Vision minus 0.5 (-0.5)
The standard table for determining visual acuity has ten rows of gradually decreasing letters.
The top ones are the largest, the bottom ones are very small. A person with 100% vision can easily distinguish all the letters in the table. The worse it is, the fewer lines you can read.
To measure the optical power of the eyes, the unit of measurement used is diopters . A value of -0.5 indicates the presence of myopia.
How does myopia affect vision?
The very name of the disease suggests that vision remains good enough only at close range. Objects located far away blur and become unclear, blurry, because the eyeball takes on an elongated shape and is not able to focus on them: light rays refracted by the lens are collected at one point not on the surface of the retina, as it should be normally, but in front of it.
To view distant objects, a myopic patient squints, when reading, brings the book close to his eyes, and moves the computer monitor to the edge of the table so that the image on the screen is as close as possible.
With vision of -0.5, all these symptoms are not as pronounced as with severe forms of myopia. Inconveniences arise only due to certain types of activities that require concentration and high visual acuity - driving a car, beading, embroidery, outdoor games: tennis, badminton, golf.
What causes the disease?
The loss of shape by the eyeball, impaired refraction of light rays by the lens, and the resulting myopia arise due to many different reasons. These include:
- Eye strain. The reason for this is failure to follow the rules of working with a computer or spending too long at the monitor or reading in low light conditions. This is the most common cause of myopia, accounting for more than half of its cases, and the most favorable in terms of prognosis.
- Chronic infections, rickets, deficiency of vitamins and nutrients and other factors that lead to general weakness of the body and thinning of the sclera.
- Hereditary predisposition. Very often, children with myopia suffer from the same problem from an early age. Therefore, if the mother or father has myopia, you should be especially careful about the condition of the child’s eyes and not neglect regular visits to the ophthalmologist.
- Connective tissue dysplasia. This systemic pathology is accompanied not only by myopia, but also by a whole complex of disorders of the cardiovascular system and musculoskeletal system.
- Congenital malformations. If there are intrauterine disturbances in the formation of the eyeball, it may acquire an elongated shape and lose the ability to accommodate.
There is also false myopia, which often develops with diabetes mellitus and the use of certain medications, such as sulfonamide antibiotics. With it, the shape of the eyeball remains within normal limits, and vision returns to its previous value when medications are discontinued or blood sugar levels are normalized.
It is worth remembering that even if you have a tendency to myopia, it will not necessarily make itself felt, and the disease can be prevented by taking good care of your vision.
Do I need glasses or contacts?
Many people believe that wearing glasses for nearsightedness and farsightedness causes the eye to become “lazy” and vision deterioration progresses faster. Actually this is not true. Moreover, in case of severe myopia, wearing them is necessary.
But with vision of -0.5, it is quite possible to do without lenses and glasses most of the time and wear them only to perform activities necessary for high visual acuity.
Is it possible to completely restore vision or improve it?
In some cases this is possible. For mild myopia (up to -2 ), resulting from eye strain, good results are achieved by gymnastics aimed at training the muscles of the eyeball. From time to time you should break away from your usual activities and do the following exercises:
- With your eyes wide open, outline a figure eight, first to the right, then to the left. Repeat 5-10 times in a row.
- Focus your vision first on a nearby object, then switch to a more distant object. Do this 5-10 times.
- Extend your hand in front of you with some object (a pencil works well) and, moving it from side to side, follow it with your gaze, keeping your head motionless.
- With your feet shoulder-width apart and your hands on your belt, slowly rotate your head left and right, focusing your gaze on objects around you. Do 20 rotations in each direction.
In severe cases, exercises are unlikely to be effective, and only surgical intervention will help the patient, however, with vision of -0.5, they are sometimes enough to return to the desired unit.
Do people with farsightedness join the army?
Farsightedness (hyperopia) is a refractive error of the eye, which results in the inability to focus the image on objects at close range.
They are not accepted into the army with a diagnosis of: farsightedness (hyperopia) of any eye in one of the meridians more than 8.0 diopters;
Hypermetropia and suitability for military service
A medical examination is carried out in accordance with Article 34 of the Schedule of Diseases.
Fitness category “D” (not fit):
If the farsightedness of any eye in one of the meridians is more than 12.0 diopters;
Suitability category “B” (limitedly suitable):
If the farsightedness of any eye in one of the meridians is more than 8.0 diopters and up to 12.0 diopters;
Suitability category “B - 3” (suitable with restrictions):
If the farsightedness of any eye in one of the meridians is more than 6.0 diopters; and up to 8.0 diopters;
Vision plus 0.5 (+0.5)
If a specialist gives this number based on the results of a vision test, this indicates farsightedness. Also known as hypermetropia, it is much less common in young people than myopia. Farsightedness mainly affects people over 45 years of age.
Hypermetropia is also common in preschool children - in this case, it disappears without a trace with the formation of the visual apparatus.
How does farsightedness affect vision?
This disease has a telling name: it is not difficult to guess that with hypermetropia, a person begins to see poorly and blurry near, while objects located far away remain relatively clear.
When reading, the patient tries to keep the book away from his eyes and steps back a few steps from the objects he is about to look closely at. Due to constant eye strain while constantly focusing on nearby objects, headaches and nausea are common.
With visual acuity of +0.5, the symptoms of farsightedness are not too pronounced, but they are already beginning to become noticeable to the patient himself, and begin to interfere with needlework, drawing and similar activities.
