Content:
- 1 Uniform load 1.1 What happens when the eye perceives objects located nearby?
- 1.2 What happens when the eye perceives objects located in the distance?
- 5.1 Beware: trap!
Description
What is it and how does it work?
The “Rucheek” eye device is used to improve accommodation and is practiced both in ophthalmology offices and clinics, and at home. The device consists of a lens, light sources and the objects they illuminate. The lens is placed in front of the patient's trained eye and creates the image that he sees. The light emitters are located at different distances and allow you to smoothly move the image formed by the lens from the closest position to the most distant one, due to which accommodation training occurs. Rotating the light sources ensures the alternation of objects, which are letters and silhouette figures. All parameters are adjusted according to the patient’s visual acuity. The device makes it possible to additionally illuminate objects with green and red light.
There are 6 standard vision correction programs; some Rucheyk models have 2 additional ones. The setting allows you to set the duration of the session and select the training mode. Behind the images is a built-in visual acuity test chart. Its backlight is turned on before the start of the procedure and at the end to compare the results “before” and “after” the exercises.
The training device is used for the treatment and prevention of ophthalmological diseases associated with impaired myopic processes. Has no age restrictions.
Why is it used?
The device will be useful for people diagnosed with astigmatism.
Eye training for myopia and farsightedness is a basic vision correction exercise for patients suffering from astigmatism, various types of amblyopia and presbyopia. The simulator is used to prevent the development of farsightedness in children, and is recommended for the restoration of visual muscles and nerves after operations. The main instructions for training sessions at Rucheyka are:
- relieving ocular muscle spasm;
- prevention of myopia and farsightedness in children and adolescents;
- relieving eye fatigue syndrome;
- training of eye muscles for astigmatism and amblyopia.
↑ Uniform load
This exercise supports and improves the accommodative ability of the eyes.
(the ability of the lens to change its configuration), and also trains the lens and ciliary muscle, which regulates its curvature, which is especially important when perceiving objects at close range (increasing farsightedness!).
When you work at a computer or typewriter for several hours every day
- and this is from month to month, from year to year - your eyes are forced to do work at close range. This is a huge burden on them.
The longer your eyes are focused exclusively on objects that are at a close distance, that is, you are forced to constantly look close, the faster they get tired due to the monotonous load.
The eye muscles begin to react sluggishly to light rays coming from outside.
↑ What happens when the eye perceives objects located nearby?
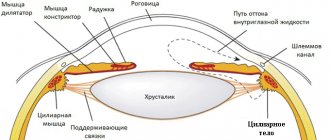
When you look at an object at a close distance, the ciliary muscle tenses to change the refractive power of the lens.
The lens thickens, which provides a clear and sharp perception of a nearby object. When looking closely for a long time, a strong load is felt on the ciliary muscles, as a result of which the eyes quickly get tired.
1 - object located at a close distance 2 - tense ciliary muscle 3 - thickened lens
↑ What happens when the eye perceives objects located in the distance?
When the eyes look at an object located at a far distance, the ciliary muscle relaxes and the lens flattens. The lens rests, since it does not require a large refractive power, as when looking at close up.
When looking into the distance, tension is relieved from the ciliary muscle and lens.
1 - removed object 2 - relaxed ciliary muscle 3 - flattened lens
Free your eyes from the monotony and immobility caused by constantly staring at a computer screen.
After every half hour of intensive work at the computer, typewriter or desk, deliberately direct your gaze into the distance.
To increase the accommodation reserves of the eye
and delay the development of farsightedness, special accommodative exercises are recommended.
Causes
The congenital form of ocular myasthenia appears due to gene mutations that lead to disruptions in the normal functioning of neuromuscular synapses, which act as a specific adapter through which the nerve interacts with muscle structures.
Experts identify a number of specific factors contributing to the onset of the disease:
- Tumor-like neoplasms of benign or malignant nature.
- Benign hyperplasia is manifested by the proliferation of glandular tissue and stroma, which leads to an increase in the organ and a change in its functioning.
- The presence of dermatomyositis - a diffuse inflammatory pathology of connective tissue. It leads to damage to muscle fibers, causing disturbances in motor functions.
