Symptoms
The disease often affects school-age children. A child with astigmatism confuses numbers and letters with similar shapes. Objects may appear blurry.
- A characteristic sign of the disease is pain above the eyebrows.
- Astigmatism causes headaches.
- A feature of the disease is asthenopia, in which the organs of vision quickly become tired.
- Symptoms include the sensation of a foreign body in the eyes.
Children with astigmatism are forced to change glasses. If the disease is at an early stage, slight blurring of vision is observed. The contours of objects are perceived as distorted. Some people experience double vision and the eyeball turns red. If the organs of vision are under heavy load, a burning sensation appears. If you detect any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor! The specialist will prescribe a comprehensive diagnosis, based on the results of which treatment will be selected.
Treatment of hyperopic astigmatism
Based on examination data, the degree of damage and the individual characteristics of the body, the doctor chooses an effective treatment for hypermetropic astigmatism.
If the disease is detected at the very beginning of its development, when the problem is mild, the patient is prescribed vision correction. For this purpose, glasses or contact lenses are used. These methods help correct vision and restore its sharpness.
An ophthalmologist will tell you how to use this device correctly. To restore vision, doctors recommend astigmatic lenses.
They come in two types:
- hard;
- flexible.
Lenses are negative or positive. The correct structure of these products helps to change the direction of light, which is focused in the required areas of the eyeball. Through this change, the error in the visual organ is corrected. Glasses are prescribed for illness in childhood.
Constantly wearing these lenses helps prevent strabismus. All these treatment methods effectively correct visual acuity. For this reason, such therapeutic options are resorted to in the early stages of pathology.
Surgical intervention
In more severe cases, as well as in order to completely get rid of farsighted astigmatism, surgical actions are required to correct the shape of the cornea. Such operations are performed by doctors specializing in microsurgery.
The most effective methods of influencing the cornea are recognized:
- Laser thermokeratoplasty.
- Laser keratomileusis.
With the help of these measures, you can change not only the shape of the cornea, making it convex-flat in the central part, but also quickly restore visual acuity. Sometimes such treatment cannot be carried out.
Diagnostics
To identify astigmatism, you need to resort to different procedures.
- A vision test is required. The examination reveals the degree of refraction.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye is performed.
- The fundus and vitreous body are examined.
- Ophthalmometry is performed.
- An integral part of the diagnosis is computer keratotopography.
- Ultrasound of the eye and measurement of intraocular pressure are also necessary.
Early diagnosis improves the prognosis of the disease. If you start treatment on time, you can achieve good results and correct your vision as much as possible.
Therapy cannot be delayed, otherwise the disease will progress: vision will begin to deteriorate, amblyopia will intensify.
Diagnosis of astigmatism
Diagnosis of astigmatism consists of a set of step-by-step studies with the ultimate goal of making a more precise diagnosis to prescribe the most effective treatment.
- Visometry
is a test of visual acuity by examining a table with letters or pictures for children familiar from the ophthalmologist’s office (Sivtsev-Golovin table). The study is carried out in a darkened room with a illuminated table located 5 meters from the patient. One by one, starting from the right eye, visual acuity is determined, gradually moving from large letters to small symbols. - Skiascopy
is Kanye's shadow test for studying refraction. The doctor, turning the ophthalmoscope mirror vertically and horizontally, looks at the reaction of the pupil to the shift of light and shadow. This determines the ability of the eye to refract rays of passing light. - Ultrasound examination of the eyes
is a modern effective way to observe the anatomy of all eye structures and their pathological changes in a three-dimensional image. Before the procedure, a local anesthetic is injected into the conjunctival cavity. There are no contraindications. - Direct ophthalmoscopy
- a special device is used to examine the fundus of the eye and determine the transparency of the optical media of the eye. During the examination, inflammation, trauma, degenerative changes in the retina, eye vessels, and vitreous are visible. The high-precision method reveals the smallest pathologies when the fundus is magnified by 15-20 times. Contraindications include glaucoma, cataracts, and vitreous opacities. - Measuring intraocular pressure
- determines the dynamics of the outflow and inflow of intraocular fluid. Contact tonometry according to Maklakov using weights is currently being replaced by non-contact pneumometry. - Biomicroscopy of the eye
is a method of microexamination of the conjunctiva, eyeball, lens, vitreous body, cornea and iris. Accurately identifies defects in the microstructure of different parts of the eye using a binocular microscope and a slit lamp. The method is painless, non-invasive and has no contraindications. - Ophthalmometry
- measuring the curvature of the cornea with a keratometer. Optical sensors capture the reflected image from two parallel points on the cornea. The result is calculated by a computer. Determines the degree of astigmatism. - Computer refractometry
is a hardware examination of the eyes to determine the refractive power of the optics of the eye to its longitudinal axis. The method is modern, accurate, and allows you to identify emerging deviations at an early stage. Contraindications include patients with cataracts, corneal cataracts, or vitreous opacities. - The computer keratotopography method
gives an idea of the curvature of the anterior and posterior surface of the cornea. The result is color images of areas with different sphericity, shown in blue, yellow, red and green.
