Eye neoplasms – what are they?
The tissues of the visual apparatus are delicate and sensitive, they are vulnerable to many harmful environmental factors.
Radiation, poor ecology, burns, injuries, viral diseases - all this negatively affects eye health. The definition of “cancer” hides a variety of tumors of the organ of vision, each of which has its own name. The most common form is carcinoma. This is a malignant neoplasm, which consists of epithelial cells. Under a microscope, carcinomas resemble small crabs in appearance, which is why the second name for the disease is eye cancer.
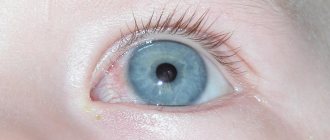
Tumors can appear in any structure of the visual apparatus, it all depends on the initial localization of mutagenic cells. In some cases, the progression of oncology is noticeable visually: when the iris, conjunctiva or meibomian gland is damaged.
Causes of eye cancer
It has not yet been determined why an eye tumor forms, but there are several risk factors:
- Heredity;
- Weakening of the body's protective barrier (especially with infections of viral origin);
- Poor environmental conditions;
- HIV infection;
- Formation of pigment spots on the surface of the visual apparatus;
- Light shade of the epidermis;
- Age over fifty years;
- Depression or nervous disorder;
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight on the eyes;
- Contact with chemicals.
Bad habits and intoxication of the body can also become a “stimulus” for the appearance of a tumor.
Causes
Factors that provoke the appearance of eye cancer:
- Hereditary predisposition (if close relatives have had cancer in a generation, then the likelihood of developing cancer increases).
- Influencing harmful substances (chemical substances play a role: salts of heavy metals, radionuclides, acids and others).
- Poor environment and poor quality food.
- Ultraviolet radiation (if a person does not protect his eyes from the sun in summer).
- Cancer of other organs in the body that “invades” unaffected tissues and organs.
- Reduced protective functions of the body and immunity.
- Chronic diseases.
- Nevi on the ocular surface and age spots.
- Diseases of endocrine origin.
- Bad habits: smoking, alcohol, drugs.
- HIV, AIDS, hepatitis B and C.
Types of eye cancer
All forms of visual oncology are divided into benign and malignant. In the early stages of the development of the disease, it is difficult to determine the type of neoplasm. To clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy is performed.
Benign eye tumors
They grow slowly, do not metastasize throughout the body and do not have a toxic effect. However, the risk of their transformation into malignant formations remains. This group includes:
- Papillomas. Small growths on the epidermis or conjunctiva of the eye;
- Nevi (moles);
- Hemangiomas. Vascular tumor of the skin of the eyelids and mucous membrane of the visual apparatus. It is a plexus of vessels of a rich red hue;
- Keratoacanthoma. A small neoplasm on the epidermis of the upper or lower eyelid with an internal crater;
- Fibroma. Soft tissue formation that does not have a capsule;
- Myoma. Affects the muscles of the iris;
- Teratoma. A rare form of congenital orbital tumor. Develops from the remains of germ cells, prone to rapid growth;
- Syringoadenoma. A neoplasm that forms on the sweat glands of the epidermis of the eyelids;
- Neuroma. Damage to nerve endings;
- Lipoma (fat). Oncology that appears only on the skin;
- Trichoepithelioma. Congenital papule from an immature hair follicle;
- Myxoma. Connective tissue tumor of the orbit, containing contents of mucous consistency. It is extremely rare.
Malignant neoplasms
They grow quickly, destroying nearby tissues and synthesizing harmful toxins. Together with the blood flow, they easily spread throughout the body and can give metastases (secondary foci).
These include:
- Melanoma. Develops from pigment cells responsible for the production of melanin. Doctors call the disease retinal cancer. The impetus for the development of the disease is sunburn. Most often diagnosed in women aged forty to seventy years;
- Retinoblastoma. Pediatric oncology is formed in the tissues of the visual apparatus from embryonic cells. May affect both eyes at the same time. In this case, the anomaly is hereditary;
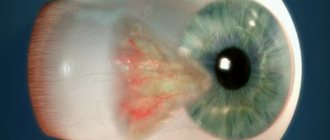
- Carcinoma. Corneal cancer;
- Cylinder. The tumor is in the orbit and is large;
- Sarcoma. Affects all tissues of the visual apparatus and can move from one layer to another. The disease is considered more aggressive than cancer.
