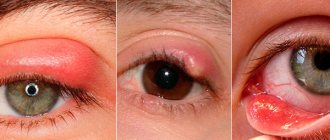
How to treat conjunctivitis with medication?
Conjunctivitis in a 4-month-old child can be cured with a limited amount of medication. The reason is that not all medications are suitable for infants. Many drops and ointments that are designed specifically to treat conjunctivitis cannot be used on four-month-old infants due to the high likelihood of side effects.
- "Tobrex" is an eye ointment with an antibacterial effect. It must be placed in the corner of the eye once a day for 10 days. It is best to do this before bed;
- "Ophthalmoferon" is a drug that has an antiviral effect. It is used 1 drop every 2 hours, after which the number of instillations is reduced to 3-4 times a day;
- "Vitabact" are eye drops that are used for at least a week, but no more than 10 days. The drug should be administered 4 times a day, one drop;
- "Tetracycline ointment" is one of the most common drugs used to treat conjunctivitis in four-month-old children. It is placed 2-3 times a day in the corner of the eye after washing it;
- "Albucid" - the children's version of these drops should be a 1% solution. It is allowed to use it up to 8 times in the first two days of illness, then up to 4 times a day.
Even if only one of the baby’s eyes is affected by conjunctivitis, drops must be instilled into both: into the sick eye for treatment, and into the healthy eye for prevention. During instillation, it is important not to touch the baby’s cornea with the pipette or “spout” of the bottle. By the way, the pipette can only be used with a rounded end.
Rhinoplasty of the bridge of the nose
A wide bridge of the nose is the second most common reason for which people turn to plastic surgeons. It introduces serious discord into the harmonious interaction of all facial features.
With normal width, the proportions of the external appearance are not disturbed.
But what to do when harmony of appearance is out of the question? Rhinoplasty of the bridge of the nose is the ideal solution to this problem, once and for all.
Width of the upper third of the nose
Excessive width of the bridge of the nose is caused by nasal bones that are spaced too wide. They successfully distract attention from the eyes, creating a unique appearance for the owner of a non-standard nose. After rhinoplasty of the bridge of the nose, the emphasis automatically falls on the eyes.
Since a wide bridge of the nose is mainly due to a congenital defect, many people develop complexes due to this problem literally for life.
But there are cases when the width of the bridge of the nose increases visually due to an injury or previous surgery, which is especially scary for some people, since this factor once again reminds them of what happened to them. The only solution to this problem is rhinoplasty.
A wide bridge of the nose visually not only makes the nose large and flattened. It also changes the expressiveness and attractiveness of the look. The overall impression of the face and how it looks when reflecting different emotions also changes.
How to eliminate a wide bridge of the nose?
The wide bridge of the nose is visible especially clearly from the frontal view. This problem appears due to excess bone tissue, the width and thickness of its structure.
Many people try to hide this drawback by using a huge amount of decorative cosmetics of different shades - foundation, blush, powder. But this is rather a temporary solution that will only create an optical illusion.
In some cases, doctors recommend wearing a special rhinocorrector splint for the nose.
But the tricks of a makeup artist are not always able to fully help in solving this problem. That’s why you should consult a doctor and arrange for rhinoplasty of the wide bridge of the nose. This is done in one of three ways.
Osteotomy
Osteotomy, or controlled fracture of the nasal bones to move them closer together. This forces the nasal bones inward, narrowing the appearance of the bridge of the nose. To perform this procedure, an osteotome is used, a special medical cutter that allows sufficient mobilization and displacement of the nasal bones.
This procedure is most often done with the removal of a hump on the nose, even if the bridge of the nose itself was not wide before the procedure. This is done specifically so that when the first defect is removed, the second one does not visually manifest itself. This procedure has a second advantage: in addition to correcting the defect, it is possible to avoid the formation of a flat bridge of the nose.
An osteotomy removes segments of bone that were separated using an osteotome. The rips are made along the sides of the nose and look somewhat like holes around a postage stamp. This gap is controlled.
But if the patient has previously suffered an injury, then it is impossible to determine the fracture line. It is impossible to predict how the bone tissue will behave in this case. This can cause bone fragments to migrate.
This leads to a negative result. This is why you should definitely tell your doctor whether you have had any injuries in the facial area, even in early childhood.
If rhinoplasty of the nose was performed with injections, the surgeon should also be aware.
Cartilage transplantation
A cartilage graft on the bridge of the nose makes it possible to change its configuration. This makes it possible to visually narrow it. It is better to use native cartilage taken from other parts of the body, but sometimes a synthetic analogue is also used.
If the patient’s cartilage tissue is taken, then only from the nasal septum or in the area of the ribs. Ideally, take it on the ribs, since there it is most resistant to deformation. The ear cartilages are too curved and their use is gradually being phased out. Moreover, they often change shape, creating unevenness on the bridge of the nose.
Set of methods
In some cases, the doctor combines both methods to achieve the best result. Typically, this approach is used for complex operations and when it is necessary to restore the structure of the nasal tissues after injuries or unsuccessful previous procedures.
Augmentation rhinoplasty
It is used if the nose has a wide and flattened shape, which is also called negroid. In this case, there is only one solution - to raise and enlarge the bridge of the nose. A kind of frame is installed under the skin in the right place, which creates the desired shape. For this purpose, the patient's own tissue is usually used.
Actress Jennifer Aniston once resorted to this procedure. Marilyn Monroe did not hesitate to seek such help at the very beginning of her career. This type of rhinoplasty was the first step in her own acting life for Halle Berry, who with her newfound appearance went to the star Olympus by leaps and bounds.
How does the healing process occur?
After surgery, this part of the face heals at about the same rate as any other bone tissue in your body. This depends on the characteristics of a particular organism, and therefore you will have to not only wear a special cast for some time, but also follow a number of rules and procedures.
During the healing process, the formation of initial material called callus occurs. It is he who brings the shape of the nose back to normal after such an intervention.
But the problem is that some patients return with indignation to the surgeon because of the growing callus at the intervention site.
