Methods for treating fungus on eyelashes
If signs of the disease appear, you should visit an ophthalmologist.
Self-treatment is not recommended, and it is undesirable to use traditional methods without a doctor’s prescription. Incorrect therapy will aggravate the situation, worsen the condition and cause complications. At the appointment, the doctor will definitely examine the area affected by the fungus and collect tests to identify the type of mycosis pathogen. The specialist will review the medical history to identify possible chronic diseases and existing ophthalmological ailments. He will find out whether the patient is taking medications. Correctly prescribed treatment will depend on the information.
If the skin of the eyelids is damaged, the patient needs to consult a dermatologist or mycologist. To determine the diagnosis, a scraping of the affected skin will be required. After the tests, therapy is prescribed, including taking pills, applying ointments and creams, and drops. In advanced cases, injections are prescribed. Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, only severe cases require medical supervision and inpatient treatment.
Ointments, creams
An ointment for treating manifestations of fungus on the eyelids consists of components that provide an antifungal effect. Usually prescribed ointments and creams:
Using a cotton swab, apply to the eyelid from the inside. It is better to use the medicine at night.
Drugs
To enhance the therapeutic effect, drugs are prescribed:
- Okomistin drops are effective in combating infectious eye diseases and various types of fungal infections. Drops are used up to five times a day, the course duration is about 7-10 days. Dezmistin drops have a similar effect;
- Miramistin is available in the form of ointment, cream, spray. To combat eyelash fungus, it is more effective to use a solution. The eyes are washed with liquid 4 times a day. The solution is instilled into the eye using a pipette, 1 drop per day. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. The product quickly eliminates unpleasant symptoms;
- Tablets with an antifungal effect are prescribed orally for a comprehensive fight against the pathogen. Doctors prescribe Fluconazole, Imidazole, Lamisil, Diflucan, Terbizil.
Injections
If the disease is severe, the drug Amphotericin B is prescribed. The medicine is administered by injection and helps to quickly eliminate the pathogen. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, with regular examinations and consultations.
Treatment should be comprehensive, with the agreement of the doctors prescribing the therapy. To effectively get rid of fungus on the eyelids, ointments, creams, drops, tablets, and, if necessary, injections are prescribed.
In case of inflammation of the internal tissues of the eyeball, surgery is performed.
Treatment
Therapy of acute conjunctivitis of a fungal nature requires local and systemic use of antimycotic drugs. The doctor prescribes instillations into the conjunctival cavity of solutions such as Natamycin, Nystatin, Amphotericin B. Fungistatic and fungicidal preparations in the form of ointments and drops are prepared extemporaneously (to order at the pharmacy).
To treat fungus in the eyes, use a systemic antifungal drug, for example, Itraconazole or Fluconazole. In case of extensive inflammation, the patient is indicated for intravenous administration of Amphotericin B. On average, treatment takes 4-6 weeks, and it must be carried out under the supervision of an ophthalmologist. After complete clinical recovery, scrapings from the conjunctiva are taken again. This is necessary to confirm the patient’s recovery and to exclude the pathology from passing into a latent form.
Local treatment
With the development of bacterial conjunctivitis, antibiotics in the form of drops (0.25% solution of chloramphenicol, sodium sulfacyl) are prescribed for the treatment of pathology. If fungal eye diseases are accompanied by copious discharge, the conjunctival sac is washed with solutions of furatsilin, potassium permanganate and oletethrine ointment is placed in it (a couple of times a day for severe cases, once for mild cases).
Antibacterial drops
For therapy, special antibiotics are used in the form of drops, which act primarily on the mucous membrane of the eyes and practically do not enter the bloodstream. This helps to preserve the normal microflora of the whole body during intensive antibacterial treatment of the organs of vision. For conjunctivitis, your doctor may prescribe one of the following topical medications:
- Albucid. The drug inhibits the growth of bacterial flora, including fungi, streptococci, gonococci, chlamydia, etc. Available in concentrations of 20 and 30%. Use drops up to 6 times a day, instilling 2-3 drops. The main contraindication for Albucid is an allergic reaction to sulfacetamide. The disadvantage of the drug is a burning sensation in the eyes during use.
- Tobrex. The active component of the drug is the antibiotic tobramycin, which has a wide spectrum of action. The product is characterized by a bacteriostatic effect against Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci, fungi, etc. In acute cases of fungal conjunctivitis, drops are used every 4 hours. The downside of Tobrex is swelling, allergies, redness of the eyeball and eyelids when using the drug. In addition, an allergic reaction to the drug occurs relatively often.