Return to contents
Causes of pathology
The development of retinal cancer is in most cases hereditary. It is based on a mutation at the gene level. The RB1 protein prevents cells from dividing excessively, but at some point it becomes inactive. Subsequently, the defective gene is passed on from generation to generation, which is the cause of the development of retinoblastoma.
Most cases of bilateral eye cancer are hereditary. The diagnosis is made before the age of 2.5 years, and the presence of the mutated gene is confirmed in 90% of cases. The first symptoms of the disease can be noticed already in the first year of a child’s life. A congenital tumor can lead to the development of glaucoma.
There is a sporadic (non-hereditary) form of retinoblastoma, which occurs due to random glitches in the gene program and mutations. It is detected in adolescence. Provoking factors are the late age of parents, their employment in hazardous industries, and unfavorable ecology. This pathology of the retina is unilateral and develops locally.
In adults, cancer of this form is extremely rare, and its causes remain unidentified.
Classification
Neoplasms affecting the visual apparatus are divided into several forms, depending on the location of the damage.
Tumors inside the orbit of the eyeball
Pathology can cause the following deviations:
- Strabismus. The visual axis is deviated from the direction of the object in question, which disrupts the coordinated functionality of the eyes and causes problems with fixation on the object;
- Exophthalmos. Bulging of the organ of vision resulting from the displacement of the eyeball forward;
- Diplopia. Split image;
- Limited movement of the eyeball.
Introocular tumors
Such neoplasms penetrating into the vitreous cavity cause detachment of the retina and are accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity. Patients also complain about the appearance of defects in the optical fields, loss of visible zones and the formation of “blind spots”.
Neoplasms of the conjunctiva
Oncology affecting the mucous membrane is divided into two types:
- Benign. These include papillomas, nevi and dermoids. Typically, removal of such tumors is carried out for cosmetic purposes. However, if the risk of malignancy remains, the formations are completely removed;
- Malignant. This category includes melanoma (dense black nodules), intraepithelial neoplasia (papillary growth of a pink shade), Capos sarcoma. The latter form of the anomaly is a slow-growing tumor often diagnosed in patients with AIDS. It appears as flat lesions of bright red color.
Iris neoplasms
Characteristic manifestations:
- Nevus. A pigmented tumor, in the area of which there is a deformation of the pupillary edge, eversion of the choroid, or a node with a diameter of up to three millimeters, located in the lower part of the iris;
- Deformation of the pupil, characterized by eversion of the choroid and clouding of the lens;
- Xanthogranuloma in the form of a pedunculated papule, prone to regression.
Tumors of the ciliary body
The neoplasm is small in size. It is detected during ophthalmoscopy. Characterized by wide “sentinel” episcleral vessels. In this case, detachment of the retina often occurs.
Tumors of the eyeball located inside the orbit
Provoke:
- Development of strabismus;
- Limited movement of the eyeball;
- Protrusion of the organ of vision;
- Double image (diplopia).
Return to contents
Choroidal tumors
Varieties:
- Nevus. Develops without symptoms. It can be detected during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist. It has a round or oval shape, blurry contours. It reaches up to five millimeters in diameter;
- Melanoma. Dome-shaped prominence in the vitreous region. Characterized by visual field defects;
- Choroidal hemengiomas. It is formed from channels of different sizes. Accompanied by blurred vision, scotoma formation;
- Melanoma. Rapidly developing pigmented neoplasm. More often diagnosed in women with dark skin. It is a brown tumor in the eye with foamy edges;
- Bone choristoma. Slow-growing neoplasm. It is colored yellow-orange and has clear, curved edges. May be accompanied by loss of vision.
Formations located on the retina
The following forms fall into this category:
- Astrocytoma. It does not pose a threat to vision as it is a benign tumor. Has a yellow tint and does not require therapy;
- Hemangioblastoma. Cancer of the retina, which can lead to blindness. It is a rounded formation of red-orange color;
- Hemangioma. In appearance it resembles bunches of grapes accumulated on the periphery of saccular aneurysms;
- Lymphoma. Consists of large B lymphocytes with large multilobed nuclei.
Structure of the eye
- The sclera is the opaque outer layer of the eyeball.
