Indications for use
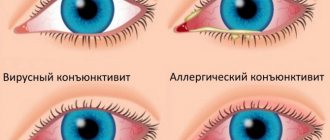
In case of infectious and bacterial damage to the visual apparatus, the mucous membrane and cornea are primarily affected. Signs such as sensitivity to light, mucous or purulent discharge, redness, itching and burning appear. Visual acuity gradually decreases.
With such symptoms, taking antibacterial drugs cannot be avoided. They are prescribed for the treatment of the following infections:
- Blepharitis. There are several clinical forms of the inflammatory process of the eyelid margin: simple, ulcerative, scaly, meibomian. Each type of blepharitis requires the use of antibiotics to cure. It manifests itself as a feeling of discomfort, narrowing of the palpebral fissure, swelling, redness, and accumulation of discharge in the corners of the eyes. In the ulcerative form, yellow crusts appear, after removal of which ulcers form.
- Hordeolum is the most recognizable eye pathology. It manifests itself as a slight swelling, increasing every day. Most often, barley is caused by staphylococcus, also caused by streptococcus, fungi and Demodex mites. If you do not start treatment with antibiotics or squeeze out the contents of the sac, the infection will spread not only to the other eye, but also to the brain. This can result in blood poisoning and meningitis.
- Creeping corneal ulcer. The causative agent of the pathology is pneumococcus, staphylococcus, streptococcus. Bacteria penetrate into the thickness of the cornea after injury. Causes decreased vision, lacrimation, severe pain and photophobia. The creeping ulcer spreads quickly and within a few days covers most of the cornea. You cannot delay treatment.
- Dacryocystitis develops due to the inflammatory process of the lacrimal sac, located between the nose and the inner corner of the eyelids. The disease is often unilateral and causes pain, redness, swelling and discharge from the eye.
- Keratitis can be infectious, viral and parasitic. In the first and last cases, antibiotics are prescribed. Keratitis causes sensitivity to light and spasmodic contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle and eyelid.
Antibacterial drops are prescribed for the treatment of conjunctivitis, uveitis, chronic and acute inflammatory processes of the eye and its appendages.
Indications
Antibacterial agents are recommended for ophthalmic infections of bacterial origin, such as:
- conjunctivitis - inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- keratitis - damage to the cornea;
- blepharitis is an infectious disease of the lower or upper eyelid;
- stye is a purulent-inflammatory process in the sebaceous pilosebaceous sac in which the eyelash grows;
- anterior uveitis - inflammation of the iris and ciliary body;
- Dacryocystitis is a purulent-inflammatory lesion of the lacrimal sac.
The following signs may indicate the onset of infection:
- pain, pain, itching, burning and discomfort in the eyes;
- weakened vision;
- swelling of the eyelids;
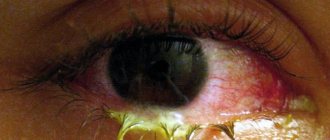
- mucopurulent discharge from the eyes;
- sticking of eyelids and eyelashes after sleep;
- photophobia;
- increased tearfulness;
- eye hyperemia;
- gluing eyelashes;
- local hyperemia and thickening of the ciliary edge of the eyelid (these symptoms occur with barley).
Typically, a bacterial infection affects only 1 eye.
When these signs appear, an eye disease of bacterial origin can be suspected and antimicrobial agents are recommended. These dosage forms are prescribed for the prevention of infectious and inflammatory diseases after injury, surgical therapy, and laser eye correction.
Classification of drugs
Drugs are more often used to treat bacterial diseases, less often - for fungal and viral-bacterial ones.
Antibiotics in ophthalmology are divided into:
- aminoglycosides (Gentamicin, Neomycin, Tobramycin, Netilmicin);
- chloramphenicol (Levomycetin ointment and drops);
- fluoroquinolines (Ofloxacin, Oftaquix, Oxolinic ointment, Tsipromed, Tsiprolet, Floxal);
- sulfonamides (Albucid).
There is also a second classification of antibacterial drops. They are divided into four groups:
- the first includes drugs that affect a specific group of pathogens, that is, with one type of antibiotic (Fucitalmic, Levomycytin drops, Maxiflox);
- to the second - agents acting against several pathogenic microorganisms (Albucid);
- the third - antibiotics in combination with anti-inflammatory substances (Maxitrol, Neomycin, Tobradex, Sofradex, Garazon);
- to the fourth - antiseptics (they are universal medicines that can destroy viruses, fungi and infections), Okomistin, Vitabact.
