Kinds
Symptom identification can be carried out in three ways.
The choice of technique depends on the patient’s well-being, his state of health, and the available position that he can take:
- Sitting or lying down. Then the doctor puts his hand on the lumbar region, and with the other rib or fist makes several gentle blows.
- If the patient can only assume a sitting position, then use your fingers to tap the border zone between the lumbar muscles and the lower part of the ribs.
- Bedridden patients are turned onto their backs. The doctor then places one hand under the lower back and gives several pushes.
Pasternatsky's symptom is not the usual “beating”. In the second case, you do not need to submit your urine for analysis. This is included in the Pasternatsky method, when pain during tapping and an increase in red cells in the urine are combined. A urine test is done only after the test.
For ordinary “effleurage”, only physical sensations are enough. However, pain may appear due to gastrointestinal pathologies, problems with the pancreas, and liver. This is why a follow-up urine test is necessary.
Stages and degrees
A negative symptom on both sides indicates a hidden course of the pathology and requires additional diagnostics. The test is considered positive if, during medical procedures, discomfort appears in the rib area. Especially if the biomaterial contains an increase in the concentration of red blood cells and white blood cells.
After diagnosis, the patient urinates in a sterile container. If the vibration from impacts provoked the entry of leached red blood cells into the urine, this indicates a positive Pasternatsky symptom. To make sure of this, testing is carried out on the left and right side of the kidney, identifying the patient's response.
When children are examined, tapping is performed with the pads of the fingers. However, at this age, Pasternatsky’s symptom rarely appears, usually on one side. Glomerulonephritis can be excluded if the child has recently suffered from influenza or infectious diseases of the nose and throat.
Women are not tested during menstruation. A positive right-sided symptom in women occurs when the kidneys prolapse. Sometimes it can develop for years after childbirth. Kidney tumors are more often diagnosed in men. Then Pasternatsky’s symptom will be right- or left-positive.
Pasternatsky's symptom is not an independent diagnostic method, as it provides little information. The main advantage of diagnosis is that it can be performed in bedridden patients, when a more complex examination is impossible or difficult.
With a positive symptom, pain will be felt on the left, right, both sides plus ertrocyturia. This often indicates the presence of urolithiasis. How the results are interpreted depending on the location of the pain.
If the symptom is positive:
- weak – in the area of the kidneys the sensations are unclear;
- with average pain is tolerable, moderate;
- sharply positive - the sensations are so strong that the patient winces and screams;
- on both sides - pain occurs on the left and right, which indicates serious kidney damage.
Pasternatsky's symptom
A negative bilateral test does not always indicate the absence of disease. If there are no red cells in the urine, then additional diagnostics are required. The cause of the pain may not be the urinary system.
Sometimes a negative symptom indicates kidney prolapse. Pain when tapping can occur due to existing kidney diseases or pelvic dystopia (displacement of organs beyond the lumbar region).
Pasternatsky's symptom
When identifying diseases of the urinary system and abdominal cavity, an important role is played by identifying Pasternatsky’s symptom. The name was fixed after the therapist F.I. Pasternatsky established the relationship between pain when tapping the lumbar area and the appearance of erythrocyturia in the urine. In modern medicine, when conducting an examination of persons with suspected pathologies of the kidneys and peritoneum, determining the Pasternatsky symptom is mandatory.
How is it carried out?
There are 3 options for identifying a symptom. The choice of the optimal technique depends on the health status, well-being of the patient and the position in which he may be:
- if the patient is able to sit or lie down, the examination technique is as follows: the doctor places the palm of one hand on the lumbar area, makes several blows with his fist or the side of the second hand, without applying any physical effort;
- if the patient is only able to take a sitting position, the technique changes: the doctor makes tapping movements with his fingers in the border area between the lower ribs and the lumbar muscles;
- examination in a supine position: the patient lies on his back, the doctor places his hand under the lumbar area and makes several pushes.
After the manipulations have been performed, the patient is asked to urinate into a sterile container. If leached (without hemoglobin) red blood cells are found in the urine, this indicates a positive Pasternatsky symptom. For the reliability of the study, all manipulations (tapping, effleurage) are performed on both sides to identify reactions from the right and left kidneys.
