What is Down syndrome
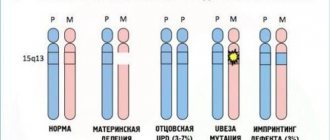
Normally, the human chromosome set contains 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes. But under certain conditions, 21 pairs are capable of mutating (more often tripling), leading to a genetic defect. This is what is called Down syndrome.
The first time manifestations of the disease were recorded in 1866 by a doctor from England, John Down. His name gave the syndrome its name. However, the relationship between the disease and chromosome pairs was established only in the 50s of the 20th century.
Wikipedia interprets this concept as a genomic disorder in which the karyotype contains 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. This happens because 1 of 23 pairs of chromosomes - 21, has 3 copies instead of two.
But this interpretation includes the most common type of defect - trisomy 21 pairs, which develops in all cells of the body. This is the most severe type of disease with pronounced pathologies.
Another variant of the syndrome is Robertsonian translocation. It is found a little less frequently than the first option. With it, 21 pairs are not tripled, but, on the contrary, its chromosomes are glued together, and the total number of chromosomes is 45.
And finally, another type of pathology is mosaic Down syndrome. Its peculiarity is manifested by the fact that the notorious pair of chromosomes is tripled, but the pathology affects only part of the cells.
Mosaicism - general characteristic
The mosaic form of Down syndrome is also called mosaicism. This is the rarest type of this disease, which occurs in two out of a hundred cases. It is characterized by less pronounced symptoms, that is, we can say that this is a mild degree of the disease.
It develops at the earliest stage of embryo formation, which is why not all cells are involved in the process. This feature of this type of pathology significantly complicates its diagnosis.
The severity of this type of syndrome depends on which tissues and how many are involved in the process.
Children with the mosaic form of Down syndrome are able to develop quite normally, their appearance can be quite harmonious. But there are some special signs of pathology.
Some difficulties in such children develop at an early age. During this period, children experience a lag in psychomotor development. As they grow older, these defects are smoothed out, and the mental development of such people is not much different from the average. However, they have a peculiar perception of the world around them and nuances of speech, but similar features are also found in ordinary individuals.
Causes and contributing factors
There are several reasons why mutation of chromosome pair 21 occurs:
- pathological zygotic division;
- chromosomal discrepancies during mitosis;
- recombination of chromosomes;
- inheritance from parents.
Such pathological changes are provoked by a number of factors:
- First of all, this is the age of the parents. It is noteworthy that the age of the father has a greater influence here. The chances of having a sick baby increase significantly after 35 years of age.
- Incest. A child born as a result of sexual intercourse between blood relatives has a high probability of acquiring a genetic disease.
- Alcoholism, smoking, and drug addiction lead to deformities, including at the chromosomal level.
- Heredity, and the instigators can be not only the father and mother, but also the closest relatives. Some scientists believe that the occurrence of the syndrome is influenced by the age of the grandmother at which she gave birth to her mother.
The disease has no gender, race or geography. It is distributed throughout the globe. And diabetes, as such, is the most common genetic disease.
External signs of mosaic syndrome
As already mentioned, people with a similar form of the disease may not differ much in development and appearance from their peers. Among them there are even very attractive children and adults.
Although, on the other hand, many carriers of this defect have the same symptoms as with the common trisomy.
Children with mosaic Down syndrome are often short in stature and growth occurs very slowly. The limbs are disproportionate to the body and are reduced in size.
In 90% of cases, such people have a flat face and brachycephaly - a shortened skull with a flat back of the head. The neck is usually short with a thickened skin fold. A similar sign is noticeable already in the neonatal period.
Characteristic facial features in people with a similar defect are a flat bridge of the nose and a small nose; in 30% of cases, strabismus (squint) may develop.
The most striking manifestation of Down syndrome, which accompanies all its forms, is epicanthus. This concept refers to a fold of skin that hangs slightly over the inner edge of the eye. Because of this feature, Down people resemble representatives of the Mongoloid race. And that is why the discoverer of the defect initially called it Mongolism, and the patients - Mongoloids.
Other facial features include a distorted arched palate and abnormal teeth. These defects and muscle hypotonia make it difficult to close the mouth, so it is always half open. The tongue in children with the mosaic form of the syndrome is grooved. Together with the gothic palate, they make sucking difficult, which is why such a child does not gain weight well. However, for a mild degree of the disease, which is mosaicism, this is not always typical.
