Cataracts are characterized by clouding of the lens, a sign of which is deterioration of visual acuity. It can be localized in two eyes at once or only in one and affect the entire lens or part of it. Today, the disease is well studied and treatable, just like other ophthalmological problems:
- glaucoma,
- chalazion,
- retinal detachment,
- astigmatism.
In the treatment of cataracts, drug therapy is auxiliary, and the main method of treatment is surgery. The most gentle method is laser cataract removal; in addition, after this type of treatment, complications are practically eliminated, and the rehabilitation period lasts several hours.
Indications and contraindications
Laser cataract surgery has certain indications and contraindications. Indications for laser treatment:
- clouding of the lens with decreased visual function;
- people with altered corneas (dystrophic changes, small thickness);
- swollen, overripe forms of cataract;
- cataract in combination with secondary glaucoma;
- secondary turbidity.
Contraindications to laser treatment of cataracts:
- infectious diseases of the eyes or other organs;
- period of exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- disorders of the blood coagulation system;
- uncorrected cardiovascular pathologies;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- diabetes mellitus with unstable glucose levels;
- increased ICP;
- oncological neoplasms.
Laser treatment is not recommended for pregnant women due to changes in hormonal status. The decision to undergo laser treatment for children under 18 years of age is made on an individual basis.
Ultrasound phacoemulsification
The presented cataract surgery is one of the most modern surgical techniques. It was first used about 40 years ago and is considered today the “gold standard” for the treatment of this pathology. Ultrasonic phacoemulsification is considered to be a truly perfect method, since it leaves virtually no risk of possible complications. According to statistics, side effects are observed only in 1% of cases. As a rule, some patients may complain of inflammation, photophobia, redness of the visual organs, and swelling of the cornea.
The operation is usually performed in the early stages, making it much easier for the patient. There is no need to wait for the moment when the cataract matures completely and at the same time continue to lose visual functions. The advantage of it is the simple recovery period, which can easily be carried out right at your home. After the intervention, the surgeon operating on you will prescribe a set of eye drops that will shorten the rehabilitation period and eliminate hospital stay.
Ultrasonic phacoemulsification is not traumatic and does not require mandatory suturing of the incisions made during it. The fact is that they are so small in size that they can be liquidated on their own. Another advantage of removing cataracts this way is that there is no need for general anesthesia. As a rule, local anesthesia is sufficient for its implementation. Most often, the drip method is used, thanks to which the patient begins to see well within an hour after the end of the procedure. The very next day after surgery, most people report good color vision and a desire to return to daily activities.
Causes of cataracts
Cloudiness of the lens (cataract) can occur at any age and the factors predisposing to the occurrence of cataracts are quite extensive:
- aging of the body
- hereditary predisposition
- eye injuries (concussions, penetrating wounds)
- inflammatory eye diseases
- concomitant eye diseases (glaucoma, high myopia, etc.)
- chemical, ultraviolet, ionizing or radiation effects on the body
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypo- and hyperthyroidism, etc.)
- immune and metabolic disorders, etc.
Preparation for the event
Before laser cataract removal, you need to consult a therapist, cardiologist, dentist, or ENT doctor. The mandatory set of tests includes blood, urine, ECG, and FLG tests.
If the operation is planned for the morning, then the last meal should be the night before no later than 20 hours. If the operation is planned for the afternoon, you can drink sweet tea in the morning.
It is prohibited to drink alcohol the day before the procedure. It is not recommended to smoke on the day of treatment. If you are very nervous, you can drink a herbal sedative or herbal tea at night.
How do cataracts form?
The lens of the eye is a transparent lens that is located between the vitreous body and the iris. Our lens has the ability to transmit and refract light rays, focusing them on the retina.
While a person is young, he has a transparent and elastic lens of the eye, which easily focuses and changes its shape. Thanks to this “sharpness adjustment,” we can see clearly at both far and near distances.
After 37-40 years, vision weakens as a result of a decrease in the elasticity of the lens and its ability to accommodate. This visual impairment can be corrected with glasses or contacts.
After 60 years, age-related blurring of vision begins, which appears as a result of the general aging processes of the body (cell breakdown - metabolism - begins to exceed restoration - regeneration).
With cataracts, the lens becomes partially or completely cloudy and begins to transmit only part of the light rays, so the image becomes blurred. Typically, the disease develops over several years, but in some cases, cataracts can “mature” in several months.
Cataracts are most common in older men and women, but can develop even in childhood, which is why it is important to have regular eye exams.
When a diagnosis of cataract is made, treatment must be started immediately, even if serious vision deterioration has not yet occurred. The disease tends to progress, and the lack of timely treatment can lead to complete blindness. It is cataracts that rank first among diseases leading to absolute loss of vision.
Cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser
Vision is one of the most important senses. It provides spatial orientation and helps you enjoy the world around you. However, vision may become weakened when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy. In this case, doctors talk about clouding of the eye lens or cataracts. Typically, cataracts begin to develop after a person's 60th year of life, however, children and young adults can also be affected. Symptoms such as decreased vision contrast and increased blurred vision affect about 40 percent of the population worldwide. If treatment is not carried out promptly, a gradual increase in cloudiness of the lens can lead to complete blindness in the eye affected by cataracts. The exact cause of cataracts is still not known, but treatment options exist. One of them is laser eye surgery. Previously, the clouded lens of the eye was crushed using ultrasound and then suctioned (aspirated) from the eye. Today, eye cataract extraction surgery is performed using a femtosecond laser.
Introductory information
Cloudiness of the lens of the eye occurs mainly in older people and laser eye surgery, especially cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, is currently a fairly common practice. However, although laser eye surgery technology is on the rise, femtosecond laser cataract surgery is not performed in all eye clinics. The reason for this is, on the one hand, the high costs of purchasing equipment, and on the other hand, doubts about new technologies. In Germany, cataract surgery using a femtosecond laser is a new and still young method of laser eye surgery. This method is practiced with great success, mainly in the United States. Until now, laser eye surgery has been used to correct vision. The femtosecond laser is also used for precise calculation of artificial lenses. This method is significantly more accurate than methods previously used to determine optimal lens power. Research in this area is helping more people improve their vision and thereby improve their quality of life.
Explanation of the term - femtosecond laser
Depending on the technology, laser devices can have different durations of light pulses. Longer light pulses are visible as a red beam. Looking directly into the laser beam may cause serious eye damage. In femtosecond laser cataract extraction surgery, laser eye surgery uses a femtosecond laser that sends out pulses of light that are in the femtosecond range. Thus, the term femtosecond laser means that the duration of the light pulses sent by the laser is in the femtosecond range, which corresponds to a quadrillionth of a second. They are invisible to the human eye. When these rays enter the eye, very high energy is released. In femtosecond laser cataract extraction surgery, a laser device is used to make a precise cut. This incision is so precise that the surrounding tissue is kept intact, resulting in a faster healing process. The radiation energy is discharged inside the tissue and small bubbles of water and carbon dioxide are formed there. The more pulses are received, the more bubbles are formed, which merge with each other and, thus, a very clean, thin cut is formed. During the operation, OCT (optical coherence tomography) and three-dimensional video are used as control, in addition, intervention by the surgeon is possible at any time during the operation; This laser eye surgery is considered the safest and most accurate today.
Preliminary studies and preparation for surgery
Eye cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser has been practiced for five years. To be able to prepare well for laser eye surgery, for cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, there are certain preliminary studies. During these studies, it will first be clarified what should be achieved through laser eye surgery. In addition, since cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser replaces the natural lens of the eye with an artificial lens, the desired type of artificial lens must be determined. Here the question is raised about the use of two types of artificial lenses (intraocular lenses, IOLs) with different degrees of refraction (refraction). In this regard, the focus is on the use of a monofocal intraocular lens (IOL) for implantation. It can be installed during laser eye surgery, during cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, and its advantage is that in the future it provides the patient with excellent distance vision. This means that after laser eye surgery and femtosecond laser cataract extraction surgery, near vision (reading or manual tasks) requires minor vision correction with glasses. Lenses that correct both nearsightedness and farsightedness are multifocal lenses and their difference from other lenses is that they have several foci. There is a fairly common belief that after laser eye surgery - cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser - monofocal lenses provide better quality of vision. If wearing glasses does not bother you, then after laser eye surgery (cataract surgery using a femtosecond laser), a monofocal lens may be selected for implantation.
During the preliminary studies for laser eye surgery—cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser—the patient is given eye drops to dilate the pupils. Only in this way can an accurate calculation of the future intraocular lens be made. After the study, motorists should not drive for some time, since vision is temporarily impaired due to instillation of drops. At the end of laser eye surgery—cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser—an intraocular lens (IOL) should be available for implantation.
Risks of laser eye surgery
With laser eye surgery—cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser—the risks are very low. When using suction (aspiration) with a laser device during femtosecond laser cataract extraction surgery, intraocular pressure increases only very slightly. Laser eye surgery, specifically cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, is performed exclusively on adults. This is due to the fact that the structure of the eyes in adults no longer changes, in contrast to the eyes of adolescents, in whom they continue to grow. Otherwise, there are no risks that could prevent laser surgery, or cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser.