- The choroid is a layer that is located between the two membranes of the eye: it covers the posterior part of the sclera, on the other side the retina is adjacent. There are no nerve endings in the choroid, which is why when it is diseased there is no pain, which causes the late detection of pathological processes in it.
- The retina is the light-sensitive membrane of the eye, which consists of nerve and photoreceptor cells.
- The optic nerve is one of the most important structures of the visual analyzer, since it helps transmit signals from nerve endings to the brain.
About 50 years ago, a new independent clinical direction was identified in ophthalmology, the main function of which is to resolve issues of diagnosis and treatment of eye tumors - ophthalmo-oncology. Tumors of this localization are distinguished by a unique clinical and biological course, as well as large polymorphism. Diagnosis of eye tumors is difficult; to carry it out, it is necessary to carry out a set of instrumental research methods; these studies are carried out by ophthalmologists. In addition, knowledge and skills in applying diagnostic measures that are used in general oncology are required. Significant difficulties in the treatment of tumors of the eyeball and its adnexa arise due to the fact that anatomical structures that are of great importance for visual function are concentrated in small volumes of the orbit and eye - this greatly complicates the treatment while preserving visual functions.
The incidence of tumors of the organs of vision (according to patients) every year is about 110 per 1 million population. In children, the annual incidence is 10-12% of the incidence rate in the adult population.
Symptoms of the appearance of ocular tumors
In oncology, the first signs make themselves felt only after the tumor reaches a decent size. In the early stages of development of the pathology, no manifestations are noted. However, a number of signs should alert you and serve as a “push” to undergo an examination at the clinic:
- Decrease in visual acuity;
- The appearance of a spot on the iris;
- Displacement of the eyeball;
- The appearance of flies and “blind spots” in optical fields;
- Development of strabismus;
- Formation of growth on the eyelid;
- Limited mobility of the visual apparatus;
- Detachment of the retina, accompanied by severe pain;
- The appearance of a white film on the cornea.
Of course, such symptoms do not always signal the development of cancer, but they definitely should not be ignored. Return to contents
Symptoms
Different types of eye tumors manifest themselves differently. During a preliminary examination, the first signs you can notice are changes in the eyelids and outer membrane.
Symptoms also vary depending on the location, size of the tumor, stage of development and degree of vascular damage.
In the first stages of development, no symptoms are observed. Gradually, as the tumor grows, vision deteriorates, pain in the area of the visual organ bothers, and bleeding appears. Upon detailed examination, retinal detachment is observed.
Conjunctiva
Affects the outer shell. It is characterized by rapid growth and externally resembles a white growth or a cloudy tuft. The patient experiences pain and the ability to see deteriorates.
Neoplasms on the eyelids
There is thickening of the eyelids and the appearance of growths similar to warts. Accompanied by excruciating pain and lacrimation, vision is impaired. In severe cases, when the tissue is eaten away by ulcers, the eyeball becomes displaced.
On the choroid of the eye
The main symptom of choroidal pathology is decreased visual acuity, possibly the appearance of dots before the eyes. In the early stages, signs are difficult to identify. Gradually, the tumor can lead to strabismus or secondary glaucoma.
On the eye sockets
The bones around the eyeball are affected, the eyes widen and the retina detaches. Eyelid hyperemia and diplopia are observed.
General signs
Both children and adults experience symptoms characteristic of all types: blurred vision, swelling of the upper and lower eyelids, the presence of cloudy growths or film, pain, tearing, unexpected external changes. In advanced stages - bulging or shifting of the eyeballs, spread of cancer to nearby cells. Intoxication of the body causes nausea, elevated body temperature, weakness, and migraines.
Symptoms of eye cancer
Eye tumors have a number of symptoms that are regarded as potentially developing into cancer. This:
- vision decreases
- spots appear on the iris of the eye
- blurred visions, spots, light flashes appear in the eye
- the eyeball is clearly moving
- squint appears
- Severe pain appears in the eye or area around it
- growths and thickenings form on the eyelid
- with tumors of the conjunctiva, pronounced nodules appear; a dense whitish film with a bright vascular pattern is also possible
- if a tumor appears in the lacrimal gland, then pain and profuse lacrimation begin
- With retinoblastoma, photophobia and possibly severe strabismus are manifested.
The appearance of each of the above symptoms is a reason to contact a specialist, preferably an oncologist.