Brushfield pigment spots may be present on the iris and around its circumference. Another feature is abnormal ears, which are located below the eye line. They are deformed, often protrude and can cause hearing problems.
Anomalies also affect the musculoskeletal system. They are manifested by joint lability and bone deformation. For example, the sternum has a keeled shape. The pathognomonic symptom is clinodactyly or curvature of the little finger. The ribs and spine are also deformed. This is due to underdevelopment of bone tissue.
The appearance of excess skin folds is a common sign of downism. They are formed due to underdevelopment of bones, so the skin between them does not stretch well. In addition to the neck, folds across the palm and in the elbow are also characteristic.
External deformations often cause disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Irregular bone shape, muscle hypotonia and other features lead to the following internal pathologies:
- abnormalities in the development of blood vessels and the heart;
- problems with vision and hearing;
- digestive system disorders;
- underdevelopment of the kidneys;
- hypothyroidism
Let us note once again that down people with the mosaic variant do not always have all the symptoms combined. Many of them do not appear, making it difficult to recognize the disease.
Pathological anatomy
A morphological study of the nervous system of deceased patients is characterized by a decrease in the size and weight of the brain, underdevelopment of the frontal lobes; reduction of the lateral ventricles; the grooves and convolutions of the brain are poorly differentiated. In some cases, there are anomalies in the development of the brain and large cerebral vessels. Histological examination reveals impaired differentiation of nerve cells and insufficient myelination of nerve fibers of the brain and spinal cord.
Almost all endocrine glands, especially the thyroid gland, adrenal cortex and gonads, are hypoplastic. Internal organs are reduced in size. In the liver - fatty vacuolization, fibrosis. The aorta is narrow, its walls are thin, large vessels are smaller. Congenital heart defects are common.
Psychomotor and mental development
Defects in the development of children with this syndrome appear for several reasons:
- decreased vision and hearing, due to which the child is unable to perceive information. As a result, cognitive impairment also occurs;
- muscle hypotonicity - babies begin to hold their heads up, roll over, and walk late. Motor skills suffer;
- problems with the musculoskeletal system;
- Deformation of the palate, teeth and tongue causes speech difficulties, so the speech of such people may be incomprehensible.
With the mosaic form of the disease, there may not be such defects, so these children develop quite well, their mental development practically does not suffer. Special programs are being developed for them, and parents play a big role here. His future abilities and successes depend on how well and consistently they work with their child.
Children with mosaicism are very capable of learning. They can attend regular kindergarten and school, and even do better than some of their healthy peers.
Their capabilities, abilities and development in general are very different. On forums, mothers of such children share their achievements and describe their babies with a similar syndrome in different ways.
For example, one mother says that her son, who is already 8 years old and suffers from a mosaic form of diabetes, still does not speak. Although they are undergoing rehabilitation at the appropriate center.
While another mother, whose youngest baby has this disease, claims that he is no different from the older one, even more resourceful.
Many children with mosaic type DS sublimate their defective characteristics into incredible achievements.
Aya Iwamoto is a girl with mosaicism from Japan, whose parents told about her illness only in her second year at the institute.
She attended kindergarten and successfully graduated from school and university. She studied two languages: English and French, and is engaged in foreign translations. She teaches at schools and universities, took part in an international conference. Together with her mother, she published a book about a trip to France. Regularly supports and fights for the rights of people with Down syndrome.
Raymond Hu is a guy with mosaic Down syndrome from the USA who paints pictures using ancient Chinese techniques. He creates them with watercolors and ink on rice paper.
The group of people with a similar defect includes many actors. One of the most famous such personalities is actor Pablo Pineda. He got the main role in the film “Me Too.” He is also a frequent guest on various television shows, where he covers problems of pedagogy and child development.
Jamie Bauer, who played in American Horror Story, Pascal Duquenne, Chris Burke - all these actors have mosaic Down syndrome.
People with this diagnosis find themselves in different areas of life. Tim Harris is the owner of the restaurant. Ronald Jenkins is a famous musician who tamed the synthesizer. He has no equal in electronic music. Miguel Tomasin is a popular drummer and member of the band Reynols. Karen Gafnii is a girl who goes in for swimming. She became the first to cover a distance of 15 km. The water reached a temperature of +15.