- The presence of scleroderma is a systemic disease of connective tissue, which is characterized by changes in microcirculation, inflammatory processes and fibrosis.
In medical practice, there are quite a lot of cases where myasthenic muscle weakness manifests itself in oncological anomalies localized in the following organs:
- prostate gland;
- testicles;
- lungs;
- liver.
Additional causes of acquired myasthenia gravis include:
- excessive physical activity;
- emotional disorders;
- depression.
If we describe the pathology more schematically, we can say the following: the process of a neuron is covered with a membrane that allows certain substances to pass through it. They play the role of specific mediators that transmit impulses from the nerve cell to the muscle receptors. If their work is disrupted, the connection between the transmitter and neuromuscular transmission becomes very difficult. And as a consequence, antibodies destroy auxiliary receptors.
Expert opinion
Author: Olga Vladimirovna Boyko
Neurologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences
Myasthenia gravis is one of the autoimmune diseases. The disorders affect various muscle groups. Doctors note an annual increase in new cases of morbidity. According to statistics, 5-7 people out of 100 thousand people suffer from this disease. In women, myasthenia gravis is diagnosed 2-3 times more often than in men. The onset of the disease occurs at the age of 20-30 years. The exact causes of the autoimmune disorder have not yet been identified.
The ocular form of myasthenia gravis is not as common as other types of the disease. The disease has similar symptoms to other pathologies, which makes diagnosis difficult. To detect myasthenia gravis, CT and MRI are performed at the Yusupov Hospital. The latest medical equipment will quickly determine the location of the pathological focus in the brain. A blood test for antibodies to acetylcholine receptors is carried out in a modern laboratory. Based on diagnostic data, appropriate treatment is prescribed. The therapeutic plan is developed for each patient individually. The prescribed drugs meet European quality and safety standards.
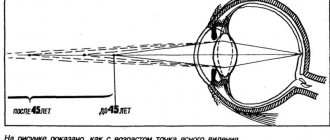
↑ 1. Eye focusing exercise
• Perform the exercise without taking off your glasses. Thanks to this exercise, the ciliary muscle and lens relax.
• Move your gaze several times from nearby objects to objects located at a considerable distance from you (see figure).
Perform the exercise slowly so that you have time to focus on both a close and distant object.
Gymnastics for the eyes during spasm of accommodation
At the first symptoms of eye fatigue or when false myopia is already developing, eye exercises for accommodation spasms are most effective as prevention. Basic exercises:
- horizontal and vertical eye movements (up and down, left and right);
- movements of the eyeballs in a circle (clockwise or counterclockwise);
- intense blinking: intense squeezing and opening of the eyelids;
- movement of the eyes to the bridge of the nose: to do this, place your finger on the bridge of the nose and direct your gaze to the finger;
- diagonal eye movements: first direct your eyes to the lower left corner and then up, in the opposite direction.
↑ 2. Exercise for stepwise focusing of the eyes
• Take off your glasses before performing the exercise!
• Shift your attention away from nearby work at a computer, typewriter, or desk and look into the distance.
• However, unlike the previous exercise, do this in stages, moving your gaze from a close object to a more distant one, then to an object located even further and, finally, to a very distant one.
• When you move your gaze to the next object, take your time, giving your eyes the opportunity to tune in to it, to “sharpen it.”
• When your gaze reaches the farthest object, hold your attention on it for a few seconds, and then move your gaze in the opposite way, i.e. from the farthest to less and less distant, and finally stop your gaze on a closely located object (see pic).
While performing the above exercises, observe the following conditions:
- blink more often when you move your gaze from close to distant objects, while breathing evenly, deeply and without tension;
- if you want your eyes to rest even better, then, after finishing the step-by-step eye focusing exercise, do palming for a few minutes.
Before continuing to work, stretch well, yawn with pleasure, make a few voluntary movements with your arms, shake your hands, move your legs, wiggle your toes, and then get to work with renewed vigor!
You can learn more about the treatment, prevention and restoration of vision from the “Seeing Without Glasses” program from Michael Richardson. The unique method of Natural Recovery will allow you to restore and improve your vision and health up to 100 percent or more. Click here to get rid of diseases forever.