Advantages of cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser
In this laser eye surgery, or cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, the necessary incisions are made using a laser. Until now, during laser eye surgery, the surgeon opened the lens capsule manually using a sharp scalpel. The method of cataract removal using a femtosecond laser is much gentler and more accurate than previously practiced conventional laser eye surgery. So that the lens capsule can be accessed, an incision must be made in the cornea. Also, during cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, higher safety is provided, since the surgeon with this laser eye surgery always has full control over the operation. Femtosecond laser cataract extraction surgery is performed with the support of OCT as well as 3D video. The term 'OCT' is an abbreviation for 'optical coherence tomography'. This method is mainly used in ophthalmology. Using this method, the fundus can be accurately measured and displayed in three dimensions. With other methods, this is not possible. The reason for this is the size of the pupil and the distance separating the cornea and retina. Another advantage of femtosecond laser cataract extraction surgery is the ability to accurately plan cataract surgery. The operation's progress and results can be accurately determined. Also, this laser eye surgery is much gentler because cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser generates less heat compared to cataract extraction surgery using ultrasound. Among the advantages of this laser eye surgery, not least is the ability, during cataract surgery, to also correct any curvature of the cornea, which is another advantage of cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser.
Methods and procedure for laser eye surgery
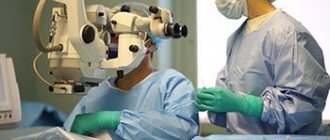
First, before laser surgery begins, anesthetic drops are placed into the eye to be surgically treated. At the patient's request, cataract surgery using a femtosecond laser can be performed under general anesthesia. Then, to perform laser eye surgery (cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser), the femtosecond laser is activated. During cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, a targeted effect on the patient's eye occurs through a device that is a conical lens. The contact is very gentle and does not cause damage to the eye. The next stage of laser eye surgery—cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser—is to destroy the nucleus of the clouded lens. To do this, the nucleus of the lens is fragmented and subsequently turns into an emulsion. Currently, in laser eye surgery, respectively, during cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, there are two possibilities for carrying out the subsequent stage of the operation. Either the surgeon manually opens the lens capsule to be preserved, or the femtosecond laser takes over this task. It is important that the opening of the capsule is circular, which will make it possible to obtain its stability. In cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, the hole - created by the laser - is perfectly round.
In this way, extremely high precision can be achieved. In order to replace the contents of the lens capsule, an additional incision is required along the edge of the cornea. In laser eye surgery, during cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, this incision is also made with a femtosecond laser. If the patient has a curvature of the cornea, then during cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, through a targeted arcuate incision of the cornea made with a femtosecond laser, the curvature of the corneal surface can be eliminated. Thus, as they say colloquially, “you can kill two birds with one stone.” With this laser eye surgery, the surgeon always has complete control over everything that happens. Femtosecond laser cataract extraction surgery is performed using 3D video and OCT (optical coherence tomography). Optical coherence tomography allows for non-contact measurement of various structures of the eye and revision of the surgical field, and also makes it possible to accurately visualize the fundus.
In cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, a new type of laser eye surgery, the contents of the lens are sucked out using a vacuum. Here, too, there are two methods. Until now, in laser eye surgery, the suction of lens fragments from the capsule was carried out using a very thin ultrasound probe. Extreme caution was required in this case, since the use of ultrasound puts great strain on the eye. During cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, a new type of laser eye surgery, suction (aspiration) is also carried out using a laser.
Now, during cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, the time comes to implant an artificial lens. To do this, in this laser eye surgery, during cataract surgery using a femtosecond laser, an intraocular lens (IOL) is inserted into the capsule where the lens was previously located. It is also possible to manually bring the intraocular lens “to its destination” using a special tool. The lens is then carefully unrolled inside the eye and securely secured behind the iris in the “capsule bag” of the natural lens.
Cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser is completed. The incision in the eye that is made for laser cataract treatment is very small, so it does not need to be stitched and usually heals well on its own. However, it can also be closed using a regular thin seam. After new laser eye surgery—cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser—the patient must wear a gauze bandage over the operated eye for a short period of time. After surgery, the patient should avoid heavy lifting to avoid compromising the healing of the eye. Only in very rare cases does a cataract affect only one eye. For this reason, cataract surgery using a femtosecond laser (a new type of laser eye surgery) is first performed on one eye, and after a few days, surgery is performed on the other eye using the same technique.
Postoperative treatment
After cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, the patient often requires treatment lasting up to several weeks with special eye drops. In this way, eye inflammation can be avoided. Just a few weeks after cataract surgery using femtosecond laser, an advanced laser eye surgery, your eye doctor will help you choose the right reading glasses for your patient. For clear distance vision, the patient will no longer need optical devices to improve vision in the future.
Conclusion
Laser treatment of cataracts (cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser) is one of the most important areas in the field of ophthalmology. The advantages of this laser eye surgery, cataract surgery using a femtosecond laser, compared to methods using ultrasound, are truly revolutionary. Cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser has not yet been practiced for long. However, femtosecond laser cataract extraction surgery has been proven in laser eye surgery in over 600 cases. Laser eye surgery is becoming increasingly popular because it provides the opportunity to fully restore visual acuity.