Looking at such examples, it is difficult to predict how a child with a mosaic form of Down syndrome will develop. One thing is clear: for him to become successful and developed, painstaking work is needed on the part of both the child and his parents.
Clinical picture
Rice.
1. The face of a child suffering from Down's disease: slanted palpebral fissures, flattened wide bridge of the nose. Rice. 2. Schematic representation of the palpebral fissures in a healthy child (1) and a child with Down syndrome (2), a characteristic additional skin fold at the inner corner of the eye (epicanthus) is pronounced. Rice. 3. Palmar surface of the hand of a healthy child (left) and a child of the same age with Down syndrome (right): the hand is short and wide, the fingers seem to be chopped off; 1 - triradius t' (the point at which the papillary lines of three directions converge); 2—highly located additional triradius t, characteristic of Down’s disease; 3 - transverse fold. In severe cases D. b. there is a combination of mental retardation with a combination of a number of signs: oblique palpebral fissures (Fig. 1), a wide flattened bridge of the nose, an additional skin fold at the inner corner of the eyes (epicanthus, Fig. 2), a half-open mouth, an enlarged tongue with hypertrophied papillae and deep grooves, high vaulted palate, deformed ears, short neck; whitish spots are often visible along the periphery of the iris - Brushfield spots; feet and hands are short and wide; the fingers seem to be chopped off, the little finger is shortened and curved, has one flexion fold instead of the normal two; on the palm they often find a transverse fold and a high location of the additional triradius t” (Fig. 3), which is a point at which the papillary lines of three directions converge; on the feet the gap between the first and second toes is increased. Patients are stunted from birth and begin to hold their head up, sit, and walk late. Teeth erupt late and in an unusual order and have an irregular shape. Sexual development is sharply delayed. The ability to bear children has been described in isolated cases. Approximately a quarter of patients have congenital heart defects.
In the blood serum of patients, there is an increase in the concentration of immunoglobulin G and a decrease in immunoglobulin M. Resistance to infectious diseases is reduced.
Nervous system changes
dominate the clinical picture of Down's disease. Most patients have a reduced head circumference and a tower-shaped skull (microbrachycephaly). From the first days of a child’s life, muscle hypotonia is detected; the Moro reflex (see Newborn) is absent. There is strabismus, usually converging, weakness of convergence (see Convergence of the eyes), asymmetry of facial innervation, horizontal nystagmus (see). Some children with D. b. Coordination disorders are detected, which manifest themselves when performing locomotor tests and fine movements. All patients have autonomic-endocrine disorders: dry skin, predisposition to obesity, dermatitis, persistent red dermographism, degenerative changes in bones. With age, patients tend to normalize muscle tone and improve coordination of movements.
Mental disorders
characterized by ch. arr. dementia of the type of mental underdevelopment - oligophrenia (see). The diffuse nature of dementia is noted, in which not only intellect and thinking are underdeveloped, but also other mental functions (perception, attention, memory, speech, emotional and volitional sphere). Along with this, there is a predominant underdevelopment of the most differentiated ontogenetically young functions - thinking and speech, with the relative preservation of evolutionarily more ancient elementary functions - emotions and instincts.
Mental underdevelopment with Down's disease in 75% of cases reaches the level of imbecility, in 20% - idiocy and only in 5% - debility. The judgments of patients are primitive, abstract thinking is inaccessible to them. Speech develops late, vocabulary is poor, pronunciation is defective. Characterized by sluggishness and inertia of thinking, poor switching ability, patients easily get lost in an unusual environment. Attention is unstable and easily distracted. Mechanical memory is relatively well developed. Characterized by pronounced imitation. The emotions of patients are little differentiated; they are passive and dependent.
Patients are characterized by increased suggestibility. Due to the characteristics of temperament, the more common option is D. b. with a predominance of ereticism, i.e. excitability and irritability combined with motor restlessness, less often torpidity (lethargy, passivity and psychomotor slowness). There are signs of early involution, which can now be noted thanks to the increased life expectancy of patients with D. b.
Diagnosis
usually simple, in most cases it is installed in the maternity hospital. Down's disease most often has to be differentiated from hypothyroidism (see). In case of erased clinical signs, a cytogenetic study is necessary (see Cytogenetics). The latter is also carried out in cases of determining the risk of recurrent disease in the family, especially in young parents (possibility of chromosome translocation).