Exercises to improve accommodation
Below is an indicative diagram for the prevention of violations of the accommodative abilities of the organ of vision:
To complete the task you need to take a sheet of text.
- Exercise with a sheet of paper. The patient is recommended to sit near a window and cover one eye with his hand. A sheet with text written on it is slowly approaching another. At the moment of loss of focus, the sheet begins to move away. Then the same is done with the other eye.
- Looking at objects up close. For this purpose, it is optimal to take the same sheet of text and place it as close as possible to the eyes. They try to look at the text for a minute. Then you should give your eyes a rest.
- Defocus. The patient should try to “look into space” for several minutes. At the same time, a “veil” appears before the eyes and the ciliary muscle relaxes.
- Alternately looking at objects far and near. To do this, identify an object outside the window, from which the gaze is sequentially transferred to something located directly in front of the eyes.
- 2 dots on the window. They are drawn or pasted. Then the patient sits on a chair in front of the window and focuses his gaze on one of the points, while at the same time trying to see the other with his side gaze.
↑ 3. Exercise with a calendar
Start working at your desk by picking up a calendar. With its help you will perform a kind of “lens massage”!
Here's how it's done:
• Do the exercise with your glasses off!
• Cover your right eye with the palm of your right hand.
• Take a calendar in your left hand (it can also be a photo, business card, etc.).
• Bring the calendar very close to your open left eye.
• Without straining, focus your gaze to see the numbers on the calendar as clearly as possible.
• Now slowly move the calendar away from your eye until your arm is completely extended (see figure).
• While your eye is adjusting to any part of this distance, blink frequently and breathe deeply evenly.
• Now, just as slowly, return your hand to its original position, bringing the calendar to your left eye. At the same time, exhale.
Repeat these movements several times, performing the exercise for each eye for 20-30 seconds.
• Don't forget to blink often!
Let's work on the other eye
• Change your starting position and cover your left eye with the palm of your left hand.
• Take the calendar in your right hand and do the same movements with it as described above.
• Blink frequently, breathe deeply, evenly and without strain.
Perform each of these exercises until you feel that your eyes are rested.
Perhaps 10 seconds per eye will be enough for you. The main thing is that you feel comfortable.
Do not forget:
After the exercise, do palming for each eye for 1-2 minutes, if possible.
The main set of exercises for farsightedness
Bartsok-course of exercises for the eyes
With farsightedness, the oblique muscles are weakened, and the rectus muscles, on the contrary, are chronically tense. These exercises should strengthen the oblique oculomotor muscles while increasing their mobility and relieve chronic tension in the rectus oculi muscles.
The location and directions of movement of these muscles are shown in the diagram.
Training any muscles is most effective when they are statically tensed for 5-6 seconds, followed by complete relaxation and new tension after a few seconds. This is exactly how you need to train weakened oblique muscles of the eyes (exercises 1 - 4). For chronically contracted rectus muscles, on the contrary, dynamic exercises are useful to relax and increase the mobility (flexibility, softness) of the muscles (exercises 5 - 8).
The complex also includes exercises to increase the flexibility and performance of the ciliary muscle (exercises 9 and 10) and a convergence exercise (gaze, 11).
All exercises should be done 5-7 times a day (not necessarily in a row). When performing exercises, be careful: do not let your eyes get tired, do not allow pain, pain or other discomfort, try to relax as much as possible all the external and internal muscles of the eyes that do not work in this exercise, achieve a gradual increase in the smoothness and amplitude of movements, replace tension with attention, looking at objects in static positions of the eyeball. Give more time and attention to the eye that sees worse by doing more repetitions of exercises. High-quality exercise should gradually reduce your farsightedness. Check weekly to see if you have managed to improve your vision at least a little.
The starting position corresponds to correct posture: the head is turned so that the top of it looks up; shoulders, neck, facial muscles and eyes are relaxed; the gaze is directed forward.
