CAD ) is not one disease, but a whole group of hereditary diseases. A disease associated with impaired synthesis of adrenal hormones is called CADC. Hello, dear reader. You are on the blog “Hormones are normal!” My name is Dilyara Lebedeva, I am the author of this blog. Read about me on the About the Author page to get to know me better.
CDN is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, i.e. the disease manifests itself with the same frequency in both boys and girls. Adrenogenital syndrome, adrenal hyperplasia - all these are synonyms for CAH.
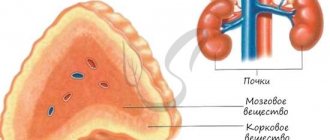
Numerous enzymes are involved in the synthesis of adrenal hormones (corticosteroids), which include cortisol, aldosterone and androgens. A genetic defect in any of them leads to one form or another of this disease. Therefore, there are a lot of different forms of congenital hyperplasia, most of them are incompatible with life. Therefore, newborns with such forms die soon after birth.
In 90% of cases, congenital adrenal hyperplasia is caused by a defect in the enzyme 21-hydroxylase (P450c21). The remaining forms are considered rare.
This article will focus specifically on this form of congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. You can read about other forms in the article “Rare forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.”
CAH caused by 21-hydroxylase defect
The prevalence of this form of congenital adrenal dysfunction varies greatly among people of different ethnicities. In Caucasians, 21-hydroxylase deficiency occurs in approximately 1:14,000 newborns. This figure is significantly higher among Ashkenazi Jews - up to 19% of newborns. Among the Eskimos of Alaska - 1 per 282 newborns.
How does VDKN develop?
Due to a genetic disorder of the enzyme, there is a decrease in the synthesis of only cortisol and aldosterone, which causes adrenal insufficiency. A decrease in adrenal hormones leads to an increase in ACTH (a pituitary hormone that regulates the functioning of the adrenal glands). ACTH, in turn, causes adrenal hyperplasia and increased androgen synthesis.
Since 21-hydroxylase is not involved in the synthesis of androgens, there is no block to the synthesis of these hormones, and their synthesis is enhanced by the action of ACTH. As a result of an increase in androgen levels, hyperandrogenism develops, which causes changes in the genital organs, as well as hair growth in unwanted places. That is why this disease was previously called adrenogenital syndrome. I recommend that you read the article “Is hirsutism in women always a pathology?”, with which you can assess the degree of hirsutism and find out the approximate nature of increased hair growth.
The severity of symptoms may vary. This depends on the degree of defect of the 21-hydroxylase enzyme. Depending on the severity of the defect, there are 3 variants of VDKN.
- Salt form.
- Simple virile form.
- Non-classical form (post-pubertal).
More details about each form below.
Salt form
When the 21-hydroxylase enzyme is completely blocked, a salt-losing form of CAH develops. In this form, the synthesis of both glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids is disrupted, the main representatives of which are cortisol and aldosterone, respectively.
As aldosterone levels decrease, sodium and water are lost, which is why this form is named as such. It accounts for about 75% of all cases of congenital hyperplasia associated with a defect in 21-hydroxylase. Thus, the salt-wasting form is the most common form of this disease.
In the clinic of the salt-wasting form of CAI, 2 syndromes are distinguished:
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Excess androgens
The development of congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex begins in fetal development. Manifestations of this disease are noticeable already at the birth of a child.
In girls it manifests itself as follows:
A newborn girl already exhibits so-called female hermaphroditism, since there is an excess of androgens during fetal development.
Female hermaphroditism is when the genotype is female, and the genitals are formed according to the male type.
In a girl with CDN, hermaphroditism can manifest itself in different ways: from a simple enlargement of the clitoris to fusion of the labia with the formation of a pseudoscrotum and a penis-shaped clitoris with the opening of the urethra. The structure of the internal genital organs (vagina, uterus and ovaries) with adrenal dysfunction is always normal.
In boys it manifests itself as follows:
In boys, there is an increase in the size of the penis and hyperpigmentation of the scrotum (dark-colored scrotum).