How to diagnose the disease
Down syndrome can be recognized in the prenatal period, that is, during pregnancy. As for its mosaic form, in some cases its diagnosis at this stage is difficult due to the paucity of manifestations and not all chromosomes are affected. In this case, it is revealed only after childbirth.
The disease can be detected using several methods:
1. Ultrasound diagnostics. It is performed every 3 months of pregnancy. Already in the first trimester, from 8 to 12 weeks, some signs of diabetes can be recognized. For example, thickening of the collar area.
2. In the second trimester, an ultrasound will show defects in the development of the central nervous system, digestive organs, excretory system and hearing, as well as heart defects. At the third ultrasound, the specialist will see minor developmental anomalies.
3. Maternal blood analysis. The first trimester (from 8 to 12 weeks) determines the amount of substances that the fetus produces:
- pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A);
- human choriogonadotropin (hCG). If the hCG level is increased and PAPP-A is decreased, this may indicate pathology;
4.The second trimester (from 18 to 21 weeks) determines the following indicators:
- alpha-fetoprotein;
- hCG;
- free estriol.
Such studies do not provide a 100% guarantee of the presence or absence of pathology. If a pregnant woman is at risk, that is, the listed tests show a non-standard result, the woman undergoes invasive procedures. They allow you to obtain fetal material to clarify the diagnosis:
- Chorionic villus biopsy - the procedure makes it possible to obtain tissue samples of the fetus. It is carried out using a puncture of the abdominal wall, as well as through the cervix with special forceps or a catheter. Carry out in the early stages of pregnancy, at 8-12 weeks;
- amniocentesis is performed between 14 and 18 weeks. A puncture of the fetal membrane is performed to collect amniotic fluid;
- cordocentesis is performed in late stages of pregnancy. Blood is collected from the umbilical cord.
These invasive methods are quite dangerous, as there is a risk of rupture of the amniotic sac, miscarriage, as well as infection of the mother and child.
Tests and diagnosis of Down syndrome
Modern doctors know how to determine the risk of having a baby with this syndrome. First of all, an important step is the diagnosis of Down syndrome during pregnancy. This disease can be suspected in the fetus based on the results of screening and ultrasound examination. All pregnant women are recommended to undergo an alpha-fetaprotein test. The following studies are also carried out during pregnancy:
- First trimester . During this period, the test for Down syndrome in pregnant women is the determination of hCG ( human chorionic gonadotropin ), which is produced by the fetal membrane. Pregnancy-associated protein A (PAPP A) is also determined. If a blood test shows abnormal levels of these indicators, fetal development disorders may be suspected.
- Second trimester . During this period, an ultrasound is performed. As for whether Down syndrome can be determined by ultrasound, fetal developmental disorders are noticeable during ultrasound examination already during this period. At this time, a study of alpha-fetoprotein (alpha-FP) levels is carried out. Low levels indicate an increased risk of disease. estriol is also examined , low levels of which may also indicate a disease in the child.
Taking into account the results of all tests performed in modern laboratories, the risk of Down syndrome is calculated. Using this calculation, the risk of having a baby with a pathology is determined already in the early stages of pregnancy. To do this, a series of analyzes is carried out (study of alpha FP, hCG, PAPP-A, estriol) and their subsequent interpretation. Ultrasound data is also taken into account, after which all information is analyzed to ultimately determine the expected risk of trisomy 21, 18, 13. In addition, other indicators are taken into account: maternal age, number of fetuses, chronic diseases in previous pregnancies, the presence of diabetes mellitus and etc. The doctor will comment on what the test standards are and how high the risk is after receiving the final results. It is especially important to conduct such a study for those women who are at risk of having children with Down syndrome.
If normal levels of trisomy 21 are significantly exceeded, a series of follow-up studies are carried out.
- Amniocentesis - a sample of amniotic fluid is taken and further examination of the fetal chromosomes is performed.
- Chorionic villus biopsy - a sample of chorionic villus tissue is taken. This test makes it possible to detect chromosomal abnormalities. If a chorionic villus biopsy confirms the possibility of having a baby with this syndrome, subsequent consultation with a geneticist is recommended.
- Umbilical cord blood testing allows you to identify chromosomal abnormalities. It is carried out if all other studies have not been effective.