Symptoms
Each type of eye cancer develops differently and is characterized by different symptoms. What signs can be seen during visual inspection? If a cancerous tumor has formed externally, it is easy to identify. The following picture is observed: swollen eyelids, pigmentation at the location of the tumor and discomfort in the eye. Also, the first symptoms may be swelling, decreased vision, pain, and squint.
Important! It is necessary to pay attention to the mobility of the neoplasm: the main difference between eye cancer and chalazia or barley is spread into adjacent tissues. The cancerous tumor is motionless under the skin, does not have a capsule, and its borders are not felt.
For neoplasms on the eyelids, the symptoms depend on the type of tumor. Epithelial tumors form in the inner corner of the eyeball and in the lower eyelid area. As cancer develops, it grows onto the cartilage of the lower eyelid and further onto adjacent tissues. Squamous cell formation develops more rapidly and involves the lymph nodes in the process. Basal cell carcinoma of the lower eyelid (basal cell carcinoma) appears as a small nodule the color of healthy skin with a small depression in the middle. The edges of the nodule may be pearlescent. Symptoms do not appear in the early stages.
With sarcoma, which is localized in the eye orbit, exophthalmos (protrusion of the eye) develops in a short time, and pain is felt when the eyeball moves. The main symptom of sarcoma is swelling and increased eye pressure; in many cases, the affected eye ceases to see. With fibrosarcoma, a bluish nodule with pronounced vessels appears under the skin on the upper eyelid. Further development of the tumor leads to drooping of the eyelid (ptosis) and displacement of the eye.
With carcinoma (squamous and basal cell), seals appear on the eyelid in the shape of a small pea or lump. In an advanced stage, it can spread not only to the eyes, but also to grow into the sinuses between the nose and on the surface of the cheeks. A fairly common type, it occurs most often in elderly patients.
With adenocarcinoma of the sebaceous glands, a yellowish thickening forms. As the tumor grows, it pulls the eyelid into the conjunctiva, on the surface of which dirty pink growths appear. The tumor grows aggressively and forms metastases. In the last stage, ulcers appear that almost destroy the eyelid, and the eye often becomes displaced.
In melanoma, malignant cells affect the iris, choroid, or ciliary body. Vision gradually deteriorates, the shape of the pupil changes, black spots appear on the iris or in the patient’s field of vision. Metastases actively spread and spread to other organs. In some cases, secondary glaucoma may develop. A common type of eye cancer, symptoms appear in late stages.
With cancer in the conjunctival area, a rapidly growing dense whitish film of a pterygoid (vascular) or papillomatous form is formed, and swelling of the eyelid is often observed. One of the neoplasms of the conjunctiva is Kaposi's sarcoma. Forms in the form of flat-red foci of inflammation in the corner of the eye.
With a malignant neoplasm in the area of the lacrimal gland, the following symptoms are observed: red lumps in the inner corner of the eye, swollen eyelid, unpleasant and painful sensations in the area of the eye orbit, the eye loses mobility, displacement of the eyeball.
With retinoblastoma, there are four stages of the disease:
- The first is a neoplasm at rest and is difficult to detect. The main feature is the white pupil (“cat’s eyes”). This can cause loss of central and side vision, which is the cause of strabismus. The eyeball may become red, vision decreases;
- second – glaucoma has developed, the manifestations of which are constant tearing, painful perception of light, inflammation in the area of the iris, increased eye pressure;
- third - the main symptom is exophthalmos - displacement or protrusion of the eyeballs (“cancerous eyes”), metastases appear in adjacent tissues;
- the fourth is the most severe, metastases develop to distant organs. Severe pain in the head, intoxication and loss of strength are observed.
Eye cancer in children
The most common form of cancer in children. Every year, the disease is diagnosed in three hundred children in America. In Russia, the anomaly affects even more young patients - about five hundred people. If a tumor is detected at an early stage, it responds well to therapy. In 90% of all children, it is possible to completely restore visual function and get rid of cancer.
Retinoblastoma affects not only the retina, but also the nervous matter located in the posterior part of the eyeball. The anomaly may be congenital or acquired. In most cases, oncology is detected in children over the age of one year. The main manifestation of retinoblastoma is the formation of a light spot in the center of the pupil, surrounded by a dark halo of the iris.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Decrease in visual acuity;
- Progressive strabismus;
- Light spot in the center of the eye;
- An abnormality of the iris, which in appearance becomes similar to a cat's eyes.