Eye ointments
The presence of any form of eye disease requires complex diagnosis and therapy, which is selected by an ophthalmologist. Treatment for fungal conjunctivitis includes the use of eye ointments. Effective among them are:
- Tetracycline ointment. The drug contains the antibiotic tetracycline, which is practically not adsorbed into the blood when applied topically. An ointment is prescribed for bacterial and fungal conjunctivitis. The advantage of the drug is maximum safety, so treatment with Tetracycline ointment is possible even during pregnancy. The disadvantage of the drug is that it is prohibited for use by children under 8 years of age.
- Torbex. The ointment is optimal if you need to quickly relieve the symptoms of the disease. The drug contains tobramycin, which can be used to treat children. Torbex is used for the treatment of eye infections, keratitis, barley, endophthalmitis, aspergillosis and other fungal lesions of the organ of vision. The great advantage of the ointment is that it can be used to treat even newborns, starting from 2 months of age.
Routes and methods of infection
Fungi can invade the eye tissue from the environment or from mycotic lesions on the skin or mucous membranes on other parts of the body. Depending on this, there are two main routes of infection: exogenous and endogenous. The first is also called contact or household. It involves the penetration of the pathogen into the body from the environment, which leads to invasion and the development of inflammation. The source of danger in this case is:
- non-sterile doctor's instruments;
- fungal lesion on the skin;
- mycosis of eyebrows;
- own hands;
- volatile spores of some fungi.
With endogenous infection, the pathogen invades tissue from other lesions. It spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream. This route is otherwise called hematogenous. It is rarer, but at the same time very dangerous. The causes of the fungus through the endogenous route of infection can be:
- sinusitis;
- frontal sinusitis;
- otitis;
- candidiasis of the mouth or nose;
- onychomycosis.
At-risk groups
Since many fungi live in the soil, residents of rural areas are at risk, including workers in mills, feed mills, elevators and granaries. Their activity may cause eye injury or the entry of dust and foreign bodies. The same applies to workers in weaving factories. Children and adolescents are at risk because they are more often in large groups, for example, in a kindergarten, school, or sports section. In addition, compared to an adult, a younger child has not yet fully developed immunity.
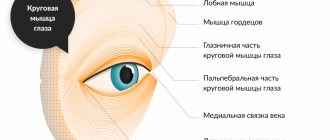
What is fungal conjunctivitis
This is ophthalmomycosis, which is characterized by subacute or chronic inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyelid and eyes, caused by pathogenic fungi. Depending on the type of causative agent of the disease, it may have a purulent or catarrhal form. The patient may experience the formation of nodules or films on the mucous membrane of the organ of vision. In some cases, fungal conjunctivitis develops into keratoconjunctivitis. Infection occurs for various reasons, and pathogens live on the eyelids, lacrimal ducts, in the conjunctival sac, or enter the membrane of the eyeball from the outside.
Features of the average salary by region of Russia in 2020
The average salary in the regions of Russia in 2020 is calculated by Rosstat, a special statistical body operating at the federal level.
The average income of a citizen in the Russian Federation is considered an unstable indicator, which is influenced by a number of internal and external factors
For example, until recently, when calculating it, only the employee’s salary was taken into account. At the moment, not only salary is taken into account, but also all amounts recorded as a person’s income for the reporting period (allowances, bonuses, etc.)
Thus, average earnings are an economically significant value; they are also closely related to the indicators of the subsistence level (LM) and the minimum wage. In particular, the indicated dependence is expressed in the following aspects:
- legislation fixes the volume of subsistence food, formed on the basis of data from the food basket and the list of products necessary for citizens for standard life activities. These are those goods that can provide a person with his minimum daily needs. At the same time, the volume of the indicator under consideration is formed at the federal level, but it can be increased by regional authorities depending on the inherent characteristics of the area;
- based on the PM value, the minimum wage indicator is formed;
Until 2020, the values under consideration were different and independent of each other. Since 2020, this provision has been eliminated and the minimum wage began to correspond to the volume of the monthly wage.
The minimum wage is the minimum amount of wages that a manager must provide to a subordinate.
Thus, the indicators of PM, minimum wage and average earnings correlate. Regional authorities and employers can increase these values, but it is prohibited to set them in a volume lower than that noted at the federal level.
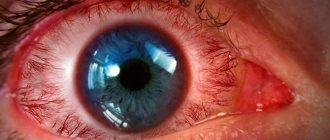
Symptoms of a fungal eye infection
With an external infection, the first complaints may be:
- pain;
- “flies” before the eyes;
- scotomas are small dark spots located in the field of view;
- loss of vision.
