Home / Correction / Laser correction
Doctors often recommend laser coagulation to pregnant women for vision problems. This is explained by the fact that natural childbirth places a very heavy burden on the body. Changes in the eye vessels or a high degree of myopia can lead to severe deterioration of vision after childbirth. Typically, pregnant women are prescribed a full ophthalmological examination in the first months of pregnancy, after which the doctor prescribes surgery, which can be done until the 35th week of pregnancy.
The laser coagulation method is designed to stop the development of the degenerative process in the retina in a timely manner. This process begins due to various eye diseases (blunt trauma, myopia, tumors, retinitis, etc.), as a result of which the retina is greatly stretched and torn. Its detachment from the vessels entails a disruption of the blood supply and the person begins to go blind.
Why is laser coagulation necessary?
Pregnant women who have serious vision problems greatly increase their chances of having a caesarean section. Every woman wants to give birth to her child on her own. An increase in hormones in the expectant mother’s body affects every organ. Eyes are also no exception. This does not mean that pregnancy will necessarily worsen your vision. Only possible complications of pregnancy can negatively affect the condition of the eyes: toxicosis, vomiting, which can lead to hemorrhages in the retina; due to edema, retinal vascular damage may develop.
To avoid all this, an operation is performed.
Laser coagulation of the retina is prescribed to pregnant women due to the following advantages:
- the ability to carry out using a non-contact method, without pain and without blood;
- outpatient implementation;
- duration no more than 30 minutes;
- the use of local anesthesia, which helps to avoid possible complications associated with general anesthesia.
Is laser coagulation of the retina performed during pregnancy?
Low-traumatic laser strengthening of the retina during pregnancy is a common procedure that is often prescribed to women in the early stages of gestation. In order not to miss the pathology, which is almost always asymptomatic, gynecologists refer patients for examination by an ophthalmologist. If an examination of the fundus reveals a degenerative process, the doctor will prescribe laser correction.
Good to know! During pregnancy, before giving birth, a fundus examination by a laser ophthalmic surgeon is mandatory. Based on the results, recommendations are issued on the possibility of independent delivery and, if necessary, preventive peripheral laser coagulation (PPLC) is prescribed.
Doctors call the optimal time for intervention the period from 12 to 30 weeks of pregnancy.
The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia, that is, it does not involve the introduction into the bloodstream of substances potentially dangerous to the fetus. The operation itself is not accompanied by a violation of tissue integrity, discomfort or the need to take specific medications during rehabilitation. This means that there is no danger for the unborn baby, as well as for his mother. Therefore, pregnancy is not a contraindication for the procedure. Moreover, the operation helps women with visual impairments to get rid of them and give birth to a baby on their own.
Possible complications in pregnant women
After laser coagulation in pregnant women, there is a possibility of complications:
- Swelling of the cornea of the eye. Usually appears for a short time and is accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity. However, vision quickly returns as the swelling decreases.
- The contour of the pupil may be deformed due to the formation of posterior synechiae. May occur when using excessive amounts of coagulant.
- Laser exposure to the lens of the eye can lead to the development of cataracts.
- Deterioration of vision in the dark.
- Swelling of the ciliary body and closure of the anterior chamber angle can cause increased pressure inside the eye.
- Dark spots appear in the vision area.
- In very rare cases, retinal hemorrhages, vitreous detachment and disruption of the optic nerve occur due to inaccurate application of coagulants.
Often, for pregnant women, if it is necessary to coagulate a significant part of the retina, the doctor prescribes an operation in several stages in order to avoid the development of possible complications.
Rehabilitation period
To prevent laser coagulation of the retina during pregnancy from causing complications, a woman must follow a number of rules for 4 weeks after it:
- do not engage in active sports;
- do not visit the sauna and bathhouse, public swimming pool and beach;
- limit fluid intake to 2 liters per day;
- give up alcohol and smoking;
- limit the consumption of salt and hot spices.