However, a similar clinical picture is also typical for other diseases, so you should not immediately panic and make a premature diagnosis. The final verdict must be made by the doctor after the examination.
For more information about retinoblastoma, watch the video.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment regimens for the visual organs in children should be as gentle as possible, with surgical intervention being the last resort. Can also be used:
- Chemotherapy with intramuscular, intravenous and intra-arterial administration of substances that suppress retinoblastoma.
- Radiation therapy.
- Brachytherapy, in which a radioactive substance is placed into the tumor, thereby avoiding damage to nearby healthy tissue.
- Cryotherapy involves freezing malignant cells with liquid nitrogen.
- When photocoagulation is used, a laser forms blood clots in the vessels, cutting off the nutrition of cancer cells.
- In especially severe cases, in order to avoid the spread of metastases, enucleation is used, which involves the complete removal of the eyeball by surgery.
Other alternative techniques may also be used. At the same time, when choosing the main method, specialists take into account the characteristics of the lesions:
- Unilateral or bilateral formation of a cancerous tumor.
- Visual acuity in children.
- The extent to which cancer cells have spread to the optic nerve.
- Growth of the tumor into the orbit of the eye, into the nervous system, development of distant metastases.
Endophytic retinoblastoma
With endophytic retinoblastoma, the inner layer of the retina, the substance of the vitreous body, is affected. The surface of the tumor is usually lumpy, whitish-yellow, and not translucent. In the vitreous next to the retinoblastoma, conglomerates of malignant cells are formed, represented by stearin drops or tracks. With the rapid growth of the tumor, metabolic processes are disrupted, which leads to the formation of necrosis, curdled decomposition, and calcifications. If the opus is located in the preequatorial zone, malignant cells can settle in the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye. In this case, a picture of a pseudohypopyon is formed, which has a whitish-gray color from a true hypopyon. Quite early, an inversion of the pigment border of the pupil occurs, and massive synechiae, tumor nodules and pathological vessels form on the surface of the iris.
The fluid in the anterior chamber of the eye becomes cloudy, and it itself becomes smaller. Gradually, the tumor fills the entire volume of the eyeball, destroying the trabecular apparatus and other structures. This leads to an increase in intraocular pressure. Young children may develop buphthalmos, which results in thinning of the sclerolimbal area. Due to this, the tumor grows into structures adjacent to the eye. When the posterior sclera of the eye is damaged, symptoms of cellulite occur, which is observed in 0.2-4.6% of cases.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is sent to undergo a thorough examination, which includes a number of procedures:
- Ultrasound. Carried out to analyze the structure of the visual apparatus;
- Ophthalmoscopy. Examination of the eye using bright light or a special lens;
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography;
- Drawing blood to check white blood cell levels;
- Biopsy. Analysis of a sample taken from the affected area;
- Fluorescein angiography (photograph of the organ of vision).
If, after diagnosis, the doctor confirms the initial diagnosis, then immediate therapy is required.
Treatment methods
There are several ways to combat cancer. An individual course of therapy is prepared for each patient depending on the type of tumor.
Laser surgery
Modern equipment is used to carry out the intervention. The impact is only on the damaged area, while healthy tissue remains untouched. This treatment method is considered expensive because it is carried out by high-level specialists and requires innovative equipment.
Eye surgery
During surgery, part of the eyeball can be removed or the damaged element can be completely removed. Such radical measures are used in severe forms of the disease, when other methods have no effect. After the eye is removed, the patient is given an implant.
However, there are also gentle types of surgery that involve removing only cancer cells, while leaving the organ of vision in place. Depending on the complexity, such intervention is divided into several types:
- Microsurgery (excision of tumor);
- Laser correction (the tumor is removed using a modern device);
- Radio wave (cancer cells are evaporated, there is no contact with the eye).
| These techniques help not only to preserve vision, but also to avoid eye removal. The effect is applied directly to the affected area, while healthy tissue is not affected. The main disadvantage of such operations is the high cost. |
Return to contents
Radiation therapy
There are two varieties: internal and external.