In cataract extraction surgery using a femtosecond laser, in addition to removing the cataract, it may also correct the curvature of the corneal surface, which will help get rid of astigmatism. Research in the field of laser eye surgery continues to evolve. New laser eye surgery technologies are coming soon.
Main stages
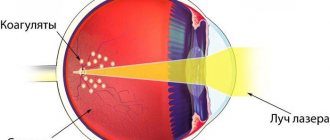
The laser machine is equipped with a computer on which the operation process is simulated. The doctor determines exactly where the corneal incision needs to be made. The built-in tomograph allows you to see the entire working area during laser cataract removal.
Stages of laser treatment:
- The person is placed on the couch.
- Local anesthesia is performed.
- Drops are instilled to dilate the pupil.
- Using a laser beam, surgical access is created on the cornea.
- The lens is crushed using a laser or ultrasound to form an emulsion.
- The destroyed parts of the lens are aspirated, that is, removed.
- Rinse the eye cavity.
- An intraocular lens (IOL) is placed.
- Final treatment is carried out with antiseptic solutions.
No stitches are needed. Cataract surgery takes 10–30 minutes. If everything went well, the person can go home on the same day.
If a person develops repeated opacification after a while, then laser dissection of the secondary cataract is performed. The essence of laser dissection is to create a hole in the back of the lens capsule and remove the cloudy film. For secondary cataracts, laser treatment is considered the safest method for preserving the IOL.
After surgery, follow the rules of the rehabilitation period and do not refuse the prescribed therapy. This will avoid possible complications and speed up the recovery of the eye organ.
Additionally, see the process of removing eye cataracts using a laser:
Why laser cataract treatment is better than ultrasound
Laser cataract removal is the safest treatment. Modern laser systems provide high accuracy and safety, as they are equipped with an additional tomograph and scanning system. The doctor can create a 3D model of the internal elements of the eye in real time and calculate all actions down to the smallest detail. Based on these data, the computer makes calculations, assesses the position of the lens, the condition of its capsule and ligaments.
This approach is very important when removing complicated cataracts when there is subluxation of the lens or defects of the ligamentous apparatus. The laser system allows you to assess the degree of complications and safely perform the operation, taking into account all the nuances. According to calculations, the computer directs the laser strictly to a specific point.
With conventional phacoemulsification, such complications may be a contraindication, since during the operation the surgeon inserts instruments into the eye and can aggravate the defects with ultrasound. Exposure to ultrasound can lead to damage to the lens capsule, ligaments and other elements. The laser eliminates such complications.
Benefits of laser cataract treatment
- Remote influence. The main advantage of the femtosecond laser is the remote destruction and removal of the lens. Laser surgery does not require any incisions or instruments. The use of a laser allows the use of minimal level ultrasound to remove the smallest pieces of crushed lens.
- Safety. Laser surgery is the safest method of treating cataracts. The surgeon sees a three-dimensional cross-sectional model of the working field and all, even the smallest, structures of the eyeball. This allows you to act very accurately and accurately. The laser makes it possible to reduce the number of errors when removing cataracts and preserve the integrity of all eye structures.
- High accuracy. The femtosecond laser provides unparalleled precision. The main stages of the operation take place automatically, without the participation of a surgeon, which allows for accuracy down to one micron.
- Fewer complications. The laser delicately moves the tissue apart and forms an ideally shaped cut, which cannot be done with a knife. Incisions made with laser quickly self-seal, remain stable and heal quickly.
- Precise installation of the artificial lens. The laser makes a perfect circular cut (capsulorhexis), which has smooth edges and ensures correct installation of the intraocular lens.
- Quality of the result. Laser surgery helps to quickly restore vision and maximize its quality. Since remote intervention takes place, the number of complications after cataract removal has been significantly reduced. After laser surgery, patients recover very quickly and without unnecessary discomfort.
Modern intraocular lenses are capable of performing almost all the functions of the natural lens. All lens models are biologically compatible with the structures of the eye and do not need to be replaced. However, to work properly, such lenses must be perfectly positioned in the eye, especially multifocal and toric lenses.
At the moment, only the femtosecond laser provides perfectly accurate positioning, stabilization and centering of the artificial lens. Because the laser creates a perfect capsulorhexis, intraocular lens implantation does not injure the capsular bag. Laser surgery allows you to choose any model of artificial lens.
Surgery is the only way to cure cataracts. No drops will help get rid of cloudiness completely. If earlier ophthalmologists recommended waiting until the cataract has fully matured, modern methods make it possible to remove the lens already at the initial stage of opacification.
Sources used:
- Eye microsurgery. Guide for doctors / A.I. Gorban, O.A. Jaliashvili. - M.: Medicine, 1982.
- Revelations of a surgeon. How I did the world's first eye transplant / E. Muldashev. - Moscow: Lights, 2010.