Newborns are also tested for this diagnosis. First of all, the presence of characteristic features of appearance is taken into account. If necessary, a unique test is also performed to determine Down syndrome in newborns - a study of chromosomes for the presence of abnormalities. If the test confirms the presence of abnormalities, a number of additional studies are carried out. In particular, you may need an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, echocardiography, as well as examination by a number of highly specialized specialists.
Help your child
The mosaic version of DM, despite its milder course, requires constant work with such children. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely get rid of the pathology, but with the help of multidisciplinary therapy, you can help the child better adapt to society and not feel deprived.
It is very important for children with Down syndrome to undergo massage and physical therapy. They will increase muscle tone and strengthen them, eliminate contractures, stabilize the functioning of joints and the entire musculoskeletal system.
Massage is indicated from 2 weeks of birth. But not all techniques can be used at this age. Kneading is not used for children under 3 months. If your baby has heart problems, you should consult your doctor about massage techniques.
Among the physical therapy methods, be sure to use ball exercises. Thanks to them, motor reflexes and coordination develop.
Swimming lessons are indicated for children with diabetes. It performs the function of hydromassage.
Particularly highlighted are such treatment methods as hippotherapy and dolphin therapy.
Hippotherapy is a therapeutic effect achieved through communication with horses. This method provides:
- development of balance and attention;
- gives self-confidence;
- the warmth that comes from the horse calms the child and gives him a feeling of security.
This is an excellent method for balancing the nervous system of people with any type of Down syndrome. But it requires certain conditions to be met:
- It is important that the horse is big, not a pony. They are overly fussy.
- Before you mount a horse, you need to establish contact with it: talk, feed, pet it.
- The animal must be without a saddle or horseshoes.
- It is not recommended to ride on asphalt.
Dolphin therapy provides relaxation and improved mood, gives self-confidence, and helps to acquire communication skills. This method also stimulates physical development. The ultrasound produced by dolphins restores normal biocurrents.
Other methods of therapy include:
- prescription of medications - hormones, psychostimulants, neurometabolites, vitamin complexes;
- consultations with a psychologist and psychotherapist;
- diet therapy - often such patients suffer from obesity, which can lead to other pathologies. Therefore, you should follow a proper nutrition system to prevent excessive weight gain;
- constant supervision by specialized specialists.
Risk factors for having children with Down syndrome
The birth of a child with Down syndrome is not related to the lifestyle, ethnicity or region of residence of the parents. The only reliably established factor that increases the risk of having a child with Down syndrome is the age of the mother. So, if in women under 25 years of age the probability of having a sick child is 1:1400, by 35 years old it is already 1:400, by 40 years old it is 1:100; and by 45 - 1:35. First of all, this is due to decreased control over the process of cell division and an increased risk of chromosome nondisjunction. However, since the birth rate in young women is generally higher, statistics show that 80% of children with Down syndrome are born to mothers under the age of 35. According to some reports, the father's age over 42-45 years also increases the risk of developing Down syndrome in the child.
It is known that if one of the identical twins has Down syndrome, the other will have this pathology in 100% of cases. Meanwhile, for fraternal twins, as well as brothers and sisters, the likelihood of such a coincidence is negligible. Other risk factors include the presence of persons with Down syndrome in the family, maternal age under 18 years, carriage of the translocation by one of the spouses, consanguineous marriages, random events that disrupt the normal development of germ cells or the embryo.
Thanks to preimplantation diagnostics, conception using ART (including in vitro fertilization) significantly reduces the risk of having a child with Down syndrome in parents at risk, but does not completely exclude this possibility.
Psychomotor development
Teaching people with Down syndrome is a very rewarding endeavor. Every achievement brings them extremely much joy. They approach this process with great enthusiasm and put in a lot of effort.
From a very early age, people with diabetes require close attention and careful work with them. Children with a mosaic form are close to normal in their development, but still have some features that need to be corrected.
It should be understood that the thinking of such children is slightly different. It is more inert, often it is difficult for such a baby to concentrate, he lacks perseverance. Therefore, the process of teaching them needs to be approached creatively, preferably in a playful way.
New information should be presented to them in short phrases, repeating them several times, since short-term memory is not sufficiently developed. But the main thing is to do it in an interesting and exciting way. Keep in mind that such students get tired faster than others, so you should take breaks during classes and alternate mental activity with physical activity.
