Minimally invasive treatment methods in ophthalmology include laser dacryocystorhinostomy, which involves the creation of a new lacrimal duct into the nasal cavity. This is a rather complex technique, but its effectiveness has already been proven. Dacryocystorhinostomy is performed in different ways, but the use of a laser has significantly reduced the risk of intraoperative and long-term complications. It is important to know what this operation is and when its use is appropriate.
Indications
Dacryocystorhinostomy is performed in the following cases:
- chronic dacryocystitis;
- traumatic damage to the lacrimal canal;
- purulent eye diseases;
- blockage of the lacrimal sac.
The journal “New in Ophthalmology” published the results of a study confirming the restoration of the connection of the lacrimal canal with the nasal cavity using laser dacryocystorhinostomy in 89% of patients without complications, which confirms the effectiveness of this technique.
Dacryocystorhinostomy, what is it, how is the operation performed, consequences, reviews
Dacryocystorhinostomy is a specific operation that allows you to drain the cavity of the lacrimal sac by connecting to the nasal cavity, bypassing the nasolacrimal duct. Direct indication is the ineffectiveness of treatment of dacryocystitis through conventional surgical intervention (probing).
The procedure is performed to drain the cavity of the lacrimal sac and restore the unimpeded outflow of tear fluid or pathological discharge.
Modern technologies used by ophthalmologists make it possible to perform surgery with minimal cosmetic defects.
In the last decade of the last century, laser and endoscopic methods for the treatment of chronic dacryocystitis began to actively develop. There are 2 main ways to access the lacrimal sac and create a nasal stoma:
- Extranasal (common among ophthalmologists).
- Endonasal (mainly used in otorhinolaryngology).
Transcananicular laser endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (TLED)
Temporary intubation of the tear ducts with a silicone stent is used. The advantage of the laser is instant coagulation of blood vessels.
This avoids excessive bleeding and significant blood loss.
In the early stages of the development of laser technology, there was a possibility of brain injury from too intense laser radiation. In modern medicine, this problem has been completely eliminated.
There are many contraindications for the extranasal method, including the presence of acute purulent inflammation: phlegmon or abscess.
There are fewer contraindications for endonasal surgery; surgery can be performed when phlegmon and other purulent lesions of the lacrimal sac form.
In addition, laser endonasal formation of the anastomosis can be performed at almost any age, does not require special preparation of the patient and has a shorter rehabilitation period.
Dacryocystorhinostomy
Dacryocystorhinostomy is a method of surgical treatment of disorders of the outflow of tears from the eye. Allows you to normalize the functioning of the nasolacrimal duct and restore communication between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity.
Why is proper functioning of the tear ducts so important for eye health?
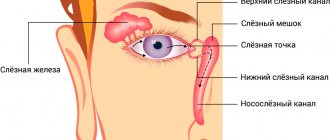
The lacrimal glands produce tears, which moisturize the surface of the eye, ensuring adequate refraction of light rays at the front surface of the cornea, its ideal transparency, cleansing, nourishing and preventing drying. For normal nutrition and washing the surface of the eye, at least 1 ml of tears is required, distributed over the surface of the cornea. When crying or irritation of the eye, up to 20-30 ml of tears can be released.
Coming from the lacrimal glands, the tear washes the eyeball, then entering the “lake”, which is located in the inner corner of the eye.
There are also clearly visible lacrimal openings, which serve as the entrance openings of the canaliculi and flow into a special sac.
Each lacrimal sac passes into the nasolacrimal duct, which opens into the nasal cavity. Thus, the tear is evacuated into the nasal cavity through the nasolacrimal duct.
Finding the tear duct is quite easy. It is presented in the form of a small elastic formation in the inner corner of the eye at the junction with the bridge of the nose.
Lacrimal canal - its blockage and inflammation: how to treat dacryocystitis in adults
When the nasolacrimal duct is blocked or narrowed, adults can develop a dangerous eye disease - dacryocystitis.
Without proper diagnosis and quality treatment, this disease is fraught with irreversible consequences, which in advanced cases can even lead to the death of the patient.
Therefore, in this article we will consider all aspects of this disease, symptoms and modern treatment methods.
What it is?
Dacryocystitis is an infectious and inflammatory disease characterized by damage to the lacrimal sac of the eye. Typically, this disease is most often observed in people aged 30-60 years. In women, this disease occurs more often due to the narrower anatomical structure of the nasolacrimal ducts.
As a rule, in adults, the lesion with dacryocystitis is always one-sided.
