Imaging methods for adrenal cancer
Simultaneously with the hormonal examination of the patient, a careful examination is carried out in order to establish the location, size of the tumor, as well as its interaction with surrounding organs.
The size of the tumor is one of the important parameters to suspect that a patient has adrenal cancer. Currently, scientific research shows that the average tumor size for adrenocortical cancer is more than 11 cm, while benign adrenal tumors (adenomas) are usually less than 5 cm in size. The main diagnostic problems arise when identifying tumors ranging in size from 3 to 10 cm, which can have both benign and malignant structure.
Unfortunately, at present there is not a single diagnostic method that could confidently reject the diagnosis of adrenal cancer, but computed tomography with intravenous administration of a contrast agent
. In this case, three main parameters are assessed:
— tumor density before contrast injection (native density);
— tumor density at the time of contrast injection;
— tumor density 10 minutes after contrast injection (delayed phase, washout phase).
When a tumor is detected with a native density of less than 10 Hounsfield units on computed tomography, the likelihood of cancer is extremely low.
Also uncharacteristic of adrenal cancer is the active accumulation of contrast with an increase in density at the time of contrast administration and then the active washout of contrast after 10 minutes (a drop in density by more than 50% of the maximum after 10 minutes is a sign of a benign tumor).
In the case of adrenal cancer or metastases of other cancers to the adrenal gland, there is usually a delay of contrast in the tumor with a slight decrease in density in the delayed phase of the study after 10 minutes.
Positron emission tomography with 18-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) is used as an additional and important research method.
. Active accumulation of FDG is characteristic of both adrenal cancer and pheochromocytomas, metastases of other tumors to the adrenal gland. It is believed that if a patient has a high cumulative SUV (standardized uptake value) criterion - more than 3 - the probability of adrenocortical cancer becomes extremely high.
, a computed tomography scan of the lungs and abdominal cavity is mandatory.
,
magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
. The purpose of these studies is to search for possible tumor metastases, since their identification allows us to more clearly determine the stage of the disease and prescribe adequate treatment.
Adrenal biopsy for suspected cancer
Unlike tumors of other organs (thyroid, mammary glands), a biopsy for suspected adrenal cancer is not only not mandatory, but also not directly recommended in most recommendations
. A biopsy of the adrenal gland most often does not exclude malignant lesions of this organ, and the biopsy is often accompanied by complications. Puncture of the tumor capsule with a puncture needle can lead to the development of metastatic foci along the puncture canal.
Currently, a biopsy is considered necessary only if there is a suspicion of metastatic damage to the adrenal gland from a malignant tumor of another organ, as well as if there is a suspicion of adrenal lymphoma. In both of these cases, a biopsy can provide an informative answer with a probability of 80-85%, and the resulting diagnosis can significantly change the patient's treatment strategy.
Symptoms
With an adrenal tumor, the symptoms are very diverse; more often than not, several of them occur simultaneously:
- Weight gain, accompanied by the appearance of stretch marks on the skin;
- Muscle weakness;
- The appearance of coarse facial hair in women, hair loss on the head;
- Irregularity of menstruation;
- Enlargement of the mammary glands in men, problems with potency;
- Nausea and vomiting that recurs without obvious cause;
- Loss of appetite;
- Bloating;
- Back pain;
- Increased body temperature;
Any of the listed symptoms is a reason to seek medical advice, but a combination of several of them most often requires an in-depth endocrinological examination.
Adrenal cancer - stages of the disease and rules for their establishment
Adrenocortical cancer is usually detected in late stages. Studies show that in 80% of patients the tumor is more than 10 cm in size at the time of detection. Tumor metastases are detected in 30-40% of patients at the time of surgery. If large tumors (more than 10 cm in size) are detected, adrenal cancer metastases occur in more than 80% of patients.
Determining the stage of the tumor is an important stage of the diagnostic process, since staging allows not only to determine the possible prognosis of adrenal cancer
, but also to determine which
treatment for adrenal cancer
is more appropriate.
The most widely used classification of adrenal cancer is developed by ENSAT (European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors), a European working group on the study of adrenal tumors. This classification evaluates the parameter T (tumor, tumor = size and spread of the primary tumor), N (nodus, lymph node = damage to regional lymph nodes), M (metastasis, metastasis = the presence of distant metastases of the tumor in other organs). Staging according to the TNM system is generally accepted - this classification is also called the AJCC (American Joint Commission on Cancer)/UICC (International Union Against Cancer) classification.
| ENSAT | TNM | Definition |
| I | (I) T1N0M0 | Primary tumor size <5 cm |
| II | (II) T2N0M0 | Primary tumor size >5 cm |
| III | (III)T1-2N1M0 (III-IV)T3-4N0-1M0 | Metastases in regional lymph nodes, tumor invasion into neighboring organs and the kidney and/or development of tumor thrombosis of the inferior vena cava |
| IV | T1-4N0-1M1 | Detection of distant metastases |
Adrenal tumors
The adrenal glands produce hormones that regulate metabolism, blood pressure, and female and male sex hormones. So the main manifestations of an adrenal tumor are associated with the action of the hormone that it produces in excess.
