Clinic La Salute Articles Mental retardation in children
Growing up, children always strive to explore everything around them and learn something new. Every day they pass through a huge amount of information. But, if the child is not very interested in this, doctors can diagnose mental retardation.
ZPR implies various difficulties in interacting with society and analyzing information. Children suffering from this disease experience significant difficulties in learning, it is difficult for them to complete the school curriculum and interact with others. Let's look at the symptoms and signs of mental retardation to understand when you should see a doctor.
Pediatric neuropsychology
What is ZPR
Mental retardation is a slowdown in the normal rate of mental development, when a child exhibits disturbances in attention, thinking, motor skills, and emotional manifestations.
Often the pathology is expressed in decreased concentration, poor memory, immaturity of thinking and rapid fatigue. If a child at the age of 4 has a delay in one of these areas, this may be a symptom of mental retardation.
Some types of illness exhibit the following disorders:
- hyperexcitability;
- hypertensive abnormalities;
- cerebrasthenic complications;
- hydrocephalic problems.
In other cases, delayed intellectual and psychological development predominates.
Important:
- Children with mental retardation quickly catch up with their peers if they receive corrective and pedagogical assistance in a timely manner.
- Most often, the diagnosis of mental retardation is made in a situation where the main symptom is a low level of memory and attention, as well as the speed and transition of all mental processes.
- It is extremely difficult to diagnose mental retardation in preschool age, and almost impossible at the age of 3 years (unless there are very obvious signs). An accurate diagnosis can only be made after psychological and pedagogical observation of a child at the age of a primary school student.
Types and classification
ZPR, as a rule, is divided into 4 categories, which differ both in the causes of occurrence and in the characteristics of the course of the disease. Determining the type of disease is necessary to develop an effective treatment regimen.
ZPR of constitutional origin
This type can be described as mental infantilism. The child behaves as if he is younger than he actually is. Underdevelopment can be detected even at an early age by the following symptoms:
- lack of independence and feeling of security without parents;
- difficult adaptation;
- frequent mood swings;
- too strong display of emotions.
Children suffering from mental retardation of constitutional origin do not differ visually from their peers, however, they are less developed emotionally. This directly affects learning ability.
ZPR of somatogenic origin
Unlike the first type, children with mental retardation of somatogenic origin have a weakened body. Severe diseases suffered at an early age directly affect the central nervous system, delaying its development. Signs of pathology:
- loss of attention and concentration;
- rapid physical and mental fatigue;
- lack of interest in the outside world;
- constant anxiety;
- passive behavior.
Such children are often placed on an individualized regimen of education and physical activity. The child is less present in the group, as a result of which his socialization worsens.
ZPR of psychogenic origin
This type of mental retardation is based on attention deficit or overprotection, which provokes the following symptoms of mental retardation in children:
- shyness;
- fear of expressing feelings and emotions;
- changeable mood;
- emotional instability;
- aggressiveness.
A child who does not receive proper attention and does not have the opportunity to see normal family relationships interacts poorly with peers, which leads to a lack of socialization and further difficulties with communication.
ZPR of cerebral-organic origin
A characteristic feature of this type is immaturity of emotionality and cognitive activity. Symptoms are individual and depend on the degree, nature and location of damage to the central nervous system, but the main ones are considered to be:
- increased suggestibility;
- lack of imagination;
- irretention;
- lethargy;
- lack of brightness of emotions.
Since patients have minor impairments in brain function, children can still fully communicate with peers and easily socialize, but for this they should visit a specialist.
Classification of ZPR
ZPR in preschool children. To systematize violations, the classification of K.S. is usually used. Lebedinskaya, a famous children's defectologist and psychiatrist.
Mental retardation in children is divided into 4 types:
- Somatogenic. In this form, violations are caused by excessive parental care of children, when loved ones do everything for a crumb, not allowing them to show independence, without which exploration and knowledge of the world around them is impossible. The second cause of somatogenic mental retardation can be long-term and frequent illnesses of a child at an early age, in this case all the body’s forces are aimed at recovery, weakness and decreased activity are noted, and in such conditions the development of the psyche slows down.