Conservative way
Astigmatism requires optical vision correction. The doctor recommends wearing glasses or special contact lenses.
In most cases, glasses with cylindrical lenses are prescribed. The latter can be positive or negative.
The choice of glasses depends on the form and type of disease. This attribute is affordable and allows you to quickly correct your vision.
Expert opinion
Smirnova Ekaterina Anatolevna
The doctor is a general category therapist. Work experience - 7 years. Annually improves qualifications within educational programs
Wearing glasses has its downsides. They fog up: the child cannot play sports. Therapy using glasses leads to impairment of lateral vision, as well as the stereoscopic effect.
If this attribute breaks, eye injury may occur. As we have already noted, contact lenses are used to correct vision.
Previously, hard lenses were in demand. They are not as easy to use as modern ones.
Today, doctors recommend toric, spherical lenses. An ophthalmologist selects lenses.
Orthokeratology lenses are used to correct vision. They are made of high-quality gas-tight plastic. These lenses are recommended for night wear. They influence the surface of the cornea - correct its curvature. Orthokeratology lenses should be applied before bedtime.
Conservative treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Glasses and contact lenses must be changed, taking into account the progression or retreat of the disease. The doctor makes changes to the treatment method.
Treatment
There are currently no drugs that can cure astigmatism completely. Therefore, depending on the type and degree of refractive pathology, different types of correction are used.
In case of a simple disease of the hypermetropic type, spectacle correction is sufficient, which can completely remove all interfering symptoms. For this purpose, cylindrical lenses are used, the selection of which usually does not cause any difficulties.
In case of complex pathology, toric lenses are required, one part of which corrects farsightedness, and the other part corrects astigmatism itself. Means of optical correction require careful selection in accordance with the degree of the disease.
Surgically
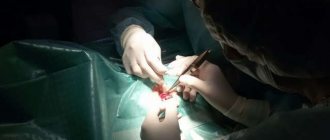
Let us remind you once again that conservative methods do not guarantee a complete cure. They temporarily correct vision. For astigmatism, surgery is often prescribed. Excimer laser correction is a progressive treatment method.
The procedure is similar to surgery and lasts 15 minutes. During the process, a local anesthetic is used. Microtomes are used to carry out Excimer laser correction.
It helps to separate the surface of the cornea. The laser is launched into the deep layers. Using it, the doctor vaporizes the surface of the cornea. Then a flap is placed in place of the optic organ (collagen is used for fixation).
The advantage of laser treatment is the absence of stitches. The epithelium near the flap is restored without outside help. Laser treatment does not require a long recovery period. The procedure gives almost instant results. After one and a half to two hours, vision improves. Within a week the improvement becomes more noticeable.
The most popular treatment method is Astigmatomy. This is a surgical procedure in which micro-incisions are made into the cornea.
This manipulation is recommended for people who have myopia or mixed astigmatism. The operation may involve refractive lens replacement. This type of procedure is prescribed for severe deformation of the visual organ.
Astigmatism degree
- There are three degrees of astigmatism:
- Weak. Up to three dioptres (3 D). With mild astigmatism, the patient may not notice any changes. Some patients complain of eye fatigue, especially after hard work, headaches, and periodic blurred vision (especially in poor lighting). For correction, special lenses are selected that have a cylindrical or spherocylindrical shape. These glasses or contact lenses look no different from regular corrective lenses, but they have a component that compensates for the irregular shape of the cornea or lens.
- Average. At this degree, astigmatism is 3 - 6 diopters. This degree of refractive error rarely goes unnoticed. Vision without correction means is low and the patient usually asks to be prescribed glasses or contacts.
- Strong. The degree of astigmatism is 6 diopters or more. The quality of life with this degree of astigmatism in the absence of correction is very low. Children with such astigmatism need to carefully select corrective optics and undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist. As for adults, the option of surgery cannot be ruled out.