In fact, the doctor is not to blame here, since this is truly a feature of a particular organism. In such cases, only minor corrections are needed.
Considering that the base of the nose has been changed, you may experience a feeling of stuffiness due to the narrowing. And at first, due to swelling, you may also experience a runny nose. The feeling of nasal congestion often occurs precisely because of the growth of bone tissue, which physically reduces the space allocated for the nasal cavity.
If the bridge of the nose remains wide
There have been a certain number of cases where patients complained of a wide bridge of the nose after rhinoplasty. This could be for a number of reasons:
- The doctor performed the osteotomy inadequately or incorrectly.
- Extremely wide nasal bones may require an intermediate osteotomy, which will only be a step in preparation for the final correction of the bridge of the nose.
- Due to the wide horizontal sections of the nasal bones. By removing the medial parts of the nasal bone tissue, this problem is solved.
It is not always possible to get the ideal shape right away. If the doctor did not stipulate that this operation would be intermediate and this is not indicated in the contract, then this is a clear mistake by the surgeon. In this case, it is better to go to another clinic for revision rhinoplasty. But do not rush to sound the alarm until the swelling and bruising on your face completely disappears.
Sometimes they create the effect of a wide bridge of the nose. Over the course of a year, the shape will become stable and you can adequately decide whether to schedule a repeat operation.
According to the unspoken rule of plastic surgeons, if the first plastic surgery was unsuccessful, then the second one is free, but it’s up to you to decide whether you should contact the same specialist.
After rhinoplasty of the bridge of the nose
Full healing occurs throughout the year. The doctor will tell you how rehabilitation is going in your specific case. But in general, the process of complete recovery occurs in two stages.
During the first, postoperative swelling on the face subsides. The speed at which this stage passes depends on whether there has been previous surgery in this area, as well as on whether there is scar tissue.
The individual characteristics of the patient’s body also play an equally important role.
If the patient has thin skin, tissue swelling may persist for months. People with thick skin can retain swelling for up to several years, during which the shape gradually changes.
Once the swelling has gone down, healing continues. The scar tissue should shrink over time, lighten and become visually invisible.
By the way, people with thick skin take much longer to recover.
It should be borne in mind that with the gradual reduction of the nose, the skin envelope should gradually shrink, repeating the anatomical shape. If the skin is thin and the nose is large, then this process can take many months. Therefore, dissatisfaction with one’s appearance in the early stages haunts literally all patients.
If the nose has been significantly reduced, then the skin may not recover to the desired size, creating a new deformation. That is why you should look for a more qualified specialist who, during the first operation, will take into account all the nuances and possible complications, because such problems can be solved.
Source: https://rinoplastikanosa.ru/rinoplastika-perenosicy/
How to wash a baby's eyes with conjunctivitis?
It is necessary to begin treating conjunctivitis by washing the baby's eyes. You should not use antibacterial drugs if the baby’s visual organs have not been cleared of secretions and disinfected. To wash your baby's eyes, you should prepare an antiseptic solution. You can do it yourself. Decoctions of medicinal herbs are suitable for this purpose:
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- sage
Any conjunctivitis - bacterial, viral, allergic - can be treated by rinsing with a solution made from oak bark or aloe. The liquid for cleaning the eyes must be of a weak consistency. The procedure itself should be carried out every two hours during the daytime and 1-2 times at night when the baby wakes up.
Decoctions and solutions must be carefully filtered in advance. At the pharmacy you can purchase a special medicine called “Furacilin” for rinsing. Both the solution itself and tablets for its preparation are available for purchase. Furacilin should be stored in the refrigerator. It must be used within one day. The pharmaceutical solution, supplied ready-made, can be stored in a tightly closed bottle for no more than two weeks.
Conjunctivitis in a 3 year old child
From the age of 3, a new danger arises - allergic conjunctivitis , as a rule, the occurrence at an earlier age is unlikely, although possible. The child suffers from colds less often, does not get into the dirt and knows that he needs to wash his hands, so the risk of viral and bacterial forms is reduced.
It is not necessary for a child to be allergic; this can only be a one-time reaction of immature immunity to an irritating factor. Children's allergic conjunctivitis is also divided into subtypes, depending on which they determine what needs to be treated. As a rule, this is a whole range of activities:
- Determination of the allergen (flowering plants, household chemicals, animal foods, etc.) and removing it from the child;
- Relieving symptoms with antihistamines, drops and tablets;
- In severe cases, corticosteroid drugs are used;
- Prevention - removing all possible allergens, maintaining frequency, avoiding any substances with a strong odor.
What is the danger of conjunctivitis?
Conjunctivitis in babies under one year of age can be successfully cured with timely consultation with a specialist and initiation of therapy. Self-therapy at home is strictly unacceptable. If conjunctivitis is suspected, a small child should be examined by at least two doctors - a pediatrician and then an ophthalmologist.
If symptoms of conjunctivitis appear in children, you should not use advice gleaned from forums on the Internet. The external manifestations of various ophthalmological diseases can be very similar, and only a specialist will be able to determine the true cause after taking the appropriate tests. Successful treatment of conjunctivitis in a child under one year of age depends on following all the specialist’s recommendations.
Hypertelorism
The term “ocular hypertelorism” has been used to refer to the increased bony distance between the orbits.
It was first proposed by LG Greig in 1924 and implied a delay in the displacement of the orbits in the medial direction during fetal development, their fixation in the prenatal state and the resulting resulting increased distance between their medial walls.
Subsequently, P. Tessier proposed a term that more correctly characterizes this condition - orbital hypertelorism. It should be differentiated, first of all, from telecanthus - an increase in the distance between the medial canthus of the palpebral fissures without changing the bone distance, which also imitates hypertelorism.
Therefore, we can highlight
- true hypertelorism , when the eye sockets are widely set due to abnormally wide bone formations between them,
- false (epicanthus) , when the distance between the medial corners of the palpebral fissures is increased, despite the fact that the bone distance between the orbits is within normal limits.
The increased distance between the inner edges of the orbits is usually a consequence of excessive development of the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone. At the same time, the eyes are widely spaced, the bridge of the nose is wide, and the bridge of the nose is flat.
