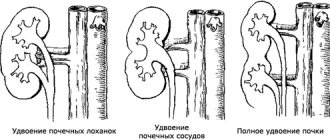
If the bud buds are closely located, a double bud is formed during fusion. With symmetrical fusion, each kidney is on its own side, fusion at the poles produces a horseshoe-shaped bud, and a biscuit-shaped bud throughout the entire mass. With asymmetrical fusion, one of the kidneys is displaced contralaterally, resulting in an I- or S-shaped kidney.
In a fused kidney, polycystic degeneration, hypoplasia or atrophy of one kidney with vicarious hypertrophy of the other, duplication of the pelvis, hydronephrosis, stones, and urinary infection often occur.
Important!!! By compressing neighboring organs and vessels, fused ectopic kidneys can cause pain. When a child persistently complains of pain in the navel area, and along with this a urinary tract infection is found, it is always necessary to think about a fused kidney. For persistent pain, surgical dissection of the isthmus may be required.
Fused kidneys are often combined with malformations of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system and musculoskeletal system.
Horseshoe kidney on ultrasound
With a horseshoe-shaped anomaly, the kidneys are fused with the same poles: in 90% of cases, the lower ones, very rarely the upper ones. The vessels to the horseshoe kidney arise from the lower part of the aorta or from the iliac arteries, but sometimes, along with the aberrant vessels, there may be a normally located renal artery. The ureters are usually shorter and cross the isthmus by passing over it. The microscopic structure of the kidney is often not disturbed.
Types of fusions:
- Fusion of the lower poles through a parenchymal isthmus, which is located above the aorta and inferior vena cava, usually at the level of L3-L5;
- The parenchymal isthmus is located just above the lower poles;
- The isthmus is located under the aorta and the inferior vena cava or between them;
- The isthmus between the lower poles consists of fibrous tissue;
- Fusion of the lower poles directly;
- Fusion between the upper poles.
Click on pictures to enlarge.
Drawing. The anatomy of horseshoe kidneys is extremely diverse.
| Photo. Anatomical preparations of a horseshoe kidney. With a horseshoe bud, one or both buds are often lobulated (3, 4), due to the preserved germinal grooves that separate the embryonic primordia in the early stages of development. |
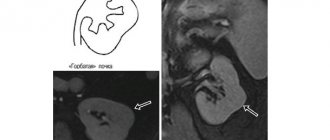
A change in the location of the longitudinal axis of the kidney should alert the doctor to fusion anomalies. Since in 95% of cases fusion occurs at the level of the lower poles, the longitudinal axis of the kidneys will be located at an angle to the spine, and this angle will be open upward. Much less often, the kidney can be located parallel to the spinal column. When scanning through the back, the lower poles of the kidneys are not clearly visible.
If you suspect a horseshoe kidney, be sure to scan from the anterior abdominal wall. The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. In the peri-umbilical zone, in front of the spine, the junction of the kidneys is determined - the isthmus. Visualization of the isthmus is indisputable evidence of renal fusion.
Drawing. On ultrasound, both kidneys are identified in the pelvis (bladder as a screen), the lower poles are connected to each other by a narrow isthmus (1, 3), parenchymal differentiation is preserved, blood flow is traced to the capsule (2, 3). Conclusion: Anomaly in the relative position of the kidneys - horseshoe kidney, pelvic dystopia.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a complete urological examination is necessary - urography, scintigraphy.
How does pathology affect a patient’s life?
The effect of the anomaly on the body depends on the symptoms accompanying it. Often a person learns about the U-kidney only after 40 years of age, so the pathology does not affect the quality of life in any way.
If the diagnosis is known, but there are no alarming symptoms, then the “owner of the U-kidney” can engage in any kind of sport, except those associated with lifting weights; it is not advisable to engage in sports professionally.
If a pathology was detected in a child, then he should be registered with a urologist and be observed by a specialist at least 2 times a year. Complications.
The presence of such a kidney, unfortunately, often contributes to the occurrence of various complications. As a rule, these are disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular and urinary systems; often the pathology provokes the development of varicose veins and, as a consequence, edema of the lower extremities.
Sometimes pathology causes the development of disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, which can lead to mental disorders.
Unfortunately, in children this anomaly, in tandem with other anomalies, provokes multiple disorders in the body:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- chronic heart disease;
- severe disorders of the musculoskeletal system;
- horseshoe kidney tumors;
- hydrocephalus.
Typically, these diseases develop in children in utero, or at an early age; the older the child becomes, the lower the risk of developing pathology.
Ultrasound description of a horseshoe kidney
Boy, 9 years old. Weight 26 kg, height 132 cm.
The right kidney is 87×33 mm, parenchymal thickness is 12 mm, cortico-medullary differentiation is preserved. ChLS are not expanded. There are no stones. The blood flow is traced to the capsule.
The left kidney is 82x30 mm, parenchymal thickness is 12 mm, cortico-medullary differentiation is preserved. ChLS are not expanded. There are no stones. The blood flow is traced to the capsule.