The disease occurs due to blockage of the nasolacrimal canal. As a result, tear fluid accumulates in the lacrimal sac and cannot penetrate outside. Due to the disruption of the outflow of tear fluid, active proliferation of microorganisms occurs, which leads to inflammation and the formation of mucopurulent discharge.
Source: https://medana-st.ru/diagnostika-i-lechenie/dakriotsistorinostomiya-chto-eto-kak-prohodit-operatsiya-posledstviya-otzyvy.html
Preparation
Transcanalicular laser endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy, abbreviated as TLED, requires careful investigation. This requires an examination by a laryngologist, ophthalmologist, therapist and anesthesiologist. Ophthalmoscopy, rhinoscopy, MRI or CT of the nasal sinuses and lacrimal canal are used. Only after a complete examination of the patient and proof of the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment can laser correction be applied.
The type of anesthesia depends on the age of the patient and the complexity of the procedure, and the dosage is selected individually.
Pain relief is carried out by a combination of local and intravenous anesthesia. For an adult, it is possible to use only local anesthesia, since with dacryocystitis, the sensitivity of all areas where the intervention is performed can be reduced. Children are more often given combined anesthesia, which is explained by the smaller area of the surgical field, the complexity of the procedure, and the child’s significant mobility. The dosage of drugs is individual for each patient.
Carrying out the procedure
Laser dacryocystorhinostomy is performed with the patient lying down. Depending on concomitant diseases and the characteristics of the intervention, there are 2 ways to perform the operation:
- extranasal;
- endonasal.
Extranasal method
This method is used if there are defects in the walls of the nasal cavity, polyps, or atrophy of the mucous membrane. These conditions make it impossible to penetrate the lacrimal sac through the nose, so percutaneous penetration is used. A window is formed in the bone to drain fluid and the lacrimal canal is directed into the hole. Afterwards, sutures are placed for closer contact of the mucous membranes.
Endonasal technique
The intervention requires precision from a specialist, since capillaries can be damaged, which will cause bleeding.
The operation process includes the following steps:
- A special tube is inserted through the nasal passage - an endoscope - with which you can visualize the tear duct.
- A diode or erbium laser makes an incision in the center, removes tissue and creates a bone window connecting two cavities - the nasal and lacrimal.
- In order to prevent tissue fusion, sutures are applied.
Ophthalmologists note that surgery on the lacrimal canal using the endonasal method using a laser speeds up the procedure time and makes it possible to minimize the size of the incisions. Dacryocystorhinostomy requires a careful and thorough approach, since damage to blood vessels is possible with the development of heavy bleeding, which makes it impossible to continue the operation.
dacryocystorhinostomy: reviews, description of dacryocystorhinostomy techniques
Dacryocystorhinostomy is a specific operation that allows you to drain the cavity of the lacrimal sac by connecting to the nasal cavity, bypassing the nasolacrimal duct. Direct indication is the ineffectiveness of treatment of dacryocystitis through conventional surgical intervention (probing).
The procedure is performed to drain the cavity of the lacrimal sac and restore the unimpeded outflow of tear fluid or pathological discharge.
Modern technologies used by ophthalmologists make it possible to perform surgery with minimal cosmetic defects.
In the last decade of the last century, laser and endoscopic methods for the treatment of chronic dacryocystitis began to actively develop. There are 2 main ways to access the lacrimal sac and create a nasal stoma:
- Extranasal (common among ophthalmologists).
- Endonasal (mainly used in otorhinolaryngology).
Extranasal method
Extranasal dacryocystorhinostomy involves access through the skin. This is a complex orbital-nasal intervention, which is characterized by high trauma and a long rehabilitation period. It is performed primarily on children, so general anesthesia is preferable.
Local anesthesia is performed through infiltration anesthesia. Use:
- 2% novocaine solution;
- 10% lidocaine aerosol.
- 1% dicaine solution;
The posterior ethmoidal nerve, nasociliary nerve, and lacrimal sac itself are anesthetized with novocaine. Internally - 10% lidocaine aerosol, after which a cotton-gauze swab moistened with a solution of dicaine is introduced.
The operation is a modification of the Toti method, which involves the formation of a direct funnel-shaped anastomosis by connecting the cavities of the lacrimal sac and the nose through resection of the dividing bone wall.
Sequencing:
- An incision is made in the skin, soft tissue and periosteum along the intraorbital edge (~3.5 cm).
- The periosteum is separated along the incision.
- Using a chisel, a bone window is formed, the underlying ethmoid bone is removed, and the edges are carefully trimmed with nippers.