Photo: Adam Gregor / Shutterstock.com
If the lesion is located on the periphery of the retina or if the patient is in critical condition, eye fungus may be asymptomatic.
Features of manifestation
The clinical picture may be different: it all depends on what stage of development the pathology is at. The main symptoms are presented in the table (Table 1).
Table 1 - Symptoms
| Stage | Locus of the lesion | Symptoms |
| Blepharitis | Eyelids | Swelling, redness. |
| Sensation of a speck behind the eyelid. | ||
| Pustules, compactions or erosions along the eyelash line. | ||
| Rapid eye fatigue. | ||
| Eyelash loss. | ||
| Dacryocystitis | Lacrimal sac | Narrowing of the palpebral fissure. |
| Consolidation in the area of the lacrimal sac (at first it is hard to the touch, but after a while it becomes soft.) | ||
| Redness in the area of the nasolacrimal duct. | ||
| Pain in the eyes. | ||
| Fever. | ||
| Conjunctivitis | Conjunctiva | Yellow or gray film on the inside of the eyelid (candidiasis). |
| Swelling of the conjunctiva, the formation of papillary growths on it, prone to ulceration (with aspergillosis). | ||
| Granulomatous growths, accompanied by swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. If they open, pus is released (observed with actinomycosis). | ||
| Keratitis | Cornea | Redness of the mucous membrane of the eye and surrounding soft tissues. |
| Increased sensitivity to light. | ||
| Pain in the eyes of a cutting nature. | ||
| Tearing. | ||
| Fog before the eyes. | ||
| Flakes, a white coating on the eyeball (appears when infected with Candida fungus). | ||
| Scleritis | Sclera | Red whites of eyes. |
| Pain in the eyeballs, aggravated by pressure or movement. | ||
| Swelling, drooping eyelids. | ||
| Decreased vision. | ||
| Headache. | ||
| Increased tear production. | ||
| Yellow spots on the sclera (appear during necrotic processes). | ||
| Chorioretinitis | Ophthalmic vessels | Flashes, spots before the eyes. |
| Slight or vice versa – severe decrease in vision. | ||
| Deterioration of visibility at night (“night blindness”). | ||
| Distortion of the shape of perceived objects. | ||
| Endophthalmitis | Vitreous body | Redness and swelling of the affected eyelid. |
| Stripes on the lower edge of the iris are yellow or white. | ||
| Blurred vision or complete loss of vision. | ||
| Pain in the eye, head. | ||
| Deformation of the pupil, presence of a yellowish spot on it. | ||
| Increased intraocular pressure. | ||
| Copious discharge of pus. |
If at least one of the symptoms of eye fungal damage occurs, you should consult a doctor: the sooner treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of a quick recovery.
Symptoms
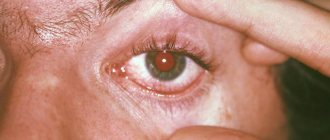
The primary symptoms of the disease are redness of the eyeballs, mild burning and/or itching, and increased tearing. Since conjunctivitis develops rapidly, the clinical picture is quickly complemented by other symptoms, including:
- sharp reaction to light;
- increased itching, burning;
- redness of the skin around the eye (conjunctival hyperemia);
- swelling of the conjunctiva;
- the formation of nodular infiltrates, which open over time, causing mucous discharge to appear;
- in the morning there is the presence of crusts in the corners of the eyes (as in the photo);
- the appearance of purulent ulcers with a greenish coating on the conjunctiva;
- in the conjunctival area, films of a yellow or gray tint are noticeable, which are easily removed.
Against the background of the main pathology (fungal-type conjunctivitis), people often develop purulent-type lymphadenitis, in which an additional clinical picture appears. The symptoms in this case are:
- drowsiness, malaise;
- weakness;
- headache;
- slightly elevated temperature, which is accompanied by chills and bouts of fever;
- thickening, tenderness of the regional lymph node;
- loss of appetite;
- redness of the skin near the inflamed lymph node.
Types of eye fungus
The following types of microbes that lead to damage to the organ of vision are differentiated:
- Fusarium. They develop in the environment. Capable of affecting many human organs, they enter the body from plant foods.
- Aspergillus. The fungus is able to penetrate the lungs, digestive tract, and nervous system. Affects the skin and eye membranes.
- Candida usually lives on human skin. They are classified as conditionally pathogenic, but under certain favorable conditions they cause inflammatory processes in the body.
- Actinomycetes are fungi that cause actinomycosis of various types.