When we, doctors, talk about astigmatism and its treatment in adults and children, we divide this disease into two types:
- Correct astigmatism. This is usually a congenital abnormality that can be easily corrected by fitting glasses or contact lenses.
- Irregular astigmatism. This type of astigmatism develops throughout life. Deterioration of vision can be caused by injury, inflammation, or the consequences of eye surgery. In case of irregular astigmatism, conventional methods of vision correction are ineffective. In some cases, laser vision correction may help.
Ophthalmologists also use the following classification:
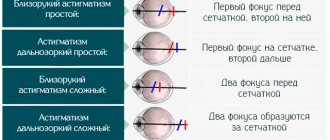
- Hypermetropic astigmatism in children and adults is characterized by a violation of the focusing of rays. In this case, normal refraction of rays occurs in one meridian and weakened refraction is observed in the other meridian. As a result of hypermetropic astigmatism, part of the rays entering the eye stop at a point located on the retina, and the second part of the rays is focused behind the retina.
- Complex hypermetropic astigmatism is characterized by weakening of refraction already in two meridians. In this case, image formation occurs outside the retina, or rather behind it. As a result, all objects appear distorted to the patient.
- Myopic astigmatism. In this case, correct refraction occurs in one meridian, but in the other meridian the refraction is too strong. As a result, one part of the rays is focused on the retina, and the rays passing through the astigmatic meridian are collected in front of the retina, so the image is unclear.
- Complex myopic astigmatism. With this type of astigmatism, too much refraction of rays occurs in both meridians. At the same time, the degree of refraction is different. The image is formed in front of the retina. The patient does not see objects clearly, only blurred contours. ·
- Mixed astigmatism. One of the meridians has a strong refraction, while in the other the refraction of rays is weakened. This leads to a partial formation of the image in front of the retina (these are rays passing through the meridian with strong refraction), and the second part of the image is formed behind the retina (rays passing through the meridian with weak refraction). Patients note blurriness and blurriness of objects.
Prevention of hypermetropic astigmatism
In most cases, hypermetropic astigmatism in children is a congenital defect. For this reason, prevention of pathology should be carried out from an early age.
For this purpose it is necessary:
- Perform special eye exercises to strengthen the eye muscles. These are glances in different directions and circular movements of the eyeballs, slow blinking.
- Choose the right lighting mode for the workplace area.
- Play sports (running and swimming).
- Organize hardening procedures.
- Provide a balanced diet.
- Perform eyelid massage.
What it is?
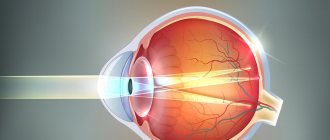
Let's look at what hypermetropic astigmatism is in one and both eyes. To begin with, it is worth noting that normal vision primarily depends on the condition of the cornea and lens. Normally, they should have a smooth spherical surface, which, in turn, ensures refraction of light rays with correct focusing.
In this case, the rays are collected at one point and an inverted image of the observed object appears on the retina, which is recognized by our brain. As a result of exposure to a number of external or internal factors, the shape of the cornea changes. Becoming more elongated and flattened, it causes refractive error. This results in multiple focal points and makes near vision blurry.
In some cases, the shape of the lens changes, which in turn causes fewer symptoms of the disease and is less common. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that the cornea has a greater refractive power than the lens.
When astigmatism is combined with hypermetropia, a difference in the strength that refracts parallel light rays occurs in the two main meridians located behind the retina.
The focusing of rays occurs both on the surface behind the retina itself and on it, which makes vision blurry both near and at a far distance.
A decrease in the clarity of vision at different distances is associated with a deterioration in the accommodation of the eye. The vision of objects in the surrounding world is greatly impaired and a person is able to see only a distorted picture. In this case, the disease can equally affect both one and both eyes.
Causes of hypermetropic astigmatism
Often the disease of both eyes is detected in children. Almost all babies experience this pathology from the moment of birth. This defect is caused by improper development of the apple of the eye.
Therefore, the child begins to develop astigmatism: the lens or cornea becomes slightly bent. These structures of the eye ensure that light is refracted correctly. Due to their deformation, the image visible to the child is not focused on the retina.
Typical causes of the development of congenital pathology are:
- heredity;
- exposure to harmful factors on the fetus;
- complicated pregnancy;
- premature birth.
In adults, the disease develops due to eye injuries that cause deformation of the lens or curvature of the cornea. Often, farsighted astigmatism is a consequence of cataract surgery or other surgical interventions affecting the anterior part of the eyeball.