When conducting an examination in children, all actions are replaced by light tapping with the pads of the fingers. In women during menstrual bleeding, the Pasternatsky symptom is not determined. Pasternatsky syndrome is not used as an independent diagnostic method due to insufficient information content. However, a significant advantage of the symptom is its ability to be used in bedridden patients, when other complex diagnostic procedures are difficult or impossible.
Differentiation from the “effleurage” symptom
Many urologists confuse Pasternatsky's symptom and the "tapping" symptom. The difference between these diagnostic methods is in the urine analysis. To correctly determine Pasternatsky's symptom, the key role is played by the combination of pain when tapping the lumbar region with the detection or increase in the number of red blood cells in the urine.
To determine the usual symptom of "effleurage", the patient's confirmation of pain is sufficient. During examination, such a symptom appears in the area of the projection of the kidneys and may indicate:
- consequences of injuries, bruises of the kidneys and spleen;
- diseases of the digestive system (acute pancreatitis, cholecystitis, inflammatory bowel diseases);
- vascular ischemia with the formation of necrotic areas;
- pathologies of musculoskeletal tissues (myositis, osteochondrosis, radiculitis);
- chronic gynecological diseases in women (endometriosis, metroendometritis, fibroids, ovarian cysts).
Decoding the results
The disease is positive if during the study a person feels pain on the right, left or both sides, in combination with erythrocyturia. A sharply positive symptom means increased pain when tapping or its provocation, which often indicates urolithiasis.
The interpretation of the symptom depends on the intensity and location of the pain:
- weakly positive symptom - during examination the patient experiences unclear sensations in the area of the projection of the kidneys;
- positive symptom - the patient feels pain, but it is moderate and tolerable;
- strongly positive - the pain is severe, the patient may scream or wince;
- Pasternatsky’s symptom is positive on both sides - pain is felt on the right and left sides, which indicates serious kidney damage, for example, with pyelonephritis;
- Pasternatsky’s symptom is negative on both sides - this interpretation does not always indicate good health; if there are no red blood cells in the urine, the “tapping” symptom is positive, advanced diagnostics are required, perhaps the cause of the pain is not in the urinary system.
If Pasternatsky's syndrome is negative on one or both sides, the cause sometimes lies in prolapse of the kidneys. Thus, there will be no pain during examination using the tapping method even in the presence of confirmed renal pathologies, if the kidneys are displaced beyond the lumbar region (pelvic dystopia).
What does it indicate?
The combination of erythrocyturia and pain during effleurage (tapping) indicates the development of the following pathologies:
- urolithiasis and nephrolithiasis with the formation of salt deposits in the ureters;
- acute and chronic pyelonephritis - a catarrhal process that affects the renal pelvis, calyxes and parinchema, including with a purulent form of inflammation;
- perinephritis and paranephritis - ailments associated with inflammation of the perinephric fat layer and fat capsule;
- malignant kidney tumors (carcinoma) and benign (adenoma, fibroma, cystic formations);
- acute or chronic glomerulonephritis - an autoimmune process associated with damage to the renal tubules and glomeruli;
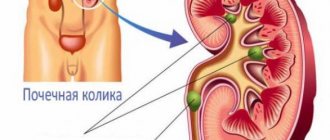
- renal colic;
- kidney injuries.
Advanced Diagnostics
If a positive Pasternatsky symptom is detected, additional examination is necessary to establish a reliable diagnosis and prescribe appropriate therapy. An in-depth examination includes:
- blood tests, general and biochemistry - tests for glucose levels, total protein, electrolyte concentrations, alpha-amylase, creatinine;
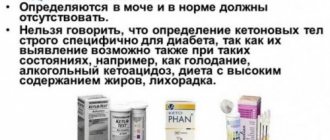
- general analysis of urine with determination of the level of protein, leukocytes, erythrocytes, sugar, bilirubin, ketone bodies, flat cylinders, bacteria, specific gravity and density, microscopic examination of urinary sediment;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky test;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- radiography with the introduction of contrast into the urinary tract;
- cytoscopy with biopsy (in the presence of suspicious lesions);
- magnetic resonance imaging.
