Astigmatism is a disease of the organs of vision, as a result of which the refraction of a light ray inside the eyeball is disrupted. This leads to the fact that the light beam is not concentrated on the retina, but is scattered across it.
Most often, the condition occurs in children as a result of inheritance of a pathological gene or intrauterine development defects. The earlier an ophthalmologist diagnoses the disease, the higher the chance of completely restoring eye functionality.
Reasons for development
Pathology can develop in children for the following reasons:
- inheritance of a pathological gene from one or both parents;
- the presence of scars on the cornea due to mechanical damage, conditions after an inflammatory disease, complications due to surgical intervention;
- keratoconus – excessive thinning of the cornea;
- clouding of various refractive elements of the eyes (cornea, lens, vitreous body);
- Keratitis is an inflammatory disease of the cornea.
As a result of a hereditary factor, uneven pressure is formed on the eyeball over the eyelids, as well as an incorrectly distributed load from the extraocular muscles. The shape of the eyeball does not change.
If the cause of the disease is acquired factors, the refraction of the light beam is disrupted. It disperses across the retina.
Causes
In addition to the hereditary factor, other factors can lead to the development of myopic astigmatism. Their number is quite large. However, most often the formation of the disease is caused by the following:
- Unsuccessful surgical intervention;
- Problems with intraocular blood circulation;
- Injuries;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Negative environmental impacts;
- Regular overvoltage.
Congenital, as a rule, is a simple type of astigmatism. The complex type of this disease, in most cases, is acquired. The ICD 10 code for myopia and astigmatism is different - H52.1 for the first disease, and H52.2 for the second.
Risk group
The following categories of children are most often susceptible to the disease:
- one or both parents suffer from astigmatism and other ophthalmic diseases, such as strabismus;
- survivors of intrauterine infection, exposure to harmful substances, hypoxia;
- premature newborns;
- children who had a history of inflammatory diseases, mechanical damage, or eye surgery.
These categories of patients should undergo periodic examinations by an ophthalmologist and apply the prescribed treatment.
Symptoms
The signs of this pathology are in many ways similar to some diseases that can also affect both eyes. And many people know firsthand what it is. The most common of these symptoms are:
- Visual acuity decreases;
- The eyes quickly get tired and watery;
- It is difficult to see distant objects.
- It becomes difficult to concentrate your gaze on any object;
- Periodic headaches and dizziness are observed;
- Objects may have blurry contours, become distorted and double;
- As a rule, people suffering from this disease can only see an object by bringing it close to their eyes.
Symptoms of childhood astigmatism
Since the disease does not manifest itself visually, it is impossible to determine it independently in early childhood. As the child grows up, he begins to talk. He complains of the following clinical manifestations:
- inability to concentrate on a specific subject;
- decreased visual acuity, inability to see near (with hypermetropia) or distant objects (with myopia);
- severe headache, especially while watching TV, using the computer, or reading;
- fatigue, which can occur even in the middle of the day;
- squinting of eyes;
- redness, pain in the eyes;
- doubling of objects before the eyes, which is quite rare;
- difficulties in determining the distance to the required object.
Based on these symptoms, parents can assume some kind of ophthalmological disease. But an ophthalmologist can confirm it and identify the type of astigmatism.
Classification of disability groups
By and large, visually impaired people are limited in their work only by objective requirements or at the discretion of the employer.
In some cases, people even remain in the same jobs and businesses.
But officially, when registering a disability group, the restrictions according to which a person cannot work are documented:
- under stressful conditions that provoke neuropsychic tension;
- with high humidity and high noise levels in the work area;
- in places with irregular work schedules;
- in chemical production, where activities may be associated with exposure to harmful production factors.
It is obvious that visually impaired people cannot work in places where it is necessary to operate complex mechanisms or perform actions related to the need to concentrate attention and vision.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that determining membership in any disability group rests entirely with the ophthalmologist.
According to current legislation, vision that is no more than 0.03, or the presence of complete blindness, is a key reason for recognizing the degree of disability on a permanent basis. In simple terms, you won’t need to go through the commission again every year.
But there is a small nuance: if a person confirms his disability for 10 years annually, he has the right to be issued 11 times on a permanent basis.
If we talk about the classification of visual disability, it is as follows:
- First disability group. This group can be assigned if there is a 4th degree of visual impairment. The main criterion for this group is considered to be:
- complete blindness
- presence of visual acuity less than 0.04 diopters;
- a pronounced narrowing of the boundaries of the visual field of each eye to 100 directly from the point of fixation.
- Second disability group. It can be assigned only if there are malfunctions in the operation of the visual analyzer. If we talk about the criteria by which the second group can be appointed, they are as follows:
- presence of visual acuity ranging from 0.05 to 0.1 diopters;
a pronounced narrowing of the boundaries of the visual field of each eye to 10-200 directly from the point of fixation.