These restrictions cannot be called complex, since any pregnant woman has to comply with them. To monitor the condition of the retina, the patient is recommended to have preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist twice a year. If there are no new detachments, you can visit the doctor annually.
Recommendations in the postoperative period
The effectiveness of laser coagulation of the retina can be judged only after two weeks. This is exactly how much time is needed for the final healing of coagulants and the formation of strong adhesions. In order to avoid possible complications, pregnant women need to follow several recommendations during the postoperative period:
- Avoid physical activity completely for a while.
- Do not lift heavy objects.
- It is necessary to wear dark glasses when leaving the house.
- Avoid spending long periods of time in front of the monitor, TV and reading.
- Various mechanical injuries to the eyes and head should be avoided.
- Women suffering from hypertension should regularly monitor their blood pressure.
- In case of diabetes mellitus, constantly maintain blood sugar levels.
- During the first six months after surgery, be examined by an ophthalmologist every month. And then see a doctor every six months.
How is the operation performed?
Laser coagulation of the retina during pregnancy is carried out routinely in a specialized ophthalmology clinic or clinic at the place of residence of the woman in labor. It does not require specific preparation or hospitalization. The only thing required for treatment is to undergo a preliminary ophthalmological examination and examine the fundus. The woman arrives at the appointed time and immediately goes to the laser room. Anesthesia is not required for this type of treatment.
There is no discomfort when “soldering” the retina. In isolated cases, a woman may feel a slight tingling sensation in the temporal region.
The patient is seated on a chair in front of the device. Her head is fixed in a special frame: her chin is placed on a support, and there are limiters on the sides. The procedure follows the standard procedure:
- Pupil dilation using special drops
. Through it, the doctor can examine the entire retina and visualize areas with detachment and degeneration. - Installation of a Goldmann lens
, an optical device that helps the doctor focus laser beams on pathological areas of the retina. It does not come into contact with the surface of the eye. - After focusing, the doctor turns on the laser for short periods of time
. Outwardly, it looks like a series of instantaneous flashes. During the operation, the patient does not feel any discomfort.
After treating all weakened and detached areas, the woman remains under observation for several minutes, after which she receives recommendations for further recovery and leaves the clinic.
What will the birth be like?
Will I need a caesarean section or will I be able to give birth on my own? - this question greatly worries any woman who has any visual impairment. It is very difficult to answer this question unambiguously, because the decision on the method of childbirth is made taking into account many factors: the condition of the fundus and retina, the age of the woman in labor, the general condition of the body, etc.
A Caesarean section is a surgical operation to remove the fetus through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and uterus. When it is carried out, the risk to a woman’s life and health increases 12 times compared to spontaneous childbirth. Because of this, a caesarean section is prescribed strictly according to indications, like any surgical operation.
Indications for a cesarean section are the impossibility of independent delivery or danger to the life and health of the mother or fetus. It should be noted that degenerative processes in the retina are one of the most common reasons for cesarean section.
Myopia and dystrophy
Is it possible for a woman with poor vision to give birth on her own? This question worries many expectant mothers who, as a rule, suffer from myopia, less often from eye diseases such as astigmatism, farsightedness, congenital cataracts, as well as those who have undergone eye surgery - scleroplasty, strabismus surgery, laser vision correction.
Of course, there are contraindications and restrictions to natural childbirth due to eye conditions, but most of them are temporary. In obstetrics, for a long time, there has been an opinion that high myopia (more than -6.0 diopters) is an indication for cesarean section.
However, modern practice shows that childbirth through the birth canal is possible with this pathology. Myopia in itself, even of a high degree, cannot be a limitation, and, moreover, a contraindication to delivery through the natural birth canal.
The determining factor that can influence the decision to deliver is the condition of the retina. It is important to know that the degree of myopia does not matter when there is a threat of complications from the retina.