Such an examination makes it possible to establish the true cause of lower back pain and the presence of red blood cells in urine, and to identify abnormalities in the functioning of the organs of the urinary system and the abdominal cavity. Modern diagnostic methods (MRI, X-ray with contrast) allow you to clearly assess the condition and internal structure of problem organs.
Further tactics of the doctor’s actions
After an extensive examination of a patient with a positive Pasternatsky symptom and establishing the cause of the deviations, comprehensive treatment is carried out. The prescription of treatment depends on the diagnosis.
- For urolithiasis, treatment is aimed at using conservative methods, including taking medications that relieve painful spasms, dilate the ureters, increase diuresis and relieve inflammation. If the stones are urate, use products with a dissolving effect. If the stones are large and there is a risk of blockage of the ureter, they resort to endoscopic removal methods and surgical intervention.
- During acute catarrhal processes in the kidneys (purulent forms of pyelonephritis), they resort to intravenous or intramuscular infusion of antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins or penicillins. If the process is complicated by the formation of purulent cavities, they are opened, the contents are removed, and the lesion is washed with antiseptic solutions.
- The disease often indicates kidney failure. Her treatment comes down to the most gentle diet with the exclusion of salt and protein limitation, normalization of metabolic processes. In severe cases (stages 4-5), hemodialysis is indicated to save life.
- For oncological processes in the kidneys, treatment tactics depend on the type of tumor, stage and presence of metastases. If the tumor is benign, it is removed. For malignant tumors, surgical intervention followed by restorative therapy is indicated.
Pasternatsky's symptom allows you to identify obvious and hidden pathologies of the kidneys, urinary tract, and neighboring organs. Some doctors consider the method outdated, but it does not lose its relevance and, in combination with more accurate diagnostic methods, is actively used to detect urolithiasis, various inflammatory kidney diseases, and oncological processes.
Symptoms
The main symptom during testing is pain. It can be mild, moderate, moderate, acute. In the latter case, it is characteristic of spasms and movement of stones. Sharp pain on only one side (rarely on both sides) occurs with purulent inflammation (apostematous nephritis) and damage to the perinephric tissue.
Mild pain plus “clean” urine indicate a false-positive Pasternatsky symptom. It is observed with incorrect location of internal organs, small tumors, and non-aggravated chronic inflammation.
Some symptoms indicate the need for diagnosis:
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes;
- the appearance of swelling in the legs, on the face, its puffiness;
- pain in the lumbar region (this is the main symptom of infectious diseases - pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis);
- frequent headaches;
- chronic pyelonephritis is characterized by several symptoms at once - high fever, hypertension, severe fatigue;
- temperature increase;
- general weakness;
- pain spreading along the spine (without high fever or numbness);
- deterioration in the color and odor of urine;
- reduction in the amount of urine excreted.
However, even in the absence of pain during tapping, it cannot indicate the absence of diseases. They can be in latent form and appear much later.
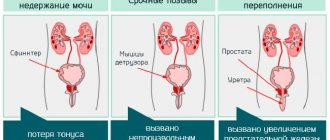
Positive and negative result
When pain occurs with light blows to the lower back in the area of the projection of the kidneys, we can talk about a positive symptom - tapping, when there is no painful sensation - a negative one.
Sometimes there is a false-negative symptom of effleurage. For example, in the case of kidney prolapse (nephroptosis) or dystonia (abnormalities in the location of the kidneys).
Normally, the kidney is capable of moving up and down by a maximum of 2 cm; with nephroptosis, the mobility of the organ goes beyond these boundaries.
With dystonia, the kidney can be located either simply lower than usual, either in the iliac fossa, or in the chest cavity, or between the bladder and rectum; in rare cases, the organ can move to the other side, and then both kidneys will be located only on the left or only on right.
In such patients there will be no pain when tapping the lumbar region.
If kidney disease is in remission, then there may also be no pain when tapping in the area of the 12th rib.
Therefore, if the symptom is negative, it is worth conducting an X-ray examination and ultrasound of the genitourinary system.