- Third disability group. It can be prescribed if there is a 2nd degree of dysfunction of the visual organs. The main criteria for assigning group 3 may be:
- presence of visual acuity ranging from 0.1 to 0.3 diopters;
- a pronounced narrowing of the boundaries of the visual field of each eye from 20-400 directly from the point of fixation.
It is worth noting the fact that with this disability group, you can carry out your work activity only in specially equipped places where you can perform manual work without visual inspection.
In simple terms, group 3 is assigned to people who can visually inspect the environment.
This classification also applies to minor citizens of our country. Only here there is a small nuance: they are assigned the status of a disabled child.
READ MORE: Fashionable women's glasses 2020: photos of current models and fashion trends
Before passing the ITU, many people are interested in who is given which group. A visually impaired person is recognized not by how many diopters the person being examined has, but by a number of other, but very important criteria.
Depending on the severity of eye pathology, the chances of partial restoration of their functionality, as well as the assigned degree of disability, citizens are given different disability groups. During the examination, all criteria are taken into account, including the degree of impairment of the functionality of the visual analyzer, which consists of four indicators: functional acuity, visual field, electrophysical indicators and eye performance.
Based on a series of diagnostic measures, the treating specialist will determine which disability group the subject belongs to and refer him for examination.
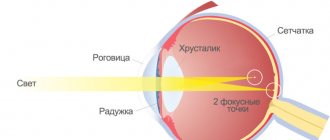
If a person's eyes are healthy, the light entering them is focused on the retina, allowing them to see a clear image. In individuals with myopic astigmatism, this does not occur because light is collected in front of or behind the retina.
Classification of astigmatism
Depending on the age of onset of the disease:
- congenital form;
- acquired form.
The congenital form is divided into several categories:
- physiological – reduction in visual acuity to 0.75 diopters;
- pathological – the decrease in visual acuity exceeds 1 diopter.
According to the degree of disturbance, pathological forms of congenital and acquired diseases are divided:
- weak degree - up to 3 diopters;
- medium degree - from 3 to 6 diopters;
- high degree - from 6 diopters and above.
By type of meridian violation:
- direct form - the highest refractive power is in the vertical meridian;
- reverse form - the highest refractive power is in the horizontal meridian;
- shape with both oblique axes.
There are 2 types of disease:
- correct view - two meridians are perpendicular to each other;
- incorrect view - the meridians are located obliquely.
The correct form is divided into several subtypes:
- simple – one meridian has normal refractive power, the other – pathological;
- complex – both meridians are characterized by myopia or hypermetropia;
- mixed - the most severe form, one meridian is characterized by myopia, the other by hypermetropia.
Depending on the combination with other ophthalmological pathologies:
- myopic form, that is, the patient sees well near, but poorly in the distance;
- hypertrophic form, that is, the patient sees well in the distance, but poorly near.
Depending on the location of refractive error, the disease is divided into 2 types:
- corneal – pathology is localized on the cornea;
- lenticular - the cause is a violation of the curvature and transparency of the lens.
The doctor is obliged to fully classify the disease. This is done using diagnostic tests.
Causes of astigmatism in children
Astigmatism can be:
- congenital;
- acquired.
As mentioned above, it is present to one degree or another in every person. But even a child under the age of 1 year can have astigmatism greater than 1 diopter. It is caused by both genetic predisposition and complications during pregnancy that affect the condition of the lens or cornea.
With astigmatism, the child sees surrounding objects blurry
Acquired astigmatism occurs and develops after birth. It may be a consequence, for example, of injury or an inflammatory disease affecting the cornea of the eye.
Congenital astigmatism most often affects both eyes. Acquired visual impairment can occur in both eyes or in one of them.
A child usually does not feel astigmatism up to 1 diopter. In general, if its value does not exceed 3 diopters, then this degree of astigmatism is called weak.
From 3 to 6 diopters - average degree. With it, the child notices that the clarity of perception of the surrounding world is worse.
More than 6 diopters – high degree. Most often it occurs with pathologies of the cornea, and problems with a clear perception of the surrounding world are often combined with pain in the eyes and headaches. In this case, you cannot do without vision correction, but correcting high-degree astigmatism is not easy.
Diagnostics
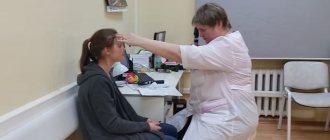
At an appointment with an ophthalmologist, the diagnosis is determined based on a general examination and diagnostic tests:
- Interviewing parents, collecting anamnesis. The doctor will know when symptoms or decreased visual acuity begin to bother them.
- General examination of the child. Visually, no symptoms are detected. He may squint slightly to look at objects.
- Application of diagnostic tables. They depict pictures or letters that the child must identify as directed by the doctor. The more he sees them, the better his visual acuity.
- Autorefractometry. A study that determines the degree of refraction of light rays by the eyeball.
- Fundus examination. Atropine is first instilled into the patient's eyes, after which all intraocular elements are examined.
- Biomicroscopy. This is a device that studies the cells of the surface structures of the patient’s eyeballs during life. An inflammatory condition and degenerative diseases of the cornea are determined.