- Constitutional . This type of mental retardation is due to heredity, when similar disorders occurred in close relatives of the baby. This form manifests itself in the underdevelopment of the emotional-volitional background. Such children are characterized by the inability to make independent decisions without the help of loved ones, rapid changes in emotions and their turbulence. By the school period, children with a constitutional form of mental retardation do not show a desire for cognition and learning; they prefer primarily play activities.
- Cerebral-organic . This is the most common form of mental retardation with the most negative prognosis. In this case, the disorders are caused by organic lesions of the child’s central nervous system due to pathologies of childbearing, birth injuries, prematurity or neuroinfection. Children have MMD - minimal brain dysfunction, mild developmental disorders, manifested in a variety of areas related to mental activity. Such kids are not emotional and have a lack of imagination.
- Psychogenic . The reasons for this type of mental retardation are social disadvantage in children’s families, when there is aggression or violence at home, and children are left to their own devices and no one cares for them. As a result, such children are not taught the rules of behavior in society, and the level of knowledge about the world around them is at a fairly low level.
Children with mental retardation are teachable. Teachers help instill skills and abilities that healthy children can master on their own in children with mental retardation.
Symptoms and signs of development of children with mental retardation
Often, mental retardation can be identified only when a child is sent to first grade, because it is then that all the difficulties with studying and learning information are revealed. But with proper monitoring, some symptoms are noticeable much earlier.
Intelligence
Intellectual disability in children affects the following aspects:
- attention;
- memory;
- thinking;
- speech.
Also, under the influence of the disease, the perception of the surrounding world disappears or becomes inaccurate and slow. As a result, it is difficult for the child to form complete images. Children with mental retardation have the worst developed auditory perception, so the teaching format using live speech is the least effective.
Attention
Children suffering from mental retardation cannot concentrate their attention on one object for a long time. They do it superficially. Any extraneous factors can distract them.
Memory
Children with this disease cannot choose from the information they hear exactly what they need to remember. Their memory is visual-figurative and mosaic.
Thinking
These children think best in a visual and actionable format. For example, it is easier for them to count numbers on specific, existing objects. Their imaginative thinking is not developed, and abstract-logical thinking is completely absent. They cannot analyze and compare information, as well as formulate conclusions and conclusions.
Speech
Children with mental retardation often experience delayed psycho-speech development, that is, they distort the articulation of many sounds, experience difficulties with vocabulary, control of grammar and formulation of the correct statement. This is often combined with dyslexia and dyslalia. The difficulty is that it is necessary to identify the problem and begin treatment as early as 3 years old in order to avoid deterioration in speech skills.
Emotions
A child with this disease is usually very unstable in his emotions. His mood often changes, and his mind is easily suggestible. Manifestations of aggressiveness, poor coordination and motor skills, anxiety and conflict are also possible. Such children are generally withdrawn, self-contained and avoid contact with peers.
Physical parameters
Height and weight below normal are another sign of mental retardation. Outwardly, a child with pathology often looks several years younger.
How are mental development disorders classified - the main groups of mental development?
This classification, which is based on etiopathogenetic systematics, was developed in the 80s by K.S. Lebedinskaya.
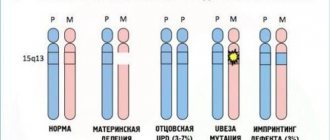
- ZPR of constitutional origin. Signs: frailty and growth below average, preservation of childish facial features even at school age, instability and severity of expressions of emotions, delay in the development of the emotional sphere, infantilism manifested in all areas. Often, among the causes of this type of mental retardation, a hereditary factor is identified, and quite often this group includes twins whose mothers encountered pathologies during pregnancy. For children with this diagnosis, it is usually recommended to attend a special school.