Tablet antibiotics
Most often, drops are prescribed.
For serious bacterial infections of the body that have caused complications and visual organs, broad-spectrum antibiotic tablets are used.
For the most part, their appointment is made by the attending physician, basing the final decision on the degree of damage to the patient and the individual characteristics of his case.
The specificity of “tablet” antibiotic therapy is quite high, so it is not advisable to engage in it without consulting a professional doctor.
The following broad-spectrum antibacterial tablets are popular in modern ophthalmology:
- Tetracycline;
- Amoxicillin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Ertapenem;
- Chloramphenicol;
- Streptomycin.
Each of the marked products has individual characteristics, therefore, before using any drug, it is extremely important to study in detail the instructions attached to it.
Based on its provisions and the doctor’s recommendations, antibacterial therapy should be organized using tablets. A different approach to such treatment is not desirable, especially when it comes to getting rid of rather specific eye lesions.
Antibiotics for adults
When choosing a medicine for an adult, you should rely on the results of an antibiogram. Only after the examination, the ophthalmologist will prescribe the patient a medication that most actively destroys the pathogen.
Dexon
The drug is effective against the inflammatory process of the edges of the eyelids, the outer shell of the eye, the iris, deep and superficial keratitis. Dexon drops should be used in accordance with the instructions to avoid an overdose. For mild forms of eye diseases - 1 drop, for severe ones - 2 drops.
Frequency of use: 4–6 times a day. Duration of therapy is 7–14 days. Cost 150 rub.
Oftaquix
The active ingredient of the drug is levofloxacin. Used for infections of the eye and its appendages in patients older than 1 year. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is recommended not to use the drug.
Oftaquix is used up to 8 times a day, 1-2 drops per eye requiring treatment. Price 407 rub.
Normax
Prescribed for the treatment of keratitis, blepharitis, corneal ulcers, conjunctivitis. Not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age. Normax is prohibited in case of individual intolerance to quinolones, pregnant and lactating women. After first opening the bottle, store for no more than 4 weeks. Cost 147–163 rubles.
Tsipromed
Used in ophthalmology for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases. Prescribed to patients with keratitis, chronic dacryocystitis, uveitis, bacterial ulcers. The dosage regimen of Tsipromed depends on the severity of the inflammatory process. The drug is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolones. Price 120 rub.
List of antibacterial drops for adults
Let's look at the most popular bactericidal eye drops.
Albucid
Albucid eye drops
The sulfanilamide agent has antimicrobial and antibacterial properties. Albucid simply does not allow pathogens to multiply further. The remedy is prescribed for blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, and gonorrheal eye diseases.
The active component of the drug is sulfacetamide, a bacteriostatic substance. This means that the drug substance stops the active growth of pathogens, interfering with normal functioning. The active component of Albucid blocks the production of vital substances in a bacterial infection, which is why it ceases to be active. Staphylococci, streptococci, chlamydia, gonococci, E. coli and other bacteria are sensitive to sulfacetamide.
Important! Fungi and viruses are insensitive to the effects of Albucid.
Place two drops in each eye four to six times a day. During the procedure, patients may experience burning, discomfort, and excessive lacrimation.
Azidrop
The main active ingredient of the drug is azithromycin, a drug from the group of macrolides. The principle of action of Azidrop is based on inhibition of the synthesis of proteins that are essential for the growth and reproduction of bacteria. Large concentrations of the drug can have a bactericidal effect, in which pathogens have no chance of existing.
Azidrop eye drops contain azithromycin
Drops have a wide range of therapeutic effects. They are even prescribed for such serious diseases as trichomonas and chlamydial conjunctivitis, as well as purulent bacterial diseases.
It is recommended to instill Azidrop one drop into the conjunctival sac in the morning and evening for three days. Do not forget about the likelihood of side effects: itching, tingling, hyperemia, lacrimation, sticking of eyelids, sensation of the presence of a foreign body.
Tobrex
This is an antibiotic with a wide spectrum of action, which is prescribed for the treatment of such diseases: keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis, dacryocystitis, blepharitis. Drops are also prescribed for prophylactic purposes after surgery.
Place one or two drops of Tobrex in each eye. In the acute period, it may be necessary to use drops every hour. Next, the drug is prescribed to be instilled at intervals of four hours. It is prohibited to use Tobrex during lactation.