Especially if the patient has other signs of the disease:
- bags under the eyes;
- facial pastiness
- swelling of the lower extremities and internal organs;
- cloudiness of urine, changes in its color and odor;
- increase or decrease in daily diuresis;
- nocturia;
- pain when urinating;
- hematuria;
- purulent discharge from the urethra;
- light greenish-jaundiced tint, pale and dry skin;
- weight gain due to fluid retention in the body;
- the patient lies in a forced position, legs bent at the knees;
- the patient's breath smells of acetone, he experiences weakness, delirium and hallucinations.
Pain intensity
Based on the severity of pain, the following types of symptoms can be distinguished:
- the patient may experience unclear sensations when tapping in the projection of the kidneys, then they speak of a weakly positive symptom;
- if the patient experiences tolerable pain, the symptom is positive;
- when the pain is severe (the patient winces or screams) - sharply positive.
In addition, the symptom of effleurage may differ in localization; it can be unilateral (left or right) and bilateral.
It must be remembered that this is a preliminary research method. And even when the symptom is positive, it cannot be said with certainty that this is due to urological problems.
Additional examinations are necessary.
But in any case, the appearance of pain when tapping in the lumbar region is a cause for concern and you should not hope that it will go away on its own and without consequences.
Proper and timely treatment is required.
Reasons for appearance
The main reasons for the appearance of a positive Pasternatsky symptom are inflammatory diseases, swelling of the kidney tissue (amyloidosis, congestion in the organ), concussion and stretching of the organ capsule.
The list also includes:
- Chronic and acute pyelonephritis. This is an infectious kidney disease in the area that is responsible for the outflow of urine. The pathology affects the renal pelvis, parinchema, and calyces.
- Glomerulonephritis. Affects the renal glomeruli.
- Apostematous nephritis. It provokes the appearance of purulent processes in the kidneys. At the same time, many lesions are formed in the cortex.
- Paranephritis and perinifritis. This is a purulent inflammation of the fat capsule and perinephric fat layer with destructive changes.
- Nephrolithiasis (otherwise known as urolithiasis). When stones form in the urinary tract and kidneys.
- Internal organ injuries. These may be vascular lesions, multiple wounds, bruises and tissue ruptures affecting the urinary system.
- Renal colic.
Also, the cause can be any neoplasm (especially malignant) - carcinoma, adenoma, cysts, fibroma, etc., as well as frequent colds that disrupt the functioning of the kidneys and urinary system.
Interpretation of results
A positive Pasternatsky symptom is detected when painful sensations appear on the right or left in the area of effleurage. It is considered strongly positive if the pain increases significantly and is provoked by the research method. This result most often occurs with urolithiasis.
If the patient does not feel any discomfort, then the symptom is considered negative. The medical documentation must indicate the results taking into account both sides. A plus (+) or minus (-) symbol is often acceptable.
We must not forget about the classic description of the procedure. This means that the patient must take a urine test before and after the procedure and compare the content of red blood cells. If an increase in hematuria is detected, then this sign is counted as a positive symptom.
The connection between pain and increased hematuria is important, since pain during tapping can occur not only with an inflammatory process in the kidney or perinephric tissue, but also in cases of pancreatic pathology, myositis, and osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
If Pasternatsky’s symptom is negative on both sides, you cannot calm down and stop testing for renal pathology. The cause may be abnormalities in the localization of the kidneys or the latent stage of a chronic inflammatory process.
In diagnosis, it is important to compare complaints and signs of the disease
Diagnostics
Pasternatsky's symptom is the initial examination of the patient. If the result is positive, additional diagnostics are required. The method requires a mandatory urine test.
Therefore, it is submitted for analysis, which reveals the level:
- leukocytes;
- squirrel;
- Sahara;
- red blood cells;
- ketone bodies;
- bilirubin;
- bacteria;
- flat cylinders.
Indicators of density and specific gravity are also assessed, and urinary residue is examined.
They take blood for analysis (do a blood test and biochemistry), check it for the level of:
- glucose;
- squirrel;
- electrolytes;
- creatinine;
- alpha amylase.
