What can a cough be and what is the nature of its origin?
The beginning of symptomatic treatment is the prescription of drugs that dilute sputum and promote its rapid removal from the bronchi or lungs. A wet productive cough is often quite difficult to cure without the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. In parallel with such medications, antibiotics or antiviral agents are prescribed. They are especially needed when the cough was caused by an infection.
Antibiotics are used in rarer cases. When symptomatic therapy is ineffective and antiviral drugs do not work, antibiotics are prescribed to relieve inflammation.
Speaking about a non-productive dry cough, it should be understood that it most often occurs in the first stage of the disease. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and cough suppressants or mucolytic drugs. A dry cough can be caused by an allergic reaction. In any case, therapy should be prescribed by a doctor.
Diagnosis of metamorphopsia
Doctors use several methods, most using charts or graphs with lines, to help diagnose metamorphopsia. People who see line distortions when there are none are more likely to have a retinal or macular problem and subsequent metamorphopsia.
- Amsler mesh. Your doctor may want you to look at something called an Amsler mesh. Like the grid used in geometry class, it has evenly spaced horizontal and vertical lines with a central focal point.
- Preferred Hyperactivity Perimeter (PHP). This is a test in which dotted lines with artificial distortions flash in front of you. You will be asked to choose which lines are offset and which are not.
- M-graphics. These are diagrams with one or two vertical lines made up of small dots, also with a central focal point.
Central retinal dystrophy, symptoms, treatment
Involutional central retinal dystrophy is one of the main causes of vision loss (and in many cases significant) in people over 40-50 years of age. Therefore, it is often called senile.
Symptoms of central retinal dystrophy
It is important to know the initial symptoms of central retinal dystrophy in order to consult a doctor in time.
In the early stages of the disease, vision may decrease slightly, both when looking at distance and near. An alarming and very common symptom of central retinal dystrophy is distortion, curvature of straight lines.
A telegraph pole or doorway appears slightly curved and irregular in shape, giving the impression of looking through waves of warm air. A dark or gray spot appears in front of the diseased eye, and when reading, it seems as if individual letters in words are falling out.
If you look into the distance with an eye affected by dystrophy, objects may appear reduced in size and have a different color tone than when viewed with a healthy eye.
If you discover at least one of these symptoms, see an ophthalmologist as soon as possible, he will prescribe the appropriate treatment. You can check your vision yourself and continue to constantly monitor its condition.
One of the reliable and simple ways to check central visual acuity, which allows you to notice even minor initial disturbances, is the use of the Amsler grid. It is easy to make from a regular notebook sheet in a cage.
Draw a square with a side of 10 cm on a piece of paper and place a black dot in its center. The rules for using the Amsler grid are simple:
- put on reading glasses;
- close one eye (the test must be performed for each eye separately);
- look at the central point without looking up, do not move your eye to the sides;
- Keeping your eyes fixed on the dot, make sure all the hash lines are straight and all the small squares are the same size.
If you find that some area on the square is distorted or blurred, or has changed in color compared to others, do not hesitate to visit the eye office.
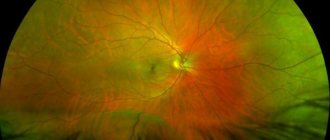
As a rule, when examining the fundus of the eye in the initial stage of the disease, a doctor discovers yellowish small round-shaped lesions on the retina - drusen.
Located on the retina, drusen usually do not reduce vision; however, they require dynamic medical supervision, since further progression of the process can lead to the development of a dry (non-exudative) or wet (exudative) form of the disease.
The non-exudative (dry) form of central retinal dystrophy is most favorable. It occurs as a result of the pressure of drusen on the layers of the retina, contributing to their atrophy. Treatment of this form of the disease is mainly aimed at improving the blood supply to the retina.
For this purpose, the doctor may prescribe vasodilators, vitamin therapy, and drugs that have a beneficial effect on metabolic processes. Courses of drug therapy are usually carried out twice a year. To enhance retinal nutrition, various surgical treatment methods are also used.
You can also improve your vision by using special magnifying lenses for close-up work and telescopic glasses for distance work.
Treatment of central retinal dystrophy
Unfortunately, modern ophthalmological science does not have sufficiently effective methods for treating central retinal dystrophy that could restore the desired visual acuity. However, regular treatment and constant monitoring by a specialist make it possible to delay the progression of the disease and maintain existing visual functions for a long time.
The dry form of dystrophy can turn into a wet, edematous - exudative one. In some cases, retinal drusen begin to merge with each other and this causes separation of the layers of the retina, between which fluid-exudate accumulates. With this course of the disease, vision loss becomes more significant.
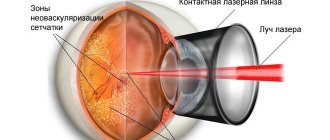
Over time, due to the edema that forms in the central zone of the retina, its blood supply sharply deteriorates. Abnormal blood vessels begin to develop under the retina, which lift the retina in the same way that tree roots growing under asphalt gradually lift and destroy the asphalt.
Pathological vessels have a porous wall and can leak fluid, bleed and further delaminate the retina. As they grow, retinal swelling increases and extensive hemorrhages appear, which sharply reduces visual function.
Timely use of laser therapy in some cases with the exudative form of the disease can stop vision loss, but this treatment method does not guarantee its complete preservation.
The goal of laser therapy is to try to eliminate swelling, destroy pathological vessels, and stop their growth.