This is caused by the need to make incisions directly in the cornea during surgery. Afterwards, the edges sometimes fuse incorrectly, causing astigmatism.
A healthy eye is characterized by uniform refraction of light rays and their concentration directly on the retina. Therefore, a person is able to see the clearest outline of objects.
When the lens or cornea is deformed, light rays are refracted unevenly, causing them to focus behind the retinal layer.
Code according to ICD 10
According to the international classification of diseases, astigmatism in adults is assigned code H52.2.
- The use of international classification is used to form a database of diseases. Thanks to this, you can see the overall picture of morbidity in a region or country.
Author: ophthalmologist Kuryanova Irina Valentinovna
Astigmatism is a common visual defect, often diagnosed in both adults and children. What is eye astigmatism, what causes it in a child, how it manifests and is treated, we will learn from the article.
Let's understand the types and classification of pathology (ICD-10 code). Let's find out what consequences it can lead to and whether it is possible to prevent the development of visual impairment in childhood.
How to treat astigmatism
In the treatment of astigmatism, non-surgical and surgical methods are used. A special diet, special gymnastics, surgery, and medications can help in getting rid of visual impairment. Often the listed methods are combined with each other.
In choosing the appropriate method for eliminating pathology, specialists are guided by the degree of astigmatism, the patient’s age, and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Nutrition for astigmatism
Proper nutrition for astigmatism helps maintain the tone of the visual apparatus, saturate the eye tissue with important substances. Patients are recommended to eat food rich in minerals, trace elements, vitamins, and antioxidants.
The introduction of natural products into the diet will bring benefits:
- tomatoes;
- pumpkins;
- carrots;
- cucumbers;
- cabbage;
- beets;
- citrus fruits;
- sunflower seeds;
- nuts;
- greenery;
- melons;
- fish, meat;
- fermented milk products.
You should eat berries such as blueberries, grapes, cranberries, currants, as well as compotes and fruit drinks made from them. Instead of mayonnaise or sauces, you need to season your dishes with a variety of vegetable oils.
Useful exercises
Patients with astigmatism are recommended to perform special exercises up to 5 times daily. A popular complex for astigmatists includes the following exercises:
- Directing your gaze into the distance and then focusing on a nearby object (the interval between manipulations is 30 seconds).
- Close your eyes tightly for 5–10 seconds. After each movement they are opened as wide as possible.
- Turns the eyes in different directions.
- Rotation of the pupils in the direction of movement clockwise and counterclockwise (alternately with open and closed eyes).
Between each exercise, you must perform 20 frequent, rapid blinks.
Surgery
For progressive astigmatism, surgical intervention is often performed. The operation can be performed either traditionally or using modern techniques.
Patients with astigmatism are prescribed:
- keratotomy, which consists of making microsurgical incisions;
- thermocoagulation, based on the removal of part of the corneal stroma through exposure to a certain temperature;
- PRK (photorefractive keratectomy).
Surgical intervention is sought after the astigmatist reaches the age of 18. Until this age, the visual apparatus is in a state of formation, and surgery can become unsafe.
Laser treatment of astigmatism in adults
The surgery performed with a laser is known as laser-assisted intrastromal keratomileusis (LASIK). This method is a modern way of correcting visual impairments, allowing the patient to be treated without dangerous complications.
The principle of the operation is to apply a laser to the surface of the epithelial layer of the cornea, form a flap, and remove the required part of the cornea by evaporation. In most cases, LASIK is tolerated without complications and does not require long-term postoperative rehabilitation.
Ultrasound therapy
This method consists of exposing the damaged cornea or lens of the eye to ultrasonic vibrations. Prescribing such therapy becomes effective if the patient suffers from postoperative and post-traumatic astigmatism, but does not provide the necessary results in the congenital form of the disease.
Ultrasound therapy is contraindicated during pregnancy, heart disease, central nervous system, oncology, hormonal imbalances, and anorexia.
Are medications effective?
The use of medications is most beneficial at an early stage of the disease. Modern drugs that help fight pathology include the following drops for astigmatism:
- Balarpan;
- Emoxipin;
- Ujala;
- Korneregel.
Such products help restore corneal tissue and provide adequate nutrition. Often, drugs in the form of drops are combined with taking ophthalmic complexes with lutein.
Prevention
- It is necessary to follow a daily routine and rest on time.
- Lighting when working must be correct.
- Periodically, you can massage your eyes and perform specialized gymnastics.
- An active lifestyle is recommended.
- Vitamins with lutein are indicated (check with your doctor before taking).