Orbital hypertelorism is not an independent disease and accompanies such anomalies as craniostenosis of the sutures of the anterior cranial fossa, anterior and basal cranial hernias, clefts of the craniofacial skeleton, craniofacial dysplasia, as well as craniofacial tumors and post-traumatic deformities.
Hypertelorism is considered pathological if the interorbital-circumferential index (IOCI) is more than 6.8. MOI is the result of dividing the head circumference by the distance between the inner canthuses, multiplied by 100.
Classification of orbital hypertelorism
The main anatomical characteristic of the OG is an increase in the width of the ethmoid bone in the horizontal plane. The perforated plate in OH is often located at a lower level than is normal. An increase in the width of the cells of the ethmoidal labyrinth is more often observed in the anterior part of the sinus and less often in its posterior part.
In accordance with this, the angle of divergence of the sagittal axes of the orbits from the midline in OH can reach 60°, whereas normally it does not exceed 30°. These anatomical characteristics of the OG are of decisive importance when choosing a method for approximation of the orbits and surgical correction of the middle zone of the facial skeleton.
Tessier classification of orbital hypertelorism
Tessier's classification is based on measuring the interorbital distance (IOD) between the middle of the anterior lacrimal crests.
- with grade I OH, the MOR is 30-34 mm,
- with stage II OH, the MOR is 35-39 mm,
- with grade III OH, the MOR is 40 mm or more.
Tessier himself called this classification “artificial”, since the degree of OH does not indicate the depth of prolapse of the perforated plate of the ethmoid bone. And the latter is crucial in determining the method of surgical intervention.
Classification of orbital hypertelorism V.A. Belchenko
Classification by V.A. Belchenko is based on the difference in measuring the interorbital distance (IOR) at the beginning of the upper third of the orbits, i.e. in the area of the junction of the frontal, lacrimal and maxillary bones and MO in the standard measurement location - between the middle of the anterior lacrimal ridges.
- OG l degree 1st type - MOR between the middle of the anterior lacrimal ridges - 30-34 mm, MOR between the inner edges of the orbits at the level of the beginning of the upper third of the orbits - no more than 34 mm.
- OG l degree of the 2nd type - MOR between the middle of the anterior lacrimal ridges - 30-34 mm, and at the level of the beginning of the upper third of the orbits - 35-39 mm.
- OGII degree, type 1 - MOR between the middle of the anterior lacrimal ridges - 35-39 mm, MOR at the level of the beginning of the upper third of the orbits - no more than 39 mm.
- OG II degree 2nd type - MOR between the middle of the anterior lacrimal ridges - 35-39 mm, and at the level of the beginning of the upper third of the orbits - 40-44 mm.
- OH III degree, type 1 - MOR between the middle of the anterior lacrimal ridges is 40 mm or more, and MOR in the area of the beginning of the upper third of the orbits exceeds this figure by no more than 4 mm.
- OH III degree of the 2nd type - MOR between the middle of the anterior lacrimal ridges is 40 mm or more, and MOR at the beginning of the upper third of the orbits exceeds the first one by 5 mm or more.
The type of OG is determined by the difference in measurements between the MOR at the beginning of the upper third of the orbits and the MOR between the middle of the anterior lacrimal ridges. For type 1, this difference does not exceed 4 mm; for type 2, it is 5 mm or more.
In addition, there are asymmetrical variants of hypertelorism, when in addition to the wide distance between the orbits, rotation of the orbits and differences in height are possible.
Etiology
The intrauterine development of hypertelorism occurs when some kind of failure occurs in the process of bringing the eye sockets together. The reason for this may be the adverse effects on the body of a pregnant woman and the fetus of various factors.
Conventionally, there are several groups of causes that lead to the occurrence of hypertelorism:
- Premature fusion of the sutures of the skull (craniostenosis), namely the sutures of the anterior cranial fossa
- Cranial hernia
- Craniofacial clefts
- Craniofacial malformations (cranial bone dysplasia, Crouzon syndrome, Apert syndrome, etc.)
- Other conditions (craniofacial tumors, post-traumatic changes in the skull bones, etc.)
False forms of orbital hypertelorism
Among the causes leading to the occurrence of false forms of orbital hypertelorism, the most common are trauma to the nasal-orbital-ethmoidal complex with an increase in the interorbital distance and various neoplasms occupying the space of the ethmoid and nasal cavity. And although these manifestations are in most cases regarded as false orbital hypertelorism, the methods for eliminating it can be the same as for eliminating true OH.
Crouzon syndrome
Crouzon syndrome is a genetic disorder known as branchial arch syndrome. Specifically, this syndrome affects the first branchial (or pharyngeal) arch, which is the precursor to the jaw and mandible.
It is primarily formed by premature closure of the coronal and sagittal sutures. Heredity is autosomal dominant, but in 25% of cases there may be a fresh mutation.
Ocular manifestations:
- Exophthalmos due to a shallow orbit is the most noticeable sign. Develops secondarily due to growth retardation of the upper jaw and cheekbone. In severe cases, the eyeballs are dislocated and lie in front of the eyelids.
- Hypertelorism (wide distance between orbits).
- V-shaped exotropia and hypertropia.
- Vision-threatening complications include exposure keratopathy and optic neuropathy due to compression of the optic nerve at the optic foramen.
Pathology of the eyeball: aniridia, blue sclera, cataract, lens subluxation, glaucoma, coloboma, megalocornea and optic nerve hypoplasia.
Greig's syndrome (familial hypertelorism)
This autosomal dominant syndrome was described in 1928 by Scottish surgeon David Middleton Greig. In this disease, the development of the skull is disrupted at an early embryonic stage.
Common manifestations include: brachycephaly, wide nasal bridge, high palate, dwarfism, cryptorchidism.
Mental retardation, convulsive seizures, abnormalities of the jaws and teeth, umbilical hernia, clubfoot, and clinodactyly are often observed.