- Ultrasound of the eyeball. The test determines the shape of the eyeball and intraocular elements.
- Computer keratotopography. This is a study that determines the thickness and structure of the cornea.
- Skiascopy. The technique uses spherical and cylindrical lenses. Tests are used to determine the degree of change in refraction.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor determines not only the presence of astigmatism, but also the root cause. Only after this does therapy begin.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease should be carried out comprehensively. To do this, several techniques are used that allow you to correct visual acuity and the shape of the eyeball.
Optical correction
If a child has astigmatism, visual function always decreases. As a result, he strains his eyes to look at objects. This further aggravates his condition. To prevent this phenomenon, he needs to wear contact lenses or glasses with special lenses.
Gymnastics for the eyes
A simple set of exercises has been developed that allow you to stimulate the oculomotor muscles. With proper tension, the shape of the eyeball improves. It takes 5 minutes to complete the following steps:
- turning the eyeballs up and down, left and right;
- movement clockwise and in the opposite direction;
- blinking frequently for 30 seconds;
- strong compression of the eyelids, then relaxation;
- concentrating your gaze on the closest point in front of your eyes, then moving your gaze outside the window to the horizon line.
Such actions must be performed 1 time in the morning and 1 time in the evening.
Physiotherapy
To stimulate blood flow to the eyeballs, your doctor may prescribe physical therapy. These include electrophoresis, the action of magnetic waves, UHF therapy, and the use of ultraviolet radiation. Due to increased blood flow, more nutrients are supplied to the eyeballs, therefore metabolism increases. This leads to an increase in the rate of regeneration of damaged tissue.
Surgical intervention
You can change the shape of the eyeball using various surgical techniques:
- Keratotomy. During the procedure, the doctor makes small incisions on the cornea, due to which the eyeball lengthens.
- Laser or thermocoagulation. Using a laser or high temperatures, the cornea is cauterized, so it becomes more convex.
- Excimer laser. The technique is indicated for patients who develop mild disease. A section of the cornea is cut out, the bed is cauterized with a laser, and then the flap is installed back.
- Implantation of an intraocular lens. The technique is mainly used for cataracts. This formation is removed and an intraocular lens is installed in its place. It has a hypoallergenic composition, so it does not cause a reaction from the immune system.
The methods must be agreed upon with the doctor; after the operation, the patient undergoes a rehabilitation period.
Komarovsky about astigmatism in children
Dr. Komarovsky talks about how physiological astigmatism is often observed in newborns. This phenomenon should not be corrected; during the development of the eyeball, it is eliminated on its own. If a child suffers from astigmatism with more than 1 diopter, treatment by an ophthalmologist is necessary.
He will prescribe the necessary method of therapy after the examination. Astigmatism must be treated in early childhood to prevent a severe decrease in visual acuity and frequent headaches.
Degrees of myopic astigmatism
There are 5 known degrees of eye disease.
- The first one is not so scary, it is easy to treat, the error is 0.1–0.2. Vision is almost intact.
- The second degree of impairment is visual acuity of 0.5–0.7 units.
- The third is considered a turning point, here the visual error is about 0.6 units in the minus.
- The fourth is marked by a prescribed sharpness of 0.05–0.2.
- The deplorable fifth is difficult to recover, its indicators are below 0.05.
High myopia with astigramtism, depending on the severity of the distortions, is divided by doctors into 3 degrees:
- Weak, characterized by a deviation of no more than 3 diopters. In this case, a person may well not notice the disease, since its symptoms practically do not appear.
- Average. Here the deviations range from 3 to 6 diopters, and the distortion of objects is very clearly visible.
- High – over 6 diopters. In this case, surrounding objects seem elongated to the patient. All this significantly worsens the quality of vision, and the patient requires qualified medical care.
Prevention
Congenital astigmatism cannot be prevented. You can stop its development due to the appearance of a primary disease:
- timely treatment of inflammatory processes in the eye area;
- See a doctor if there is any mechanical damage to the organs of vision;
- correct posture;
- daily gymnastic exercises for the eyes;
- proper nutrition, use of multivitamins;
- classes and work in a well-lit room.
Astigmatism can lead to severely reduced visual acuity if left untreated. Therefore, it is necessary to detect the disease in a timely manner, as well as carry out preventive procedures for children from an early age.
Causes of complete or partial loss of vision
Causes may include head and eye injuries, constant work in poor lighting, and violations of computer work rules.
In addition to the hereditary factor, other factors can lead to the development of myopic astigmatism. Their number is quite large. However, most often the formation of the disease is caused by the following:
- Unsuccessful surgical intervention;
- Problems with intraocular blood circulation;
- Injuries;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Negative environmental impacts;
- Regular overvoltage.
Congenital, as a rule, is a simple type of astigmatism. The complex type of this disease, in most cases, is acquired. The ICD 10 code for myopia and astigmatism is different - H52.1 for the first disease, and H52.2 for the second.