Depending on which membrane of the eye is affected by the fungal infection, the following types of fungal eye infection are distinguished:
- blepharitis (development of fungus on the mucous membranes of the eyelids);
- inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- damage to the cornea;
- mycotic lesion of the sclera;
- destruction of blood vessels;
- damage to the internal eye tissues by a fungal infection.
There are these types of fungal diseases based on the type of pathogen:
- aspergillosis;
- candidiasis of the eyes;
- sporotrichosis;
- actinomycosis.
Candidomycosis and aspergillosis are more common. As a rule, pathologies appear as a result of a decrease in the body’s immune defense. Sporotrichosis affects the eyes due to improper hygienic care. Trying to insert a contact lens with unwashed hands greatly increases your risk of getting sick. The disease often occurs in children who do not wash their hands after a walk and rub their eyes.
Actinomycosis refers to chronic fungal pathologies. It is difficult to treat. A feature of actinomycosis is the formation of widespread foci of changes in tissue structure. Typically affects the eyelids.
Causes
Fungus on the eyes is part of the microflora of the conjunctival cavity and normally does not cause an inflammatory process. About 50 species of fungi are considered pathogenic for the organs of vision, including such parasitic types as Coccidioides immitis, Pennicillium viridans, Actinonomicetes, Sporotrichum. Exudative forms, which are characterized by purulent discharge, are caused by yeast-like fungi - Candida albicans and Aspergillus. Sources of infection can be water, soil, sick people or animals.
People with diabetes, skin mycoses, caries, HIV-infected people, and those taking antibiotics or hormonal medications for a long time have an increased risk of developing the disease. Fungal infections on the conjunctiva are facilitated by:
- ocular radiation burns;
- microtrauma of the mucous membrane;
- mycotic blepharitis;
- use of contact lenses in violation of the rules for their use or storage.
Folk remedies to speed up treatment
At the initial stage of development of eye fungus, you can try to stop its spread using traditional methods. The following unconventional means can cope with this task:
- Spilled tea. Freshly brewed tea is not suitable for treatment, since it does not have time to form substances useful for this procedure. The drunken drink is used for compresses and lotions. They can be done several times a day. A folk remedy will not help to completely cure a fungus. But with its help it will be possible to reduce the severity of the symptoms of the disease;
- A decoction of calamus and yarrow. To use this product, you need to mix the plant material in equal quantities. After 2 tbsp. l. The resulting mass needs to be poured with 500 ml of boiling water. After cooling, the resulting decoction can be used to wash the eyes;
- Fresh cucumbers. Another proven and safe method of treating eye fungus. To prepare this remedy, you need to peel and chop a fresh vegetable. Afterwards, pour 500 ml of boiling water. It is recommended to add 0.5 tsp to the same mixture. soda The infusion should stand for 1 hour. Afterwards, you need to moisten a clean swab and apply it to the sore eye for 15 minutes.
Folk remedies must be combined with drug treatment. They are used until the patient achieves recovery.
Diagnosis of mycosis
To make a diagnosis, at the first symptomatic manifestations of oculomycosis, the infected person should contact a dermatologist or ophthalmologist as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct a full interview with the patient and perform an examination using special equipment to check for fungal eye infections.
To clarify the preliminary diagnosis, additional diagnostic measures may also be required, including analysis of samples of biomaterial obtained by taking scrapings from the area affected by the fungus. After receiving the test results, the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment.
Important!
Self-diagnosis is strictly prohibited, since without the necessary qualifications, an error may occur in prescribing therapy, which will lead to undesirable consequences.
Diagnosis of blepharitis
Diagnosis of eye blepharitis is based on the clinical picture of the disease. It consists of the patient’s complaints (history), examination data, identification of concomitant diseases and laboratory tests.
Initially, the ophthalmologist determines the patient's visual acuity. To identify myopia, astigmatism, presbyopia, hypermetropia, the doctor examines the state of accommodation and refraction of the eyes.
Then biomicroscopy is performed. This is a visual examination to determine the structure and condition of the tear film, conjunctiva, eyelashes, cornea and eyelid margins. The examination uses a slit lamp (ophthalmic microscope).
1.
If necessary, additional analysis is done at the diagnostic center. It reveals the microbial, cellular composition of scrapings from the conjunctiva, the separated base of the eyelashes and the secretion of the glands located there.
2.
Demodectic blepharitis is diagnosed by microscopic examination of removed eyelashes. Five of them are taken from both eyes. The diagnosis is confirmed if the laboratory technician detects 6 or more motile Demodex, their larvae at the ciliary roots. If there are fewer ticks, then the person is a carrier, but not sick.