If treatment is not started, the disease progresses rapidly. Bone growth zones quickly close, and patients remain short in stature. Girls who are exposed to excess androgens will not experience menstruation.
Adrenal insufficiency develops due to a decrease in the synthesis of cortisol and aldosterone. Symptoms of deficiency begin to appear as early as 2-3 weeks of a child’s life.
In a newborn, adrenal insufficiency is manifested by sluggish sucking, vomiting, dehydration, decreased mobility, as an important symptom - an increase in hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin). You can read more about the manifestations of adrenal insufficiency in the article “Adrenal Insufficiency.”
Simple virile form
With moderate preserved activity of the 21-hydroxylase enzyme, adrenal insufficiency does not develop. But the same pronounced excess of androgens remains, which causes changes in the external genitalia, as in the salt-wasting form.
Non-classical form (post-pubertal)
When the genetic defect of the enzyme is minor, the decrease in cortisol and aldosterone is moderate. Therefore, ACTH is slightly increased, which, in turn, does not greatly increase the synthesis of androgens.
Therefore, in the non-classical form of CAH, adrenal insufficiency does not develop, and no abnormalities in the structure of the external genitalia are detected at birth.
Pathology is detected when a woman begins to be examined for infertility and menstrual irregularities - in 50% of cases, for hirsutism (increased hair growth) - in 82% of cases, for acne (pimples) - in 25% of cases.
But sometimes any clinical manifestations or decreased reproductive function may be completely absent, i.e. there is a genetic defect, but it is not so pronounced that it does not cause any significant health problems.
Features of the therapeutic approach in patients with non-classical variant of P450c21 deficiency
- GCS therapy is prescribed to patients with a non-classical form of 21-hydroxylase deficiency only if there are symptoms of progressive hyperandrogenism.
- In prepubertal children, GCS are prescribed when bone age increases and there is an unfavorable growth prognosis.
- In adolescent girls and young women, GCS are prescribed for progressive hirsutism, oligomenorrhea, and infertility
NB!
- Dose selection - individually, under the control of 17-OH-progesterone, DHEA, testosterone (should be at the upper limit of normal).
- Mineralocorticoid replacement therapy is not required.
- There is no need to increase the dose of GCS in urgent situations.
Sources:
- Andreeva E.N., Uzhegova Zh.A. Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex (adrenogenital syndrome). Screening, diagnosis, treatment. Guidelines. Moscow, 2010
- Witchel SF, Azziz R. Nonclassic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology
. 2010;2010:625105. doi:10.1155/2010/625105.
Diagnosis of congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex
As a result of blockade of the synthesis of cortisol and aldosterone, the synthesis of not only androgens, but also their precursors increases, since the increased level of ACTH (a pituitary hormone that affects the functioning of the adrenal glands) still has increased stimulation of the adrenal cortex.
The main marker of CAH caused by a defect in 21-hydroxylase is the cortisol precursor 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHPg). The normal level of 17-OHPg in the blood is up to 6 nmol/l.
If the level of 17-OHPg is more than 30 nmol/l , then this confirms the presence of a deficiency of the 21-hydroxylase enzyme. In patients with classic forms of CDCN, the level of 17-OHPg is more than 45 nmol/l.
If the level of 17-OHPg is borderline (6-30 nmol/l), then a 24-hour test with Synacthen (ACTH) is recommended.
The test is carried out as follows. After determining the basal level of 17-OHPg, 1 mg of synacthen depot is injected into the muscle, then repeat 17-OHPg after 24 hours. If the level of 17-OHPg does not exceed 30 nmol/l, then this diagnosis can be excluded.
But recently there have been some problems with the test due to the lack of the drug, so all patients with questionable results undergo a genetic study for the presence of mutations in the CYP21 gene.
In addition to an increase in 17-OHPg, this form of CAH is characterized by an increase in androgens : dehydroepiandrostenedione sulfate (DHEA-S) and androstenedione.
And the salt-wasting form is characterized by an increase in plasma renin activity , which reflects aldosterone deficiency. In addition, in classical forms, ACTH levels will be increased.
