When to see a doctor
As soon as the first signs of adrenal cancer appear, you should consult a doctor. This is what the oncologist does. You can find qualified and experienced specialists at JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic), which is located near the Mayakovskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Belorusskaya, Tverskaya, and Chekhovskaya metro stations.
Classification of tumors
All tumors of the subcortical type are divided into neoplasms of the medulla and tumors of the cortical layer. In addition, cancer can be primary (in turn divided into active and inactive cancer) and secondary.
The following forms are distinguished: corticosteroma, androsteroma, aldosteroma, corticoandrosteroma, pheochromacytoma, neuroblastoma, carcinoma. Adrenocortical adrenal cancer is a malignant tumor that originates from the cortex. Adrenocortical adrenal cancer is also known as corticoblastoma.
Risk factors
The following factors are distinguished:
- unbalanced diet with high consumption of carcinogenic substances;
- abuse of smoking, alcoholic beverages and other toxic substances;
- lack of physical activity;
- frequent stress, overwork, including emotional;
- living in a polluted environment;
- long-term use of medications without doctor's permission;
- congenital pathologies in the production of hormones in the adrenal glands.
Due to these factors, a tumor may appear and signs of adrenal cancer may develop.
Stages of disease development
Symptoms of adrenal cancer vary depending on the stage:
- first. The tumor will be up to 50 mm;
- second. The tumor is more than 50 mm, there is no invasion;
- third. Neoplasms have different sizes and local invasion, but do not grow into nearby organs;
- fourth. Tumors of different sizes are located on different organs.
The treatment methods used at JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) in the Central Administrative District depend on the degree of development of the oncological disease.
Risk factors for adrenal cancer
Age. Cancer is most often detected in children and people aged 40-50 years.
Morbidity in the family. Most cases of adrenal cancer are not associated with heredity. Li-Fraumeni syndrome is a rare inherited condition that causes a significantly increased risk of developing breast, prostate, leukemia, bone and adrenal cancers.
Multiple endocrine tumors (MEN-1) is an inherited condition that results in a high risk of tumors in three glands—the pituitary gland, parathyroid glands, and pancreas. In 1/3 of such patients, cancer of the adrenal cortex may also develop, which is usually asymptomatic.
Lifestyle and known environmental risk factors significantly influence the incidence of many forms of cancer, but do not influence the occurrence of adrenal cancer.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of adrenal cancer appear in women or men, it is necessary to urgently undergo diagnosis at the first suspicion. This can be done at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) in Moscow.
The following studies are being carried out:
- chest x-ray. Helps find metastases in the lungs and other organs;
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This technique is especially recommended if there is a suspicion of metastases in the spinal cord or brain;
- ultrasound diagnostics. Allows you to identify a tumor and the presence of metastases;
- CT. Makes it possible to visualize adrenal cancer;
- blood and urine tests. Makes it possible to determine hormone levels.
All these techniques allow you to accurately make a diagnosis.
Symptoms of adrenal cancer
Signs of adrenal cancer are nonspecific and specific. The former indicate the development of cancer in general or can be mistakenly interpreted as symptoms of another disease. The latter clearly indicate the type of neoplasm.
Nonspecific symptoms are high blood pressure, hypertensive crises, frequent urination, loosening of bones (osteoporosis), cramps, muscle weakness, dizziness, fainting, loss of appetite or obesity, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, dry throat, dry tongue, neurotic disorders (neurosis, depression), psychopathy, paralysis.
At a late stage, a malignant tumor of the adrenal gland begins to put pressure on neighboring organs, which is manifested by pain in the kidney area and heaviness in the abdomen.
Specific symptoms of adrenal cancer in men and women are associated with hormonal imbalance.
- Symptoms of corticosteroma.
This type of tumor causes excessive synthesis of cortisol, which is manifested by a symptom complex known as Itsenko-Cushing syndrome.
Its symptoms are obesity and weight gain, plump cheeks, a red, moon-shaped face, the formation of a fatty hump below the back of the head, swelling of the upper body with thinning arms and legs, the appearance of many bruises (due to the fragility and fragility of blood vessels), muscle weakness, thinning skin.