Ocular manifestations:
- hypertelorism,
- epicanthus,
- deformation of eyebrows and eye slits,
- enophthalmos,
- weakness of convergence,
- high degree of astigmatism,
- bilateral abducens nerve palsy,
- atrophy of the optic nerve as a result of narrowing of the optical canal, in some cases - pigmentary degeneration of the retina.
Toast syndrome
A complex of hereditary abnormalities (probably autosomal dominant inheritance). Bilateral microblepharon, lagophthalmos, eyelash dysplasia (tetrastichiasis, trichiasis), fused eyebrows.
Complications – chronic conjunctivitis, damage to the corneal epithelium. In addition, hypertelorism, epicanthus, sometimes heterophoria, excessive convergence of the eyeballs. Platonychia.
Diagnostics
A preliminary diagnosis is made based on a primary external examination. The distance between the inner corners of the eyes is measured. The presence of maxillofacial deformities is established. Attention is drawn to the shape of the skull. Possible visual and olfactory impairments are identified.
The diagnosis is confirmed by instrumental examination data: X-ray examination and computed tomography of the head, and in some cases MRI to exclude combined anomalies of brain development (cranial hernia, etc.).
An x-ray of the skull bones determines the presence or absence of hypertelorism and the degree of asymmetry of the orbits.
Computed tomography gives a more detailed picture of the existing pathology and allows you to more accurately determine the amount of treatment.
The complex of diagnostic measures must necessarily include an examination by an ophthalmologist, ENT specialist, neurologist, as well as other specialists, depending on the cause of the development of hypertelorism (cranial hernia, craniostenosis, etc.).
Stereolithographic biomodeling
The creation of a real 3-dimensional model significantly increases the possibility of planning surgical intervention. A real operation plan, performed on a model, greatly facilitates the surgeon’s orientation and helps to predict the course of the operation and the detailed implementation of individual stages.
Treatment
Hypertelorism is treated only surgically. The volume, tactics and methods of surgical intervention are determined depending on the cause, severity, and concomitant pathology.
Surgical planning
The optimal timing of surgical intervention depends on a combination of factors, among which the primary ones are:
- Degree of deformation and increase in deformity
- The psychosocial effect produced on the child's parents, other relatives and peers.
At the age of up to one year, the need for correction of craniostenosis may involve simultaneous correction of hypertelorism - orbital displacement.
However, if the severity of orbital hypertelorism is insignificant, its complete extra-intracranial correction with movement of both orbits is difficult at the age of 1 to 2 years and practically impossible until 12 months.
At the age of over 2 years, the bones of the craniofacial skeleton are already quite compact, which greatly facilitates the operation.
Indications for surgical intervention up to 2 years are:
- initially high interorbital distance (28-30 mm at birth)
- their increase to 45-50 mm by the end of the first year of life
In cases of hypertelorism caused by a tumor or fibrous osteodysplasia, indications for surgery are dictated by the manifestations of the underlying process. It is optimal to eliminate hypertelorism during primary surgery, i.e., when removing a tumor or pathological tissue in patients with fibrous dysplasia.
In cases where hypertelorism is combined with facial clefts (upper lip, oblique facial cleft, cleft palate), the clefts are first eliminated - from the first months of life.
Surgical methods for correcting hypertelorism
There are two main methods of surgical correction of this condition: subcranial osteotomy and correction of orbital hypertelorism using an intracranial approach.
Surgical correction for OH syndrome involves mobilization of the orbits (or one orbit) along the external and internal contours, their movement in the required plane and subsequent fixation in a normal physiological position. The orbits are considered as a rigid bony framework containing soft tissues (eyeballs, muscles, etc.)
Obviously, the movement of the orbits should be carried out in the horizontal and vertical planes, but correction can also be achieved by rotating parts of the orbit (the lateral wall in relation to the medial wall or by moving the lower wall of the orbit anteriorly).
Along with mobilization of the orbits, it is also necessary to remove the dilated central nasal part and hyperpneumatized sinuses of the ethmoidal labyrinth, median cerebral hernias, and then perform medial movement of the orbits.
This creates the opportunity for medial transposition of the eyeballs and optic nerve and achieves a satisfactory cosmetic result.
The operation aimed at eliminating grade Ill OH, developed by Paul Tessier in 1963 and improved by him in 1969, still remains the basic method of treating patients with significant lateralization of the orbits. The main stages of such an operation are:
- bifrontal craniotomy;
- creation of a frontal rim, the so-called bando, which is a guideline for the formation of the forehead and upper orbital margins;
- resection of excess bone in the area of the fronto-nasoethmoid complex;
- circular osteotomy of the orbits;
- medial dislocation and fixation of osteotomized orbits;
- bone grafting of defects in the area of the outer walls of the orbits;
- bilateral medial transnasal canthopexy;
- formation of a bone autograft for the dorsum of the nose and fixation to the frontal bone.
© 2013–2020, Eyes for me!
Source: https://eyesfor.me/home/eye-diseases/pathology-of-orbit/hypertelorism.html
Conjunctivitis at three months: what happens?
Conjunctivitis in a child 3 (or more) months old can occur due to exposure of unfavorable microorganisms to the eyes: viruses, infections, fungi. Sometimes this disease appears against the background of a common cold or flu, but it can occur suddenly, on its own. It happens that parents notice the souring of the baby’s eyes after the introduction of new complementary foods.
In this case, we are often talking about the allergic form of the disease. In some cases, conjunctivitis in a child takes on a specific form - dacryocystitis. This pathology, as a rule, manifests itself already 8-10 days after birth and can acquire a chronic form in the absence of proper treatment.
Dacryocystitis appears against the background of an inflammatory process associated with stagnation of tears. Elements of embryonic tissue that accidentally enter the tear canals during the birth process block the normal outflow of tear fluid, as a result of which it stagnates and microorganisms that enter the palpebral fissure are not removed in a timely manner.
What type of conjunctivitis can a child have:
- Viral. Occurs due to viruses entering the baby’s eyes during ARVI, influenza and other diseases. Often accompanied by a runny nose and fever.
- Bacterial. This type of conjunctivitis is caused by various bacteria. The process is usually accompanied by the appearance of purulent yellow-brown discharge of varying consistency.
