Men often consider the prostate gland to be their “second heart,” since sex life, the activity of the urinary system, and psycho-emotional mood depend on its functioning. The prostate gland is the main auxiliary sex gland of a man, responsible for performing an important secretory function. However, a man’s prostate gland does not always work like a clock, and the reason for this is an adenoma.
Prostate adenoma is a hyperplasia that is benign in nature. It is characterized by the slow proliferation of glands that are located in the neck of the bladder. At the beginning of the disease, a man develops a small nodule that is constantly growing. Over time, this node in the prostate gland begins to compress the urinary canal and problems with urination arise.
What is prostate adenoma, prostate adenoma, BPH?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a benign tumor of the glandular epithelium of the prostate. Has a lot
synonyms: prostate adenoma , prostate adenoma , nodular prostatic hyperplasia, paraurethral gland adenoma, dishormonal adenomatous prostatopathy).
Histologically, BPH is detected in 50 - 60% of men aged 60 years, in 80 -90% of men aged 80 years.
Description of the pathology
Benign prostatic hyperplasia grade 1 is an enlargement of the prostate that is not associated with cancer. The normal volume of this organ depends on the age of the patient. In men 20-55 years old, the permissible dimensions of the prostate are from 20 to 30 cm3. With age, the size of the gland increases due to the natural aging processes of the body. Therefore, in patients over 55-60 years of age, the normal prostate volume is 30-35 cm3.
If the size of the organ slightly exceeds the age norm, then doctors suggest a diagnosis of BPH of the 1st degree. What it is? This means that glandular and stromal tissue grows excessively in the prostate, but no pronounced clinical signs of adenoma have yet been observed. This is the earliest stage of pathological changes in the prostate gland. At the initial stage, the disease is quite easy to treat.
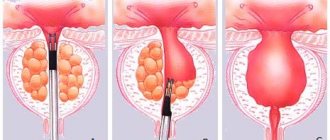
The photo on the right shows an enlarged prostate, on the left a normal-sized gland.
Prostate adenoma is a very common disease. It is diagnosed by ultrasound examination in approximately half of men over 60 years of age. However, grade 1 BPH should not be associated solely with age-related changes. If treatment is not carried out at an early stage, the disease will progress and enter more severe stages.
Stages of prostate adenoma
Outstanding urologist , nephrologist , Doctor of Medical Sciences , academician of the Academy of Medical Sciences of the USSR (ASMS USSR), chairman of the All-Union Society of Urologists , chairman of the Russian Scientific Society of Urologists , editor-in-chief of the journal “Urology” Nikolai Alekseevich Lopatkin (February 18, 1924 - September 16, 2013) in 1999 he developed a classification according to which there are 3 stages of prostate adenoma (benign prostatic hyperplasia).
1. Compensation ( stage 1 prostate adenoma ). The patient has urinary disorders when the bladder is completely emptied; patients note a sluggish stream of urine, the appearance of an imperative urge, especially at night, and somewhat difficult urination, but there are no pathological changes in the kidneys or upper urinary tract.
2. Subcompensation ( stage 2 prostate adenoma ). The patient experiences more significant changes in the bladder, and residual urine appears. The stream of urine becomes thinner and very sluggish; after urination, a man experiences a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, since after urination some of the urine remains in the bladder. The amount of residual urine reaches 100 - 200 ml or more. At this stage there may be acute urinary retention, difficulty in the outflow of urine from the upper urinary tract, and impaired renal function.
3. Decompensation ( stage 3 prostate adenoma ). Complete atony of the bladder develops, paradoxical ischuria occurs, dilatation of the upper urinary tract occurs, and renal dysfunction progresses.
Some urologists in Saratov distinguish 4 degrees of prostate adenoma (1, 2, 3, 4 degrees).
Diet
Diet is an important part of the treatment of stage 1 prostatic hyperplasia. Without this, it is impossible to achieve positive treatment results. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that irritate the prostate. These include:
- fat meat;
- salo;
- alcohol;
- spicy dishes;
- smoked meats;
- marinades and pickles;
- coffee and strong tea;
- scrambled eggs and fried omelet;
- ketchup;
- mayonnaise;
- carbonated drinks;
- fast food.