If this is a congenital disease, then how can it be detected in newborns? For this purpose, neonatal screening is carried out in our country, as well as in developed countries. It consists of taking blood samples from the heel of a newborn on days 4-5 and determining the main marker of this pathology, i.e. 17-OHPg, as is the case with the detection of congenital hypothyroidism, phenylketonuria and other congenital diseases.
Non-classical form of P450c21 deficiency
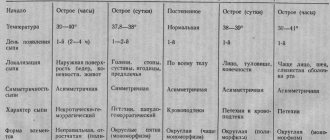
Clinical manifestations:
- hirsutism - 60%
- oligo- or amenorrhea - 54%
- acne - 33%
- infertility - 13%
There is no virilization of the external genitalia
Available:
- accelerated growth
- advance of bone age relative to passport age
- early closure of growth zones
- early initiation of pubic and axillary hair growth
Laboratory diagnostics:
- 17-OH-progesterone may be within normal limits (basal values of 170–300 ng/dL can be used as screening markers);
- the gold standard is a diagnostic test with 1-24 ACTH (Synacthen).
Currently in Russia a modification of this test is used with 1 mg of 1-24 ACTH (Synacthen-Depot).
The physiological level of rise in cortisol and its precursors should exceed the basal level by 2-3 times.
Test with Sinatken
- Determination of basal levels of 17-OH-progesterone.
- Administration of 0.125 mg 1-24 ACTH.
- Determination of 17-OH-progesterone after 60 minutes.
- VDKN is indicated by an increase in 17-OH-progesterone to 1500 ng/dl;
- in older patients, non-classical CAH may also be indicated by an increase of 1000-1500 ng/dL.
Test with Synacthen-Depot
- Determination of basal levels of 17-OH-progesterone.
- Administration of 1 mg 1-24 ACTH.
- Determination of 17-OH-progesterone after an hour.
- VDKN is indicated by an increase in 17-OH-progesterone more than 4-5 times (>45 nmol/l).
- A similar increase in 17-OH-progesterone and 11-DOC may indicate 11-β hydroxylase deficiency.
- An increase in DHEA-S by more than 3 times is a non-classical variant of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency. Extremely high levels of DHEA-S that do not change after stimulation - androgen-secreting adrenal tumor .
The final confirmation of the diagnosis is molecular genetic analysis.
Treatment of VDKN
First of all, I would like to say that the treatment of this pathology consists of lifelong medication, since the enzyme defect is genetic and there is no way to influence it.
In the case of the salt-wasting form and the simple virile form, in order to treat adrenal insufficiency, children are prescribed hydrocortisone in tablets at a daily dose of 15-20 mg per square meter of body surface or prednisolone - 5 mg per square meter of body surface. Doses are divided so that 1/3 is taken in the morning and 2/3 at night for maximum ACTH suppression.
Also, for the salt-wasting form, fludrocortisone (mineralocorticoid) is added at a dose of 50-200 mg/day.
When a woman’s genotype is diagnosed late and the genitals are already developed according to the male type, then surgical intervention may be necessary for plastic surgery of the external genitalia.
Unwanted hair is removed using various hair removal methods.
The non-classical form is treated when there are pronounced clinical manifestations in the form of cosmetic defects (increased hair growth or acne), as well as when reproductive function is reduced.
With this form, 0.25-0.5 mg of dexamethasone or 2.5-5 mg of prednisolone is prescribed at night to suppress the production of ACTH by the pituitary gland. Also, acne and hirsutism respond well to treatment in women with the help of antiandrogens, such as cyproterone, which is part of oral contraceptives, for example, Diane-35.
In men, the non-classical form of 21-hydroxylase deficiency does not require treatment.
Forecast
The prognosis depends entirely on the timely diagnosis, which prevents pronounced disturbances in the structure of the external genitalia in girls. The adequacy of the therapy is also important, i.e. if the dose of drugs is insufficient or there are signs of overdose, then most patients remain short, and women have a masculinization of their figure.
All this leads to disruption of psychosocial adaptation. But with adequate treatment, even in women with the salt-wasting form, normal pregnancy and pregnancy are possible.
With warmth and care, endocrinologist Dilyara Lebedeva