1. Smoothly move your gaze from the center to the upper right corner. It should be exactly above your right shoulder. Move your gaze in that direction as far as you can without pain. Try to carefully, but without tension, examine what is in this corner. Look at the object for 5-6 seconds, then smoothly return your gaze to its original position. After a few seconds, repeat this contraction of the superior oblique muscle of the right eye.
2. Do the same careful consideration of what is in the upper left corner to train the superior oblique muscle of the left eye.
3. To strengthen the inferior oblique muscle of the right eye, gently move your gaze to the edge of your right shoulder to carefully and relaxedly examine it for 5-6 seconds. Then gently return your gaze to the starting position.
4. In the same way, glance at your left shoulder and carefully examine it for 5-6 seconds.
5. Smoothly, without moving your head, move your gaze upward as you exhale. You will see your eyebrows and what is at an angular distance close to them. Without pausing, also gently return your gaze to the starting position. As you exhale, look up again. With smooth, almost pendulum movements, lift your gaze as high as possible (within the limits of what is comfortable and painless) up and lower it to the starting position. Try to avoid speeding up and jerking your eye movements.
6. In the same way, exhale, smoothly move your gaze all the way down and, without pausing, return your gaze to its original position.
7. Smoothly, as you begin to exhale, move your gaze all the way to the right. The left eye will simultaneously see the nose. Without stopping, slowly return to the starting position. You seem to swing your gaze, as if on a swing: to the right and back, ever softer, ever further. Make sure that as you move to the right, you do not lower your gaze, moving the inferior oblique muscle of the right eye.
8. In the same way, move your gaze all the way to the left and return to the starting position. The nose now sees the right eye.
The first eight exercises of the complex can be done separately for one, worse-seeing eye, covering the second eye with your hand.
9. Stick a small piece of paper on the glass of the window. Draw a bold cross or other clear sign on it. Stand opposite the window at the maximum distance so that you can still see the sign clearly, and move a little closer to the window. Cover one eye with your hand. Look either at the sign or through the window into the distance, trying to move your gaze as smoothly as possible. Staying on the sign for 5-6 seconds, try to see it clearly. Don't pull your head back or tense up. Try to ensure the clarity of the image. Help the eye mentally, as if drawing the sign towards you (or draw it into yourself along with your inhalation). After training the muscles of one eye, close it with your hand and train the other. Don't forget to give your eyes time to rest. If there is such an opportunity (for example, a bush outside the window), look into the distance, gradually increasing the distance and also then decreasing it, returning your gaze to the sign. Curtains or blinds can also be used for this purpose. Through open blinds or tulle, you can view distant objects, a mark on the window, and themselves.
10. Take in your hand some object that you can clearly see in all details at least at arm's length. Slowly bring the object closer to your eyes. Go slightly beyond the limit of clarity of vision. Stop the movement and try to get a clear image. Give your eyes a rest, then move it closer to you again. You may physically feel the resistance of your eyes to the approach of an object. Make sure your eye muscles are relaxed, don’t squint, look at the center of your eyes. Don't let the image blur for a long time and don't force things by bringing the subject too close to your eyes. Help your eyes psychologically by mentally pulling the object towards you. Do the same for one eye, covering the other eye with your hand, then change the training eye. Do the exercise either for two eyes together, or for each of them separately, devoting more time to the eye that sees worse.
11. While exhaling, focus your gaze on the bridge of your nose for 5 seconds (yogis call this place the third eye), then smoothly move your gaze in an arc for a few seconds into the distance - at this time you can inhale, then, while exhaling, look for 5 seconds at the tip of your nose and again look into the distance, then again to the bridge of your nose, and so on.
As needed, regularly use a variety of ways to rest and relax your eyes, including our audio recordings.
Like
Modifications
The basic model of “Rucheyok” - TAK-6.2 contains the following components: 8 lamps, letters and silhouettes for vision training, a lens, red and green backlight, a table for testing vision and a frame on which all components of the simulator are fixed. The improved Tak-6.3 model is additionally equipped with black shields that protect the border of the device and create a shadow area around the patient’s face, which helps during the procedure not to be distracted by extraneous irritants and light sources.
Equipment
Perimeter "PERIKOM"
Perigraph "PERIKOM" is a modern domestic perimeter that meets the European standard for reliability, functionality and service capabilities.