Psycho-emotional symptoms of corticosteroma are tearfulness, sudden mood swings (emotional lability), panic attacks (attacks of fear), depression, psychosis.
Corticosteroma is characterized by increased fatigue, lethargy, headaches, blurred vision, and high blood pressure (hypertension).
In children, corticosteroma is manifested by accelerated puberty, and in adults by early decline in sexual function. In men, signs of feminization appear - female-type breast enlargement (gynecomastia), decreased potency, testicular hypoplasia.
In women, corticosteroma causes male-pattern hair growth, deepening and deepening of the voice, growth and enlargement of the clitoris.
Complications of this type of cancer are often urolithiasis, pathological fractures (due to osteoporosis), and pyelonephritis.
- Symptoms of androsteroma.
The development of androsteroma causes early puberty in boys and pseudohermaphroditism in girls, and in women 20-40 years old - symptoms of virilization (development of secondary male sexual characteristics). The development of the tumor is accompanied by increased production of androgens (testosterone, androstenedione, etc.).
Adrenal cancer in women is manifested by male-pattern hair growth on the face and chest (mustache, beard), cessation of menstruation, deepening of the voice, shrinkage of the mammary glands, hypotrophy of the uterus, enlargement of the clitoris, reduction of subcutaneous fat with increased libido.
In a child, the disease manifests itself as accelerated sexual development, rapid growth of muscle mass, deepening of the voice, and the appearance of acne on the face.
- Symptoms of pheochromocytoma.
Signs of pheochromocytoma are hyperhidrosis (sweating), high blood pressure, shortness of breath, headaches, tachycardia (rapid heart rate), pale skin.
Hypertensive crises are accompanied by dizziness, chest pain, trembling, profuse sweating, panic, fever, and headache.
- Symptoms of neuroblastoma.
Signs of neuroblastoma are bulging eyes with the formation of dark circles under the eyes, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, intense bone pain.
- Symptoms of corticoesteroma.
The development of this type of malignant tumor is manifested by muscle weakness, paralysis of the arms or legs, convulsions, high blood pressure, and malaise.
In girls, corticoesteroma is manifested by accelerated sexual development - the growth of mammary glands, pubic hair, and enlargement of the labia.
In boys, on the contrary, it manifests itself as delayed sexual development, and adrenal cancer in men - feminization: atrophy of the penis and testicles, squeaky voice, enlarged mammary glands (gynecomastia), lack of hair on the face and chest, impotence, rounding of the hips and increased fatty tissue according to the female type.
- Symptoms of aldosteroma.
The signs of this tumor are associated with an imbalance of aldosterone, a hormone that regulates mineral-salt metabolism. It is manifested by seizures, increased blood pressure (hypertension), muscle weakness, headache, shortness of breath, bleeding in the fundus of the eye, constant thirst, frequent urination or urination at night (nocturia).
Exacerbations of symptoms have the nature of crises with intense headache, vomiting, loss of vision, and flaccid paralysis. Complications of such conditions may include acute coronary insufficiency and stroke.
In general, the symptoms of adrenal cancer in men and women depend on the form of hormonal imbalance that occurs - an increase in the level of male or female hormones. As a result, there is the development of male secondary sexual characteristics in women or the development of secondary female sexual characteristics in men, acceleration or deceleration of puberty in children, early cessation of reproductive function, increased or decreased libido in adults.
The type of malignant tumor can be judged by the nature of the clinical picture. Symptoms of aldosteroma indicate an imbalance of water-salt balance, symptoms of corticosteroma are associated with metabolic disorders, androsteromas have a masculinizing effect, and corticoesteromas have a feminizing effect.
Corticoandrosteromas are manifested by multi-vector (metabolic-virile) dynamics of symptom development.
Treatment
JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) provides treatment for adrenal oncology. Doctors practice several drastic but effective measures.
