease
There are no reliable facts about the occurrence of eye hemangioma. In most cases, the disease affects children in the first weeks of life. However, eye hemangioma in an adult cannot be ruled out. Modern medicine has data on the conditions predisposing to the development of this type of illness. If a tumor on the eyelid appears in newborns immediately after birth, the source of the disease lies in the pathological processes that occur in a woman during pregnancy:
- problems with the endocrine system;
- late stages of pregnancy;
- premature birth;
- multiple pregnancy;
- unfavorable environment;
- a pregnant woman suffered a viral infection at a time when the fetus’s circulatory system was forming;
- bad habits: alcohol and smoking;
- a hereditary factor cannot be excluded;
- Rhesus conflict.
If the disease affects an adult, the cause may be eye injury or thrombus-forming processes.
Scientists have developed several theories to explain the mechanisms of the onset and development of the disease, but none of them completely covers all aspects of the development of the disease.
In most cases, hemangioma affects children in the first weeks of life.