There are no specific preventive measures. You can reduce the impact of astigmatism or prevent its development by doing the following:
- Doing exercises every day, preferably several times a day in short sessions of 6-10 minutes;
- Supplementing your diet with eye-healthy foods;
- The use of vitamin complexes for the eyes;
- Compliance with lighting conditions;
- Timely treatment of eye injuries;
- Dosage of visual loads;
- Eyelid massage performed with careful and gentle movements.
Such preventive measures can reduce the intensity of the impact of astigmatism on a child’s life.
You may also find it useful to learn more about what moderate hyperopia with astigmatism looks like.
Norm and pathology
Translated from Latin, astigmatism means lack of focus.
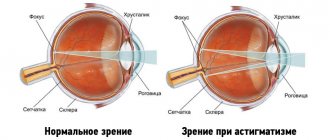
Astigmatism is a refractive error characterized by varying degrees of refraction of rays passing through the optical media of the eye. The rays are collected not in one, but in several foci in front or behind the retina. The result is blurred vision: images appear blurry and distorted, appearing double.
In newborns and infants up to one year of age, visual impairment may be a physiological norm due to the underdevelopment of the visual analyzer. In this case, vision does not deteriorate, and the refractive difference does not exceed 1 diopter. Physiological astigmatism does not require special therapy or correction.
Expert opinion
Smirnova Ekaterina Anatolevna
The doctor is a general category therapist. Work experience - 7 years. Annually improves qualifications within educational programs
The problem disappears on its own as the child grows, his visual apparatus matures and the correct focus is formed. With pathological astigmatism, the degree of refractive error exceeds 1 diopter, which is accompanied by a decrease in vision.
In 90% of cases, the defect is physiological in nature. In 10% of children, astigmatism is a disease that, in the absence of adequate therapy, leads to a sharp and pronounced decrease in vision, the development of strabismus, and amblyopia.
Causes of the disease
According to the nature of its occurrence, hypermetropic astigmatism can be congenital or acquired.
Genetic causation is considered to be prevalent: the disease is inherited by the child from one or both parents. In this case, visual defects will appear immediately after birth.
If the visual impairment due to a congenital disease does not exceed 0.5 diopters, experts talk about functional astigmatism: it occurs in most newborns and, most likely, will not affect visual acuity and binocularity and will go away as they grow older. If the violations reach 1 diopter or higher, the baby will need treatment and special optics to avoid the development of the disease and complications.
Sometimes the disease occurs during life. Causes of acquired hypermetropic astigmatism:
- pathologies of the dentofacial area: with such diseases, the walls of the eyeball can be deformed, causing curvature of the lens and cornea;
- eye injuries;
- consequences of ophthalmological operations: mainly due to synechiae, scars and uneven tension of sutures;
- subluxation of the lens;
- diseases of the cornea: ulcerative, dystrophic lesions, cataract;
- deep keratitis;
- coloboma, cataracts and other diseases of the lens.
Basic information
Patients often ask what farsightedness is. The ophthalmological terminology for this disease is hypermetropia, which is considered a disease of old age, but this is only partly true. The disease occurs in young people and even children. Farsightedness is a refractive error in which the quality of vision decreases when viewing objects that are close to the eyes. This is caused by the fact that the image is focused not on the retina, as in normal vision, but behind it.
Despite the widespread prevalence of farsightedness, I am often asked questions, and this indicates a lack of awareness among people. Not everyone knows that a person is born farsighted. Natural farsightedness in children is associated with some delay in the development of the ocular apparatus, which, in the vast majority of cases, disappears as the child grows, and visual function stabilizes and begins to correspond to the norm.
Acquired hyperopia at the initial stage can only be detected by chance, since it occurs in a latent form, so farsightedness in adults is usually diagnosed when the defect reaches a moderate degree and it is no longer possible to restore vision to normal. That is why there is an opinion that no one can avoid this disease, although early diagnosis can prevent the progression of the disease and further deterioration of vision.
Without timely correction, farsightedness can lead to serious complications. Constant tension of the eye muscles disrupts microcirculation in the structures of the eyeball, which causes diseases such as conjunctivitis and blepharitis.
Moderate hypermetropia in a child without the use of corrective lenses is often complicated by convergent strabismus, spasm of accommodation, myopia, and amblyopia. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend that parents regularly bring their children for examination to a doctor and not ignore the child’s complaints and characteristic symptoms.
Degrees of the disease
When diagnosing hypermetropia and choosing a treatment method, the doctor is guided by several criteria, the most important of which is the degree of this refractive error.