- In the first case, local anesthesia is used. The essence of the procedure is to install a radioactive board. A few days after the operation it is removed. The second name of the technique is brachytherapy;
- With external therapy, the damaged area is exposed to radioactive pulses.
Typically, this type of treatment is practiced for melanoma. This technique can lead to the development of cataracts and glaucoma.
Chemotherapy
Medicines are taken in tablet form or injected into the spinal cord. Medicines can also be injected into the organ of vision or intravenously. The maximum effect of the technique is observed in the treatment of retinoblastoma and lymphoma.
Chemotherapy has several unpleasant side effects. Patients complain of constant nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, increased hair loss and poor health. The body’s protective barrier also significantly weakens, and accordingly, the risk of contracting an infectious disease increases.
Stereotactic radiosurgery
In addition to the classical options for treating a tumor, the following methods are practiced:
- Laser infrared radiation;
- Burning using a laser system;
- Impact of low temperatures on neoplasms.
Stereotactic radiosurgery uses a special metal frame that radiates energy to the damaged area. The device is installed using screws that are attached to the cranial bones. It is important to set the correct direction of radiation so that the flows fall directly on the tumor.
The technique is accompanied by pain, so before the intervention the patient is given anesthetics. However, medicine does not stand still and devices have already appeared that do not require mounting on the head.
Enucleation of the eye
The essence of the operation is to remove the damaged organ of vision. Intervention is carried out not only for benign, but also for malignant formations. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
The palpebral fissure is fixed using an eyelid speculum to eliminate the risk of blinking during the enucleation process. The mucous membrane and Tenon's capsule are cut off from the sclera along the entire circumference. The end of the muscle hook is inserted under the rectus tendon and cut off from the protein membrane. The external muscle is not crossed at the sclera, but stepping back a little from it so that a small piece remains, the eyeball is fixed on it using tweezers.
The eye is pulled forward and Cooper scissors of a curved shape, equipped with closed jaws, are inserted into the wound. Using an instrument, the doctor feels for the optic nerve and crosses it. Then the eye is removed from the orbit.
The operation is accompanied by bleeding, which I block with a cotton swab dipped in hydrogen peroxide. Three sutures are placed on the wound, a 30% sulfacyl solution is instilled and a pressure bandage is secured. Return to contents
Brachytherapy for intraocular tumors
A neoplasm in the visual apparatus is sometimes a consequence of the spread of metastases from other organs. However, eye cancer can also develop as an independent pathology. Most often it is melanoma or retinoblastoma. The second form is usually diagnosed in children, the first in patients over sixty years of age.
One of the modern methods of fighting cancer is brachytherapy. Radioactive boards are installed in the visual apparatus, which act on the tumor from the inside. The procedure helps reduce the size of the tumor. Most often, cancer occurs without symptoms and is detected during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist.
Brachytherapy is carried out in two stages:
- Radioactive circuit boards are implanted into the visual apparatus. The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia;
- The next step of therapy is the extraction of established elements. The boards are removed a few days after the operation. The duration of the element's presence in the eyes is determined by the doctor, depending on the size of the neoplasm and the nature of the course of the disease.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital, and the patient is under the supervision of a doctor throughout the entire period.
Brachytherapy can cause a number of complications:
- Redness of the eyes;
- Infectious pathologies inside the organ of vision;
- Detachment of the retina;
- Increased intraocular pressure;
- Partial or complete loss of vision.
Complications occur in rare cases. The operation makes it possible to save the eye and stop the development of the tumor at an early stage.
Alternative Treatments
When fighting cancer, it is additionally recommended to relieve stress, meditate, and take infusions of medicinal herbs. After chemotherapy, it is worth taking a course of acupuncture. Some methods are absolutely safe and help to significantly improve the patient’s well-being.
| However, the use of any alternative technique must be agreed with the attending physician. |
Signs of pathology development
Depending on the stage of the pathology, its symptoms are also distinguished. If cancer forms in the retina of the visual organ, the following signs may be observed:
- The initial stage is called the “resting stage.” Its earliest symptom, noticeable upon examination, is leukocoria, or “cat's eye.” Reflecting bright light, the affected pupil produces a light – white or yellow – glare instead of red. Strabismus may also appear in the initial stages.
- In the second stage, glaucoma develops, the symptoms of which include lacrimation, photophobia, inflammation in the iris, pain, high eye pressure and impaired fluid outflow. Quite often in children, primary glaucoma transforms into secondary.