- Current issues in ophthalmology / ed. T.V. Shlopak, Ustimenko Ustimenko I L.L. etc. I. - M.: Kyiv, 1986.
- Facts about cataracts
Difference between ultrasound and laser cataract removal
All operations aimed at eliminating the “film” are reduced to crushing and removing the affected lens, followed by the installation of implants, which are intraocular lenses. The use of a laser in this area has made it possible to increase the effectiveness of the operation and minimize the risk of complications.
The incision made in the cornea closes itself, so no stitches are required. The patient can return home several hours after surgery.
Corneal incision
Manipulation is carried out using a diamond knife; it ensures maximum precision and accuracy of the cut. The femtosecond device creates a “notch” of an ideal shape. The cut must be straight, stretched or crooked will not maintain tightness and stability. In this case, the risk of complications increases.
Formation of capsulorhexis
The lens is housed in a special capsule, which is supported by numerous ligaments. To get the contents you need to cut the “packaging”. Using a surgical instrument, the doctor makes a small round hole in the capsule. The laser carries out a similar procedure several times faster and more accurately, which allows you to achieve perfect alignment.
The cut should be circular so that the tension force is distributed evenly over the entire surface and the capsule does not tear. It is almost impossible to carry out such filigree work manually; the hole turns out torn, so the tension force in the meridians is not uniform.
| This threatens in the future rupture of the capsule and, accordingly, further problems with vision. The laser helps to make an even cut, which eliminates the risk of complications. |
Lens destruction
During phacoemulsification, the doctor inserts the tip of an instrument into the damaged eye and crushes the lens using ultrasound. The laser creates flashes of energy in the thickness of the clouded mass, cutting the structure into microscopic cubes. They are sucked out of the cavity using a tip. In advanced situations, the doctor can simultaneously use laser and ultrasound, but sets a lower power so as not to harm other structures of the eye.
Reducing the force of the devices will help keep the corneal endothelial cells intact and avoid eye burns. Return to contents
Laser phacoemulsification
The last one in our article, but by no means the last in its significance, is laser phacoemulsification. Despite the fact that this particular operation is the most modern today, it is not yet as popular as the one we presented earlier. According to scientists, the reason for this is the increased complexity of the procedure, which requires the maximum level of concentration from the doctor. In addition, in our country, not every ophthalmology clinic has the necessary equipment. Its rather high cost makes laser cataract removal inaccessible to many clinics and patients. Despite this, both doctors and researchers in the field of optometry are confident that this procedure is the future in the treatment of cataracts.
As you know, working with a laser is unconditionally accurate, which is the main advantage of this procedure. With its help, the surgeon is able to eliminate the smallest particles of the damaged lens, which completely eliminates the possibility of recurrence of the disease and other common complications. The femtosecond laser acts on the lens cells in a targeted manner, which protects the posterior layer of the epithelium from damage. Complications after such a procedure are much less than with any other methods. The cuts are made with maximum precision, and surrounding tissues cannot be injured. This type of operation is performed without hospitalization. A couple of hours after the procedure, the patient can go home. It is known that he begins to see with the operated eye immediately after the procedure.
The laser method of cataract correction can rightfully be called the safest for patients. The risk of complications, as a rule, does not exceed 0.1%, which is 15-20 times less than with surgical treatment with an ultrasound phacoemulsifier. The most common complications include bleeding, displacement of the artificial lens, and detachment of the retina. Some patients may complain of increased intraocular pressure and the development of secondary glaucoma. Remember that following your doctor's recommendations and maintaining visual hygiene is the best way to avoid any complications.
Rehabilitation
The postoperative period lasts up to six months. During this time, there is a gradual improvement in vision clarity. After laser cataract extraction, it is necessary to protect the operated organ from adverse effects:
- protect eyes from ultraviolet rays and foreign particles;
- do not use decorative cosmetics (2 weeks);
- avoid getting soap and shampoo into your eyes;
- limit physical activity and heavy lifting (1 month);
- limit time spent on the computer and TV;
- do not visit the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool (up to 1 month).
For preventive purposes, eye drops are prescribed:
- Antibacterial for the prevention of infection: “Albucid”, “Levomycetin”.
- Moisturizing: Visine, Systane.
- Anti-inflammatory: Indocollir, Diclofenac.
In the first days of the postoperative period, to relieve pain, you can take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets: Nimesulide, Ibuprofen.