What causes the disease?
Flattening of the eyeball or disruption of the refraction of sunlight by the lens leads to the fact that light rays are focused not on the surface of the retina, but behind it. The main cause of farsightedness is age-related changes. It occurs in almost all people over 65 years of age.
In children, hypermetropia is observed from birth until the age 5-6 years due to the underdevelopment of the visual organs. It usually goes away with age, but with intrauterine developmental disorders of the eye it can remain for life and lead to concomitant diseases such as strabismus and amblyopia.
Do I need glasses or contacts?
Many people with visual impairments are afraid to wear contact lenses and glasses because they are afraid of the progression of the disease. There is an opinion that without constant strain, the eyes will begin to see even worse. However, this is a misconception.
If farsightedness does not exceed +0.5 , you can do without glasses most of the time. They should only be worn for work that requires good vision.
Is it possible to completely restore vision or improve it?
The prognosis for farsightedness is usually worse than for nearsightedness - age-related changes in the eyeball are almost impossible to reverse. The only radical method is laser vision correction surgery. However, eye exercises will help slow down the progression of the disease. To do this, you need to do the following exercises twice a day:
- Standing in front of the wall clock, you need to alternately focus on the numbers 9 , 12 , 3 and 6 , making rotational movements with your eyes, first clockwise and then counterclockwise. It’s better to start with 2-3 2-3 every day .
- Make quick eye movements left and right, and then up and down. The number of approaches is similar to the previous exercise.
- Just as with myopia, focus your vision first on a nearby object, and then transfer it to a more distant object. This should be done 5-10 times.
This will strengthen the muscles of the eyeball and improve blood circulation in it, reducing eye fatigue.
Determination of visual acuity + video
Description
Developer:
Medelit 2006
Definition
To
study visual acuity,
special tables are used containing letters, numbers or icons of various sizes, and for children - drawings. They are called optotypes. In physiological optics there is the concept of the minimally visible, distinguishable and recognizable. The subject must see the optotype, distinguish its details, and recognize the represented sign or letter.
The creation of optotypes is based on an international agreement on the size of their details, distinguishable at a visual angle of one minute, while the entire optotype corresponds to a visual angle of 5 minutes.
In our country, the most common method for determining visual acuity is the Golovin-Sivtsev table.
, placed in the Roth apparatus.
The bottom edge of the table should be at a distance of 120 cm from the floor level.
The patient sits at a distance of 5 m from the exposed table. First, visual acuity of the right eye is determined, then the left eye. The second eye is closed with a shutter. The table has 12 rows of letters or signs, the size of which gradually decreases from the top row to the bottom. The table is constructed using the decimal system: when reading each subsequent line, visual acuity increases by 0.1. To the right of each line, visual acuity is indicated, which corresponds to the recognition of letters in this row. On the left opposite each line is indicated the distance from which the details of these letters will be visible at a viewing angle of 1', and the entire letter at a viewing angle of 5'. So, with normal vision, taken as 1.0, the top line will be visible from a distance of 50 m, the tenth line - from a distance of 5 m.
There are people with higher visual acuity
— 1.5, 2.0 and more. They read the eleventh or twelfth row of the table. A case of visual acuity equal to 60.0 is described. The owner of such vision could distinguish with the naked eye the satellites of Jupiter, which are visible from the Earth at an angle of 1”.
With visual acuity
below 0.1, the subject should be brought closer to the table until he sees its first line. Visual acuity should be calculated using the Snellen formula:
VIS= d/D
Where d is the distance from which the subject recognizes the optotype, D is the distance from which this optotype is visible with normal visual acuity.
For the first line D= 50 m.
For example, the patient sees the first row of the table from a distance of 2m
. In this case VIS= 2/50= 0.04. Since the thickness of the fingers approximately corresponds to the width of the strokes of the optotypes of the first term of the table, it is possible to demonstrate to the subject spread fingers (preferably against a dark background) from various distances and, accordingly, determine visual acuity below 0.1 also using the above formula.
If visual acuity
below 0.01, but the subject counts fingers at a distance of 10 cm (or 20-30 cm), then VIS is equal to counting fingers at a distance of 10 cm (or 20-30 cm). The patient may not be able to count fingers, but can detect the movement of the hand in front of the face.
This is considered the next gradation of visual acuity.
The minimum visual acuity is light perception with correct or incorrect light projection.
Light projection is determined by directing a beam of light from an ophthalmoscope into the eye from different sides. In the absence of light perception, visual acuity is zero (VIS = 0) and the eye is considered blind.
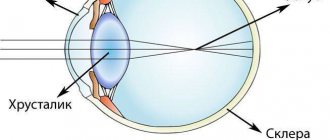
How accommodation affects visual acuity
Accommodation is a dynamic change in focal length from far to near due to tension - relaxation of intraocular muscles and a whole complex of changes in the structures of the eye.
In the context of this article, you need to understand that habitually excessive tension of accommodation (we call it PINA) or spasm of accommodation (as discussed earlier) can significantly reduce visual acuity and cause the appearance of “false” myopia, especially in childhood or during prolonged work at the computer. Laser vision correction does not cure this condition.
In such cases, instillations, sets of exercises, hardware treatment are prescribed, and the need for visual hygiene arises. In this case, thoughtless “additional correction” is not only unnecessary, but even dangerous!
Accommodation scheme