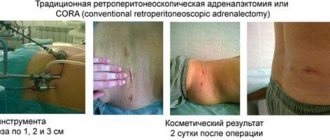
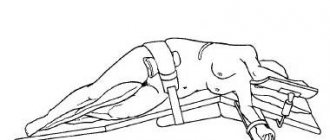
Surgical intervention
Adrenal cancer is a symptom of actively growing tumors that require surgery to remove. This radical method is the most effective for adrenal cancer. But the operation depends on the stage of adrenal cancer.
Laparoscopic intervention is available in the first phase, when the tumor is no more than 50 mm and there are no metastases. At the second stage, the effectiveness of the procedure will depend on the results obtained from CT and MRI. At the third stage, abdominal surgery is performed. During it, nearby organs are checked, since adrenal cortex cancer can quickly metastasize. As a rule, at the last stage the tumor is no longer operated on, since new foci of the oncological process are actively appearing.
Radiation therapy
If the symptoms of adrenal cancer intensify and it is inoperable, then radiation therapy is used. This method is also used for the spread of adrenal cancer metastases. Radiation therapy has no effect on primary malignant tumors, since they are not sensitive to radiation. Typically, the technique is used in the postoperative period to destroy remaining cancer cells and metastases of adrenal cancer.
Chemotherapy
Treatment of adrenal cancer is carried out through chemotherapy in cases where the tumor is inoperable, that is, surgery cannot be performed for any reason. This technique is effective for some types of tumors. As a rule, this method is prescribed when the pathological process has spread greatly, that is, the tumor has increased significantly, and metastases of adrenal cancer have begun to spread. Special chemotherapy drugs are prescribed to suppress the symptoms of adrenal cancer in men and women.
Hormone-active adrenal tumors
Hormonally active neoplasms are of greatest importance for humans, because as a result of their secreting activity, the hormonal balance of the body is disrupted, which leads to various kinds of diseases. Glucosteroma. They are the most common tumor of the adrenal cortex that produces glucocorticoids. Glucosteroma causes Cushing's disease and is one of the causes of obesity, early puberty, early decline of sexual function, and arterial hypertension. Aldosteroma. It produces aldosterone, which causes dysregulation of mineral-salt metabolism and is the cause of Conn's syndrome, and aldosterone also causes arterial hypertension, alkalosis, hypokalemia, and muscle weakness. In the vast majority of cases it is a benign neoplasm (96-98%). Corticoesteroma. This adrenal tumor produces estrogens, which causes sexual weakness in men. Unfortunately, corticoesteroma is most often malignant, but it is rare. Androsteroma. This adrenal tumor produces androgens. In half of the cases it is malignant, but it is rare - in 1-3% of all adrenal tumors (women are affected 2 times more often than men). Androsteroma causes very rapid puberty in childhood and rapid decline in sexual function in adults. Pheochromocytoma. This adrenal tumor produces catecholamines. Pheochromocytoma in nine cases out of ten is a benign neoplasm. Causes an adrenaline crisis, various complications of the cardiovascular system, arterial hypertension and sometimes causes the development of diabetes mellitus.
Forecasts
Prognosis for adrenal cancer depends on many factors. This is primarily influenced by the prevalence of the pathological process. This will be noticeable in the symptoms of adrenal cancer.
Successful prognosis for adrenal cancer at stages 1 and 2 of the disease is approximately 80%, since therapy will produce positive results. The prognosis for stage 4 adrenal cancer is already negative. This is due to the fact that metastases of adrenal cancer have spread widely. The survival rate at this stage is only 10%. At the third stage they are 20%.
Adrenal carcinoma has an unfavorable prognosis. Patients live no more than 1.5 years. Even if the disease is diagnosed in the early stages, life expectancy will be short.
Stages of adrenal cancer
Knowing the stage (prevalence) of the tumor process allows doctors to choose the most optimal treatment and assess the prognosis (outcome) of the disease.
There are 4 stages of adrenal cancer - from I to IV (as the process spreads).
Thus, in stage I of the disease, the size of the tumor does not exceed 5 cm and the surrounding organs and tissues are not involved in the process.
In patients with stage IV, the tumor affects nearby organs and tissues or there are distant metastases.