Prices for IOLs implanted during surgery
| Name of intraocular lens | Country of Origin | IOL price (RUB, 1 piece) | |
| MZ60BD Silco | USA | 5 000 | |
| Hydro-Sense Aspheric Rumex Ltd | Great Britain | 9 000 | |
| Acrysof Multi-Piece Alcon | USA | 19 500 | |
| Acrysof Natural Alcon | USA | 19 500 | |
| Acrysof IQ Alcon | USA | 22 000 | |
| ZEISS CT ASPHINA 509 M | Germany | 23 500 | |
| Acrysof ReSTOR Alcon | USA | 48 000 | |
| Acrysof SND1T5 Restor Toric Alcon | USA | 70 000 | |
| ZEISS AT LISA 809 M | Germany | 51 000 | |
You can find out more information about the prices for cataract surgery and artificial lenses from the administrators of our ophthalmology center by calling the numbers listed on the website.
Complications
Failure to comply with the rules for maintaining the rehabilitation period, concomitant pathologies, and violation of the surgical technique can lead to the development of complications:
- IOL displacement;
- protrusion of the cornea;
- retinal disinsertion;
- hemorrhage;
- retinal swelling;
- infectious complications;
- secondary cataract.
If you notice that after surgery your quality of vision has begun to deteriorate, inflammatory signs have appeared (severe redness, swelling, pain, discharge from the eyes), or the shape of the eyeball has changed, then consult a doctor immediately. The sooner the doctor begins proper treatment, the greater the likelihood of avoiding repeated surgery.
Consequences of cataract removal
After surgery, patients may encounter some problems:
- Increased lacrimation. This symptom indicates that an infection has occurred. During the operation, the entry of pathogenic microorganisms is excluded, since the procedure is carried out under sterile conditions. But if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed (rubbing the eyes, getting water into the organ of vision, etc.), the “pest” could easily penetrate;
- Redness of the eye. Is a sign of developing infection or hemorrhage;
- Swelling of the cornea. Some swelling is normal for three hours after surgery. They usually resolve without outside help;
- Painful sensations. Sometimes intraocular pressure increases after cataract removal. Most often, the reason is in the solution that is used during the intervention. If it cannot pass freely through the drainage system, side effects are observed;
- Retinal detachment. The risk group includes patients suffering from myopia;
- Implant displacement. This happens very rarely. Most often, this complication causes capsule rupture;
- Endophthalmitis. An extensive abscess of the eyeball is one of the most dangerous consequences of cataract surgery. May cause blindness;
- Cloudiness of the capsule. The reason lies in the growth of epithelial cells on the posterior wall. Reduces visual acuity, occurs very often (approximately 25% of cases).
| Complications after cataract removal can be caused by a doctor’s error, concomitant pathologies, or non-compliance with the rehabilitation regime. |
What is the difference between laser cataract treatment and traditional surgery?
“Femtocataract” is not a special type of disease. This term (perhaps not very successful) refers to one of the methods of treating cataracts, which is based on the use of ultrashort pulse (femtosecond) lasers. Reducing the duration of photon exposure is of fundamental importance: the shorter the light “injection”, the less traumatic, the more limited the surgical field and the lower the risk of undesirable consequences. Therefore, in the technological evolution of pulsed lasers, the count has long been on such small time intervals that it’s not even easy to imagine them - it’s even difficult to write them down in numbers. Thus, a femtosecond is 0.000000000000001 fraction of a normal second.
However, femtosecond lasers today are no longer a technological limit: the release of the first laboratory samples of generators with an attosecond pulse (“femto” = 10 15, “atto” = 10 18) is reported. When replacing a cataract lens, a femtosecond laser is used at the most dangerous stage and area in terms of consequences: to depressurize the eyeball and create access to the lens capsule. Compared to contact microsurgical instruments, the laser scalpel shows such obvious advantages that, apparently, in the near future this technique will be included in standard IOL implantation protocols.
Treatment and surgery for cataracts
There are several modern techniques that help get rid of a clouded lens and restore vision:
- Extracapsular method;
- Use of ultrasound;
- Application of laser.
The essence of the first technique is that the posterior capsule of the lens is preserved, leaving a small space between it and the anterior part of the eye. Only the nucleus of the affected element and cell masses are removed. The main disadvantage is the use of sutures, since a large incision is made to carry out all the manipulations. We will consider the other two methods in more detail below.
Cataract surgery with femtosecond laser
The device automatically performs all the complex stages of surgery to remove the lens and install the implant:
- Corneal incision;
- Performing an anterior capsulorhexis;
- Phacofragmentation.
The femtosecond laser makes the ideal cut according to individually specified parameters for each patient. Jewelry precision allows the hole to remain sealed after the operation is completed and speed up the recovery process.
The opening of the capsule is also calculated down to the millimeter; this parameter is especially important when implanting premium intraocular lenses. Laser crushing of the lens reduces the amount of ultrasound used, which significantly reduces the level of stress on the cornea and minimizes the risk of complications.