In many cases, after laser treatment, patients no longer see dark spots in front of their eyes; The curvature of the lines also disappears. In addition to laser therapy, at this stage of the disease, medications are also prescribed to help reduce retinal swelling and resolve hemorrhages.
I would like to warn you: visual acuity after laser therapy, as a rule, does not increase, and in some cases it may become slightly worse. However, practice shows that the consequences of decreased vision as a result of laser treatment are usually much less severe than if it had not been carried out, and vision would have catastrophically decreased due to the progression of dystrophy.
In conclusion, some practical advice.
Whatever form of involutional central retinal dystrophy you suffer from, be sure to register at the eye office and visit an ophthalmologist at least once every 5-6 months.
In addition, monitor your vision yourself daily using the Amsler grid. And if you find even very minor changes, consult a doctor immediately.
Avoid strenuous physical activity, do not lift heavy objects, and do not work for long periods of time with your torso bent down. Do not take hot baths or showers. Follow a diet: exclude fatty, cholesterol-rich foods (fried meat, especially pork, eggs, butter) from your diet. Consume mostly plant-based fats. Limit salt and sugar.
On bright, sunny days, wear tinted glasses. Visual loads, if sufficiently high visual functions have been preserved, are, as a rule, not limited. You only need to take care of good lighting that is comfortable for the eyes.
If the work requires prolonged, significant eye strain, do not forget to take 10-45 minute breaks every 30-40 minutes.
People who have relatives suffering from central retinal dystrophy should be especially careful about the condition of their eyes. Let me remind you: this disease can be hereditary.
Once occurring, dystrophic changes in the retina are not subject to reverse development and are very difficult to treat.
I would especially like to emphasize: a lot depends on you - the earlier treatment is started, the more effective it will be, the longer you will be able to maintain your vision and lead an active, fulfilling life.
A few words about the structure of the eye
The word “dystrophy” means nutritional disorder. Consequently, retinal dystrophy is based on insufficient blood supply to the central zone of the retina, which can arise for a variety of reasons.
The name itself—involutional, or senile, dystrophy—suggests a possible connection between this disease and the aging process of eye tissue.
Disorders of metabolic processes in the retina, vascular changes, hypertension, atherosclerosis, leading to disorders of blood microcirculation in the vessels of the eye, can also play an important role in the development of the degenerative process.
The disease is sometimes hereditary and often occurs in members of the same family.
Conventionally, the eye can be compared to a camera. The lenses at the front of the camera allow light to pass through and allow the image to be focused on the film on the back of the camera.
The eye works in a similar way. Its front parts (cornea, pupil, lens) are transparent, and light easily and unhindered passes through them into the eye. The cornea and lens focus light onto the back wall of the eyeball. The thin layer of tissue covering this wall is called the retina.
The retina, figuratively speaking, is the “seeing tissue”. The light carrying the image is focused on it, and the image travels through the optic nerve to the brain. This is how we see it. The retina is a very thin nervous tissue. It consists of several layers and is divided into two zones: central (macular) and peripheral.
If you imagine the back wall of the eyeball in the form of a hemisphere with the retina lining it, then the macular zone is located in the center, next to the optic nerve. It is very small in area, but only this area of the retina has the ability to provide clear vision. It is central vision that allows us to clearly see the details of objects, read, thread a needle, and drive a car.
The large area of the retina, located around the central zone and occupying about 95% of the total area, is the peripheral zone. Here the sensitivity of the retina is hundreds of times less. This zone provides us with the opportunity to see what is on the sides.
Benefits of symptomatic treatment for cancer
With radical removal of cancer, symptomatic therapy is also necessary, since any interventions in the body are fraught with the most unexpected responses. At the stage of postoperative recovery with weakened immunity, rehabilitation of the vital functions of the entire body is necessary.
Symptomatic treatment of cancer patients poses the following tasks:
- correction and mitigation of difficult to tolerate manifestations of a malignant tumor;
- increasing the patient's life expectancy and improving its quality.
The symptomatic course becomes the only and main method of therapy for cancer patients at the fourth stage of cancer.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the patient’s condition and identify the cause of the disease, the doctor prescribes several tests:
- Anamnesis collection. This is data obtained from the words of the patient or his close relatives. Based on these, the doctor may prescribe further studies.
- General examination of the patient. In the presence of psychiatric diseases, alcoholism and drug addiction, the doctor determines behavior that is unusual for healthy people. With prolonged use of alcoholic beverages and drugs, the color of the skin changes to yellow, the sclera becomes red.
- Laboratory research. They do a general analysis of urine and blood, blood biochemistry. General parameters of the state of biological fluids and organs are identified. Additionally, a toxicological analysis is carried out, which reveals the substance that caused the disease.
- Assessment of the condition of the fundus. The study is carried out to exclude damage to the internal structures of the eyes, especially the retina. First, a solution is instilled into the patient’s eyes, which temporarily disrupts the accommodation of the pupil. The doctor looks at the condition of the lens, eye chambers, retina, microcirculation vessels.
- CT, MRI. As a result of the study, a layer-by-layer image of the eyeballs and brain will be visible. The analysis reveals the appearance of a malignant or benign tumor, inflammatory diseases of the nervous tissue and disruption of blood flow through the vessels.
Diagnosis and treatment of metamorphopsia
The Amsler test is used to diagnose this condition. It helps to confirm or refute the presence of macular degeneration in the patient, which can also affect the appearance of visual distortions.