Farsightedness is classified according to severity as follows:
- Mild hypermetropia – up to two diopters.
- Moderate hypermetropia – up to four diopters.
- High degree of hypermetropia - over four diopters.
A mild degree of the disease often does not manifest itself in any way, and the person may not be aware of the existing problem. The quality of visual functions is compensated by the intense work of the eye muscles, and there is no deterioration in the general condition. As the compensatory mechanism is exhausted, the symptoms increase.
Many older people know what grade 2 hypermetropia is. They notice blurred vision near and, to a lesser extent, distance, blurred vision in a darkened room, and other symptoms indicating farsightedness. In moderate cases, the patient realizes the need to see a doctor and begins to use glasses or contacts.
With a high degree of farsightedness, difficulties arise when viewing both close and far objects.
The weakening of visual function occurs gradually as the body ages. Elderly patients are characterized by the presence of hypermetropia in both eyes.
Degrees of development of hypermetropic astigmatism
Doctors distinguish different degrees of development of hypermetropic astigmatism. This indicator allows you to determine the refraction value of rays.
Traditionally, ophthalmologists distinguish the following degrees of the disease:
- Weak degree is the most common variant of the disease. It responds well to conservative therapy.
- Moderate hypermetropia is a less common dysfunction.
- High degree hypermetropia develops due to serious pathologies in the cornea.
The higher the degree of the disease is diagnosed, the more complex the treatment will be. As soon as the first symptoms of a problem are identified, you should immediately visit an ophthalmologist. The specialist will perform a series of diagnostic examinations, based on which he will prescribe an adequate therapeutic course.
The patient must scrupulously follow the doctors' recommendations to ensure vision restoration.
Classification
Based on the characteristics of refractive error and changes in the shape of the cornea, the severity of the pathology, and combination with myopia and hypermetropia, astigmatism is classified into several types.
According to the characteristics of the curvature of the cornea, astigmatism is distinguished:
- regular (correct) – diagnosed when there is a uniform change in the curvature of the stratum corneum of the outer shell of the eyeball;
- irregular (irregular) – characterized by uneven curvature of the cornea.
Astigmatism in children is often combined with myopia or farsightedness.
According to the nature of the focus disorder, eye astigmatism in children occurs:
- Myopic (otherwise myopic). It is characterized by normal refraction of one meridian and enhanced refraction of the second.
- Farsighted (aka hypermetropic). The refractive power of one meridian is weakened, the second is normal.
- Mixed. Combines two types of anomaly (myopic or hyperopic refractive error is noted in both meridians).
- simple (one-sided violation);
- complex (affects both eyes).
Based on the severity of refractive error, there are 3 degrees:
- weak (up to 3 diopters);
- medium (3-6 diopters);
- high (from 6 diopters).
Astigmatism according to ICD-10 has code H52.2. Belongs to class VII (diseases of the eye and its adnexa), category H52 (impaired refraction and accommodation). Code H52.2 denotes all forms of the disease, since they do not have significant differences in treatment methods and level of danger to the health and life of the patient.
Astigmatism - what kind of disease is it?
Astigmatism is a visual impairment in which a person sees image distortion in the form of blurriness, curvature of straight lines and other deviations.
The main cause of astigmatism lies in changes from the normal shape of the cornea of the eye or its lens. This in turn leads to a defocusing of the light beam on the retina from one point to another.
In addition to blurry vision, symptoms of astigmatism include headaches, eye pain, and increased fatigue.
The formation of pathology usually occurs in childhood, in the first three years of a child’s life, and if due attention is not given to the problem during this period, there is a possibility of permanent deterioration of vision. Therefore, astigmatism is most often diagnosed in children.
Development of the disease (pathogenesis)
How to describe astigmatism in simple words? Let's write a couple of simple lines about the structure of the eye, then post a photo of astigmatism and describe how it is formed, as well as its degree. So…
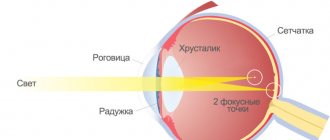
Directly involved in the visual function of the eye are the cornea (the outer and outer shell of the eye), the pupil (the entrance portal for light inside the eye), the lens (actually, this is a lens that corrects the focusing of the light flux), the retina (consists of photoreceptors and nerve endings, where the light flux is transformed into nerve impulses transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve). Of course, this is a very simplified diagram of the eye, but it conveys the essence. The path through which the light flux passes is described in the order in which we indicated the components of the eye.