There are primary and metastatic adrenal tumors
Primary adrenal tumors belong to one of the important and difficult diagnostic and therapeutic areas of clinical oncology. These diseases combine a group of different types of tumors, which include hormonally active adrenal tumors. It is generally accepted to classify adrenal tumors into benign and malignant. This has important practical significance regarding the prognosis of the disease, since surgical removal of a benign tumor leads to complete recovery, while the prognosis for malignant tumors is questionable. At the same time, the morphological signs of malignancy of adrenal tumors are still debated.
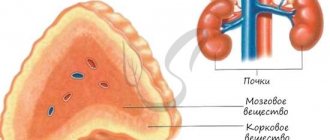
If until recently it was believed that adrenal tumors are a rare pathology and account for no more than 0.6% of all malignant tumors, now, thanks to the widespread introduction into everyday clinical practice of such non-invasive but very informative diagnostic methods as ultrasound, CT, MRI , the number of detected neoplasms in the retroperitoneal space has sharply increased. Some of these formations are localized in the adrenal gland and in most cases are tumors emanating from either the cortical or medulla layers. The adrenal glands have a complex histological structure and consist of two embryologically and morphologically different layers - the cortical and medulla.
In domestic and foreign literature there are a large number of different classifications of adrenal tumors. Currently, the classification based on the histogenetic principle :
- Epithelial tumors of the adrenal cortex: adenoma,
- carcinoma.
- myelolipoma,
- pheochromocytoma,
One of the most convenient clinical and morphological classifications is the classification proposed by Micali F. et al. (1985).
Malignant adrenal tumors require clinical classification into stages. One of the first to try to solve this problem was Macfarlan DA in 1958, and then Sullivan M. in 1978, who modified the Macfarlan DA classification according to the TNM system:
- T1 – relatively small tumor size – up to 5 cm.
- T2 – relatively large tumor size – more than 5 cm.
- T3 – any tumor size with local invasion of surrounding tissues.
- T4 – any size of tumor with invasion into surrounding organs, liver, kidneys, pancreas, inferior vena cava.
- N0 – regional lymph nodes are not enlarged.
- N1 – there are metastases to the para-aortic and paracaval lymph nodes.
- N2 – there is damage to the lymph nodes of other locations.
- M0 – no distant metastases.
- M1 – there are distant metastases.
- Stage I – T1N0M0
- Stage II – T2N0M0
- Stage III – T1N1M0, T2N1M0, T3N0M0
- Stage IV – T4N2M0, T4N2M1.
However, this classification needs improvement and is not widely used in medical practice. proposed by O.V. is most often used. Nikolaev (1963), according to which tumors are divided into the following types: corticosteroma, androsteroma, corticoandrosteroma, aldosteroma, corticoestroma and combined tumors . Each of them can be benign or malignant.
Adrenal cancer - prognosis
Tumor staging is extremely important to determine the prognosis of the disease. Thus, stage I tumor according to ENSAT is accompanied by a 5-year patient survival rate of 81%, stage II – 61%, stage III – 50%, and the last stage, stage IV – 13%. It is clear that the more advanced the tumor is detected, the wider the adrenal cancer has spread, the more difficult it is to treat. However, modern treatment options (both surgical and chemotherapy) make it possible in a significant number of cases to dramatically change the patient’s prognosis and ensure long life after treatment.
Diagnostic methods in
Diagnosis of adrenal cancer most often begins at an appointment with an endocrinologist, who, based on the results of tests for the level of adrenal hormones, may suspect the presence of a tumor. The most important laboratory tests are the levels of cortisol, aldosterone, androgens and estrogens.
At the next stage of diagnosis, the tumor is detected using computed tomography (CT) or MRI. Then it is possible to conduct diagnostic laparoscopy with the selection of material for research (biopsy). The resulting tissues are examined using various histological methods to determine the type of tumor.
Surgical treatment of adrenocortical cancer
Surgery for adrenal cancer is the only radical method that can, in some cases, completely cure the patient. Given the rapid metastasis of adrenal cancer, tumor removal should be performed as quickly as possible after its identification and assessment of hormonal activity.