During testing, the patient is given a sheet divided into equal squares with a dot in the center. The patient is asked to focus his gaze on this point alternately - first with the left, then with the right eye. After this, he must tell the doctor how he sees this mesh (smooth, with wavy lines, concave, etc.).
Other examination methods are also additionally prescribed:
- examination by a neurologist, ophthalmologist, narcologist, psychiatrist;
- MRI of the brain;
- EEG (electroencephalography).
Only after a complete examination and careful collection of the patient’s medical history is the cause of the pathology identified and treatment prescribed. It can be either conservative or surgical. The prognosis is individual in each case and depends on the complexity of the pathology that caused metamorphopsia.
Symptoms
It is very often possible to determine the presence of somatic diseases without performing special diagnostic tests. For example, if there are stomach problems, abdominal pain and acid belching occur. Pathologies of the cardiovascular system will lead to unstable blood pressure, and infectious viral diseases will lead to increased body temperature.
Psychosomatic disorders present difficulty in diagnosing symptoms. Very often such diseases are accompanied by personality disorders, depression, and anxiety. A patient whose illness arose as a result of self-hypnosis often experiences sleep problems, sexual disorders, loss of appetite, apathy and aversion to others. The most common symptoms of psychosomatic disorders at the initial stage are the signs described below.
Appetite disturbance
Somatic disorders in women often manifest themselves in abnormal perception of food: complete refusal of it or, conversely, excessive overeating. The cause is nervous breakdowns, psycho-emotional disorders, stress, nervousness or depression. As a consequence of the appearance of such conditions in women, with a complete refusal to eat, anorexia occurs, and with an increased feeling of hunger, obesity occurs.
Sometimes somatic nervous disorders can lead to the appearance of another disease known to many - bulimia. Its characteristic signs are an increased interest in food, fatty and unhealthy foods, uncontrolled hunger, which subsequently leads to obesity. To weigh less, they drink laxatives or diuretics and artificially induce vomiting. Such regular actions lead to serious complications in the digestive tract.
Sleep disturbance
Another common symptom of a somatic disorder of a psychogenic nature is insomnia. It manifests itself due to strong internal experiences, stress, and nervous disorders. With somatic sleep disorders, a person tries in every possible way to solve the problem: he tries to take a comfortable position, takes sleeping pills, and tries to fall asleep on his own. It is extremely rare that with insomnia a person can still fall asleep on his own, but at the slightest extraneous sounds he wakes up.
Pain syndrome
The most obvious signs of somatic disorders are pain. Patients with this diagnosis may complain of stomach pain, stabbing sensations in the heart, headache, weakness in the legs or aching joints. As a rule, it is precisely the organ that, in the patient’s opinion, is the weakest in the body that suffers. Such manifestations often haunt suspicious and especially anxious people.
Sexual function disorders
Acute somatic illnesses in men are often manifested by a lack of libido, weak erection, and decreased sexual desire. In women, such diseases are manifested by the absence of orgasm, the appearance of pain during sexual intercourse and, as a result, complete refusal of sex. Psychogenic factors lead to such somatic pathologies: long-term abstinence, fear, fear of sex, a feeling of disgust towards a partner, low or high self-esteem.
Mental disorders in somatic diseases
When chronic diseases are detected and require hospitalization, some patients experience aggravation of feelings. In this case, somatic symptoms of a psychogenic nature will depend on the diagnosis, for example:
- Coronary heart disease and rheumatism are often accompanied by hypochondria, lethargy, irritability, decreased concentration and memory impairment.
- Somatic symptoms when malignant tumors are detected can manifest themselves in increased fatigue, subdepressive states and neuroses.
- With renal failure, many patients complain of muscle weakness, a sharp loss of strength, and motor retardation.
- Nonspecific pneumonia is often accompanied by hyperthermia, euphoria, underestimation of the disease, manic or hallucinogenic manifestations.
Types, symptoms and treatment of metamorphopsia
Metamorphopsia is a condition in which there is a disturbance in a person’s perception of the shape of objects, their color, size, and nature of movement. A person makes mistakes in assessing the characteristics of real-life objects. This can be either a permanent state or a transient one.
Kinds
Distortion of the perception of surrounding objects and their characteristics during metamorphopsia.
This disease belongs to the group of sensory organ disorders and indicates the exogenous-organic nature of the lesion. In this case, the periphery suffers - the organ of vision itself.
According to the etiological factors, metamorphopsia is of two types:
- Refractive;
- Receptor.
The first is due to the presence of anomalies in the structure or function of the optical system of the eye, and the receptor one is due to the possible pathological state of the receptors of the eyeball.
It is also possible to distinguish several types of perception disorders based on the type of object:
SpeciesDescriptionSubspecies
| Autometamorphopsia | change in perception of the size and dimensions of one’s own body or its parts | Micro- and macromelia |
| Exometamorphopsia | distortion of the perception of surrounding objects and their characteristics |
|
| Porropsia | a person cannot adequately assess perspective, his own position in space and the location of objects surrounding him |
|
| Chronopsia | violation of the perception of time and its passage | Disruption of temporal synthesis |
Etiology
There are many reasons for the occurrence of metamorphopsia. At the same time, patients often turn first to ophthalmologists, and only after them are redirected to specialized specialists.
Distortion of the perception of objects is often observed in epilepsy, especially during the aura period and lasts no more than a quarter of an hour.