Purpose: Perigraph "PERIKOM" is intended for identifying visual field pathologies in glaucoma (including initial ones), diagnosing retinal diseases (thrombosis, dystrophy in the initial phases, diabetic and hypertensive angioretinopathy), as well as pathologies of the optic nerve.
The PERICOM perigraph detects changes in visual fields (including initial ones) in glaucoma: paracentral, arcuate scotomas, “exposure” and expansion of the blind spot, nasal step, sectoral defects. Pathologies in retinal disease are clearly defined: occlusion of the central retinal artery, thrombosis of the central retinal vein and its branches, central chorioretinal dystrophy in the initial phases, diabetic and hypertensive angioretinopathy.
Diagnostic capabilities are significantly expanding for various types of optic nerve pathology: atrophy, retrobulbar neuritis, ischemic neuropathy, compression damage to the optic tract due to tumors of the orbit and brain, hemorrhages and cerebral circulation disorders.
Electroretinograph MBN
A specialized computerized complex for recording and analyzing evoked potentials of the retina and cerebral cortex.
Purpose:
The complex is designed to implement electrophysiological methods for studying the visual system that meet the requirements of international standards.
Namely for:
— conducting a study of various channels of the visual system and studying the mechanisms of visual dysfunction in diseases of the organ of vision of various origins, — diagnosing visual fatigue and intoxication of the body with industrial poisons, including in the zone of environmental disasters, — determining the localization of the process in various layers of the retina, the optic nerve and in the overlying parts of the visual system in case of side effects of medications, - early diagnosis of diseases, - predicting the restoration of visual functions under the influence of conservative and surgical treatment and in the process of rehabilitation.
Ophthalmomyosimulator-relaxator VIZOTRONIK
The Visotronic ophthalmic myotrainer-relaxator is intended for use in ophthalmology for the prevention and treatment of chronic visual fatigue syndrome, computer visual syndrome, spasm of accommodation and acquired myopia in children, adolescents, and young people exposed to intense visual stress in close vision mode.
The operation of the device is based on optical-distant treatment.
The required effect is achieved due to persistent reflex relaxation of the ciliary muscle, as well as increased fitness of the eye muscles, improved hemodynamics, acceleration of recovery processes, increased performance and adaptation reserves of the visual system.
Electrostimulator ophthalmic percutaneous ESOM
Ophthalmotherapeutic laser device SPEKL-M
Magnetic therapy device ATOS-A with attachment AMBLIO-1
Intended for drug-free or local drug therapy of eye diseases such as intraocular hemorrhages, iridocyclitis, optic neuritis, as well as pathologies of accommodation and other diseases accompanied by an edematous component or inflammation.
Bivisotrainer BVTR-2
Designed for training to restore binocular vision.
Operating principle.
The bivisotrainer was developed on the basis of a previously produced cheiroscope device and is a mirror divider of visual fields. During training exercises, the patient observes the image of one of the drawings included in the device with one eye, and reproduces the image on a sheet of paper with the other, thanks to which both eyes “try” to work together. Conducting training with both moving and stationary objects allows you to strengthen the central fixation of the eyes and restore binocular vision.
FORBIS device for diagnostics and diploptic treatment of strabismus
Study of the state of binocular vision and reserves of relative accommodation using three types of division of visual fields: color, polaroid and raster (Bagolini test). This significantly expands the diagnostic capabilities when examining a patient, as it allows one to identify fusional capabilities by conducting diagnostics in stages: from a color test (artificial, more “hard”) to Polaroid and raster tests (in natural light, “softer”).
Diploptic treatment of strabismus using the method of dissociating accommodation and convergence and the relaxation loading method. The device is used to treat patients with accommodative, partially accommodative and non-accommodative strabismus when a symmetrical or close to it eye position is achieved after surgery or optical correction.
Installation of laser stimulation of the retina LAST-1
Intended for the treatment of amblyopia, accommodation spasm, hemorrhage, vascular and any inflammatory eye diseases accompanied by edema.
Operating principle.