When planning the operation, the following points should be taken into account.
Surgical treatment of patients with adrenal cancer should be performed in a specialized center for endocrine surgery
, who performs a significant number of adrenal surgeries annually. Diagnostics, preoperative preparation, surgical intervention - all these stages have a lot of “pitfalls”, knowledge of which is achieved only with increasing experience of doctors after several years of work in this field. That is why performing operations on the adrenal glands in general surgery departments is unacceptable.
When preparing and performing surgery, special attention should be paid to the prevention of thrombosis.
. The main cause of death in patients after surgery for adrenocortical cancer is thromboembolic complications. They are due to several reasons:
- high levels of blood cortisol and/or male sex hormones, which increases blood clotting;
— blood loss during surgery with the need for transfusion;
— separation of tumor blood clots in the veins of the abdominal cavity during surgery;
— illiterate preparation of the patient for surgery, insufficient prevention of the development of thrombosis.
The operation should be carried out with maximum preservation of the integrity of the capsule
tumors. If the capsule is damaged, adrenal cancer recurs in 100% of cases. The absence of tumor trauma is ensured by the experience of the surgeon performing the operation, as well as the use of modern equipment - ultrasonic harmonic scalpel, bipolar coagulator with feedback, etc.
The most important rule to ensure radical surgery is to remove the tumor within healthy tissue
(so-called R0-resection).
An important stage of surgery for adrenal cancer is prophylactic lymph node dissection.
– removal of retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Some scientific studies have shown that lymph nodes are affected in 20-30% of patients - this fact alone dictates the need for prophylactic removal of lymph nodes in all patients. Scientific evidence suggests that lymph node removal improves patient survival and reduces the risk of tumor recurrence.
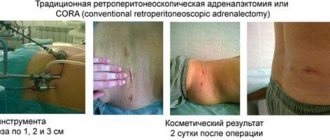
In some cases, with a small tumor, it is possible to perform endoscopic surgery to remove adrenal cancer, but the endoscopic method of surgical treatment for this tumor is not the main one
.
Traditional open access surgery allows for the most complete examination of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, performing a thorough lymph node dissection, reducing the risk of damage to the tumor capsule and the associated spread of metastases throughout the peritoneum. It should be borne in mind that the disadvantage of open surgery is its traumatic nature. In any case, any surgical intervention (open or endoscopic) should be planned only in a specialized center for endocrine surgery
- this rule is not questioned.
In case of tumor recurrence, when the tumor center or its metastasis is surgically removed, one should be inclined to repeat surgery
, aimed at completely removing cancer, since scientific evidence shows the advantages of this approach - patient survival increases. Given that tumor recurrence in adrenal cancer can be common, this recommendation is very important.
Chemotherapy for adrenal cancer
Chemotherapy is currently recommended as an additional postoperative therapy for all patients with adrenal cancer. The most effective drug for the treatment of adrenocortical cancer is mitotane.
(lysodren, chloditan). Its action, which is still not yet sufficiently understood and studied by scientists, is aimed at the degeneration of cells of the zona fasciculata and reticularis of the adrenal glands, without affecting the zona glomerulosa (which produces mineralocorticoids - aldosterone, corticosterone, deoxycorticosterone). Mitotane not only has a powerful antitumor effect, but also blocks the production of corticosteroids and reduces the severity of symptoms of hypercortisolism, which has an additional positive effect.
Mitotane has not yet been registered in Russia, but its use is the only chance for most patients with adrenal cancer. Modern scientific research shows an increase in the duration of the disease-free period in patients with adrenal cancer, as well as an increase in the overall survival of patients. In this regard, a number of specialized centers for endocrinology and endocrine surgery in Russia have developed a procedure for prescribing mitotane in compliance with the procedure for individual import of the drug into our country for use in patients.
Currently, the Northwestern Endocrinology Center accepts patients with adrenal cancer both for surgical treatment and for chemotherapy using mitotane. The drug has a fairly high toxicity and a high level of side effects, and also causes pronounced signs of adrenal insufficiency, and therefore can be prescribed and used only under the supervision of a doctor in a specialized center.
In cases where therapy with mitotane alone does not have the desired therapeutic effect, it is possible to use a regimen according to the so-called “Italian protocol” (EPD-M regimen - etoposide, doxorubicin, cisplatin with continued oral administration of mitotane. Mitotane provides blockade of enzymes that excrete adrenal cancer cells chemotherapy drugs, and increases the overall effectiveness of chemotherapy.