3.
If infectious blepharitis is suspected, a bacteriological culture of a smear from the conjunctiva is performed.
4.
If the cause of the disease is allergic reactions, the patient visits an allergist. He prescribes allergy tests.
5.
If a worm infection is suspected, the doctor will order a stool test for eggs.
6.
Chronic blepharitis with thickening of the bases of the eyelashes gives reason to suspect carcinoma, basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma. To confirm or refute the prognosis, a histological biopsy is performed.
7.
Differential examination of anterior blepharitis is carried out if the patient has eyelid cancer or keratoconjunctivitis.
Careful eyelid care is the basis of treatment for blepharitis, regardless of the cause of the disease.
Diagnostics
You cannot independently determine the complexity of the lesion. Only a consultation with an ophthalmologist and dermatologist will help make an accurate diagnosis.
To identify the pathogen, doctors prescribe bacteriological culture.
An accurate diagnosis is made as a result of the following instrumental studies and diagnostics in laboratories:
- Refractometry. The optical system of the eye is examined. As a result of the study, the refractive power is determined. An automatic refractometer is used to determine it.
- Study of visual acuity. For diagnostics, an optotype table and a special projector are used. With fungal infection, visual acuity decreases below v=1.
- Ophthalmoscopy. A fundus lens or ophthalmoscope is used to examine the fundus of the eye.
- Biomicroscopy. As a result of a non-contact method using a binocular microscope and a slit lamp, individual ocular structures are examined.
- Angiography. Photography or video is being taken. As a result of the procedure, the quality of the vessels is assessed.
Types of pathologies and causes of occurrence
Eye fungus is a group of diseases caused by mycotic microorganisms. Depending on the pathogen, the following types of this pathology are distinguished:
- Actinomycosis is common. Its development is provoked by fungi that live on the mucous membrane and in the human intestines, as well as in the body of animals, on some plants.
- Candidomycosis. This disease is caused by Candida fungus. It exists in the body as an opportunistic microflora and in the environment.
- Aspergillosis. A moldy fungus present on the skin. It reproduces exclusively on mucous membranes.
- Sporotrichosis. Fungi of this form live in the soil, on plants, shrubs, moss and hay. The carriers of infection among animals are dogs and cats.
All these fungi can live on human skin and mucous membranes and not manifest themselves in any way. Their activation and reproduction occurs when the body’s defenses decrease.
The main causes of fungus DPS-1064:
- frequent stress;
- previous colds;
- use of other people's cosmetics;
- injuries, purulent diseases of the eyeball;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules, recommendations for the processing and use of contact lenses.
Factors contributing to its occurrence include:
- visiting a swimming pool, sauna or bathhouse;
- long-term or improper use of medications: antibiotics, corticosteroids, cytostatics;
- staying in dusty, unventilated rooms (library, warehouse);
- genetic predisposition;
- living in poor sanitary conditions;
- performing work that involves contact with sources of infection;
- drinking alcoholic beverages;
- malnutrition.
Anyone can get a fungal eye infection. But the likelihood of developing pathology is much higher in those who have:
- diabetes;
- bronchial asthma;
- immunity deficiency (people with HIV infection, AIDS);
- chronic diseases of the lungs and bronchi;
- oncological diseases;
- fungus on the face DPS-1088 (infection can spread to the mucous membrane of the organs of the visual system);
- weakened immunity due to undergoing courses of chemotherapy, surgery (organ transplant).
The risk group also includes:
- drug addicts;
- agricultural workers;
- employees of weaving and spinning enterprises;
- people working in the food industry;
- veterinarians;
- staff of swimming pools, saunas, baths, fitness clubs;
- florists;
- animal trainers.
The disease is diagnosed in both children and adults. In childhood the disease is more severe
It is important to be able to recognize its first signs and consult a doctor in time
Sergey: “Ocular candidiasis is a terrible thing. The causative agent of this disease is most common in countries with hot climates, but it is everywhere, including in our latitudes.
If you do not follow basic hygiene rules, do not wash your hands after going outside or touching animals, and if you touch your eyelids, you can easily spread fungus into your eyes. Apparently, this is what happened in my case. Now I’m undergoing treatment.”
Types of fungal eye diseases
Oculomycosis is a fungal infection of the eyes. There are several types:
- Candidal blepharitis. The disease spreads only on the eyelids.
- Scleritis. A fungal infection affects the sclera and multiplies successfully in it.
- Conjunctivitis. The mucous membrane is affected.
- Keratitis. The disease affects the cornea.
- Endophthalmitis. The avascular gelatinous substance that fills the eye cavity suffers.