Problems with hearing and vision also reduce the ability to perceive information and slow down the learning process. This should also be taken into account and classes should be adjusted to these features.
Pay attention
mania for the development of figurative and abstract thinking: clarification of statements and concepts, presentation of evidence, arrangement of objects in space, their classification, etc.
Speech in children with diabetes may be slurred and poor. This problem requires sessions with a speech therapist. This will allow the speech to be delivered correctly and make it more accessible to understanding.
It is important to develop motor skills, because it allows children to take care of themselves in everyday life. Muscle weakness reduces the ability to manipulate the palm and fingers. They should be developed. For example, you can use an exercise in which the hand is fixed on the surface of the table on the edge of the palm. In this case, drawing is performed with 3 fingers, excluding the little finger and ring finger.
You can develop brushes using various techniques:
- clench your fists, imitate a tweezer grip and in the form of a pinch. Alternately touch the thumb with all fingers;
- drawing, including finger drawing, in different planes - strictly horizontal or vertical, at an acute or obtuse angle;
- modeling from any material - plasticine, clay, dough;
- play okay;
- newspaper rip;
- turning the pages of a book;
- using improvised means - arranging buttons into different categories, collecting them on a thread, making jewelry. You can sort and pour cereals. But moderation is important here so as not to tire the little student. Manipulations with jars and lids are also applicable;
- folding mosaics and puzzles. But you should select objects suitable for the child’s age so that he can assemble them on his own;
- working with scissors, laying out appliqués. Creation of patterns;
- teach your child how to dress independently, how to handle laces, zippers, and buttons. You can train him with a doll.
By working with children in this way, you can not only teach them physical skills - it provides direct communication with the baby, stimulates his mental and mental development.
There are special methods that provide direction in teaching children with disabilities:
- Zaitsev's method. The author has developed special cubes, tables and musical accompaniment, which are designed to teach reading skills. This, in turn, affects the quality of writing in the future and smoothes out intellectual problems.
- Montessori method. Its essence is to create an environment in which the child will study at his own request. He chooses his own occupation from the offered range. As a rule, training is conducted in a playful way.
- The Nikitin method is ease and freedom in learning, a relaxed atmosphere. The emphasis is on physical development and hardening. All play equipment must have an educational basis.
- Glen Doman's method is to start learning from a very early age. Already from the age of 1 year, develop speech, teach the basics of counting and reading.
- Cecile Lupan's method is to present information to the child in such a way as to interest him, so that he himself strives to learn. To do this, constantly offer something new, gradually stimulating him and expanding his knowledge himself. The main criteria are curiosity and independence.
Collective activities are very important, in which children reach out and focus on each other.
Treatment
There are no specific treatment methods yet. However, complex drug therapy in combination with physical therapy, massage, pedagogical influence, and classes with a speech therapist helps improve the condition of patients. Various methods of stimulating mental and physical development are used (aloe extract, cerebrolysin, gammalon, vitreous, niamid or nuredal), vitamin therapy, endocrine drugs (prefisone, thyroidin), glutamic acid, lipocerebrin.
Forecast
in relation to life, relatively favorable, if there is no severe congenital heart disease. The prognosis for full recovery is poor.
Bibliography
Down's disease, ed. E. F. Davidenkova, L., 1966, bibliogr.; Davidenkova E. F. and Liberman I. S. Clinical genetics, L., 1975, bibliogr.; Multi-volume guide to pediatrics, ed. Yu. F. Dombrovskaya, t. 10, p. 572, M., 1965; Fundamentals of human cytogenetics, ed. A. A. Prokofieva-Belgovskaya, p. 338, M., 1969; Sukhareva G. E. Clinical lectures on childhood psychiatry, vol. 3, p. 72, M., 1965; Benda S. E. Down's syndrome, NY—L., 1969, bibliogr.; Crome LS a. Stern J. Pathology of mental retardation, L.—Edinburgh, 1972; Down JL Marriages of consanguinity in relation to degeneration of race, Lond. Hosp. clin. Lect. Rep., v. 3, p. 224, 1866; Down's syndrome (Mongolism), ed. by V. Apgar, NY, 1970; Smith DW a. Wilson AA The child with Down's syndrome (Mongolism), Washington, 1972.
B.V. Lebedev; M. Sh. Vrono (psychiat.), E. I. Gusev (neur.).