Doctors recommend including foods containing healthy animal proteins in your menu: chicken breast, turkey, veal, and lean fish. Dishes from these products should be prepared boiled or baked.
You should try to eat foods rich in vitamins A and E. These microelements help normalize hormonal levels and reduce prostate hyperplasia. A large amount of vitamins are found in seafood, green peas, buckwheat, brown rice, red fish, and quail eggs.
With prostate adenoma, patients usually have difficulty urinating. Therefore, it is very important to properly organize your drinking regime. In the early stages of the disease, there is no need to limit the amount of fluid consumed. It is recommended to drink weak green tea, rosehip decoction, cranberry juice, mineral water, and fermented milk drinks. The main volume of liquid should be consumed in the first half of the day. Approximately 2-3 hours before bedtime, you must completely stop taking liquid food (soups, broths) and drinks.
Signs, symptoms, manifestations of prostate adenoma
Men suffering from urinary tract obstruction caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia typically experience symptoms of BPH , which are collectively referred to as lower urinary tract symptoms (prostatism). In most cases it is a combination of symptoms of irritation and obstruction. Symptoms of irritation of prostate adenoma include imperative (imperative) urge to urinate, frequent urination during the day (pollakiuria), nocturia (excretion of most of the daily amount of urine at night), dysuria, a feeling of incomplete emptying, urination in drops at the end, stress urinary incontinence, incontinence after urination, weak urine pressure in men when urinating . Symptoms of obstruction of prostate adenoma include tension, straining when urinating, difficulty starting urination, weak urine stream, intermittent urine stream, and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Important symptoms for prostate adenoma: frequent urination in men at night .
Causes
Exposure to the hormone dihydrotestosterone is the main trigger for the development of grade 1 BPH. What it is? The hormone testosterone is produced in the male gonads. Under the action of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, it is converted to dihydrotestosterone. This substance promotes prostate growth.
As men age, various hormonal imbalances occur. Dihydrotestosterone accumulates in the tissues of the prostate gland, which leads to its enlargement.
However, prostate adenoma does not only appear in elderly patients. Recently, benign prostatic hyperplasia is increasingly observed in young men. This is due to the impact of the following unfavorable factors:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hypothermia of the pelvis and perineum;
- hypertension;
- diabetes mellitus;
- excess fat and salt in the diet;
- varicose veins in the pelvic area
- obesity.
In addition, there is a hereditary predisposition to this disease. If a man’s relatives suffered from prostate pathologies, then such a patient needs to undergo regular prostate examinations for preventive purposes.
How to identify prostate adenoma?
How to identify prostate adenoma, what tests are needed for adenoma? The main diagnostic methods for BPH are digital examination of the prostate gland, general urine analysis, urethral smear, examination of prostate juice, differential local segmental diagnosis according to Mears et Stamey, determination of prostate-specific antigen - PSA (normal total PSA , PSA value for prostate adenoma less than 4 ng/ml), recording of the spontaneous rhythm of urination, uroflowmetry, pharmaco-uroflowmetry, differentiated uroflowmetry, determination of residual urine, urethral resistance, perineal ultrasound, profilometry, sphincterometry, cystoscopy, urethrocystoscopy, determination of anal canal resistance, urethrotonometry, voiding urethrography, external electromyography sphincter and bulbospongiosus (bulbospongiosus) muscle, pelvic floor, rheography of the bladder neck and urethra, pharmacodynamic study of the urethra with alpha-blockers and muscle relaxants, tests for urethral denervation, biopsy of prostate adenoma .
Endocrine status is assessed by the levels of sex hormones, FSH, prolactin.
Alternative treatment for adenoma
Drug treatment of prostate adenoma is effective only at the initial stage of the disease, when the patient can urinate freely and urine is completely removed from the bladder. Currently, there are means and drugs that can not only alleviate the course of the disease, but also reduce the volume of the enlarged gland. Unfortunately, folk treatment, folk remedies, baths, treatment of prostate adenoma with folk remedies, herbs, and homemade preparations give little effect and modest results.