On a note! The most unsafe diseases of a vital organ are those that can enter the sclera and vitreous body. Microorganisms can infect fragile capillaries and nerve endings.
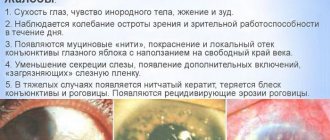
Symptoms of eye mycosis
Pathology can be recognized by characteristic signs, which are important to pay attention to and consult an ophthalmologist. Of course, you can’t tell just by symptoms what you’re dealing with. You can roughly guess the illness, but the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis
You can roughly guess the illness, but the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis.
Characteristic features:
- Redness of the conjunctiva.
- Excessive tearing.
- Cutting and pain in the eye area.
- Itching.
- Increased sensitivity to light.
- Yellow or white discharge from the eyes.
If the infection is severe, then there will be blurred vision due to the large amount of discharge. Visual acuity may deteriorate, which will become noticeable during diagnosis.
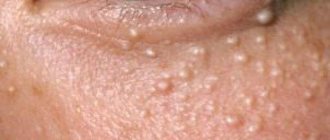
Some forms of fungal infection cause small nodules to appear on the eyelids and in the corners of the eyes. Complications may arise in which small pustules form.
If a patient has fungal conjunctivitis, then the eyelids become swollen and look unhealthy. With eye strain, the itching increases significantly, pus is observed, and people complain of pain when blinking. These are the main symptoms indicating fungal eye diseases. If they appear, then you will have to immediately go to the hospital for further diagnosis.
Prevention
Any disease is much easier to prevent than to treat. To achieve this, several important preventive measures should be followed, including the following:
- do not use other people's towels or scarves;
- In dusty rooms and regions, you must always wear safety glasses;
- when wearing contact lenses, be sure to follow the rules for caring for them (if infected with fungal conjunctivitis, old lenses must either be replaced with new ones or carefully treated with medication);
- It is important to regularly strengthen the immune system (sports, proper nutrition, hardening, etc.), since eye infections begin to develop when it decreases.
Video
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials of the article do not encourage self-treatment
Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient. Found an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything!
Article updated: 04/09/2020
Causes of eye fungus damage
Fungus on the eyebrows, eyelashes, around the cornea and other parts of the face appears after contact with the carrier of the pathogen. A number of pathogenic microorganisms enter the body through the mucous membrane or respiratory tract and affect the organs of vision.
The causes of the disease are due to a decrease in local and general immunity, which is facilitated by:
- eye injuries;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs;
- infection of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- HIV;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- diabetes.
Pathogenic fungi enter the body not only through contact with the patient, but also with dust particles. In addition, a high risk of infection is observed in rooms with high humidity (baths, swimming pools).
Wearing contact lenses or using them for longer than the prescribed period can provoke an exacerbation of fungal diseases. Dirt particles often settle on them, which can contribute to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the mucous membrane.
Etiology of the disease
Eczema is often provoked by the following external and internal factors:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- infection with worms;
- metabolic disorders and pathologies;
- hyper- and vitamin deficiency, etc.
In the initial stage, the disease is acute. Without proper treatment, it becomes chronic with periods of remission and relapse. This pathology is characterized by increased tear production and the appearance of deep cracks in the corners of the eyes. Scaly or dry inflammation of the dermis of the eyelids usually develops in adult patients. Often it is the localization of general eczema.
Over time, the inflammatory process subsides. On the weeping dermis, keratinization appears and it begins to peel off. Then the skin returns to normal.
With long-term, chronic illness, the eyelids may thicken and turn out. Complete or partial loss of eyelashes is also observed.
Eyelid eczema can lead to complete or partial loss of eyelashes.
Eczema is not an infectious pathology. Therefore, despite its danger, it is not contagious.
Causes of eczema on the eyelid and around the eyes
It is not surprising that women experience symptoms of eyelid inflammation more often than men. After all, they use cosmetics. It often contains allergic agents and synthetic substances. They cause skin sensitization - its hypersensitivity to the action of irritants. This condition of the dermis triggers allergic reactions.
Eczema is also provoked by:
- dust;
- insect secretions;
- plant pollen;
- pet hair and excretions;
- use of certain medications;
- weak immunity;
- disorders in metabolism and hormonal secretion.
Inflammation on the eyelids of a child or adult appears with increased production of histamine and decreased functionality of the body's systems and organs.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of developing eczema around the eyes:
- Reddened dermis of the forehead and eyelids.
- Severe itching and peeling of the skin.
- Swelling of the eyelids, painful sensations when touching them.