- Next, the lateral wall of the sac is removed and a direct passage into the nasal cavity is formed, with a diameter smaller than the bone window.
- The nasal mucosa from the side of the nasal cavity is pressed towards the lacrimal sac.
This is the main method invented and described by the Spanish ophthalmologist A. Toti at the beginning of the 20th century. Now there are many modifications of his method, but the basic principle remains the same.
The modern classical technique involves suturing flaps of the nasal mucosa that form the lacrimal duct.
The size of the incisions and their location have undergone changes - now it is considered sufficient to create a bone window of 1.5-2 cm.
The shape of the incision also underwent changes - according to the Toti method, the incision was made in a curved quarter-circle shape. Modern methodology involves a straight cut at an angle.
Endonasal method
This is a less invasive procedure that uses endoscopic and laser technology.
Access can be performed endonasally, that is, directly through the nasal cavity, eliminating the formation of scars on the outer skin.
Optical and laser endoscopes are inserted into the nasal cavity, all actions are performed on the inner surface of the nasal mucosa. The principle is the same as in the extranasal version, only much less traumatic.
Transcananicular laser endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (TLED)
Temporary intubation of the tear ducts with a silicone stent is used. The advantage of the laser is instant coagulation of blood vessels.
This avoids excessive bleeding and significant blood loss.
In the early stages of the development of laser technology, there was a possibility of brain injury from too intense laser radiation. In modern medicine, this problem has been completely eliminated.
There are many contraindications for the extranasal method, including the presence of acute purulent inflammation: phlegmon or abscess.
There are fewer contraindications for endonasal surgery; surgery can be performed when phlegmon and other purulent lesions of the lacrimal sac form.
In addition, laser endonasal formation of the anastomosis can be performed at almost any age, does not require special preparation of the patient and has a shorter rehabilitation period.
Source: https://ofthalm.ru/dakriotsistorinostomiya.html
Rehabilitation
The recovery period after laser dacryocystorhinostomy lasts 1-3 months and depends on the patient’s age, intraoperative complications and concomitant diseases. The patient must remain in hospital for at least 4 days for round-the-clock monitoring. After the operation, the nasal cavities are washed daily with saline; antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. For severe pain, non-narcotic painkillers are used.
After inpatient treatment, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
The postoperative period requires the use of drops for the nose and eyes, which narrow the blood vessels.
- For 2 weeks, use vasoconstrictor nasal and anti-inflammatory eye drops once a day.
- Rinse the nasal cavity 1-2 times per day.
- Avoid heavy physical activity during the rehabilitation period.
- Do not make sharp bends.
- Avoid large crowds of people.
- Don't get too cold.
- After removing the sutures, be checked by an ophthalmologist at least once a month.
After laser dacryocystorhinostomy, compliance with the rules of recovery is important to prevent the development of long-term undesirable effects.
Dacryocystorhinostomy
Tatiana Balashova says:
otorhinolaryngologist-surgeon, Ph.D.
Dacryocystorhinostomy is a method of surgical treatment of disorders of the outflow of tears from the eye. Allows you to normalize the functioning of the nasolacrimal duct and restore communication between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity.
The lacrimal glands produce tears, which moisturize the surface of the eye, ensuring adequate refraction of light rays at the front surface of the cornea, its ideal transparency, cleansing, nourishing and preventing drying. For normal nutrition and washing the surface of the eye, at least 1 ml of tears is required, distributed over the surface of the cornea. When crying or irritation of the eye, up to 20-30 ml of tears can be released.
Coming from the lacrimal glands, the tear washes the eyeball, then entering the “lake”, which is located in the inner corner of the eye.
There are also clearly visible lacrimal openings, which serve as the entrance openings of the canaliculi and flow into a special sac.
Each lacrimal sac passes into the nasolacrimal duct, which opens into the nasal cavity. Thus, the tear is evacuated into the nasal cavity through the nasolacrimal duct.
Finding the tear duct is quite easy. It is presented in the form of a small elastic formation in the inner corner of the eye at the junction with the bridge of the nose.
Dacryocystitis
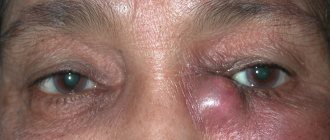
Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac, leading to its narrowing and obstruction of patency.