Benefits of cataract removal with a femtosecond laser
The procedure has several undeniable advantages over its “competitors”:
- No incisions are required; all manipulations to crush and extract the lens are carried out remotely;
- 100% safety. During the operation, the doctor sees the eye in 3D format, he can examine its smallest elements. Thanks to this, it is possible to control the progress of the intervention and maintain the integrity of all structures;
- High accuracy. The main part of the procedure takes place automatically, manipulations are performed with an accuracy of one micron. Instead of a knife puncture, the laser gently pushes the eye tissue apart and creates an ideally shaped incision. It heals in a short time because it self-seals and remains stable;
- Fast regeneration. During the operation, no surgical instruments are used; almost all actions are performed remotely. This avoids the risk of complications and speeds up the recovery process;
- Modern implants can 100% replace the human lens. It’s not for nothing that they are called “smart lenses”. The main thing is to distribute them perfectly in the capsule. And only a laser can do this with filigree precision. The IOL must be strictly in the center and maintain a stable position; even the slightest displacement will negatively affect visual acuity.
Return to contents
Ultrasound phacoemulsification
The principle of the procedure is that special equipment is inserted through a small incision on the cornea, emitting ultrasound waves. They crush the affected lens until it reaches the dispersed phase. The resulting emulsion is removed from the eye using a system of tubes.
The main disadvantage of the technique is that a large number of ultrasonic waves negatively affects the condition of nearby tissues and structures. The level of harm caused depends on the power of the vibrations.
How does phacoemulsification occur?
At the beginning of the operation, the doctor manually or using a laser makes a microscopic incision measuring about two and a half millimeters. All further manipulations are carried out through it. A universal substance is injected into the anterior chamber of the visual apparatus, designed to protect the internal structures of the eye from damage.
Then, under the influence of ultrasound, the cloudy mass is destroyed and removed from the cavity through a vacuum syringe. An implant is installed in the cleaned capsule in place of the removed lens, which will subsequently perform all the functions of its “predecessor”.
| The final stage of the operation is washing out the protective substance; an irrigation solution is used for this. |
Cost of the operation
The estimated cost of laser surgery for cataracts starts from 40,000 per eye. Pre-collection of tests not included in this amount is required. Laser treatment is carried out on the basis of specialized budget and private clinics.
Laser treatment creates conditions for rapid recovery of the eyeball, which shortens the rehabilitation period. High precision of the laser beam minimizes the risks of complications. Vision begins to recover in the first days after surgery and reaches maximum quality within six months.
Are you familiar with laser treatment for cataracts? Tell us about your impressions in the comments. Share the article on social networks. Protect your eyesight. All the best.
Symptoms
At the early stage of cataract development, symptoms are not expressed and only an ophthalmologist can diagnose the disease. Symptoms appear later:
- Deterioration of vision;
- The appearance of light sensitivity;
- Difficulty recognizing objects in the dark;
- Change in color perception (objects seem to be under a yellow film);
- Need for brighter light;
- Doubling of objects when looking with one eye;
- Flashing, stripes, circles before the eyes.
Surgical treatment of traumatic cataracts
The timing of opacification removal will depend on the severity of the inflammatory process, the need to restore vision (this applies to children with an increased risk of amblyopia), future operations and the general condition of the patient. The treatment method and timing should be determined by the doctor, taking into account the vision prognosis and the presence of concomitant pathologies. The surgical plan will be based on the severity and location of the cataract.
The most common method of cataract removal is phacoemulsification, but surgery is contraindicated for brown cataracts. The lens is removed using ultrasound through a small puncture. The entire procedure takes up to 20 minutes. The doctor breaks up the cloudy masses and sucks them out of the capsule in order to insert a special lens into the vacant space. Modern implants are no different in functionality from a natural lens. The rehabilitation period does not take much time, and postoperative recommendations do not complicate the patient’s life. In the vast majority of cases, surgery provides a complete cure for cataracts.
Sometimes they resort to extracapsular extraction. This method is used less and less, although it remains acceptable if the ligaments of Zinn are weak and there is no vitreous hernia. Technologies that make it possible to implant intracapsular rings and capsular hooks are used when removing traumatic cataracts using an anterior approach. In the presence of severe phacodonesis, lens subluxation and capsule damage, another method of removing the opacities should be considered.
Primary extraction of traumatic cataracts is advantageous in that it eliminates the cause of inflammation, normalizes the level of intraocular pressure and carries out visual rehabilitation. Disadvantages of the procedure include a long rehabilitation period and an increased risk of inflammation. It may also be that the cataract did not affect your visual function and surgery will not help restore it.
Implantation of an intraocular lens
Implantation of an intraocular lens can be carried out after cataract removal by any method (provided that there is no inflammation and the risk of infection is low). The lens can be installed in the capsular bag, anterior chamber, ciliary groove, and fixed near the sclera or iris.
In children, clouding of the lens greatly increases the chances of developing amblyopia (lazy eye syndrome). Since rapid opacification of the posterior capsule often occurs after extraction, capsulotomy and vitrectomy (anterior) must be performed along with it. When operating on a child, the doctor must minimize the impact on the developing eye.