Tobrex belongs to the group of aminoglycosides
Phloxal
The active component of the product is ofloxacin, a substance from the group of fluoroquinolones. Floxal has pronounced bactericidal properties against gram-positive and gram-negative microflora. The drug is prescribed even when it is not possible to accurately determine the bacterial pathogen. Ofloxacin inhibits the vital activity of staphylococci, streptococci, Klebsiella, gonococci, and Shigella.
Indications for the use of drops are the following diseases: keratitis, barley, conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer. Floxal is used to prevent and treat infections that appear after surgery or injury. Drops are instilled two to four times a day for one to two weeks into the affected eye.
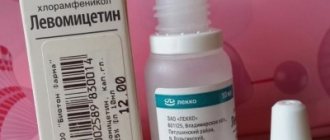
Levomycetin
The main component is chloramphenicol. It has a wide spectrum of antibacterial action and is used to combat keratitis, blepharitis, conjunctivitis and other infectious processes. Both gram-positive and gram-negative microflora are sensitive to the action of chloramphenicol. The product is instilled from four to twelve doses per day.
Dexa-Gentamicin
These anti-inflammatory eye drops are used not only for bacterial lesions, but also for allergic reactions. When treating viral infections, drops are powerless. While using Gentamicin, a burning sensation, itching, and blurred vision may occur.
Effective for conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis, dacryocystitis, as well as purulent lesions. Drops are instilled three to four times a day.
Dexa-Gentamicin is an anti-inflammatory drop with a combined composition
Antibiotics for children
In pediatric ophthalmology, only those drugs are used whose instructions allow their use. Medicines are relatively safe, but it is better to be prescribed by a doctor.
Tobrex
Prescribed for keratitis, blepharitis, hordeolum and iridocyclitis. The medicine is allowed to be used by adults and children, including newborns. Tobrex is used up to 5 times a day, 1 drop. Duration of therapy is a week. Cost 181 rub.
Maxitrol
The medication is effective against gordeolum, cholazion, conjunctivitis. There are no contraindications for children, except increased hypersensitivity. Maxitrol is contraindicated for use in chicken pox, purulent corneal ulcers, fungal and viral diseases. Price about 600 rub.
Vitabact
Prescribed to children from birth for the treatment of bacterial infections of the anterior part of the eye and dacryocystitis. Vitabact rarely causes allergic reactions and is well tolerated by young patients. Cost 351 rub.
Fucithalmic
Medicine is prescribed for keratitis, dacryocystitis, conjunctivitis and blepharitis. Fucithalmic is not absorbed into the blood, so it is prescribed to children from birth. It has no serious contraindications. Cost 263 rub.
We recommend reading: How to put drops in a child’s eyes
Drops for children
Broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs
Bacterial eye infections are noticeably more common in children under 10 years of age, so ophthalmic pharmacology is actively producing specialized antibiotics specifically for sick children.
As a rule, lesions in children are general in nature and streptococci, staphylococci, and various bacilli are almost always present in the smear of the affected eyes. Due to this specificity of childhood eye pathologies, broad-spectrum antibiotics are often used for their treatment.
The safest and most effective antibacterial drops for children are:
- Tobrex;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Phloxal.
Despite the good practice of using the indicated products, even before using them, it is advisable to consult with an ophthalmologist.
Do not forget that the body of children, especially those suffering from some damage, requires high-quality and thoughtful therapy, so it is better to exclude self-medication.
Otherwise, an incorrectly selected drug or its incorrect dosage can not only reduce the effect of treatment to zero, but also completely worsen the condition of the affected eyes. Naturally, there is no need to take risks like this.
Mechanism of action of antibiotic drops
The mechanism of action of antibacterial agents for the treatment of eye pathologies depends on the active component.
The principle of action of each group of drugs:
- Aminoglycosides penetrate the pathogenic microorganism through the cytoplasmic membrane. Inhibits protein exchange by ribosomes.
- Fluoroquinolines interfere with DNA synthesis. They inhibit the activity of the A subunit of DNA gyrase. Drugs in this group reduce accumulation in the bacterial cell.
- Sulfonamides inhibit the activity of enzymes that catalyze two stages of folic acid synthesis. They prevent further formation of para-aminobenzoic acid, which is necessary for cells for active reproduction and development.
These drugs are effective against bacterial agents. They help with viral and fungal diseases, but their effect is reduced.
What to replace it with?