- At the third stage, the main symptom becomes exophthalmos - forward displacement of the eyeball - which indicates metastasis of the tumor to the eye orbits and the brain. Children experience general weakness, lack of appetite, and vomiting.
- At the fourth stage, metastases penetrate the liver, bones, brain, a sharp deterioration in the condition is observed, symptoms include headaches and intoxication of the body.
It should be remembered that similar symptoms are also inherent in other eye pathologies, therefore the first step when one or more signs occur is to contact a specialist. Retinal neoplasms can be either malignant or benign. The danger of benign tumors is that, without disturbing the carrier for a certain time, they can degenerate into cancer cells.
If you have melanoma, symptoms include:
- loss of clarity when perceiving visual information;
- change in iris color;
- dark areas on the aperture;
- pain, redness of the eye;
- lack of lateral vision;
- convexity of the visual organ and others.
At the very beginning of the development of pathology, thickening of the retina may be observed, but such symptoms are noticeable only when examining the fundus of the eye and undergoing an ultrasound. With further growth of the tumor, complete loss of vision is possible.
How long do you live with eye cancer?
In the case of cancer, it is difficult to make such predictions. The answer largely depends on the shape of the tumor and the stage at which the disease is detected. Equally important is what structures of the visual apparatus are affected by the pathology.
According to statistics, when a small tumor is detected at the initial stage, the survival rate is 85%. If oncology is detected at an average level, then the rate drops to 64%. When the tumor is diagnosed at the last stage, the success rate of treatment is 47%.
Complications and prognosis
The likelihood of successful treatment and a positive prognosis for complete recovery from tumor formations on the eye largely depend on the stage and type of disease. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chance of beating cancer without further health consequences.
In melanoma of the lower eyelid, the thickness of the tumor affects the prognosis. The five-year survival rate for tumors up to 0.80 mm is almost 100%. If the nodes reach a thickness of 1.50 mm, only every second patient survives the disease.
A neoplasm of the choroid of the eye in most cases has a favorable prognosis for recovery. An enlarged tumor is characterized as a precancerous condition. Complications include possible vision loss.
On this topic
- Organs of vision
What are the dangers of eye hemangioma?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- August 25, 2020
With a successful course of treatment for a tumor on the eyeball in the early stages, there remains a high risk of relapse over the next five years. Damage to the anatomical structures of the body by metastases leads to death in a short time.
Tumors of the lacrimal glands are characterized by slow growth of secondary lesions. The lungs and spinal cord are usually affected. The survival prognosis for 3-5 years after diagnosis is no more than 50%. The cause of death is metastases to distant organs and the cranial cavity.
With timely treatment of hemangioma, it is possible to achieve complete elimination of the tumor without external defects.
In general, with early diagnosis of an eye tumor, a positive result is achieved in 90% of registered cases.
Treatment
Often, the treatment of tumor diseases of the visual organs is complex, and the choice of optimal methods depends on the type of pathology and the stage of its development.
In modern medicine, laser evaporation, radiosurgery using automatic systems, freezing cells using liquid nitrogen, and chemotherapy are used to remove tumors in the eyes.
Due to the large number of nerve endings and blood vessels in the eye, any of the removal methods can be dangerous to the patient’s health.
On this topic
- Organs of vision
6 effective methods for treating cysts on the eyelid
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- August 25, 2020
In the later stages of the disease, doctors may resort to surgery.
After removal of the tumor, the patient is prescribed antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
In cases of timely seeking medical help when an eye tumor develops, it is often possible to get rid of the problem using minimally invasive and safe methods.
Prevention and prognosis of retinoblastoma
The best way to prevent the disease is to conduct DNA diagnostics at the stage of pregnancy planning. If a mutation in the RB1 gene is detected, IVF should be used.
Preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist in the first years of a child’s life will help identify the disease at an early stage. A child's eyes should be monitored more closely if a family member is known to have the mutated gene.
If the disease is detected early, the prognosis is favorable. Even when cancer is detected in late stages, remission is achieved in 47% of patients. Modern methods practically eliminate death that occurs due to extensive metastases. In most cases, it is possible to save the eye and vision of a small patient, which contributes to his further harmonious and versatile development.