The therapeutic effect is based on the pulsed action of low-intensity solid-state laser radiation on a defocused red spot and the formation in it of a special microstructure of alternating dark and light spots (speckle fields). The installation is equipped with a flexible fiber light guide that transmits laser radiation to the manipulator head. The manipulator head can be mounted on any standard ophthalmological device that has a device for fixing the patient's head (for example, a slit lamp, BO).
Device for photomagnetic stimulation of the retina AMBLIO-2
The device for photomagnetic stimulation of the eye AMBLIO-2 is intended for the treatment of mild forms of amblyopia, as well as to consolidate the effect of amblyopia treatment achieved on the ATOS-A device with the AMBLIO-1 attachment.
The therapeutic effect is based on the pulsed effect of light stimuli shaped like stars with rays oriented relative to each other at 60°. Stimuli are formed in the form of red, green, blue and yellow six-pointed stars, included in various combinations. In addition, the color scheme of the presented stimuli may contain additional colors - lilac or orange. Stimuli are alternately turned on and off at a certain frequency. The impact is carried out against the background of a constant magnetic field.
The treatment method does not require fixation of the patient’s gaze, is extremely simple, is not associated with any unpleasant sensations and allows the device to be used at home, in special preschool institutions and schools for the visually impaired.
Apparatus for training accommodation RUCHEYOK TAK-6.1
The RUCHEEK device (“Medoptika-TAK 6.1”) contains a set of light emitters at different distances from the eye. When the emitters are turned on sequentially, the lens located directly in front of the eye forms an image that automatically moves from the minimally close position to practical infinity and back. Rotating the emitters ensures a change in the observed object (letter or figure) and its size in accordance with visual acuity. The speed of image movement is adjustable; in extreme positions the image is briefly fixed. The tilt of the emitter block is adjustable. The color of the emitters can change: either red or green illumination of the observed images is turned on. The digital control unit implements 6 training programs (plus two auxiliary programs). Training programs vary in session duration and the algorithm is used both clinically and at home, and is easy to use. Can be used from 3–4 years of age.
The RUCHEEK device (“Medoptika-TAK 6.1”) is designed for accommodation training. During operation, the patient observes alternately illuminated objects through the lens. Since the objects are at different distances, and the last of them is at the focus of the lens, the observed image moves from a close position (12 cm) to infinity and back. Automatic switching of emitters and adjustable switching frequency ensure ease of use of the device. Each of the eight emitters contains characters of different sizes and types (letters and figures), which are used to configure the device in accordance with the visual acuity and age of the trainee. Color switching (red/green) can also be used for customization.
The device is designed to train accommodation by discrete sequential presentation of signs at a fixed distance from the eye. Signs are observed with one eye (monocular principle of operation) during occlusion of the non-working eye. Used for the treatment and stabilization of the myopic process, relieving spasms of accommodation, for the prevention of myopia (myopia) with weakened accommodation in children and adolescents; adult patients - with initial presbyopia (farsightedness), as well as with asthenopia (visual fatigue) caused by working with a computer, microscope, etc. It can be used to stimulate the organ of vision with amblyopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and also as a postoperative rehabilitation agent.
Application area>
The device is recommended for use in ophthalmic practice for therapeutic and recreational activities. RUCHEEK can be effectively used in combination with other conservative treatment devices in vision care offices, in specialized preschool institutions, and during rehabilitation activities. On the recommendation of an ophthalmologist, the device can be used at home.
Device for low-intensity laser therapy LOT-01
Intended for the treatment of a wide range of eye diseases as part of anti-inflammatory, absorbable and stimulating therapy. The operating principle is based on the use of low-energy helium-neon laser radiation.
Tsvetotest TsT-1
The color test is intended to determine the nature and degree of binocular vision disorders.
The operating principle is based on dividing the fields of view using light filters of complementary colors (red and blue-green). This makes it possible to simultaneously present separate physiologically equivalent tests to the eyes.
Using color testing you can:
— examine the nature of vision (binocular, simultaneous, monocular); - determine the leading eye; — determine the magnitude of the strabismus angle with normal retinal correspondence; — establish the nature of the abnormal correspondence of the retinas.
The color test is a wall-mounted device. The device includes corrective glasses-light filters.