After injury to the occipital and parietal regions of the brain, patients often suffer from metamorphopsia. Organic lesions include cancer and pathology of the vascular bed. Changes in perception can be either reversible or irreversible. It depends on the severity and degree of neglect of the condition.
With paroxysmal schizophrenia, the patient may complain of a distorted perception of his body parts, their disproportion and an abnormal increase in their number. Hysterical seizures can also occur with symptoms of impaired perception of the flow of time and space.
Macropsia often occurs in patients who are prone to migraine attacks or when the occipital lobe of the brain is affected.
Consumption of large doses of alcohol and psychostimulant drugs can provoke a distortion of the perception of surrounding objects, time and space.
When taking narcotic substances, all types of metamorphospia may appear in various combinations. They are often accompanied by auditory and visual hallucinations.
Macropsia accompanies the use of hallucinogenic mushrooms; the symptoms are quite severe and can greatly frighten a person.
Clinical manifestations
The patient does not always maintain a critical attitude towards his condition. Some people do not consider the perceptual distortion to be an abnormality and may not admit it to doctors for some time.
With this disease, the surrounding space as a whole or its individual parts are distorted, lines become curved, objects have a disproportionate and skewed appearance.
Often a person’s perception of the proportions of his body is distorted. For example, one limb may appear huge or the head may appear too small. Sometimes this phenomenon occurs before bedtime (hypnagogic illusions). In some cases, there is an incorrect perception of the number of fingers, limbs, and individual parts of the body.
Macropsia is characterized by the fact that objects appear larger to a person than they actually are. If this condition is caused by the use of mind-altering substances, then the induced changes are eliminated along with the drugs.
Metamorphopsia can also include a protoanomaly. This is a violation of the perception of certain color shades. If it is not very pronounced, then a person may not notice it and not experience any discomfort. The perception of the red-orange spectrum is most often affected.
Diagnostics and principles of therapy
To diagnose this condition, the Amsler test is used. It is used to detect macular degeneration and problems with the perception of objects and space.
The test is used to identify macular degeneration and problems with the perception of objects and space.
It is a sheet divided into squares by vertical and horizontal lines. A large dot is placed in the center of the grid and the patient is asked to focus his gaze on it. First, both eyes are examined, then each in turn.
The patient must talk about how he sees this grid (smooth, distorted, “failing”). The diagnosis and definition of pathology depend on what changes he sees. With scatoma, parts of the Amsler grid fall out, with microspia, the lines converge towards each other.
And if a person has macropsia, then they are located at a remote distance.
Treatment for metamorphopsia depends on the cause of its occurrence. If these are consequences of injury, tissue compression by a tumor, or a disease of an infectious nature, then the underlying disease is treated.
Receptive metamorphopsia is less treatable than refractive metamorphopsia, although the symptoms are largely similar. This is due to a more complex receptor apparatus and the pathogenesis of damage.
Source: //ODepressii.ru/narusheniya/vosprijatija/metamorphopsiya.html
What do they look like?
When varicose veins begin to cause complications, red spots appear on the skin. The thin walls of the vessels cannot withstand the pressure and rupture, and the blood penetrates the skin, forming spots.
At first they do not cause any inconvenience, but they do not look aesthetically pleasing. But it should be taken into account that these are the primary signals of the development of varicose veins. Changes in skin pigmentation color always indicate health problems.
Causes
Initially, most patients consult an ophthalmologist. If a defect in the perception of surrounding objects is detected, he will refer you to doctors of a narrower specialty, for example, a neurologist. They can identify the cause of the disease:
- temporary decrease in the perception of surrounding objects during an attack of epilepsy;
- mechanical damage to the skull or brain;
- malignant neoplasms that form in the brain, growing, they compress the structures of the nervous tissue;
- schizophrenia and other mental disorders that contribute to the distortion of surrounding objects;
- hysterical fits;
- prolonged excessive consumption of alcohol, leading to the accumulation of ethyl alcohol in the brain, which has a toxic effect on nervous tissue;
- use of drugs that have a toxic effect on the brain;
- the presence of an infectious or viral process that has spread to brain tissue.
All of the above conditions can be treated if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. He must identify the underlying cause of the condition, since symptomatic treatment will not help.
Features of the disease
With metamorphopsia, not only the size of an object is distorted, but also its shape, color, and spatial location. Patients usually understand that the picture they see does not correspond to reality, but they cannot control their visual perception. Just as they cannot give an accurate assessment of current events based on visual information. Visual impairment can be permanent or temporary, which is determined by the causes of the disease.
Metamorphopsia is a rare disease and usually indicates serious mental problems. This is not an independent disease, but rather a symptom of a more dangerous disorder in the human body.
The patient not only sees the world around him as distorted, but also evaluates himself inadequately. A body schema disorder prevents a person from functioning normally and causes serious problems in daily life. Visual impairment often involves:
- distortion of body contours - this phenomenon is called dysmorphopsia. The patient sees the object as distorted, crooked, or moving and changing shape;
- inadequate assessment of size - the observed object seems larger or smaller than it actually is. This violation also makes it difficult to determine the exact distance to an object, which greatly interferes with a person’s everyday life and does not allow him to freely navigate in space;
- discoloration is the most harmless of the manifestations of the disease. The patient sees objects relatively clearly, but their color is distorted. Most often, the shades of the red and yellow palette change. The patient usually does not suffer from this disorder and does not even notice his problem.