- Allergic. Appears due to direct exposure to an allergen (for example, when introducing complementary foods).
- Chronic dacryocystitis associated with obstruction of the lacrimal canals.
Parents should remember that viral or bacterial conjunctivitis has an incubation period that lasts about 5-10 days. The exception is the allergic form of the disease, which manifests itself immediately.
Chlamydial conjunctivitis should be placed in a separate category. Unfortunately, in very young patients this form of the disease is quite difficult to identify, since the baby cannot complain to his parents about pain in the eyes in bright light (increased photosensitivity). The first symptoms of the pathology begin to appear only 2-3 days after chlamydia penetrates the mucous membrane. The child's eyelids swell noticeably, and pus also accumulates in the crease of the lower eyelid.
Causes of pathology, photo of epicanthus in a child, classification and removal
What is epicanthus? This is a vertical fold , which is located next to the inner corner of the eye, which covers the lacrimal tubercle. This continuation of the upper eyelid indicates the first sign of the Mongoloid race.
A special sign is pathology, which may not affect the level of vision , but reduces the field of view.
In a person with epicanthus, you may notice strabismus, since the pupil is much closer to the inner corner of the eye than in a normal person, thereby creating a false effect.
Sometimes such folds are corrected surgically. This mostly happens when it is a cosmetic defect rather than a congenital one.
Most people with this pathology want to know how the operation and the postoperative period proceed. But according to surveys of former patients, we can be proud of our medicine, because everyone likes the new reflection in the mirror, as well as a noticeable improvement in well-being.
Causes and characteristic signs of pathology
The most common and so-called adaptive feature is the fold, which is necessary under climatic and weather conditions such as wind and cold.
But the main cause of epicanthus has not yet been established . There is an opinion that the fold is needed to protect the eye from dust, strong wind or exposure to radiation.
Environmental, physical, chemical and medicinal factors have a great influence on the body of a woman who is carrying a child. To these factors you can add alcohol, nicotine and an unbalanced diet. In children, epicanthus can develop for the following reasons: prematurity, prolonged labor, premature birth or multiple pregnancy.
One of the symptoms of epicanthus is chromosomal pathology, namely Down syndrome . Epicanthus can also be observed in the following situations: blepharophimosis (pathology of the palpebral fissure), ptosis or trauma to the upper eyelid.
Epicanthus
Oddly enough, it has been proven that a characteristic sign of such a pathology is the structure of the bridge of the nose. To be more precise, the size of the fold is smaller if the bridge of the nose is higher. Scientists came to this conclusion after conducting research among the peoples of the north with nationalities such as Eskimos, Yakuts, Buryats, Kalmyks, Chukchi and Kyrgyz.
The appearance of epicanthus depends not only on the location and structure of the bridge of the nose. To a lesser extent, it depends on the fat layer located under the skin of the upper eyelid. It was previously found that epicanthus occurs much more often in patients whose fat layer is larger. In cold climates, people were saved from freezing by increased fat deposition.
Epicanthus photo of a child
In children under the age of six months, epicanthus most often spreads, and especially with a flat bridge of the nose.
Epicanthus is not considered a deviation in children of the Mongoloid race, but among Europeans it is a pathology of intrauterine development.
Despite this, it can also appear with chromosomal diseases, which is much less common. If the child’s epicanthus is insignificant, it disappears spontaneously by the age of seven.
It is possible that Down syndrome is observed with chromosomal abnormalities , one of the signs of which is a bilateral fold. This pathology does not always go away on its own; sometimes surgical intervention is required, which can only be performed after 5 years.
Classification
Depending on the type of violation, the folds of the upper eyelid are divided into:
- Congenital . This is especially true among Asians. The causes of this pathology include maternal illnesses, the development of which occurred not only during pregnancy, but also before it. For example, abortions, infections, toxicosis in late pregnancy, diseases of the endocrine system, etc. Also, one cannot ignore alcohol and smoking, which also have a positive effect on the development of pathology.
- Purchased . Develops in connection with injuries that leave behind changes in the form of a scar.
In turn, the folds differ in their origin from the degree of development and their location. There are four types of upper eyelid folds:
- Straight . The fold begins and continues only on the upper eyelid.
- Reverse: The fold starts at the top and goes down.
- Palpebral . Uniform placement of the fold on both the upper and lower eyelids.
- Superciliary . Maximum manifestation of the crease. It starts from the eyebrow arch and ends on the lower eyelid.
Removal
The simplest method is blepharoplasty - an operation that is performed if the fold is a cosmetic defect. The purpose of this operation is to change the incision, tighten the upper eyelid and ultimately change the shape of the eye.
Most often, this operation is performed by people of the Mongoloid race, since after the procedure their eyes become more expressive, and their gaze is more open, and approaches the European one. The operation itself consists of making a triangle-shaped incision from the corner of the eyelash line along the upper eyelid and removing excess fatty tissue. As a result, this incision remains invisible.
But there is a method without the intervention of a scalpel. This is the case if the skin of the eyelids is very thin and does not droop so much. To achieve a European eye shape, the technique of sutures along the eye muscles is used. The formation of a fold occurs due to remaining puncture marks.
Source: https://glaz.guru/stroenie-glaza/epikantus-chto-eto-takoe-i-byvaet-li-on-u-detey.html
Treatment of chlamydial conjunctivitis in newborns
In the case when an infant has only one lesion, namely inflammation of the conjunctiva with moderately pronounced signs of infectious toxicosis, his condition is usually assessed as a condition of moderate severity. In this case, treatment is carried out comprehensively by an ophthalmologist and a neonatologist. Broad-spectrum antibiotics (macrolides) are prescribed:
- "Erythromycin", which is used for 21 days.
- "Sumamed" - the course of treatment is 7 days.
- "Josamycin" - within a week.
Drops and ointments containing macrolides (erythromycin ointment) or combined antibacterial drugs are prescribed locally: eye drops containing colistimethate/rolitetracycline. It is important to remember that macrolides cannot be used simultaneously with chloramphenicol, penicillins or cephalosporins. Treatment is prescribed and adjusted exclusively by a doctor.