Diagnostic methods
Treatment of prostate adenoma is carried out by a urologist or andrologist. To confirm the diagnosis, the specialist palpates the gland and prescribes the following examinations:
- General blood analysis. Elevated ESR and leukocyte counts indicate that hyperplasia is complicated by inflammation of the prostate.
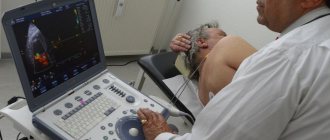
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Allows you to determine the degree and depth of damage to prostate tissue. Also, using this diagnostic method, you can determine the residual amount of urine in the bladder. It is recommended to do an ultrasound not abdominally, but transrectally. Such an examination gives more accurate results.
- Urofluometry. Helps to accurately diagnose stage 1 BPH. What it is? Using a special device, the rate of urine excretion and the volume of urine are recorded. This makes it possible to identify diuresis disturbances characteristic of prostate adenoma.
- PSA test. The test helps determine the presence of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. This protein is a marker of various pathologies of the prostate gland: hyperplasia, cancer, prostatitis.
Kidney examinations for grade 1 prostate hyperplasia are very rarely prescribed. At such an early stage of the disease, there are usually no serious complications from the excretory organs. Urography and cystography are indicated only for hyperplasia of degrees 2 and 3.
Surgery to remove adenoma
Currently, surgical methods for the treatment of BPH are most often used in the world (surgery for prostate adenoma, surgical treatment of prostate adenoma, surgical treatment of prostate adenoma, removal of prostate adenoma). If the disease is not very advanced (the bladder is emptied completely, the kidneys are not damaged), transurethral resection of the prostate (removal of prostate adenoma through the urethra) is performed. This is the least traumatic operation. In advanced disease, when BPH reaches a large size, the bladder is full of urine, and renal failure has appeared, transvesical or retropubic adenomectomy is used. These two operations are more traumatic than transurethral resection, but they provide complete cure for the disease. To perform the operation, you must contact specialized medical institutions.
Forecast
The prognosis for grade 1 BPH of the prostate gland is favorable if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. In this case, it is quite possible to prevent further hyperplasia of the gland. If treatment is delayed, the disease progresses.
In the decompensated stage of hyperplasia, the prognosis is not so favorable. Irreversible changes occur in the prostate and bladder. Only surgery can save the life and health of a patient. Otherwise, the patient may die from kidney failure.
Sexual dysfunctions after surgery to remove prostate adenoma
Dear men, we remind you that in the postoperative period after removal of prostate adenoma, the development of sexual dysfunctions and sexual disorders and disorders is possible. One of the causes of erectile dysfunction after surgery or treatment for BPH is often vascular insufficiency, which leads to fibrosis of erectile tissue and is associated with long-term sexual abstinence. And after 50 years of age, abstinence is very harmful! It is possible to develop veno-occlusive erectile dysfunction (rapid discharge of blood from the penis during an erection, which is why the penis does not stand up and quickly falls). If during surgery the mucous membrane of the proximal urethra or Zimmerman's area is damaged, retrograde ejaculation, anejaculation, lack of ejaculation, ejaculation disorders , and disturbances in the development of orgasm develop.
How to treat prostate adenoma?
To the question: “ How to treat prostate adenoma?” "We answer. Transurethral resection of the prostate gland allows you to minimize the development of postoperative complications, remain a healthy person for several more years and have a regular sex life, but after some time you will have to perform a second operation. For stages 1 and 2, conservative treatment is possible. Contact specialized medical institutions.
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Hannamonika | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Anhedonia, anhedonia treatment, sexual orgasmic anhedonia
Prolonged sexual intercourse, prolonged sexual intercourse
Syndrome of anxious expectation of failure (neurosis), STOSN, treatment
Psychosexual immaturity in men, treatment in Saratov
Sexual hysteria in men, hysteria treatment in Saratov