History of discovery
Mycetoma was first mentioned by doctors in 1842. It was in this year that materials were published that spoke about sick Indians. The province of Madura was mentioned in particular. For this reason, one of the names of the disease is “Madura foot”. The same materials mentioned the supposed causative agents of the disease: Madurella and Actinomadura. A more complete description of mycetoma appeared later, in 1874.
Today, mycetoma of the maxillary sinus and other types of the disease affect residents of tropical regions. In areas with temperate climates, mycetoma is less common. The highest risk of infection is noted in Mexico, Saudi Arabia, Senegal, Congo, Sudan and in countries with an identical climate.
Am I Alice?
Until doctors have found a cure for Alice syndrome, individuals susceptible to it are faced with a choice: allow the disorder to subjugate them and continue to feel defective, or accept it as part of themselves and learn to live with it.
Why not treat your peculiarity as a chance to open the door to a new, amazing world filled with fabulous images? The main thing to realize is that this is your world, and you are in it - Alice in Wonderland.
LiveJournal
- Related Posts
- Causes and signs of manic psychosis
- Alcoholic epilepsy
- Mistakes of relatives and friends of alcohol addicts
« Previous entry
Diagnostics
When the first alarming signs appear, you should contact an ophthalmologist. Primary diagnosis is based on medical history. The doctor must provide the following information:
- what symptoms are currently bothering you;
- how long ago did they appear;
- does their severity increase with physical activity;
- whether visual system disorders have previously been identified;
- the nature of the patient’s professional activity;
- Do your immediate family members have rhegmatogenous detachment?
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, the ophthalmologist prescribes a comprehensive examination. It includes physical and instrumental methods.
These include:
- Determination of visual acuity. This is a basic diagnostic method, the essence of which is to assess a person’s ability to perceive two different points that are located as close to each other as possible. To do this, the patient is asked to sit on a chair located 5 m from the wall on which tables with letters are located. If a person can distinguish all 10 lines with each eye, this indicates excellent visual acuity of 1.0.
- Tonometry. A method by which you can find out the intraocular pressure indicator. There are several ways to do it. Non-contact tonometry is most often used in practice. It is carried out as follows: a device is installed opposite the eye that generates an air flow. It moves at a certain speed towards the cornea. As soon as they collide, the fundus of the eye is slightly deformed. The obtained indicators are recorded by special sensors.
- Perimetry. A method that involves assessing the visual field, usually using the Donders test. The patient is positioned at a distance of 1 m from the doctor, fixing his gaze on his nose. Then the examinee closes one eye, the specialist closes the other. The ophthalmologist begins to show an object with discernible outlines, gradually leading it along conventional meridians from the peripheral zone to the central one. Normally, both people should detect the object at the same time. The study is considered reliable if the doctor’s field of vision is not impaired.
- Biomicroscopy. A method in which the doctor is able to assess the condition of the visible parts of the patient’s eye under multiple magnification. For this purpose, a special device is used - a slit lamp.
- Indirect binocular ophthalmoscopy. The doctor directs a light source into the patient's eye and then examines the eyeball using special lenses.
- Refractometry. The patient's head is fixed opposite the device. Then he must look at the picture with each eye (separately). Gradually it changes sharpness. The results of the study are displayed on the monitor. Conclusion options: good vision, myopia, farsightedness.
- Ultrasound. After anesthesia is administered, the sensor is applied directly to the open eyeball.
Based on the results of a comprehensive examination, the doctor chooses the most effective treatment method. Conservative methods of therapy for this pathology are not used. Treatment of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment involves only surgery. It should be performed as soon as possible after diagnosis. Any delay risks serious complications.
Metamorphopsia - a distorted world around us
Eye diseases › Metamorphopsia
Ophthalmologists of the Primorsky district invite St. Petersburg residents and guests of our city who are faced with various visual anomalies, including metamorphopsia, to consultations and treatment.
Metamorphopsia is a pathological condition in which a person incorrectly perceives the shape, size, volume and distance of objects.
Metamorphopsia is classified as a family of psychosensory disorders, the manifestations of which are disturbances in the visual perception of objects and the surrounding space.
The course of metamorphopsia can be either long-term or episodic, depending on the disease that caused the disorder.
This condition is often observed in epilepsy, brain injuries and eye diseases. Patients generally judge their condition critically, but may have difficulty influencing visual changes.
Classification of visual perception distortions
The main indicator of metamorphopsia is a disturbance in the perception of size, shape and space.
Currently, metamorphopsia is divided into
- exomorphopsia, external type;
- internal type, consisting of changing one’s own perception.
Manifestations of exomorphopsia are often associated in patients with cartoons or caricatures, when the natural relationships of the visual world are noticeably distorted.
Exomorphopsia is also divided into such components of the condition as
- allesthesia;
- dysmorphopsia;
- dysmegalopsia;
- polyopia;
- macropsia;
- micropsia;
- microteleopsia;
- violation of temporal synthesis;
- parropsia;
- spatial rotation symptom.
In allesthesia , images appear to be out of place.
With microteleopsy, the images are greatly reduced and distant in space.
Dysmegalopsia is manifested by a change in the shape and symmetry of objects, all visual images acquire a new, distorted appearance with disturbed proportions.
With dysmorphopsia, objects take on a distorted shape, they are severely deformed, and familiar images are difficult to recognize.
Violations of temporal synthesis consist in incorrect assessment of the passage of time, when hours turn into minutes, etc.
