Mixed astigmatism
An ophthalmological disease in which characteristic abnormalities are observed in each eye. Pathology refers to complex vision defects. Features: the problem exists in two organs of vision at once. In one of them, visual impairment in the form of farsightedness and myopia is simultaneously present. As a result, the image received by the eye is focused both in front of the retina and behind it (twice), but not on the retina directly - there is a strong distortion of objects and faces, blurriness and a veil.
With mixed astigmatism, the following structures are affected:
- retina;
- cornea;
- lens (its shape is disrupted).
Disturbances in the cornea are expressed in the fact that curvatures are observed along several meridians. In some places the shell may be thinner, and in others thicker than normal. A complex of disorders leads to the development of myopia and farsightedness simultaneously. A scar may form on the cornea.
Disease in children
Mixed astigmatism is recorded in children of any age, even from the moment of birth. According to research results, only 2% of cases are the result of injury. Other ophthalmological problems or diseases also influence the development of astigmatism. In most requests, a genetic predisposition and the influence of fetal development problems (including prematurity) are established. If parents have this disease, then in 30% of cases the problem will manifest itself in the child. When the disease affects both eyes, strabismus appears.
If mixed astigmatism develops with additional strabismus, the child may experience mental retardation. This is due to the fact that surrounding objects are perceived unclearly. Early diagnosis is necessary to begin quality treatment.
Causes of pathology
The leading factor in this vision pathology is considered to be a genetic factor - inheritance of the disease from parents.
Hypermetropia or farsightedness is often a congenital pathology, its cause is the underdevelopment of eye tissue while in the womb or premature birth.
Myopia or myopia, although it does not appear immediately, is also due to genetic reasons that code for insufficient tissue strength. It has recently been suggested that the main cause of myopia is prolonged exposure to confined spaces with unnatural lighting.
Mixed astigmatism is caused by opacities and scars of the cornea, eye surgery, trauma, changes in intraocular pressure, and impaired blood circulation in the eye.
Changes in the curvature of the lens as a result of injury also cause mixed astigmatism, but then it is called irregular.
Causes
The development of the problem is influenced by the following reasons and factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- eye injury;
- consequences of surgical interventions;
- infectious diseases affecting the cornea (herpetic keratitis);
- chemical damage;
- deformation of the dental system (trauma, birth defects);
- prematurity;
- thermal effects;
- degenerative processes occurring in the cornea or lens;
- endocrine diseases.
External factors can influence the development of the pathological process - unfavorable environmental conditions, lack of vitamins and nutrients. If keratoconus is not treated, the likelihood of this form of astigmatism increases. Dystrophy and thinning of the cornea occurs.
Surgical treatment
Thanks to timely surgical intervention, it is possible to completely relieve the patient of mixed astigmatism. The operation is performed on patients over 18 years of age. A prerequisite for a safe procedure is that the patient does not have retinal pathologies or scars in the area of the eyeballs.
The most effective and safest way to restore normal vision is correction using a laser beam. This surgical method involves making laser incisions, affecting certain layers of the cornea, giving it the correct shape. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Extremely rarely, if there are serious indications, general anesthesia can be used.
Laser treatment of mixed astigmatism allows you to have a favorable prognosis and expect a complete recovery. This form of surgery does not require long-term recovery and does not cause dangerous consequences or complications.
The second method of surgical treatment, keratotomy, involves applying micro-incisions to the eye cornea to change its curvature. During the operation, the doctor uses a special diamond blade.
Unlike laser correction, keratotomy requires mandatory hospitalization of the patient. In most cases, surgical procedures are performed under general anesthesia.
Today, keratotomy is considered an outdated method of treating mixed forms of astigmatism. In terms of frequency, this type of intervention is inferior to laser exposure, and is rarely performed due to numerous disadvantages (low efficiency, long postoperative period with regular pain, considerable likelihood of complications).
Classification
The disease has two main forms:
- congenital mixed astigmatism;
- acquired.
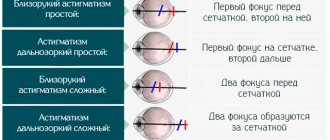
There are also several degrees of manifestation of pathology:
- weak or first – indicators up to 3 D;
- middle (second) – 3-6 D;
- high (third) – indicator above 6 D.