- ZPR of somatogenic origin. The list of causes includes severe somatic illnesses that were suffered in early childhood. For example, asthma, problems with the respiratory or cardiovascular system, etc. Children in this group of mental retardation disorders are fearful and unconfident, and are often deprived of communication with peers due to the intrusive guardianship of parents, who for some reason decided that communication is difficult for children. For this type of mental retardation, treatment in special sanatoriums is recommended, and the form of training depends on each specific case.
- ZPR of psychogenic origin. A rather rare type of ZPR, however, as is the case with the previous type. For these two forms of mental retardation to occur, severely unfavorable conditions of a somatic or microsocial nature must be created. The main reason is the unfavorable conditions of parental upbringing, which caused certain disturbances in the process of forming the personality of a little person. For example, overprotection or neglect. In the absence of problems with the central nervous system, children from this group of mental retardation quickly overcome the difference in development with other children in a regular school. It is important to distinguish this type of mental retardation from pedagogical neglect.
- ZPR of cerebral-organic origin . The most numerous (according to statistics - up to 90% of all cases of mental retardation) group of mental retardation. And also the most severe and easily diagnosed. Key reasons: birth injuries, central nervous system diseases, intoxication, asphyxia and other situations that arose during pregnancy or directly during childbirth. Among the signs, one can single out bright and clearly observable symptoms of emotional-volitional immaturity and organic failure of the nervous system.
Features of behavior at a certain age
Baby
As a rule, children with mental retardation later than others begin to hold their heads up, walk and talk independently. There is also excessive excitability, increased or decreased appetite, insomnia and gastrointestinal diseases.
Preschooler
With pathology, children aged 4–6 years do not understand the rules of most children's games and the norms of behavior in public places. Show excessive, inappropriate emotions and have difficulty communicating.
Schoolboy
Children with mental retardation who have entered the first grade find it difficult to study. They need more time to analyze the information received, especially in conditions that interfere with concentration. They often forget about the goal they are pursuing, are quickly distracted, and cannot concentrate. It is also worth noting that with high mental stress, the child experiences emotional and physical discomfort.
ZPR in children: definition and signs
Mental retardation is characterized by a child’s delay in the mental, emotional, and mental areas. It manifests itself as a violation of cognitive processes: thinking, memory, attention. This gives rise to difficulties in the educational process, which becomes noticeable at the stage of preschool education or in the primary grades, when children enter a new stage of development.
Some mental development disorders in children may be noted by parents or educators at an earlier age. However, diagnosis of mental retardation is carried out during the period when the child begins to develop serious mental activity, usually from 5-6 years of age. It is necessary to make a diagnosis and begin correction before the age of 7-8 years.
In some cases, mental retardation is noted in infancy. The child later begins to be interested in toys, babble, understand speech, etc. Physical development is not affected.
Often preschoolers and schoolchildren with mental retardation are called frivolous. Children are excessively forgetful, distracted, distracted from the topic and disturb others. During lessons, such children can talk about something of their own, walk or play. They are often slow and confused, unable to concentrate and concentrate their thoughts. Children's performance and verbal-logical thinking suffer, and cause-and-effect relationships are disrupted.
One should also suspect mental retardation if a first-grader
- does not understand the rules of children's games;
- has difficulty mastering counting, reading, and writing;
- forgets about the purpose of his activity, impulsively changes plans, does not maintain attention on the task;
- experiences emotional and even physical torment due to unusual mental activity;
- unable to learn the rules of behavior in various situations;
- shows inappropriate emotions (hysterics when trying to divide an item, laughter in a solemn or dramatic setting);
- has difficulty communicating with peers;
- silent, not independent in everyday life.
Who can diagnose mental retardation?
The diagnosis can only be made by the PMPK - the psychological, medical and pedagogical commission. A pediatrician, psychologist, speech therapist, neurologist and other doctors can identify the problem and refer the child for examination. You need to take tests and conduct various tests. For example, check for the presence of traumatic brain injuries and stress that could affect the development of the psyche, and take a neuropsychological test.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, recommendations are given for education and schooling. You can see the problem from an experienced specialist at our La Salute clinic. A neuropsychologist with extensive experience will help you here - Danilina Kamilla Kasimovna. This is a practicing doctor, an employee of the Scientific and Practical Center for Child Psychoneurology, who has published more than 30 works on child psychology. Treatment is carried out with the help of physiotherapy and exercise therapy, special medications.