Polyopia is a condition in which an increased number of surrounding objects appear in the visual field that do not exist in reality or are dividing.
Macropsia is characterized by a strong change in the size of objects, when familiar objects acquire exaggeratedly huge cycloscopic dimensions.
With micropsy, objects, on the contrary, become visually small and insignificant.
With parropsia, the perception of the depth of space is distorted, when distant objects can be felt close and, conversely, those nearby - distant.
With the symptom of space rotation, the patient perceives the world around him upside down, mainly in multiples of mathematical table values, for example, 90, 135 or 180 degrees.
A change in body perception entails a visual change in parts of the body, with legs and arms appearing caricaturedly large or small. Patients suffering from such visual perception disorders often inadequately assess the proportions of their body. In some cases, combatants may see more or fewer limbs than they actually have.
Causes of development of abnormal visual perception
Visual disturbances can be caused by many causes, conditions and diseases, including
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- epilepsy;
- astigmatism, changes in accommodation, eye diseases;
- schizophrenia and other mental disorders;
- twilight stupefaction;
- poisoning;
- alcohol tremens
- head injuries.
In some cases, neurologists refer patients with complaints of distortion of objects in the surrounding world for diagnosis and treatment to ophthalmologists.
In epileptics, visual perception may change, usually during an aura. The duration of distortions often does not exceed 10-15 minutes, manifesting as disturbances in subjective perception.
Sensory perception disorders are often caused by mental illness. Attacks of schizophrenia are caused by incorrect perception of body parts, including more or less of them than in reality.
In patients with hysteroid exacerbations, manifestations of polyopia are possible.
The cause of incorrect perception of shape can be various pathologies of the retina. Quite often, visual disturbances are caused by damage to the parietal and occipital regions of the head and various injuries or injuries to the brain. Hallucinatory microteleopsy and spatial rotation symptom are usually caused by organic disorders.
As a rule, any brain injury entails disturbances in visual and tactile perception of the surrounding world, and this condition can become final and essentially irreversible.
Drug poisoning is another cause of visual perception deformation. Persons under the influence of drugs experience any changes in visual perception, including all kinds of characteristics and properties of objects.
Course of metamorphopsia
Incorrect visual perception can be caused by alcohol poisoning of the body.
Persons who abuse alcohol constantly encounter various phantom hallucinogenic images of the surrounding reality, including observing various manifestations of exomorphopsia.
Often, in a drowsy state, the proportions of space are distorted, and what is especially dangerous is that patients cannot critically assess the state in which they are.
When taking certain medications (for example, prednisolone) or poisoning with chemicals, many patients can clearly observe visual metamorphoses, mystical and irrational phenomena, including distortions in the perception of space, dysmorphopsia, micropsia, macropsia, etc.
Suppression of the formation of spatial perception can cause the development of various pathologies of the vestibular apparatus. It is very easy to check this in practice - many young people who spent hours playing computer “shooters” like DOOM, QUAKE, BLOOD, etc., where the action develops in an imaginary space, experienced nausea and malaise.
Such disorders can cause detachment from reality and loss of self-identity.
Up
Source: //opervisus.ru/metamorphopsia.htm
Distortion of objects
Visual distortion occurs as a result of visual aberrations. In this case, objects may be blurry or have unclear spots. Metamorphopsia (distortion of the shape of objects), macropsia (enlargement of the object), micropsia (reduction of the object) also occurs.
Causes of visual distortion
Macular degeneration
In the case of age-related macular degeneration, the central zone of the retina, that is, the macula, is damaged. In this case, both eyes are most often affected.
If the patient experiences a disturbance in the perception of the size of objects, their shape, a change in their contours (metamorphopsia), and there is also a decrease in central vision and a dark spot appears in the center of the image, then you should immediately visit an ophthalmologist.
In the wet form of macular degeneration, a large number of altered vessels appear in the retinal substance, which grow from the choroid.
Despite the preservation of the peripheral zone of the retina, and, consequently, peripheral vision, the wet type of macular degeneration causes serious discomfort for the patient.
In the case of the dry form of macular degeneration, there is a metabolic disorder. This leads to the accumulation of pigment colloidal substances (drusen), which are formed from undigested proteins and polysaccharides.
Over time, the number of drusen usually increases, but the progression of dry macular degeneration is often slow. Initially, the disease may generally be asymptomatic, but then the patient experiences a feeling of blurred vision and color vision is impaired.
Central serous chorioretinitis (maculitis)
With central serous chorioretinitis, inflammation occurs that affects the central fossa of the retina.
With maculitis, the patient quickly has trouble performing precise visual manipulations that require good binocular vision.
There may also be distortion of objects or the text of a book (broken lines, letters falling out). A central scotoma appears, as a result of which visual acuity is reduced to hundredths.
Choroiditis
With choroiditis, there are usually no symptoms in the initial stages of the disease. More often, signs of inflammation can be identified during a diagnostic ophthalmological examination.
Signs of choroiditis include specific changes in the structure of the retina.
When the focus of inflammation is localized in the central zone of the choroid, light flashes, distortion of objects, or flickering before the eyes may be disturbing.
Retinal disinsertion
With retinal detachment, there is a feeling of a veil before the eyes. Also sometimes there is a loss of the field of vision, the appearance of lightning or sparks before the eyes, and distortion of objects.
Therefore, even with a successful operation, if you seek medical help late, vision recovery will be very long.