According to the literature and from personal experience, dystrophic changes and retinal breaks most often occur with an average degree of myopia from 3 to 6 diopters. What happens with myopia?
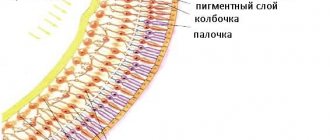
The fact is that with myopia, changes in the anatomy and physiology of the organ of vision are often detected: the length of the eye is increased compared to the norm, resulting in stretching of the membranes of the eye and thinning of the retina at the periphery.
Reduced blood circulation in the eye leads to a decrease in the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the retina, which is the cause of various peripheral retinal dystrophies (PRRD). What is the danger?
The most dangerous forms of peripheral retinal dystrophies are breaks, lattice dystrophy, retinoschisis, and mixed forms of dystrophies. Patients with retinal tears are at risk of developing one of the most serious eye diseases - retinal detachment.
Considering the above, already at the stage of pregnancy planning, it is advisable to start seeing an ophthalmologist.
Natural birth or caesarean section? There are generally accepted indications and contraindications regarding the condition of the eyes and the process of delivery. Childbirth through the birth canal is possible in the following situations:
- No pathological changes in the fundus.
- The presence of dystrophic changes (PVCD), which cannot be delineated using preventive laser coagulation of the retina, in the case of a stable fundus picture during pregnancy.
Absolute indications for surgical delivery:
- Retinal detachment during actual childbirth.
- Retinal detachment diagnosed and operated on at 30–40 weeks of pregnancy.
- Previously operated retinal detachment in the only seeing eye.
Indications for delivery by cesarean section:
- Extensive areas of PVCRD with the presence of vitreoretinal tractions.
- History of retinal detachment.
These contraindications are considered relative, because with a timely visit to a vitreoretinologist, it is possible to perform limiting laser coagulation of the retina, and, accordingly, eliminate the risk of possible complications.
Of course, it all starts with basic procedures - checking visual acuity, autorefractometry (determining the refractive power of the eye), measuring intraocular pressure, biomicroscopy (examination of the anterior segment of the eye using a special biomicroscope - a slit lamp).
A mandatory type of ophthalmological examination during pregnancy is an examination of the fundus, which is carried out through a wide pupil, since only in this state is it possible to examine the periphery of the retina, where, as a rule, dangerous changes occur.
If there are thinnings or breaks in the retina, preventive laser coagulation of the retina is required to limit them. After timely laser coagulation of the retina, and it is carried out before the 30th week of pregnancy, you can completely calmly give birth in the generally accepted way, without worrying about your vision!
In addition to myopia, there are other eye diseases. As practice shows, examination by an ophthalmologist is prescribed mainly for pregnant women with predominantly high myopia (myopia) in order to prevent retinal complications (detachment, hemorrhages in the retina or vitreous body) during childbirth.
Important
It should be noted that thinning of the retina occurs not only in myopic people, but also in people with hemodynamic disorders, less often with farsightedness, as well as in people with normal vision, but somewhat less frequently than in myopes.
Therefore, during pregnancy, a woman, regardless of the presence of vision problems, should visit an ophthalmologist at least 3 times - at the beginning of pregnancy, in the middle and at the end. Timely examinations by an ophthalmologist will help preserve your vision for a long time!
Treatment methods
Retinal detachment cannot be treated with medication; the only way to preserve the patient’s vision is timely surgery. One way to do this is to use a laser.
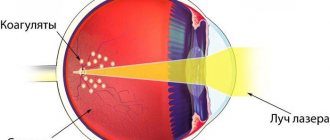
The goal of surgery is to find and repair a retinal tear by creating adhesions. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis, under local anesthesia, which is performed by instilling an anesthetic into the eye.
To direct the beam of the device to the desired location, a special contact lens is used. A three-mirror Goldmann lens focuses the laser on the affected area.
There are several types of procedure.