Pathology is formed due to disturbances in two points - the cornea (most often) and the lens.
The cornea in normal condition in a healthy person has a round, slightly convex shape, which resembles the “cap” of a sphere. A beam of light passes through it and the lens and converges at one point on the retina. If the shape of the cornea is disturbed in the slightest way, the light flux begins to be refracted in different directions and hits the retina not at one point, but at different ones, or ends in front of the retina and behind it. After all, a sphere, be it the cornea, or the globe, has meridians, the refraction of light on which differs (both in length and in direction). The difference in refraction of light flux through the cornea depending on the meridians is measured in diopters (Dopters). Thus, the higher the diopter value, the greater the spread between the central and outer meridians, which indicates a greater convexity of the cornea outward, resembling in shape not a sphere, but a rugby ball.
The same thing happens in the case of deformation of the lens - if it is bent or injured, the light beam becomes defocused in different directions.
The end result is that a person sees the image as blurred, curved, and where there are straight lines, the eye shows them in a curved form. By the way, the test for astigmatism just involves looking at a special picture with straight lines. In difficult cases, the image may be both partially distorted and blurry.
Look at the following image, which shows the cause of astigmatism:
An unpleasant point is that this visual impairment is often combined with other visual pathologies - myopia (myopia) or farsightedness (hypermetropia).
Statistics
Scientists have noticed that a slight degree of astigmatism (up to 0.5 diopter) is present in many people who, before the examination, did not even suspect the presence of this feature, because it did not affect vision.
However, as studies show, at least in the United States, of almost 2,500 children and adolescents aged 5-17 years, about 28% have a pathology of 1 diopter or more.
In addition, a higher percentage of astigmatism was observed in children of Asian (≈33%) and Latin American (≈37%) regions (racial component), while for Europeans this figure stopped at ≈26%, African children ≈20%.
Another interesting statistic is that astigmatism with myopia (myopic form) is almost twice as common as with farsightedness (hypermetropic form).
Causes
Typically, the cause of pathological childhood astigmatism is curvature of the cornea, and only in 2-3% of cases the disorder occurs due to changes in transparency or curvature of the lens.
By origin, refractive error can be:
- congenital;
- acquired.
Congenital astigmatism, often diagnosed in a newborn or infant in the first months of life, can be caused by:
- genetic predisposition (if one or both parents suffered from the disease, the likelihood of its development in a newborn increases significantly);
- congenital diseases of the visual system (albinism, keratoconus, retinal pigmentary dystrophy);
- the birth of a premature baby;
- fetal alcohol syndrome.
Among the causes of acquired astigmatism are:
- subluxation of the lens with rupture of the ciliary (otherwise known as the circular) ligament, which is responsible for the contraction of the ciliary muscle and a change in the curvature of the lens, which ensures the act of accommodation;
- injury to the eye area or previous surgery;
- infectious inflammation of the cornea, which occurs with scarring and changes in its shape;
- frequent respiratory infections, chronic pathologies of the ENT organs (sinusitis, rhinitis);
- diseases of the dental system, occurring with deformation of the orbit and facial bones.
Causes of astigmatism in children
Astigmatic refractive error in a child can be congenital or acquired. One of the causes of congenital astigmatism is heredity. If at least one of the parents has an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, then this feature can be passed on to the child. Sometimes so-called physiological astigmatism is detected in children in the first year of life. It does not pose a threat to vision and goes away on its own in about a year.
Acquired refractive error can be caused by corneal trauma, operations on the visual organs, keratoconus and other ophthalmological diseases, as well as deformation of the walls of the orbit due to improper development of the dental system.
Optical correction
In the prescription, complex glasses are indicated by two or even three parameters: cylinder, axis, sphere.
To correct astigmatism in children using optics, the following is used:
- Complex glasses. For simple forms of impairment, products with cylindrical lenses are used, for complex and mixed forms, products with spherocylindrical lenses are used. At first, such optics cause eye irritation, tearing, headaches and dizziness. Pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky and ophthalmologists recommend enduring this period. Soon the child’s eyes will adapt, the discomfort will go away, and he will see better with glasses. But if these symptoms do not disappear over time, you need to visit the doctor again and make sure that the optics are selected correctly.
- Toric contact lenses. The products are an alternative to glasses, do not cause discomfort or irritation, and do not limit peripheral vision. However, the lenses are more difficult to care for and should not be used by children under 10 years of age.