Opacities do not always progress, so the doctor must determine the advisability of surgery. If other structures of the eye have not been damaged, unnecessary intervention can only cause harm. When cataracts do not impair vision or provoke inflammation, infection or glaucoma, dynamic monitoring of the condition of the lens is recommended.
Traumatic cataracts are not always treated surgically. In cases where the clouding is not localized in the center of the lens and is not very dense, optical correction can be done. This is due to the fact that such cataracts do not interfere with normal vision.
Secondary cataract - symptoms and treatment
The main goal of treating secondary cataracts is to create a round hole in the clouded posterior capsule of the lens in order to improve visual functions.
There are two main ways to make such a hole:
- Surgical treatment (invasive method, penetrating surgery).
- Laser treatment (non-invasive, non-penetrating surgery).
In the first case, the surgeon makes incisions in the operating room, penetrates the eyeball and mechanically removes the clouded capsule, forming a round hole in it. This is a fairly traumatic method, so it is used extremely rarely, usually in the presence of absolute contraindications to laser treatment.
Currently, laser photodestruction (LPD) [4][6]. LPD is a laser dissection of a secondary cataract (otherwise called YAG laser discision of the lens capsule or laser capsulotomy ), that is, dissection of the clouded posterior capsule of the lens using a laser beam.
Precise and dosed exposure to a laser beam causes little trauma to the structures of the eye and allows one to achieve high visual functions immediately after surgery.
This type of operation does not require hospitalization. The procedure itself is painless, is done without anesthesia and lasts no more than 5-10 minutes. Only in some cases may it be necessary to instill painkillers.
Method of operation
30 minutes before the start of the procedure, a mydriatic (drops that dilate the pupil) is instilled into the patient's eye. Depending on the type of opacification of the posterior capsule and other factors, the surgeon determines the optimal laser treatment tactics and laser radiation power. The doctor focuses the laser beam on the posterior capsule; when exposed to it, the posterior capsule is cut in several places and a round hole is formed.
Indications for YAG laser dissection:
- secondary cataract (opacity of the posterior capsule of the lens).
Possible contraindications:
- low predicted result after the procedure (as a rule, this is due to concomitant diseases in this eye);
- inflammatory processes of the eye in the acute period;
- cloudy environments of the eye, which make it difficult for the surgeon to view the posterior capsule and can affect the quality of the operation.
Postoperative period
There is no rehabilitation period required after removal of a secondary cataract. The patient can lead a normal life immediately after the operation. In some cases, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory and/or antihypertensive eye drops for several days after surgery and/or limit physical activity and activities for a certain period.
Any therapy must be prescribed by the attending physician. You need to understand that each case is individual, and in order to correctly determine treatment tactics, it is important to know the general picture of concomitant diseases.
Complications during laser treatment and the postoperative period
Until recently, the appearance of laser equipment in ophthalmic practice was perceived only optimistically. However, with the accumulation of clinical experience, information began to appear about the risk of developing various complications.
- The most common occurrence is ocular hypertension (increased intraocular pressure) after laser dissection of secondary cataracts. The complication lasts no more than 3 days. In this situation, the doctor prescribes antihypertensive drops or oral medications.
- Recurrence of opacification in the post-laser period may occur in a patient with periodic inflammatory diseases of the eye (iridocyclitis), diabetes mellitus or retinitis pigmentosa. To reduce the risk of complications, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed orally or in the form of drops.
- bleeding after surgery increases if the patient has newly formed vessels in the iris or a tendency to bleeding and hematomas. In rare cases, hemorrhage into the vitreous body (hemophthalmos) may occur.
- Damage to the cornea is possible if the patient has previously identified corneal dystrophy, or due to mechanical damage from a laser beam.
- Macular edema (swelling of the central zone of the retina) and retinal detachment are extremely rare complications after removal of secondary cataracts. The risk group includes patients who have previously been diagnosed with detachment, rupture and other retinal diseases.
- Vitreous hernia is a prolapse of the vitreous into the anterior chamber of the eye due to damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the lens and displacement of the artificial lens (IOL).
- IOL displacement is the prolapse of the artificial lens into the vitreous. The main cause of the complication is a weak ligamentous apparatus of the lens.
- Damage to the IOL during laser intervention . The laser beam can damage the surface of the optical part of the artificial lens. However, today most IOLs are made from laser-resistant material (acrylic) and this complication has virtually no effect on the quality and acuity of vision after surgery.
The most important advantage of laser surgery is the formation of a stable optical opening in the posterior capsule of the lens. Precisely dosed exposure to the laser beam ensures high postoperative results. However, despite the simplicity of the surgical technique, the possibility of developing these complications requires a thorough examination of patients and taking into account all possible risk factors. This approach allows the procedure to be performed safely and to obtain a good postoperative result.