The kidneys are located in a typical location. The right kidney is displaced anteriorly. Physiological mobility is preserved. The lower contours are not traced, the dimensions are determined conditionally. When scanning in the periumbilical region above the spine, a structure up to 13 mm thick and up to 56 mm long is detected, connecting the lower poles of the kidneys, regarded as the isthmus of a horseshoe kidney.
Conclusion: Echo signs of an anomaly in the relative position of the kidneys - a horseshoe kidney.
Causes
Doctors have still not been able to name the exact cause of this pathology. The occurrence of malformations of the genitourinary system is largely due to the presence of some of the genetic syndromes in the fetus:
- chromosomal abnormalities: Down, Turner, Edward, Patau syndromes;
- non-neoplastic anomalies - Ellis-van Creveld, Goltz, Kabuki, Pallister-Hall syndrome.
However, a horseshoe-shaped organ also occurs in people without genetic abnormalities; most likely in such cases, the factors provoking the pathology are:
- infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- use of medications;
- unfavorable external factors during pregnancy, chemicals in water and food.
Asymmetric renal fusions on ultrasound
The kidneys are connected at opposite ends, the two renal pelvises are on the same side of the spine, but the openings of the ureters in the bladder are located in their usual places.
In the case of an S- and I-shaped bud, the longitudinal axes of the fused buds are parallel, and the axes of the buds forming an L-shaped bud are perpendicular. The pelvis of the S-shaped kidney faces in opposite directions, while the I- and L-shaped kidneys are located medially.
Take care of yourself, Your Diagnosticer !
Tags: video pearl lectures kidneys ultrasound
Vascular anomaly
Divided into venous and arterial anomalies. Classification:
- Quantity – one or many additional arteries at once (they only differ in size from the main one). The problem is not viability threatening.
- Location – does not interfere with the normal functioning of the kidney. Thus, based on location, the following are distinguished: pelvic, lumbar and iliac forms.
- Structure – this class includes aneurysm and stenosis of any area. In any case, this may negatively affect the work of the body.
Stenosis leads to dysfunction of the venous ducts. The level of damage in the circulatory-venous system may vary, depending on the degree of development of the stenosis. As a result, the veins begin to transform, forming bypass outflow paths, trying to compensate for the defect. The most obvious symptom of such a disorder will be varicose veins - varicocele. There is much less chance of hematuria, pain during sexual intercourse, and dysmenorrhea.
Varicocele of the kidney - external manifestations
Much less common is a congenital disorder in which the arterial vascular walls are partially transformed into venous ones. The anomaly is called an arteriovenous fistula. Typically, such a disorder affects the arcuate arteries and interlobular vessels, and sometimes the cortical ones.
Congenital vascular anomalies are harmful in that they can lead to sclerotic changes, sometimes irreversible, and then to complications.
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
A patient with developmental anomalies of the urinary system after surgery and a course of corrective drug therapy is practically no different from a healthy person. If the surgical procedure was performed at a young age, the risk of complications is almost minimal. After confirmation of the diagnosis, the adult patient has to significantly change his usual lifestyle
Such caution is due to the high risk of developing various life-threatening complications. What limitations and problems arise in patients with a horseshoe kidney:
- Prohibition on prolonged and heavy physical activity. Professional sports require high energy and psychological costs, which negatively affects the condition of patients. That is why doctors advise giving up intense training and switching to more gentle activities. These include therapeutic exercises, light running exercises and ball games. Heavy and aggressive sports (wrestling, football, basketball, volleyball, hockey, tennis and much more) are best left in the past.
- The need for constant monitoring of the condition during pregnancy. An enlarged uterus contributes to compression of the pelvic organs and retroperitoneal space, which, if the kidneys develop abnormally, can lead to serious impairment of their functions and miscarriage. Independent childbirth with this type of pathology is most often prohibited.
- Refusal to drink alcohol and the need to strictly adhere to a diet. Salty foods with a lot of fat contribute to the accumulation of water in the body, which is not excreted by the kidneys. Alcoholic drinks cause metabolic disorders and slow down blood circulation through the vessels.
The likelihood of developing an unfavorable outcome is largely influenced by the lifestyle of the victim. I had the opportunity to participate in the treatment of a patient with acute renal failure, which arose against the background of an anomaly. Due to a fracture of the pelvic bones, the man's genitourinary system was deformed. The damaged kidneys fused together, forming a single conglomerate. The patient was offered surgery to correct this defect, but he refused. The man also did not take maintenance therapy, as a result of which the situation worsened. Due to his serious condition, he was transferred to a lifelong hemodialysis procedure - artificial blood purification through a filter.
What complications may occur in patients with a horseshoe kidney:
- addition of infection and purulent-septic processes (phlegmon, carbuncles, boils);
- development of renal failure and intoxication of the body due to the accumulation of harmful substances in the blood;
- hydronephrosis - expansion of the pelvis due to excess fluid;
- urolithiasis disease;
- hypertensive crises with an uncontrolled increase in blood pressure;
- the occurrence of benign and malignant neoplasms;
- pyelonephritis - inflammatory changes in the kidney tissue.