It is also necessary to use immunomodulators - interferons - Viferon-1 is usually prescribed 2 times a day for 10 days or longer.
After completing the course of treatment, a repeat test for chlamydia is carried out 2-4 weeks later. If they are detected, a second course of treatment is required.
What other signs of Down syndrome are there in newborns?
Just these signs described above may be enough to suspect Down syndrome in a newborn child. But there are still some external differences in such babies that “pop up” during a more detailed examination and examination of the baby, which may indicate this chromosomal disorder:
- strabismus;
- pigment spots along the edge of the iris of the pupils (“Brushfield spots”) and clouding of the lens;
- a violation in the structure of the chest, it protrudes forward or sinks inward (keeled or funnel-shaped chest);
- tendency to epileptic seizures;
- stenosis or atresia of the duodenum and other defects of the digestive system;
- defects of the genitourinary system;
- congenital blood cancer (leukemia).
These signs occur in 8-30% of all cases. Also, a baby with this chromosomal abnormality may have an extra fontanel or the fontanelles do not close for a long time. But a newborn child with Down syndrome may also not have clear characteristic external features: differences will appear later.
It is noteworthy that children with Down syndrome are very similar to each other, like brothers and sisters, while it is impossible to recognize the parental features in their faces.
Traditional therapy
Treatment of inflammation of the conjunctival membrane of the eye of newborns using folk remedies is highly not recommended for a number of reasons.
They are as follows:
- If the pathology is caused by an allergen, treatment with folk remedies can cause a deterioration in the baby’s condition.
- Conjunctivitis caused by a bacterial agent will only develop more actively if not treated with medication.
- No folk remedies can eliminate viral conjunctivitis.
Before visiting the doctor, you can do a little treatment at home using folk remedies. Treat the conjunctiva with infusions of chamomile, calendula, sage, green or black tea, and aloe. To wipe, soak a cotton swab in the prepared broth, and then treat the eyes in one direction (towards the nose). Such a light medicinal massage for inflammation helps eliminate crusts and pus from the eyes, eyelashes, and eyelids.
What happens when the conjunctiva is damaged by viruses or bacteria?
The body of a two-year-old child, when first confronted with an aggressive viral and bacterial environment that is unusual for him, becomes vulnerable to adenoviruses, enteroviruses, staphylococci, streptococci, etc. Once on the mucous membrane of the eyes, the infection spreads further, penetrating deeper and affecting the integrity of blood vessels and tissues. Due to this effect, purulent discharge is formed, which is released profusely during conjunctivitis caused by a bacterial infection. Such pus consists of destroyed leukocytes, enzymes, and protein breakdown products.
The greater the number of bacteria on the mucous membrane, the stronger the toxins they produce affect the child’s body. To prevent various complications from leading to intoxication, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner and begin treatment with antiviral and antibacterial drops and ointments. Untreated conjunctivitis at 2 years of age can cause a chronic disease.
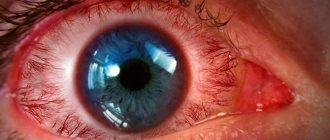
Spicy
Acute conjunctivitis occurs with a sensation of pain and redness. Mucus and pus also begin to appear. Acute conjunctivitis is accompanied by general malaise, headache and fever. A constant burning sensation and sensation of a foreign object in the eye are present in this form of the disease.
Young mothers are tormented by the question: if conjunctivitis is discovered in their baby, is it possible to walk with him on the street? Of course, it is possible if the child does not have a fever or runny nose.
Conjunctivitis in infants can occur along with a cold and goes away on its own after seven days. In adults, this period lasts longer.
Physiognomy - the whole truth at the tip of the nose
Physiognomy considers at least 24 signs related to the nose. But these are 576 possible combinations! By looking at the nose of your interlocutor, you can better understand its owner
Physiognomy considers at least 24 signs related to the nose. But these are 576 possible combinations! By looking at the nose of your interlocutor, you can better understand its owner. Let’s figure out what features immediately attract attention and are clear for interpretation
Nose length
Lorenzo Villoresi
A person with a long nose (an example is the outstanding modern perfumer Lorenzo Villoresi) is thorough and knows how to appreciate beautiful and tasty things. Attaches great importance to the aesthetic side of the issue.
He is well versed in haute couture and haute cuisine. The owner of a long nose should not be rushed - on the contrary, you should try to get into his pace.
Where the gift of diplomacy is required, long-nosed people will be simply irreplaceable.
Danielle Westbrook
People with short noses (for example, British actress and TV presenter Danielle Westbrook) are more specific, prefer to receive information quickly and immediately, in a compact form; the beauty of the packaging will not be of particular importance.
Such people give out information in the same way - quickly and compactly. True, it is not always polite - which, however, is simply perceived by the short-nosed people themselves as frankness.
Is it possible to be offended by the truth? And one more thing: people with short noses are invaluable if you need the ability to quickly navigate and make decisions.
Now the question is: which nose length is better for a sommelier, and which for a fireman?
With and without a hump
Paris Hilton
A straight nose (for example, the famous party girl Paris Hilton) is characteristic of people with the same straight character. It is usually easier to negotiate with them: they do not change the original conditions.
Adrien Brody
Another thing is a nose with a hump (for example, actor Adrien Brody).
The owners of such noses are very changeable; new ideas constantly come to their minds, forcing them to change their path and, alas, sometimes retreat from previously reached agreements.
If your child has a hooked nose, you should not ask him two weeks before his birthday what mobile phone he wants as a gift - new versions of “wants” will be announced every day.
Always remember that a person with a hump on the nose has a particularly sensitive pride. If in a conversation with him you notice that he has begun to rub his hump, know that you have inadvertently offended him.
So, the question is: will you draw up a contract in every detail or will you just take the word of a person with a hump on his nose?
Nostrils
The width of the nostrils is used to judge the degree of energy of a person (sometimes called temperament). Indeed, a person with wide nostrils is able to absorb more air at once, which serves our species homo sapiens as the main type of “fuel”.