Cosmetics can trigger eczema.
As the disease progresses, a rash appears on the skin. After the blisters, papules and pustules burst, eczema becomes a weeping form. It is very dangerous, as it may indicate a bacterial infection of the wounds.
Signs of pathology during its prolonged course:
- Increased production of tear secretion.
- Burning and stinging in the eyes.
- The dermis on the eyelids becomes dry and may crack.
- With weeping eczema, the ulcers become covered with serous crusts.
When the disease becomes chronic, the eyelids thicken and turn out. These processes are accompanied by eyelash loss. The wounds and ulcers begin to suppurate and can become infected (seborrheic dermatitis).
Women often make this mistake: instead of seeing a doctor, they mask the inflammation with cosmetics. This worsens the condition of the dermis. It becomes additionally irritated, and erosions and cracks appear in the inflamed areas.
Symptoms of the disease
Clinical manifestations depend on the form of the disease. Symptoms of fungal conjunctivitis increase gradually. First, the mucous membrane becomes red and swollen. After a few days, grainy inclusions and ulcerative defects, covered with a white-greenish coating, appear in the conjunctival area.
With granulomatous fungal conjunctivitis, purulent lymphadenitis progresses. When studying the contents of the lymph nodes, specialists identify fungi. With candidal mycosis of the conjunctival cavity, yellow-gray films are formed that are easily removed. In this case, papillary outgrowths are formed that are prone to ulcerative lesions. The main symptom of fungal conjunctivitis is purulent discharge from the eyes, which often confuses specialists and forces them to prescribe antibacterial therapy.
Read in a separate article: Levomycetin for conjunctivitis in adults: features of the drug
But antibiotics accelerate the growth of fungal flora in ophthalmomycosis. With antibacterial treatment, the symptoms of fungal conjunctivitis will only intensify.
Traditional medicine and prevention
Therapy for fungal eye diseases can be supplemented with remedies prepared according to traditional medicine recipes. Helps to get rid of the disease:
- Tea. It reduces pain, relieves inflammation and burning. Only infused tea is suitable for treatment. It is used for lotions and compresses. The frequency of procedures is 2-3 times a day. Their duration is 15-20 minutes.
- Cucumber. What you need to do: peel the vegetable, chop finely, pour boiling water, add 0.5 tsp. soda, leave to infuse. How to use to cure fungus: soak a cotton pad in the strained solution and apply to the eyelids. Carry out this procedure several times a day until recovery occurs.
Herbal infusion. You can prepare an antifungal agent from yarrow, calamus, plantain and linden flowers. Recipe: mix herbs (1 tablespoon each), pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over the raw materials, cool. How to use: soak a sterile cotton swab or natural cloth in the infusion, rinse the eye affected by the fungus. This must be done in the direction from the outer to the inner corner.
It is impossible to cure fungus with folk remedies alone. Their use is effective only in combination with drug therapy. The use of traditional medicine methods must be agreed with your doctor.
Prevention of fungus involves taking measures aimed at eliminating factors that provoke the development of the disease. Recommended:
- Maintain personal hygiene: wash your hands after contact with animals, soil and before eating.
- Wear gloves, boots, and other protective clothing when working in the garden, vegetable garden or nursery.
- Eat right, eat more foods that contain vitamins.
- Promptly treat infectious, viral and bacterial diseases and illnesses that increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Monitor the cleanliness and expiration date of contact lenses.
- Temper yourself, engage in active sports (this strengthens the immune system).
- Be periodically examined by an ophthalmologist.
Eye fungus is a disease that requires urgent treatment measures. Untimely medical care can cause the spread of pathological processes, loss of vision and the organ itself.
But if the disease is diagnosed at an early stage and all treatment recommendations are followed, the prognosis for recovery is favorable - in most cases it is possible to completely get rid of the infection and prevent the development of complications.
Diagnosis and treatment
To confirm the presence of fungus, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination. First, the doctor examines, collects anamnesis and complaints of the patient. After this, the following laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed:
Once diagnosed, it is important to begin treatment immediately. A long-term course of a fungal infection can provoke irreversible changes in the tissues of the eyeball: retinal detachment, vascular thrombosis. The presence of all these complications significantly reduces the effectiveness of antifungal therapy and the likelihood of restoring vision and saving the affected eye.
Basic principles of therapy
The doctor decides how to treat the disease after receiving the examination results. But therapy should be aimed at:
- suppression of the activity of the pathogen;
- destruction of cells of pathogenic microorganisms;
- prevention of complications.