The difference between mental retardation and mental retardation
Mental retardation and mental retardation are similar diseases, but they have a number of differences, which are described in the table.
| ZPR | UO |
| Has spasmodic dynamics of intellectual activity | Not characterized by developed emotionality |
| The disease develops difficulty with intellectual activity | Difficulty with mental operations develops |
| With the right approach, you can correct your baby’s behavior and development. | There is no perception of the playful presentation of information, the child is not able to accept help in performing tasks, does not feel the desire to analyze and understand the information read |
If a child over 10 years of age does not show signs of mental retardation, his diagnosis may be changed to either mental retardation or constitutional infantilism.
How to recognize mental retardation in a child
As a child grows up, he acquires many new skills and strives to explore the world around him. If he is alienated and has any of the symptoms listed above, you need to visit specialists for examination and diagnosis.
You cannot draw conclusions about your baby’s illnesses on your own. There are many reasons and factors that can influence a child’s behavior and perceptions. Qualified specialists must confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment and adjustment methods.
Clinic La Salute offers a proven program for correcting the condition of children with mental retardation. We have the conditions necessary to diagnose and correct the disease in the early stages, which helps prevent further deterioration in the child’s psychological health.
Symptoms of mental retardation in children at different age intervals
Sometimes signs of the disorder can be observed in children immediately after birth, and in some cases, problems begin to appear at school age and later. It is important to learn to recognize your baby’s characteristics in time.
Let's look at the main anxiety symptoms for different age categories of children:
- Mental developmental development up to one year: late starts to hold up head, crawl, walk, talk, use cutlery.
- Signs of mental retardation per year - a quiet, unemotional child, with a limited or absent set of simple words, does not show a reaction to being addressed.
- ZPR 2 years old - no desire to learn something new by repeating after others, a primitive set of words (up to 20), no ability to compose logical phrases and sentences, limited memory skills.
- Symptoms of mental retardation in children 3 years old - rapid unconscious speech with swallowing sounds, syllables or word endings, when answering a question, may think for a long time and repeat the question itself, slow movements or hyperactivity, no desire to explore the world around them, aggressiveness, increased salivation, narrow spectrum emotions, signs of cerebral palsy may appear.
- Mental retardation 4 years - tearfulness, aggressiveness, emotional instability, causeless laughter or hysteria, underdeveloped speech, ignoring requests from adults, difficulty in contacting others.
- Mental retardation in a 5-year-old preschooler - ignoring peers, aggressiveness or complete passivity, sudden mood swings, speech difficulties, especially in constructing even a simple dialogue, difficulties with memory, lack of simple everyday skills.
- Mental retardation 6 years old - behavioral disorders, difficulty concentrating, performing basic everyday skills, noticeable lag behind peers in speech, emotional and intellectual development.
- Symptoms of mental retardation in children aged 7 years - difficulties with reading, problems with logical problems and mathematical calculations, lack of emotional contact with peers, poor vocabulary, difficulties in voicing their thoughts and requests, behavioral problems (aggression, tearfulness, whining, self-isolation , unreasonable laughter, etc.).
- Features of mental retardation in adolescents - mental instability, undeveloped self-esteem, no resistance to criticism, trying to avoid the team, psychomotor disinhibition and excitability, suppressed cognitive activity, limited memory (usually short-term), impaired verbal-figurative, visual-figurative and visual-effective thinking , speech disorders, lack of motivation, development of infantilism. A characteristic symptom of psychophysical infantilism is hysteroid psychopathy and depressive states.
At an early age, it is problematic to diagnose mental retardation. The most pronounced symptoms can be observed in preschool age, when self-care skills, spatial orientation, communication skills, fully developed memory and formed speech should already be formed. Regardless of the age at which mental retardation was diagnosed, correction of this condition must be started immediately.