Congenital astigmatism appears immediately after birth. The problem must be treated therapeutically in order to reduce the severity of the disorders or completely eliminate the symptoms. Acquired mixed astigmatism is a disease that arises and develops under the influence of negative factors.
It must be remembered that children may have physiological astigmatism, which is due to the fact that the organs of vision have not fully formed their functions. In this case, the indicator is equal (in maximum value) to 1D. Visual acuity is not affected. If correction is not carried out, then the likelihood of astigmatism turning into a real disease increases, as a result of which distortions and a veil appear before the eyes.
Manifestations and symptoms
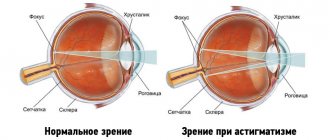
Mixed astigmatism causes the formation of a fuzzy, curved image of visible objects on the retina. If a person looks at an object from different angles, its outline on one side may appear blurrier and more distorted than on the other.
This occurs due to differences in optical power in different meridians of the astigmatic eye.
Thus, experts include the following as manifestations of this type of astigmatism:
- Deterioration of vision, with curvature of the boundaries and lack of clarity of visible objects.
- Inability to determine the size of visible objects and the distance to them.
- Rapid eye fatigue.
- Frequent dizziness and headaches.
In addition, other symptoms are often observed (irritability, frequent mood swings, etc.), which are considered common to all types of astigmatism.
Symptoms
The disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- frequent or severe dizziness;
- rapid eye fatigue while reading, working at the computer, concentrating on a specific subject;
- headache;
- nausea;
- irritability;
- increased fatigue;
- tightness and discomfort in the area of the brow ridges;
- blurred vision;
- Difficulty focusing vision while writing text or drawing.
Also, a person begins to squint his eyes, straining them in order to read the text. Children tilt their heads to look at an object or inscription.
Main symptoms
A defect in the visual organ is expressed by obvious symptoms:
- eye fatigue sets in too quickly, and it doesn’t matter how long the load lasted;
- visual acuity is lost;
- objects around are perceived in a distorted state;
- the patient finds it difficult to clearly determine the distance of objects;
- there is a feeling of pressure in the eyes;
- dizziness often occurs;
- the person constantly blinks, experiences a feeling of pain in the eye, as if sand had gotten there;
- a veil regularly appears before your eyes;
- bright light causes unpleasant, even painful sensations;
- objects within visibility bifurcate;
- vision is poorly focused.
If any of the symptoms or a series of them occur, it is necessary to urgently visit an ophthalmologist for timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Diagnostics
Only a specialist can make a diagnosis. It carries out the following activities:
- assessment of symptomatic manifestations (patient survey);
- taking an anamnesis (taking into account the presence of ophthalmological diseases in close relatives);
- conducting the Siemens test;
- measurement of visual acuity (corrective cylindrical lenses);
- measuring the refraction of the eye (refractometry) - it is possible to identify the degree of astigmatism.
If laser treatment has been previously performed, then keratotopography is performed at the diagnostic stage.
The study provides information about the thickness of the cornea. Also during the examination, bar-skiascopy is performed - an objective method for determining the refraction of light rays in the eyeball (a skiascope is used).
Additional diagnostics:
- CT scan;
- ultrasound examination of the eye;
- biomicroscopy;
- ophthalmometry.
Studies are prescribed when the information obtained is not enough to make a diagnosis or the patient is undergoing surgery.
Treatment options
To normalize visual function and prevent the progression of pathology, both conservative and surgical techniques are used. The former are more effective for mild mixed astigmatism. The second - at medium and high.
In childhood, it is better to give preference to wearing glasses. They will help eliminate the difference in refraction between the main optical axes.
But glasses have several significant disadvantages:
- lack of lateral vision;
- difficulty in selection;
- your eyes need more time to get used to them;
- do not fully correct refractive errors;
- Not suitable for active games or sports activities.
For adults, toric lenses are more suitable. They are free from all of the above disadvantages. This is a modern and convenient way to eliminate vision problems.