Peripheral laser photocoagulation of the retina
The laser coagulation procedure in some cases is carried out for prophylactic purposes. The operation prevents retinal detachment and strengthens it. Using a laser coagulator, the shell is soldered to the wall of the eyeball, when dangerous retinal dystrophy such as “lattice” or “cochlear trace” is detected.
Restrictive laser coagulation causes microburns, which contribute to the fusion of the separated area with the tissues of the choroid. This procedure has been carried out for about 40 years, helping to preserve the vision of patients. One session lasting 15-20 minutes is sufficient.
The safety of the operation is evidenced by the fact that restrictive laser coagulation is performed on pregnant women. It is indicated for peripheral dystrophy of the ocular membrane. This problem leads to a ban on giving birth naturally, since high stress can cause retinal rupture. After undergoing an examination by an ophthalmologist and identifying a vision pathology, a woman has up to 35 weeks to undergo laser retinal correction.
Peripheral restrictive laser coagulation prevents stretching and detachment of the retina and strengthens its structure.
After the operation, visual acuity does not increase; it depends on concomitant ocular pathologies. Restrictive laser coagulation improves the blood supply to the eye, prevents fluid from entering under the retina, and normalizes the nutrition of the membrane. It prevents degenerative tissue changes and vision loss.
Barrier laser coagulation of the retina
The procedure is performed around emerging tears in the inner lining of the eye. It limits the exfoliated zones, creating a kind of barrier. This type of intervention is common for flat local detachments.
Additional coagulation
It is performed at the site of a retinal tear after surgery.
What are the risks of retinal detachment during pregnancy?
Retinal detachment during pregnancy causes a narrowing of visual fields; when localized in the central zone, it leads to a significant decrease in visual acuity.
If the detachment exists for a long time, then secondary dystrophic changes may appear in the form of thinning and preretinal cysts, and the development of rigidity and decreased mobility of the retina is also possible. These changes do not allow obtaining a good result, even if surgical treatment is performed.
What should a pregnant woman do if retinal detachment is detected?
Detection of retinal detachment during pregnancy requires urgent surgical intervention.
There are various methods of surgical treatment. During pregnancy, the following methods can be used:
- restrictive laser coagulation of the retina;
- episcleral filling;
Cauterization of the retina during pregnancy is carried out only in the presence of local asymptomatic detachment to try to stabilize the pathological process. If the area of detachment is large, then episcleral filling is used.
Childbirth with retinal detachment
Retinal detachment is an absolute indication for cesarean section.
The period of pushing is excluded even if an operation has already been performed for retinal detachment and is not currently available. This is done to prevent the development of a relapse, since during pushing there is a very large load on the woman’s body.
Planning pregnancy after retinal detachment
If a woman has a history of surgery for retinal detachment, then it is necessary to plan a pregnancy. When planning, you should visit an ophthalmologist to assess the condition of the retina.
It is advisable that pregnancy occurs no earlier than 1 year after surgery for abruption, this is due to the restrictions that arise in the postoperative period.
Prevention of retinal detachment is based on early diagnosis of peripheral chorioretinal changes in the fundus, timely implementation of restrictive laser coagulation of the retina, as well as preventive medical examinations and dynamic monitoring.
Yulia Chernova, ophthalmologist, especially for Mirmam.pro
Prevention of retinal detachment in pregnant women
The risk of retinal detachment in myopic women with changes in the fundus during natural childbirth increases due to changes in blood pressure. To prevent the spread of degenerative changes in the retinal tissue and, accordingly, prevent retinal detachment, prophylactic laser coagulation (PLC) is prescribed.
The retinal laser coagulation technique involves applying several rows of coagulates to the peripheral area of the retina.
During this procedure, retinal tissue in areas affected by dystrophy is firmly “welded” by laser radiation to the underlying tissues. The targeted effect of the laser causes the process of local tissue scarring. Thanks to this, a strong connection is formed between the retina and the choroid.