Depending on the stage of the pathology and the general well-being of the patient, the following are prescribed:
- medicines for oral administration (tablets against fungus DPS-1073);
- preparations for topical use: antifungal ointments DPS-1072 and gels, eye drops.
If treatment is ineffective and the fungus has spread to all parts of the organ of vision, they resort to surgery: cornea transplantation, removal of the vitreous body or eye.
During treatment, it is important to always follow the rules of personal hygiene. Before touching your eyes, you must first wipe your hands with a sterile cloth or treat them with an antiseptic. This will reduce the risk of re-infection and complications.
Antifungal eye drops
The use of eye drops is effective in the initial stages of the development of the disease. The choice of drug is made by the doctor depending on the causative agent of the disease. Most often prescribed:
Drug therapy
In the treatment of ophthalmomycosis the following are used:
- antifungal agents;
- fungicidal preparations.
If necessary, treatment of the disease is supplemented with antihistamines, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. The infection can be completely cured in 1 month, provided that medical instructions are followed.
In the treatment of fungal eye infections of various types, Okomistin is more often used. This medicine, based on miramistin, quickly and effectively fights most common strains of infection. The instructions for its use indicate that the drug can be prescribed to children.
In severe cases, treatment is supplemented with intravenous administration of Amphotericin B. Along with this drug, antihistamines (Suprastin, Fenkarol) are prescribed.
The applied methods of therapy are adjusted when the pathological process spreads to the skin of the eyelids. If they are affected, gels or ointments with antifungal properties are prescribed. Nystatin and Miconazole demonstrate good results in suppressing the activity of pathogenic microflora. If the type of pathogen is not established, Clotrimazole ointment is prescribed.
If the eyelids are affected by fungi, ulcers may appear, for the treatment of which a solution of brilliant green is used. In case of secondary infection and suppuration of local tissues, corticosteroids and antibiotics are prescribed in the form of ointments.
Disease prevention
It is better to carry out prevention of eye diseases than long-term therapy. Normally, every person has a fungus. If conditions favorable for its reproduction appear, serious eye diseases of a fungal nature may occur. To reduce the risk of their occurrence, the first step is to strengthen the immune system:
- lead a physically active lifestyle;
- give up bad habits (abuse of alcohol, drugs, smoking);
- adjust your diet to include healthy foods. It is better to give up sweets and yeast products, which create microflora favorable for the growth of fungus;
- Take regular walks in the fresh air.
In the prevention of fungal diseases of the organs of vision, the most important thing is to carry out careful hygiene. It is especially important to properly treat the eye area for children who cannot care for themselves.
Before touching your face or the skin around your eyes, you need to wash your hands. People who regularly wear contact lenses should be especially careful about eye hygiene. Also, when choosing a solution in which the lenses will be stored, you need to consult a specialist. This will help avoid allergies, which can lead to dangerous eye diseases.
Treatment of mycosis
Treatment for eye fungus involves the use of antifungal medications. It is often carried out in a hospital setting. The doctor determines which remedy for mycosis will be effective by studying the culture result: the type of fungus, its sensitivity to certain groups of drugs.
The general principle of eye fungus therapy:
- Use of fungicidal preparations applied topically. When carrying out general therapy, you can use tablet medications, intravenous injection solutions, eye drops, and various antifungal ointments.
- Anti-inflammatory treatment, which is carried out using glucocorticosteroids. It is used in the treatment of almost all degrees of fungal eye infections. Specialists are able to eliminate the inflammatory process in the eye tissues, preserving the patient’s visual function.
- If inflammation has begun in the internal tissues of the organ of vision, surgical intervention is performed.
To stop the fungus that causes the disease from multiplying, use Amphotericin B, Griseofulvin, Itraconazole in tablet form, and also carry out intravenous and local injections. It is popular to use preparations containing iodine.
Systemic treatment is carried out in parallel with eye drops. If a patient has candidiasis, he is recommended to use the following ointments against the fungus: Nystatin, Levorin. They are placed in the conjunctival cavity, after first retracting the lower eyelid (see next photo).
If mycosis is accompanied by the appearance of an ulcer in the cornea, fungus inside the eye, or endophthalmitis, surgery is necessary. Ulcerative formations are scraped out and extinguished with iodine tincture. If they are deep, cauterization is performed using diathermocoagulation or freezing with liquid nitrogen.
When the pupil narrows due to a fungus in the organ of vision, Atropine and Tropicamide are used. If local therapy for ulcer formation does not bring results, keratoplasty is performed. Patients suffering from panophalmitis are recommended to undergo enucleation (surgical removal of the eyeball).