Causes of dacryocystitis
Inflammatory processes in the nose or paranasal sinuses against the background of acute or chronic infections, traumatic injury, allergic diseases of the eyes and nose, individual structural features of the nasolacrimal canal (for example, anatomical narrowing), spasm of the lacrimal canal.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis
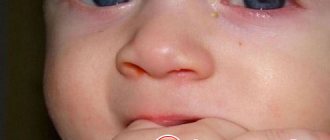
- swelling in the inner corner of the eye,
- painful sensations when pressing on the inner corner of the eye,
- sometimes - the appearance of thick discharge in the lacrimal openings,
- constant lacrimation from the eye, but no tears enter the nasal cavity,
- redness and irritation of the conjunctiva of the eyes.
Diagnosis and treatment of dacryocystitis, indications for surgery
With such symptoms, patients most often turn to an ophthalmologist.
The ophthalmologist carries out conservative treatment, including general and local anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiallergic drugs, local instrumental treatment methods - lavage of the lacrimal ducts, bougienage (non-surgical expansion) of the lacrimal canal. If such therapy does not bring the expected result, it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment, before which a computed tomography scan with contrast is necessarily performed.
Operation methods
The operation - dacryocystorhinostomy - is performed using external or endoscopic access.
External access is rarely used and has disadvantages: unsatisfactory cosmetic effect, prolonged wound healing, etc.
Endonasal microendoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy is less traumatic and less painful for the patient, helps prevent relapses of the disease and does not lead to the formation of visible scars.
This operation is performed by otorhinolaryngologists together with ophthalmologists.
It is the least invasive and most effective, which is why in our clinic we use this particular method of surgical treatment.
At the first stage, under video assistance (under the control of endoscopes of the required degree), an otolaryngologist surgeon exposes the lacrimal bone through the nasal passage on the diseased side and forms a bone window measuring about 1-1.5 cm.
Then a probe is inserted through the lacrimal canaliculi, with the help of which the lacrimal sac is identified and a wide resection of its anterior wall is performed.
Next, the permeability of the solution through the lacrimal canaliculi into the nasal cavity is checked, the lacrimal sac is left open, and if necessary, a soft catheter is left in the nasolacrimal canal for 2-3 weeks.
The operation usually brings relief almost immediately and is fairly well tolerated.
Preparing for surgery
To prepare for the operation, the doctor will prescribe a standard set of tests required before performing the operation under general anesthesia.
It will also be necessary to undergo computed tomography (CT) of the lacrimal ducts with contrast, consultation with an anesthesiologist, therapist and other specialists (determined during the examination).
You must inform your attending physician, anesthesiologist, and therapist about all medications you are constantly taking and concomitant diseases.
Rehabilitation after dacryocystorhinostomy
For several days after surgery, you need to rinse the formed nasolacrimal duct. The patient is monitored by an ophthalmologist and an otorhinolaryngologist in the postoperative period.
Effect of dacryocystorhinostomy
Endonasal microendoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy helps to eliminate the symptoms of dacryocystitis in a minimally invasive (non-traumatic) manner, without any external defects, remove the source of infection in the lacrimal sac, relieve the patient from lacrimation and prevent inflammatory eye diseases.
Contraindications to dacryocystorhinostomy
Contraindications may include any diseases that do not allow surgical treatment in principle, as well as the age of the child under 1.5 years.
Advantages of dacryocystorhinostomy in EMC
Dacryocystorhinostomy in EMC is performed:
- only under general anesthesia,
- under navigation control for maximum precision of intervention,
- two specialists - an otorhinolaryngologist and an ophthalmologist.
If it is necessary to eliminate any disorders in the nasal cavity (for example, narrowing of the nasal passage or a deviated nasal septum), EMC ENT surgeons perform one-stage operations.
Source: https://www.emcmos.ru/articles/dakriocistorinostomiya
Indications and contraindications
The operation is indicated for blockage of the tear ducts. Dacryocystorhinostomy is performed for frequently recurrent chronic, post-traumatic and postoperative dacryocystitis. If massage and probing of the lacrimal sac are ineffective, this technique is also used.
Among the main contraindications to dacryocystorhinostomy are the acute stage of dacryocystitis, purulent diseases of the eyelids and eyes.
The patient's severe somatic status, blood coagulation disorders, decompensation of chronic diseases, acute viral and bacterial infections are reasons for refusing surgery until the patient's condition normalizes.
Preparation for dacryocystorhinostomy
Preparation for surgery is carried out through a thorough examination of the nasal cavity and visual structures. An ophthalmologist performs standard diagnostics of the visual organs. An examination by an otolaryngologist using an endoscope and examination of the sinuses is mandatory.
To exclude intraoperative complications, a consultation with a therapist is scheduled. Laboratory tests involve taking blood for general and biochemical tests, coagulogram, determination of blood group and Rh factor, major infections (RW, HIV, hepatitis B and C).