- Hard orthokeratological (night) lenses. Rigid night lenses, designed to temporarily correct the curvature of the cornea, are worn before bed. Overnight, the shape of the cornea is corrected and vision improves. Over time, the cornea curves again, and the condition becomes the same. Orthokeratology lenses for children are indicated for impairments of up to 1.5 diopters.
If astigmatic disorders persist after the age of 18, laser vision correction or a corneal transplant is performed (for congenital defects or a complex form of pathology).
Types of disease
Source: vision-hyperopie.ru
Depending on the causes of the defect in the visual organs, several types of hypermetric astigmatism are distinguished:
- simple;
- difficult.
Simple hypermetropic astigmatism is characterized by distortion of the visible image in one eye. The complex form affects both visual organs, sometimes with varying degrees of severity.
The mixed form is a defect of both visual organs, but with different pathologies. The mixed form is characterized by a combination of myopia and farsightedness.
The simple type is always acquired - either after injury or after eye surgery. In general, no therapy is required.
However, if the pathology interferes with a normal lifestyle - reading text without double vision, nightly headaches, pain in the bridge of the nose - treatment is prescribed. Complex hypermetropic astigmatism requires immediate correction.
If with the initial degree of development of farsightedness a person poorly distinguishes objects near, then with a complex degree he sees equally poorly at any distance. The patient suffers from periodic headaches, tears flow from the eyes, and there is constant tension in the visual organs.
Depending on the degree of manifestation, hyperopic astigmatism is divided into three types:
- weak;
- average;
- high.
The initial degree of pathology (weak) is characterized by a complete or partial absence of symptoms. A person can function normally in the world without needing vision correction.
This is especially true for young patients. Doctors consider this condition to be a physiological norm. If the refractive angle is below one diopter, there is no reason to worry.
Moderate hyperopia with astigmatism is a serious vision problem. A person sees a blurred image of the world, he sees double, and when reading lines with written text they “jump.”
To correct pathology in childhood, medicinal glasses are prescribed. However, optics can only temporarily relieve the problem: surgical correction is necessary to restore vision.
High degree hypertropia with astigmatism cannot be treated with lenses and glasses. This is a severe defect of the visual organs, accompanied by a burning sensation in the eyes, severe headaches and tearing.
Based on the predominance of the leading meridian, three types of hypermetropic astigmatism are distinguished: straight - the vertical axis refracts rays more strongly than the horizontal one; reverse - the leading one is the horizontal meridian; oblique - the main axes are not perpendicular to each other, but diagonally.
There are 2 types of pathology. Hypermetropia develops in one eye, while emmetropia remains in the other, which is full vision.
Visual information is transmitted to the retina in one of the main meridians of the visual apparatus in a disease such as simple hypermetropic astigmatism.
This condition is considered normal for patients under 10 years of age. Then the pathology often goes away on its own.
Farsightedness of varying degrees is recorded in the two main meridians of the ocular apparatus in a complex form of pathology. Farsightedness of different magnitudes is characteristic of both eyes.
Complex hypermetropic astigmatism in children under 1 year of age is considered a normal variant. If a one-year-old child has poor vision, consultation with an ophthalmologist is required.
Hardware techniques
When asked by parents whether astigmatism in children can be treated with pharmacological agents, doctors answer in the negative. Astigmatism is not an inflammatory disease, so it is impossible to get rid of the problem with the help of medications. But to prevent impaired binocular vision, amblyopia and other complications, doctors can prescribe local ophthalmic agents to improve blood circulation and metabolic processes in the eye tissues.
Along with medications, hardware treatment methods help prevent the severe consequences of astigmatism:
- ATOS and Amblyocor (magnetic therapy devices are effective in treating and preventing amblyopia).
- Forbis (device for preventing the development of strabismus in astigmatism).
- Sokol (a device for laser therapy improves the functional activity of the visual analyzer and has a positive effect on the functioning of the ciliary muscle).
Symptoms of hypermetropic astigmatism
It is much easier to identify hyperopic astigmatism in adolescence than in younger children. The baby is not always able to understand that visual problems have arisen, so he rarely complains to his parents about this. And adults themselves are not always able to determine the presence of such a disorder in children.
The following symptoms are characteristic of astigmatism:
- distorted perception of objects in the surrounding world;
- double image, the appearance of a foggy haze before the eyes;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- eye irritation, redness;
- recurrent headaches;
- the presence of discomfort in the bridge of the nose and near the eyebrows.
It is much more difficult to detect astigmatism in children than in adults. The child is not always able to notice the development of strange symptoms; he perceives the environment as he sees it. To suspect a problem, parents must observe the child.