Analogues can be used for the treatment of eye pathologies. The drug "Benzylpenicillin" is available in powder form for the preparation of a solution. It is low toxic. It is characterized by availability and low price. Approved for use by children over 1 year of age and pregnant women. Long-term treatment increases bacterial resistance to the drug and disrupts the intestinal microflora. Another analogue is Oxacillin, which can be in the form of a powder or tablets in a blister. It is prescribed even to newborns. The disadvantages include possible side effects in the form of disorders in the functioning of the digestive system and the occurrence of allergic reactions on the skin.
How to instill medicine correctly
Often patients do not know how to use drops correctly in order to achieve maximum results in a short time. Do not bury in the inner corner. The tear duct is located there.
If you drop it there, the medicine will enter the nose and be absorbed into the blood. There is a risk of infection. There will be no result from such instillation.
Correct use of antibacterial drops:
- Wash your hands and hold the bottle in your hands to warm it up. Cold medicine is less absorbed by the mucous membrane of the eye.
- Prepare cotton swabs and napkins. Throw your head back, bring it to your eyes at a distance of 3 cm.
- Pull the lower movable cover down to form a pocket. Drop the medicine into it, close your eyelids and wait 2-3 minutes, covering the inner corner of your eye with a cotton ball. Do not close your eyes or blink too much; the medication will leak out.
If the doctor has prescribed two types of drops, wait 10-15 minutes between instillations. Sometimes 5 minutes is enough; this information is indicated in the instructions for the medications.
What are antibiotic eye drops?
For your information! Infectious eye pathologies arise due to the spread and increased activity of pathogenic microflora on the surfaces of the eye tissues (and sometimes the infection develops inside the tissues).
Such pathogens be eliminated only with the help of antibiotic drugs.
However, these agents are extremely rarely used for viral or fungal pathologies (separate agents have been developed for these microorganisms).
Antibiotic eye drops are drugs for topical use only (that is, they are intended for instillation and are not used for oral administration).
Such liquid solutions may contain various basic and auxiliary substances and differ in consistency and effectiveness.
Currently, there are several groups of antibiotics, each of which contains dozens of drugs, but in ophthalmology antibiotics of the tetracycline, macrolide and fluoroquinolone groups are used.
Reviews
Alena: The child was prescribed Tobrex drops. They don't sting and aren't oily. Used up to 4 times a day, 1 drop. The inflammation began to subside on the 3rd day, the infection was overcome after 1 week.
Edik: They prescribed Gentamicin drops and ointment, the diagnosis was stye on the lower eyelid. Initially, I only applied the ointment, I just didn’t want to return home for money. On the third day, the pain became unbearable, the eyes became more swollen. Still, I went to get some drops. I was convinced that I needed to follow the doctor’s recommendations. If drops and ointment are prescribed, use both.
Stanislav: I have a weak immune system and my eyes are always the first to suffer. If you catch a cold or scratch it with dirty hands, inflammation, redness and itching immediately begins. The ophthalmologist recommended Normax. I use it at the first symptoms of infection, after 2 days it becomes easier.
Antibiotic eye drops for conjunctivitis
The most common ophthalmic disease caused by bacteria is conjunctivitis.
Attention! Depending on the type of conjunctivitis, the severity and age of the patient, antibiotics for this disease can be prescribed in different combinations, which can combine:
- moxifloxacin;
- streptomycin;
- Oftavix;
- kanamycin;
- sparfloxacin;
- neomycin;
- levofloxacin;
- monomycin;
- norfloxocin;
- gentamicin;
- lomefloxocin;
- sizomycin;
- ofloxocin;
- netilmicin;
- amikacin and other drugs.
Application
For the treatment of ophthalmological diseases, Penicillin is used topically in the following ways:
- Instillation.
- Injections: subconjunctival;
- intravitreal.
For infectious eye diseases, a solution is made for instillation. The powder in the bottle must be diluted with boiled water, according to the instructions, shaken and rinse the eyes with the prepared product. The procedure is carried out using cotton pads, changing for each organ. This will prevent the infection from spreading. The solution can be used as eye drops, which need to be dripped into the conjunctival sac. If the pathological process is severe, the drug is prescribed for oral administration or injection to ensure the required concentration in the blood. A child's infected eyes should be washed 2-3 times a day until the signs of the disease disappear completely. Usually this period is at least 1 week.
How to wash babies' eyes
Caring for a baby's eyes is necessary from the first days of his life. Mom should learn this while still in the maternity hospital. Treatment of the visual organs has the following goals:
- protection against various infections that could be acquired during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal;
- elimination of the “dry eye” effect in an infant;
- cleansing tear ducts from secretions;
- prevention of inflammation and redness.