Surgical correction methods are used for patients aged 18 to 45 years (with the exception of emergency situations). Astigmatic keratotomy is an operation in which the surgeon manually makes incisions into the cornea. During the rehabilitation period, they heal, thereby changing the shape of the cornea. Nowadays such intervention is rarely performed. It has a number of side effects, a long rehabilitation period and does not always allow you to get the desired result.
The use of laser is a modern and highly effective technique for correcting refractive errors. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. During the intervention, the patient does not experience any discomfort. Using a laser, tissue is removed from the outer layer of the cornea and its central part, thereby increasing the optical power in the meridian. The procedure is carried out in a few minutes. There is no long rehabilitation period.
Contraindications for laser correction:
- diabetes;
- progression of the inflammatory process in the organs of vision;
- glaucoma;
- pregnancy;
- keratoconus;
- changes in the fundus of the eye.
If both conservative and surgical methods do not bring the expected result, they resort to more radical measures - lens replacement, corneal transplant, installation of an intraocular lens.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures consist of wearing glasses with special lenses. For children - on an ongoing basis for the entire period of correction. Adults may not use glasses all the time, but only when there is heavy strain on the eyes (reading, working on a computer, performing tasks that require eye strain). Surgical intervention can completely eliminate the disease. Eye exercises are prescribed to consolidate the achieved results and in the process of preventive treatment.
Optical correction
The main method of vision correction. Glasses with special diopters or contact lenses are used. The indicator is detected by the doctor at the diagnostic stage. The use of lenses is preferable, as they fit more tightly to the cornea. As a result, the optical error is reduced.
Laser correction
It is carried out to obtain a quick effect. The cornea is exposed to a laser beam, as a result of which it is possible to achieve the required vision correction parameters. There are contraindications to the procedure (it is not performed on children, patients with cataracts or glaucoma, or pregnant women).
We recommend reading: Laser vision correction for astigmatism
Surgery
It is carried out when other treatment methods have not yielded positive results. In case of damage to the retina or the presence of endocrine diseases, the possibility of such intervention is further discussed with the doctor.
Eye exercises
Allows you to relax your eye muscles and give them additional rest. It is recommended to carry out rotational movements (clockwise). You need to do it for 20-30 seconds several times a day. You should also blink frequently - this helps relieve eye strain.
We recommend reading: Eye exercises for astigmatism
Types and severity
Ophthalmologists distinguish 2 types of mixed astigmatism:
- congenital - if one or both parents have a pathology, then the child is highly likely to inherit it;
- acquired - can occur as a complication after an illness, surgery or injury to the visual organ.
Astigmatism is divided according to severity:
- for weak – the most common type (up to 3 diopters), which quickly lends itself to non-surgical and surgical treatment;
- medium - a rarer type (from 3 to 6 diopters), corrected with contact lenses, glasses or laser correction;
- severe - appears with severe violations or damage to the cornea, can only be treated with surgical methods (from 6 diopters).
Useful video
In order for treatment and prevention to be effective, it is recommended to watch the video
Following the recommendations and timely consultation with a doctor will help you avoid complications and quickly return your vision to normal.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Why is astigmatism dangerous?
Many people who notice the first signs of astigmatism are not in too much of a hurry to see a doctor. And in vain. Left untreated, it can lead to frequent headaches and sore eyes. Childhood astigmatism is especially dangerous. Without quality treatment, a child may develop strabismus and a sharp decline in vision. Many parents are trying to find out how to treat astigmatism in children at home. There are some tips for treating this condition at home. But they will only be beneficial if they are carried out in combination with high-quality medical treatment.
Limitations with astigmatism
What should you not do if you have a refractive error? People with this diagnosis should not engage in activities related to computers, precision instruments and small parts. If the sphericity of the cornea of both eyes is impaired, the following recommendations should also be followed:
- stop driving at night;
- Avoid watching TV or reading books for long periods of time;
- do not read in poor lighting;
- Avoid watching movies in 3D.
If there is a progressive refractive error, then driving a car and serving in the army is prohibited.
Is severe astigmatism treatable or not? The pathology is treated regardless of the degree, but the method of therapy may differ.