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is common among the population. With this disease, patients also complain of distortion of objects and blurring of their contours. This is due to the fact that with astigmatism there is deformation of the cornea, and sometimes the lens itself.
This causes the focal point, which is normally located in the plane of the retina, to turn into circles or dashes, so the image changes.
Diagnostics
To diagnose metamorphopsia, lethal fundus examination equipment is usually used. If there are no typical visual abnormalities in the retinal area, then a CT scan of the central retina (optical coherence tomography) is performed, which helps to identify the initial manifestations of degeneration, swelling and depletion of retinal cells.
Distortion of visual perception and its types
The main symptom of metamorphopsia is a change in the perception of shape, size and spatial judgment. There are two main types of metamorphopsia:
- external;
- internal (violations of one’s own perception).
The first type is characterized by a distortion of the perception of external objects, space, images seem deformed, modified, as in artistic caricatures. Exomorphopsia, in turn, is divided into several more subtypes:
- dysmegalopsia;
- polyopia;
- macro- and micropsia;
- parropsia;
- spatial rotation symptom;
- allesthesia;
- microteleopsia;
- dysmorphopsia;
- disruption of temporal synthesis.
With dysmegalopsia, deformation and asymmetry of objects and their parts are observed, images have a disproportionate and skewed appearance. Polyopia is characterized by an irrational increase in the number of surrounding objects; a patient with this diagnosis compared his visual distortions to a kaleidoscope. With macropsia, objects are excessively enlarged, their sizes sometimes seem unrealistically large and gigantic. Micropsia manifests itself in the opposite, reduced version, the images are microscopic and very irrational. With parropsia, spatial disturbances occur in the form of a distortion in the perception of distance, for example, distant images are perceived as close. Symptoms of space rotation are frequent companions of drowsy states, in which a person perceives the surrounding reality in a rotated form, mainly by 90 or 180°. This type of exomorphopsia is also characteristic of vegetative-vascular diseases or lesions of the frontal lobe of the brain. With allesthesia, objects seem out of place, and with microteleopsy, objects are microscopic and distant. Dysmorphopsia is manifested by distortion of the shapes of objects, images are distorted and modified beyond recognition. Distortion of time synthesis manifests itself in the inability to assess the reality of time processes. Patients with this disorder complain about the transience of the day, for example, “I went to bed last night, but it feels like I slept for only an hour.”
A violation of bodily perception is characterized by modifications of parts of the body; arms and legs seem unrealistically large or, conversely, small. Women with visual impairments often have an inadequate assessment of the proportions of their body, “the stomach seems very large, and the legs are thin and small.” There is also an irrational perception of the number of fingers and limbs; the patient seems to have several arms or a part of the body is missing.
Causes of the syndrome
Doctors call the main culprit in the occurrence of metamorphopsia a hereditary factor. Migraine with aura is in second place among the risk factors of the disease. True, out of 1000 patients with this diagnosis, only four complain of Alice syndrome. It is believed that Lewis Carroll was among them.
Signs of metamorphopsia are more often observed in children aged 5 to 10 years. Psychotherapists attribute this to the instability of the child’s psyche, its vulnerability to strong shocks. By adolescence - when the little patient is protected from stress - the disturbance of perception usually goes away without any treatment. However, children do not suffer much from the disorder, perceiving it as a fairy-tale adventure.
In adults, Alice syndrome can accompany, in addition to the migraine mentioned above, one of the following pathologies:
- epilepsy, characterized by nervous seizures with hallucinations;
- schizophrenia, manifested by the breakdown of mental and emotional processes;
- oncological disease of the brain, disrupting its functions and distorting psychoreactions;
- viral infections (for example, encephalitis or mononucleosis affecting the central nervous system).
“Escape from reality” with a complex of illusory sensations can provoke the use of drugs or hallucinogenic medications.
Why is metamorphopsia dangerous?
One of the unusual visual disturbances is metamorphopsia. The disease is directly related to vision, but is of a psychosensory nature. The disease is extremely difficult to treat, and its danger lies in the fact that the patient loses his sense of reality due to distorted perception.
Features of the disease
With metamorphopsia, not only the size of an object is distorted, but also its shape, color, and spatial location.
Patients usually understand that the picture they see does not correspond to reality, but they cannot control their visual perception.
Just as they cannot give an accurate assessment of current events based on visual information. Visual impairment can be permanent or temporary, which is determined by the causes of the disease.
The patient not only sees the world around him as distorted, but also evaluates himself inadequately. A body schema disorder prevents a person from functioning normally and causes serious problems in daily life. Visual impairment often involves:
- distortion of body contours - this phenomenon is called dysmorphopsia. The patient sees the object as distorted, crooked, or moving and changing shape;
- inadequate assessment of size - the observed object seems larger or smaller than it actually is. This violation also makes it difficult to determine the exact distance to an object, which greatly interferes with a person’s everyday life and does not allow him to freely navigate in space;
- discoloration is the most harmless of the manifestations of the disease. The patient sees objects relatively clearly, but their color is distorted. Most often, the shades of the red and yellow palette change. The patient usually does not suffer from this disorder and does not even notice his problem.
Causes of the disease
Temporary distortion of visual perception is observed during epileptic seizures. In the intervals between attacks, vision remains relatively stable.
Many diseases of the central nervous system can be accompanied by dysmorphopsia. For example, before the onset of a migraine state, the size and shape of objects may change. This phenomenon is known as “Alice” syndrome.