Rinsing and treating the affected eye is carried out in the morning and evening. If necessary, the procedure can be performed more often; the number of washes is determined by the doctor depending on the cause of suppuration and the severity of the disease.
Before the procedure, you need to prepare eye drops, cotton wool or cotton pads, and gauze. The eye treatment process includes the following steps:
- Place the baby on his back on the changing table. The baby must be awake, otherwise the procedure may frighten him.
- To protect the eye, apply a cotton pad to the baby's lower eyelid.
- Gently open the child's eyelids, lifting the upper eyelid.
- With your free hand, place 1-2 drops into the corners of the baby's eyes.
- Close the eye and lightly run your finger over the eyelid for maximum absorption of the product.
- Remove excess drops with a clean cotton pad or piece of gauze, making sure that no lint remains in the eye.
To enhance the therapeutic effect after instillation, you can massage the lacrimal sac. If pus is released from the eye, you need to carefully remove it with gauze or a cotton pad.
Types of antibiotics for eyes
There are several types of antibacterial medications for the eyes. They are classified according to the type of active substance included in the composition and its belonging to a certain group. Depending on the causative agent of the disease, which the doctor determines after the analysis, one or another antibiotic will be prescribed. They differ in effectiveness, side effects and contraindications.
Fluoroquinolones
One of the most popular is a broad-spectrum eye antibiotic from the fluoroquinolone group. It includes highly effective drugs that are absorbed into the systemic bloodstream and distributed throughout the body. Drops and ointments based on fluoroquinolones (quinolones) have many contraindications and side effects, but they are active against a wide range of bacteria and have the fastest possible effect. The composition of the drugs includes active ingredients:
- ofloxacin (representatives of Tsiprolet, Normax);
- norfloxacin (representatives of Uniflox, Floxan);
- levofloxacin (representatives of Dancil, Lofox).
They are effective against chlamydia, staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci. Drops and ointments based on fluoroquinolones are prohibited for pregnant and lactating women and children. They eliminate purulent-inflammatory processes, pain, lacrimation, itching, burning. The drugs are effective against blepharitis, conjunctivitis, meibomitis, barley, keratitis, and ulcerative lesions of eye tissue.
Aminoglycosides
Solutions and ointments based on aminoglycosides directly affect the contents of pathogen cells. Active components disrupt the permeability of cell membranes and damage the activity of microorganisms. Third generation products are used more often, they have a minimum of side effects and a quick effect. The composition of the drugs includes:
- tobramycin (Brulamycin);
- gentamicin;
- netilmicin;
- dexamethasone with tobramycin (Dexatobropt, Tobrazon, Tobradex);
- neomycin (Maxitrol, Dexon, Nettacin).
The medications are effective against purulent inflammation, inhibit bacteria and destroy them, act even in advanced cases, relieve pain, eliminate swelling, and normalize visual function. Antibiotics from the aminoglycoside group are approved for use from the age of two months, and those based on dexamethasone - from the age of one year. Gentamicin helps with iridocyclitis and dacryocystitis.
Article on the topic: To whom and when is electroneuromyography prescribed - preparation and progress of the procedure, price
Levomycetins
Eye drops with an antibiotic from the chloramphenicol group disrupt the processes of protein synthesis in bacteria and damage DNA and RNA. Synthetic products are expensive, but they have fewer side effects, so they are allowed even during pregnancy or childhood. The composition of the drugs includes chloramphenicol, chloramphenicol, boric acid (all of them contain Levomycetin-Dia, Levomycetin-Ferein, Levomycetin-Akos).
Medicines help with conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, and have a disinfectant effect. If fusidic acid (Fucitalmilk) is included in the composition, dacryocystitis can be treated with drops. Two complex substances - framycetin and gramicidin (part of Sofradex) help with conjunctivitis, inflammation of the iris or albumen, ciliary body, episcleral tissue. The effect is enhanced by the addition of dexamethasone.
Macrolides
Natural or semi-synthetic macrolides are low-toxic antibiotics. They have a gentle effect on the body, but have a high therapeutic effect. Such drugs are approved for use in children and may be prescribed with caution to pregnant and breastfeeding women. A popular drug of the group is Erythromycin. An ointment based on it eliminates infectious and inflammatory diseases of various etiologies. Another representative of the group is Azidrop based on azithromycin.