Additional diagnostic methods:
- Zimnitsky's test;
- analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- MRI (magnetic resonance therapy);
- Ultrasound of the kidneys (ultrasound examination);
- CT (computed tomography);
- X-ray with contrast of the urinary tract;
- cytoscopy with biopsy (if there are suspicious pathological foci).
This allows you to accurately determine the cause of pain, the presence of red blood cells and various impurities in the urine, and detect disturbances in the urinary system and abdominal organs.
When to see a doctor
You should consult a doctor immediately as soon as pain appears in the kidneys, lower back, or pelvic area. Also alarming symptoms are changes in the color and smell of urine and a decrease in its excretion, and urinary incontinence. The reason for the examination is a violation of the normal composition of urine and blood, the appearance of blood when urinating.
The primary examination is carried out by a therapist, then the patient is referred to a urologist with the test results. If the reason for the appearance of symptoms lies in current diseases, then the patient is examined by an appropriate doctor (oncologist, surgeon, traumatologist, etc.).
It is also necessary to consult a therapist if any diseases of the urinary system, neoplasms, or back pain occur.
Painful signs of patients
Patient's appearance – swelling appears on the face and legs. The skin of the face has a yellow tint.
Pain in the lumbar region is the main indicator for infectious diseases - pyelonephritis, and hydronephrosis - a disorder of the outflow of urine.
Fever, weakness and headaches are signs of metabolic failure and activation of the inflammatory process. Deterioration in the odor and color of urine, as well as in the amount of urine produced.
If Pasternatsky’s symptom is negative (that is, there is no pain during diagnosis), of course, one cannot assume that the patient may have completely healthy kidneys. Since some ailments may be in a latent form and not manifest themselves prematurely. Therefore, for more effective diagnosis, use:
- Blood and urine analysis.
- X-ray studies.
- Ultrasound examinations.
Prevention
Pasternatsky's symptom is a way to identify diseases of the urinary system. For chronic diseases, mandatory preventive treatment is carried out. However, there are general rules that must be followed to prevent pathologies of the urinary system.
It is important to maintain personal hygiene, use only your own towels, and carefully care for your intimate area. Avoid hypothermia, use contraceptives, and treat current illnesses in a timely manner.
You need to adhere to proper nutrition. Eliminate sweet, starchy, spicy, fatty and fried foods from your diet. Check with your doctor for the amount of water you need to drink. It can be different depending on the existing diseases. Be sure to do morning exercises or at least walk for 40 minutes. in the fresh air. Go to bed on time to get enough sleep and provide your body with proper rest.
Treatment methods
The main direction of therapy for a positive Pasternatsky symptom is medication. Different groups of drugs are selected for treatment, depending on the cause of the positive Pasternatsky symptom and the disease. However, a comprehensive approach is required for complete recovery. Additionally, physiotherapy can be prescribed, and traditional methods can be used aimed at treating the underlying disease that was discovered during diagnosis.
Medications
Diuretics are used to cleanse the kidneys. The most inexpensive are “Furasemide”, “Veroshpiron” (20-70 rubles), the cost of others is higher - “Monurel”, “Fitolysin” (330 rubles), “Canephron”, “Cyston” (400 rubles). The dosage regimen is selected individually, usually no more than 2 times a day.
Medicines are prescribed depending on the symptoms to relieve:
- Get sick. “Analgin” (20-50 rubles), “Ketorol” (70-90 rubles). Quickly eliminate negative feelings. Available in the form of tablets and ampoules for injection. They are used during attacks of pain, no more than 3 times a day.
- Spasms. Neuro- and myotropic drugs are used more often. The best and inexpensive ones include “Drotaverin”, “No-Shpu”, “Dibazol” (all from 20 to 80 rubles). The drugs are usually taken 2 times a day or when cramps or pain occur.