Mikhail Pugovkin
A person with wide nostrils (an example is actor Mikhail Pugovkin) is easy-going, quickly lights up and... alas, quickly deflates. Long-term programs are not his thing. Such people are best suited to the “eat an elephant” technique, when a large task is posed successively in small fragments.
Roald Amundsen
Narrow nostrils (for example, the traveler Roald Amundsen) endow their owner with regularity and balance. Such a person is by nature capable of long-term work at a measured pace. In other words, if the term “sprinter” is better suited to wide nostrils, then narrow nostrils are always a stayer.
Business problem: which employee is more suitable for a startup and which one is more suitable for implementing a long-term project?
Nose ridge
Tamerlane
The narrow ridge of the nose (for example, the Central Asian conqueror Tamerlane) belongs to people who are sharp, sometimes hot-tempered, always ready to rush into battle. Combined with an aquiline nose - an explosive mixture! You need to negotiate everything with such people in a friendly, calm atmosphere, eliminating stress and quarrel.
Steve Wozniak
A wide nose ridge (for example, one of the founders of Apple, Steve Wozniak) reveals peaceful, kind, and sincere natures. These characters are always looking for (and successfully finding!) a peaceful way out of the most ambiguous situations. They have the rare gift of not only avoiding conflicts, but also stopping them at the very beginning.
Question: If you were to go on a space flight, which nose ridge would you prefer to choose as your neighbor in the orbital station?
bridge of the nose
Monica Lewinsky
A wide bridge of the nose (an example is the well-known Monica Lewinsky) inclines a person to investigative behavior. In science, psychology and the practice of investigative bodies, this is a most valuable quality, but in ordinary life it can lead to conflicts. In addition, people with this feature sometimes have difficulty setting goals—they need help choosing a goal.
Prince Charles
A narrow bridge of the nose (for example, Prince Charles) gives excellent goal setting and completely predictable behavior that is comfortable for others. Although... openness in behavior does not always please those who are nearby with its frankness.
Challenge: Which bridge of your nose would you choose to be the head of security for your corporation?
tip of the nose
On this basis they look at how neat a person is and is able to delve into details.
Steve Jobs
Let's remember Steve Jobs, whose nose was as sharp as a beak. Jobs paid exceptional attention to every detail of every device produced by his company.
If you are negotiating with a sharp-nosed person, prepare for the fact that he will want to ask you about the smallest details related to the matter.
And if your marriage partner has a sharp tip of the nose, pedantry in everything will be your constant companion.
Gerard Depardieu
A blunt tip of the nose (like, say, Gerard Depardieu) betrays a person for whom the big picture is much more important than small details. Hence, there is not so much attention to order and a reluctance to delve into details. Do not expect deep analytics and scrupulousness from such a person - this is not in his nature. But it will come in handy where you need to act quickly and in “broad strokes.”
Scarlett Johansson
Snub-nosed people (for example, actress Scarlett Johansson) are most often open and optimistic people, with a cheerful and easy-going disposition. They prefer to enjoy today without thinking too much about the future.
It’s another matter if the tip of the nose hangs down (for example, Microsoft owner Bill Gates). In ancient and medieval treatises on physiognomy, such a sign was noted as a nose for money. There really is something to this.
A person with such a nose tip will not always be a millionaire, but in almost all cases he has some special talent that can be successfully monetized.
Question: Which nose tip shape would you choose as your personal financial advisor?
German Teplyakov
Source: https://econet.ru/articles/64590-fiziognomika-vsya-pravda-na-konchike-nosa
Causes of the disease
The most common causes of conjunctivitis in infants under one year of age:
- Infection in the eyes during childbirth if the mother is infected with chlamydial, gonococcal or other infection.
- Reduced immunity, which in a newborn is not yet formed and is easily susceptible to infection.
- Getting dirt into your eyes due to poor hygiene or by accident.
- The mother is infected with herpes.
- There is a high concentration of an allergen in the room to which the child has developed sensitivity.
Bacteria and viruses that cause conjunctivitis easily provoke the disease in a newborn, since the immune system is still imperfect and cannot repel an attack of infection.
Prevention is the best cure
In weakened children, conjunctivitis can occur every year, and sometimes several times a year, so it is important to strengthen the child’s immunity in accessible ways.
You can protect your child from pathology by following simple rules:
- monitor the cleanliness of the child’s hands and skin;
- maintain the cleanliness of the room in which the child is located;
- regularly ventilate the children's room;
- keep the bed, toys and other objects with which the child comes into contact for a long time clean;
- enrich your baby’s diet with healthy foods high in minerals, nutrients and vitamins;
- provide the baby with a personal towel for his hands and face;
- walk with the child in any weather (except for strong wind and rain) for 2-4 hours;
- check the quality of products used to prepare children's meals.
To prevent infection from entering the child’s body, one should avoid visiting crowded places during epidemic periods, as well as contact with sick people. It is better to postpone a visit to the clinic for a routine examination if an epidemic of acute respiratory viral infections and influenza has been declared in the city.
If a speck or sliver gets into your eye, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist in the on-duty department (they work 24 hours a day). If measures are not taken in time, bacteria can enter and damage the mucous membrane of the eye, so timely provision of medical care is the key to maintaining the health of the visual organs.
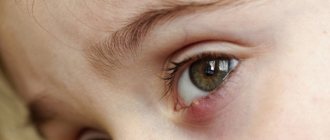
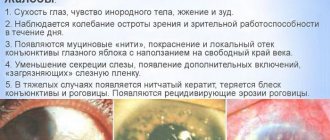
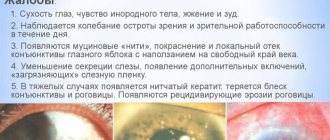
Symptoms of eye disease
The symptoms of conjunctivitis are quite easy to notice. Until 3 months of life, the baby's tear duct is not formed, which means there are no tears yet. Any discharge from the eyes of a newborn is a signal that you should consult a doctor. Symptoms of conjunctivitis depend on the nature of the inflammatory process.