In addition, before dacryocystorhinostomy it is necessary to pass a general analysis of urine and feces for enterobiasis and worm eggs.
Instrumental research methods include computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses and lacrimal sac, fluorography of the lungs and electrocardiography.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4WhiKQOURO8
Dacryocystorhinostomy involves the use of combined anesthesia using local and intravenous anesthesia. The day before the operation, an anesthesiologist is consulted, and optimal methods of dealing with intraoperative pain and emotional stress are selected.
On the day of dacryocystorhinostomy, it is forbidden to consume food, water and medicines without a doctor’s prescription. 40 minutes before the intervention, premedication is performed, including sedatives, antiallergics, painkillers and other drugs at the discretion of the specialists.
The use of cosmetics and face cream is also not recommended on the day of surgery.
Methodology
Dacryocystorhinostomy is performed in an operating room. The patient is in a supine position, the anesthesiology team performs catheterization of a peripheral vein and installation of an infusion system. The nurse anesthetist installs sensors to measure blood pressure, pulse and saturation (oxygen saturation in the blood).
The operating nurse treats the patient's face with antiseptic solutions and limits the surgical field with sterile napkins. Then the ophthalmologist performs local infiltration anesthesia using novocaine or lidocaine, specifies the scope of the intervention and the projection of the lacrimal sac, and proceeds to dacryocystorhinostomy.
A small incision is made in the skin, soft tissue and periosteum between the inner edge of the eye and the bridge of the nose. Using a special drill, a bone canal is formed, the lacrimal sac is isolated and drained. The side wall of the sac is removed, and an artificial passage into the nasal cavity is formed from its tissues for passive outflow of tears.
During dacryocystorhinostomy, sedatives, analgesics, and antihypertensive drugs are administered, blood pressure, respiratory rate and heart rate parameters are monitored, and constant verbal contact between the anesthesiologist and the patient is maintained. After the new anastomosis is formed, the surgeon checks its effectiveness by injecting saline into the lacrimal sac.
Upon completion of dacryocystorhinostomy, the assistant performs hemostasis of the wound and applies cosmetic sutures to the skin. Vasoconstrictor drops are instilled into the nasal cavity and a tampon with a hemostatic agent is placed, the surgical wound is treated with anti-inflammatory ointment and covered with a sterile napkin.
The nurse accompanies the patient to the recovery room.
After dacryocystorhinostomy
The rehabilitation period is long, ranging from 4 weeks to several months, depending on the effectiveness of the operation, the speed of wound healing and the presence of concomitant pathologies. In the first days, the patient should be in a 24-hour hospital in order to prevent complications, monitor the functioning of the new anastomosis and monitor the general condition.
In the department, the doctor prescribes antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and (if necessary) painkillers. For several days after dacryocystorhinostomy, the formed nasolacrimal duct is washed with saline solution or distilled water.
Anti-inflammatory drops in the eye and vasoconstrictor drops in the nose are prescribed for up to 2-3 weeks before bedtime.
After discharge from the inpatient department, the patient is not recommended to engage in sports or physical labor, bend over frequently, or stay in a cold and dusty room for a month.
After undergoing dacryocystorhinostomy, you should avoid large crowds of people, do not contact people with flu or colds, and do not get hypothermic.
After the wound has healed and the stitches have been removed, the patient undergoes another examination by an ophthalmologist, where the effectiveness of the operation is checked, the sinuses are examined, and the prescribed therapy is canceled or corrected. If the outcome of dacryocystorhinostomy is favorable, the patient can begin work after 1.5-2 months.
Complications
Complications after dacryocystorhinostomy can be divided into intraoperative and postoperative. Undesirable reactions during the intervention include bleeding, penetration into the orbital cavity, and damage to the nasal mucosa.
In the postoperative period, the wound may become infected with the formation of phlegmon or an abscess. Complications after dacryocystorhinostomy include the formation of a scar epicanthus and closure of the artificial nasolacrimal duct with subsequent relapse of the disease.
Cost of dacryocystorhinostomy in Moscow
The intervention is performed in multifunctional ophthalmological clinics in the city. Preoperative preparation with additional studies increases the final cost of the operation.
The price for dacryocystorhinostomy in Moscow is also determined based on the status of the clinic, its reputation, features of postoperative observation and additional manipulations.
Observation after dacryocystorhinostomy includes the use of medications, consumables, round-the-clock supervision by specialists, as well as food and a change of linen.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/treatment/lacrimal/dacryocystorhinostomy