- Inflammation. NSAIDs that are non-addictive and successfully combat fever and pain are preferred. The most common include “Ibuprofen” (20-60 rubles), “Amidopyrine” (40-80 rubles), “Indomethacin” (30-350 rubles), “Meloxicam” (70-100 rubles).
| Short description | Name | Price (in rub.) |
| Dissolve or remove stones. The choice of means depends on the type and size of the stones. | "Nifedipine" | 40-60 |
| "Tamsulosin" | 350-800 | |
| "Cyston" | 100-300 | |
| "Purinol" | 100-150 | |
| Cytostatics are used to treat glomerulonephritis | "Cyclophosphamide" | 90-500 |
| "Azathioprine" | 260-850 | |
| Corticosteroids can be used to treat pathologies of the urinary system | "Dexonal" | 200 |
| "Prednisolone" | 50-150 | |
| Herbal medicines are prescribed for kidney treatment when there are no side effects. Therefore, such funds can be taken from 1 to 6 months. They are suitable for the treatment of almost all kidney diseases. Most drugs have several effects at once - anti-inflammatory, diuretic, antiseptic, immunostimulating. Canephron is suitable for long-term treatment. | "Urolesan" | 260-380 |
| "Gentos" | 380-700 | |
| "Canephron" | 400-480 | |
| Immunostimulants enhance resistance to infections and prevent relapses | "Epifamin" | 1000-1200 |
| "Tamerit" | 1500-2700 | |
| Antihistamines eliminate and prevent allergic manifestations | "Promethazine" | 800-1000 |
| Drugs that dilate blood vessels and stimulate blood circulation | "Bilobil" | 350-770 |
| "Angionorm" | 240-550 | |
| Antiplatelet agents improve blood properties and prevent the formation of blood clots | "Courantil" | 500-600 |
| "Eiferol" | 350-500 |
For purulent-inflammatory processes, strong antibiotics are prescribed (penicillins, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones). In case of acute pathological processes in the kidneys (purulent forms), antibiotics are prescribed in the form of intramuscular and intravenous injections.
Groups used:
- Penicillin. For example, “Amoxiclav” (120-400 rubles), “Augmentin” (120-150 rubles).
- Cephalosporins. For example, “Tsepifim” (110-160 rubles), “Movisar” (70-90 rubles).
- Fluoroquinolones. For example, “Ofloxacin” (60-80 rubles).
- Aminoglycosides. For example, “Gentamicin” (20-50 rubles), “Amikacin” (30-40 rubles).
In increased dosages they are given for nephritis and paranephritis. The cost of drugs is indicated in average values. They may vary depending on the manufacturer and region.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods of treatment are based on medicinal herbs and plants. Decoctions and infusions are prepared from them for internal use. For example, clove oil successfully fights fungi, microbes, and viruses. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, helps accelerate wound healing, and relieves pain. The oil should be taken a few drops daily for two weeks.
For herbal treatment the following are used:
- sage;
- St. John's wort;
- pine buds, needles;
- stevia;
- hernia grass;
- heather;
- lovage root;
- horsetail;
- centaury;
- hop cones;
- valerian root;
- arnica flowers;
- calamus root;
- calendula.
Each herb can be brewed separately or made into mixtures. The method of preparing the infusion is usually the same. Take 1 tbsp. l. dried herb or mixture and brew 250 ml of boiling water. Then drink throughout the day. You can gargle with the infusion and wash the affected areas of the skin to relieve inflammation and irritation.
Natural uroseptics include:
- Birch buds;
- elderberry roots;
- bearberry;
- lovage;
- stinging nettle;
- juniper;
- yarrow;
- rosemary;
- horsetail
It is recommended to use watermelons as a diuretic to cleanse the kidneys. Cranberry helps reduce the frequency of relapses and inhibits the proliferation of bacteria. Garlic can be used as an antibacterial agent. It is aggressive against a wide range of bacteria and successfully fights fungi. Garlic is recommended to be consumed fresh.
Myrrh oil is used as an external remedy. It acts in several directions at once - it destroys fungi, bacteria, parasites. The product can be applied to wounds, rubbed into the affected areas, and warm compresses applied to them. Oregano oil has the same properties.
Other methods
For some diseases, it is necessary to additionally follow a diet. It is selected individually in each case, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body, drug tolerance, concomitant pathologies and age.