However, all types of this disease are characterized by:
- redness of the mucous membrane of the newborn's eyes;
- lacrimation;
- swelling of the eyelids
Viral, in addition to general symptoms, is manifested by photophobia (the child squints from the light and protests), pain, itching, non-purulent discharge, sometimes blisters appear on the baby’s eyelids. Eye damage occurs sequentially.
The bacterial one is the most difficult and is characterized by pus discharge that sticks together the newborn’s eyelids. In some forms, it is accompanied by high fever, pain and pain in the eyes, a rash on the eyelids and severe swelling.
Strabismus in infants: normal or pathological?
Not all parents know that strabismus in infants is often a physiological norm. In order to understand when you should immediately go to the doctor with such a problem, and when you should not worry, you need to understand why this happens.
What is the norm?
In an adult, the axes of the eyes normally coincide completely. Deviation from this is called strabismus, or strabismus. There is another clinical name - heterotropia. There are two main types of strabismus:
- Converging. In this case, one or two eyes slant towards the bridge of the nose. In infants this is exactly the type observed (in 90% of cases).
- Divergent. One or both eyes move towards the temple.
As a result of the fact that a newborn baby often has weakness of the extraocular muscles, heterotropia develops for this reason.
At birth, he does not always have access to control over the movement of his eyeballs. It is important for parents to know when this phenomenon occurs, since such a process cannot be started.
Only 9% of seven-year-old children of the total number of children with strabismus persist. Over time, the eye muscles become stronger, and there is no longer any reminder that the baby had strabismus.
The structural features of the skull bones and the wide bridge of the nose also lead to the fact that the child has some deviation. It goes away in a few months.
Causes of pathological strabismus
But there are a number of cases in which normalization does not occur. The causes of this pathology may be:
- birth complications;
- lack of oxygen during intrauterine development;
- infection and intoxication of the fetus;
- previous measles, scarlet fever or influenza;
- neurological abnormalities;
- hereditary predisposition;
- improper placement of toys above the bed.
Psycho-emotional stress (screaming, bright light, etc.) can lead to the temporary appearance of strabismus in a newborn.
If strobism is observed for more than six months, it leads to impaired visual acuity and the development of amblyopia.
When to go to the doctor?
Despite the fact that strabismus can go away a month after birth, or three, but normally this phenomenon should not be observed in a six-month-old baby.
It is at this age that strabismus is considered a pathological condition and is a reason to consult a doctor.
The following types of disease are distinguished:
- by time of appearance - congenital or acquired;
- permanent and temporary;
- one-sided or alternating;
- convergent, divergent and vertical.
Separately, we should highlight the paralytic type, in which the eye does not move in a certain direction as a result of damage to a muscle or nerve.
How to prevent the disease?
To prevent strobism from becoming a cause of vision loss, there is prevention of strabismus in infants .
If a baby has strabismus at the age of one month, then you need to do the following:
- Hang bright toys above the center of the crib at such a distance that the baby would not be able to reach them with his hand.
- Toys should only be large sizes.
- Do gymnastics to strengthen the eye muscles. For this purpose, you need to take a large and bright rattle and move it from side to side so that the baby follows it with his eyes.
- At the age of two months, undergo a scheduled examination by a specialist and follow all his recommendations.
Treatment options
Conjunctivitis in infants is a serious disease. Therefore, you shouldn’t joke with him while self-medicating. Any treatment should begin with a visit to your pediatrician. This is the only way to most effectively influence the virus that causes conjunctivitis. A specialist will definitely prescribe drops.
He will also select the best dosage for a particular case. The doctor will recommend cold compresses. With the correct and systematic use of prescribed medications, the child recovers quickly: within a few weeks. Sometimes it is enough to save the baby from contact with the allergen. For bacterial diseases, ointments and drops containing antibiotics are used.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in children aged 2 years
Children as young as 2 years old find it difficult to tolerate diseases such as conjunctivitis. The main difficulty is that therapeutic manipulations are painful and unpleasant, and therefore 2-year-old children begin to be afraid of them. Resistance during eye drops can lead to insufficient therapeutic effect, since the required amount of the active substance does not enter the body. Therefore, it is important for parents to establish trusting contact with the child, reassure him, and carry out treatment without using violent measures.
Why does epicanthus appear in a person of non-Mongoloid race?
Various factors can lead to the appearance of pathological epicanthus:
- infectious diseases that are transmitted from mother to child;
- chromosomal abnormalities;
- alcohol abuse by a pregnant woman, smoking and poor nutrition;
- multiple pregnancy;
- premature birth;
- Down syndrome.
Basically, the epicanthus fold in a person of non-Mongoloid race is a congenital disease that appears in children born in unfavorable conditions, as well as in the presence of physiological and hereditary pathologies in the mother.
Epicanthus can also be acquired. Injuries to the eyelids and skin around the eyes lead to the formation of folds in the inner corners of the eyes, causing scarring.
What consequences are expected if conjunctivitis in a child is not cured in time?
The disease itself is easily treated and is considered simple. But, as with any other disease, treatment is still required, and if timely assistance is not provided, serious problems may arise. In cases where the advice of doctors is neglected and the course of treatment is not completed, conjunctivitis may return, but in a chronic form.
The consequences may be different:
- The worst thing is that the child may go blind;
- Visual acuity may decrease, which cannot be restored later;
- Various formations may appear on the eyelids, which will bring both aesthetic and physical discomfort (scars, ulcers, etc.);
- the disease can develop into a chronic form.
Why does conjunctivitis occur in a two-year-old child?
The most common cause of conjunctivitis is the child's curiosity and dirty hands. The baby constantly wants to explore new things, touches everything that comes to hand, and then, without washing himself, he can start rubbing his eyes. The main breeding ground for dangers for a baby is the sandbox, because there is not only dirt and sand, but also other people’s children’s toys, which may contain viruses and infections.
The main factors that cause a baby to develop conjunctivitis are:
- Dirt on hands;
- Allergic reaction;
- Viruses;
- Fungus;
- Microbes;
- The influence of wind and frosty weather.