For example, in case of kidney failure, it is necessary to exclude salt from the diet, minimize the intake of protein foods, and balance the menu to restore metabolism. In severe cases of renal failure, hemodialysis is performed (this helps save the patient’s life).
Physiotherapy procedures can include:
- shock wave lithotripsy;
- percutaneous nephrolithotomy;
- urethroscopy.
Surgery is necessary if the pain is caused by large stones that can block the ureter. Then endoscopic surgery is performed. Surgical operations are also performed to remove purulent contents. Then the affected cavities are opened and the contents are removed. Then they are treated with antiseptics.
For cancer, treatment depends on the location of the tumor, its size, and stage. Benign tumors are removed. When the cause of pain is inoperable tumors, radiation and restorative therapy are performed. Tumors can be removed along with the affected kidney. In case of metastasis, droppers with special solutions are placed.
Further tactics of the doctor’s actions
After an extensive examination of a patient with a positive Pasternatsky symptom and establishing the cause of the deviations, comprehensive treatment is carried out. The prescription of treatment depends on the diagnosis.
- For urolithiasis, treatment is aimed at using conservative methods, including taking medications that relieve painful spasms, dilate the ureters, increase diuresis and relieve inflammation. If the stones are urate, use products with a dissolving effect. If the stones are large and there is a risk of blockage of the ureter, they resort to endoscopic removal methods and surgical intervention.
- During acute catarrhal processes in the kidneys (purulent forms of pyelonephritis), they resort to intravenous or intramuscular infusion of antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins or penicillins. If the process is complicated by the formation of purulent cavities, they are opened, the contents are removed, and the lesion is washed with antiseptic solutions.
- The disease often indicates kidney failure. Her treatment comes down to the most gentle diet with the exclusion of salt and protein limitation, normalization of metabolic processes. In severe cases (stages 4-5), hemodialysis is indicated to save life.
- For oncological processes in the kidneys, treatment tactics depend on the type of tumor, stage and presence of metastases. If the tumor is benign, it is removed. For malignant tumors, surgical intervention followed by restorative therapy is indicated.
Pasternatsky's symptom allows you to identify obvious and hidden pathologies of the kidneys, urinary tract, and neighboring organs. Some doctors consider the method outdated, but it does not lose its relevance and, in combination with more accurate diagnostic methods, is actively used to detect urolithiasis, various inflammatory kidney diseases, and oncological processes.
( 7 ratings, average: 4.57 out of 5)
Possible complications
Possible complications when making a diagnosis include the difficulty of determining the causes of pain due to effleurage.
Negative feelings can arise due to:
- malfunction of the spleen and liver;
- injuries;
- gynecological diseases;
- pancreatitis;
- intestinal inflammation;
- hematoma;
- musculoskeletal disorders;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- benign or cancerous tumors.
Therefore, a urine test is necessary. Under the indicated conditions and pathologies, it will be normal. The composition of urine changes with diseases of the urinary system.
If the symptom is positive, treatment and prognosis depend on many factors:
- development of the disease;
- its stage, severity;
- accompanying health problems (chronic pathologies);
- patient's age and gender.
Chronic forms of diseases require preventive treatment, then the prognosis will become more favorable. For tumors and purulent pathologies, surgical operations are often necessary. However, this increases the risk of death. Sometimes an unfavorable prognosis is given even with the treatment of urolithiasis, if the stones still increase in size.
If the pathology is not detected in time and timely treatment is not started, this can lead to additional health problems, disability, and the need for surgical intervention. Then the affected organs must be removed, which significantly worsens the quality of life.
Sometimes untimely treatment or lack thereof leads to death. For example, in cases where normal kidney function stops, the urinary tract becomes blocked. This leads to the accumulation of toxic substances in the body, which begin to poison the entire body.
As a result, all internal organs gradually begin to fail, and the functioning of life support systems is disrupted. Even doctors will not be able to help in advanced cases.
Pasternatsky's symptom is a way to identify pathologies of the urinary system. This diagnostic method is especially important for bedridden patients. However, the symptom should not be confused with simple “effleurage”. The Pasternatsky method is always supplemented by urine analysis.