The heroine of Carroll's tale often encountered growing and shrinking objects in the plot of the book.
Pathologies of the occipital lobe of the brain also lead to distortion of visual perception. The visual analyzer department is located in this zone, and interruptions in its operation cause disorders. Distorted perception is often a consequence of atherosclerotic vascular lesions, brain tumors, meningitis, psychovegetative syndrome, and encephalitis.
The presence of cysts in the brain also leads to problems with visual perception. Malformations of the eyes rarely cause the disease. In exceptional cases, the development of the disease is facilitated by macular degeneration.
Pathologies of visual perception are observed in schizophrenics and people with mental disorders. They are more concerned about problems with inadequate assessment of their own body. Drinkers are also familiar with metamorphopsia. It is temporary and often accompanies withdrawal symptoms. After intoxication ends, vision problems disappear.
Distortion of visible objects is observed in persons prone to hysteria. Drug addicts and people taking psychotropic drugs may experience metamorphopsic manifestations. They are usually temporary and disappear completely after appropriate therapy.
Symptoms and treatment methods
The main symptom of the disease is visual impairment. That is why the patient first of all turns to an ophthalmologist.
To identify disturbances in the perception of objects and space, the Amsler test is performed. It is a square grid with a bold dot in the middle.
When the patient focuses his gaze on it, the doctor carefully examines each eye. It may seem to the patient that the grid is distorted, the lines diverge or come closer. Based on the patient's answers, a diagnosis is made.
In this way, you can not only identify metamorphopsia, but also its varieties.
Symptoms of the disease may be less pronounced. For example, with a protoanomaly, visual pathologies are not too noticeable. Sometimes the patient deliberately keeps silent about vision problems.
Not all patients are critical of their problem and try to deceive doctors for some time.
People with mental disorders who do not want to admit that they are sick are more prone to concealing facts.
Source: //MedCeh.ru/zabolevaniya-glaz/metamorfopsiya.html
Symptoms of psychosomatic diseases
It is quite difficult to identify a psychosomatic illness the first time; only some specialists can do this. Psychosomatics often has physical manifestations, which can also be caused by somatic pathologies. For example, gastritis can be caused by both a stressful situation and the Helicobacter bacteria. The patient’s state of mind can be directly related to the operation of such systems:
- gastrointestinal tract;
- the cardiovascular system;
- nervous system;
- the immune system.
Suspicions about the mental nature of diseases usually arise after unsuccessful drug therapy specific to the treatment of a specific disease. Sometimes this requires several years of the patient visiting the offices of various specialists, but in the end it turns out that only a psychotherapist is able to help him get rid of the ailments that have tormented him for years.
This situation arises partly due to the fact that patients keep silent about existing mental problems. Some because of shyness, but most of them simply do not see the relationship between their own experiences and their physical condition. And doctors do not consider it necessary to be interested in other people's problems.
If a patient is tormented by ailments that cannot be eliminated with traditional therapy, then it is necessary to begin treatment with a psychotherapeutic focus. And if the patient is in a difficult life situation, then a visit to a psychotherapist should not be postponed at all.
Body schema disorder (Autometamorphopsia)
A disorder of the body diagram is expressed in a violation of ideas regarding its size, shape, and location of parts. For example, it seems to the patient that the head has grown and does not fit on the bed, the torso has shrunk and disappeared, and the legs start from the neck. Depending on the cause of the syndrome, its symptoms disappear when visual control is connected, or less often they persist.
Phantom limb
There are many special cases of body schema disorder. The most popular phenomenon is a phantom limb, which is represented by the sensation of the presence of a lost part of an arm or leg (less commonly, the breast, genitals, eyes). Typically, patients feel that the amputated limb hurts. The symptom occurs immediately after the amputation procedure, gradually disappears, but sometimes appears over many years.
Unilateral lack of body awareness
Unilateral lack of awareness of the affected side syndrome is a neurologically determined perceptual disorder that develops when the parietal lobe of the cerebral cortex is damaged. The patient ignores half of the body: shaves one half of the face, puts on one shoe, combs the hair on one side of the head. Doesn't notice mistakes made if others don't pay attention.
Distorted perception of body parts
Distortion of the perception of the shape and/or size of body parts is possible with migraine, schizophrenia, the development of an epileptic aura, and taking LSD. The patient may feel that the leg is enlarged or deformed, the nose is stretched, and the feet are compressed. Similar symptoms may occasionally occur in healthy people during falling asleep, waking up, or fatigue. All distortions of the body are recognized as unreal, with the exception of cases caused by schizophrenia.
Other body diagram disorders
With the phenomenon of doubling, a feeling of duality of the body or some part of it arises (two left hands, two heads). Senestopathic conditions are characterized by localized distortions of somatic awareness, for example, the nose feels like it is made of cotton wool.
Hemisomatognosis is a rare variant of the disorder, manifested by a feeling of loss of a limb. The symptom develops with hemiparesis; sometimes patients deny the presence of an arm/leg, even if they see it.
Somatoagnosia with hemiplegia is characterized by the patient’s inability to realize that half of the body is paralyzed. In the body diagram image, the affected arm and leg do not lose function, so the patient denies the presence of the disease, even when someone around him points out the inability to move the limbs. With autotopagnosia, there is an inability to recognize, name and indicate (as requested) parts of one’s own/other’s body.
What diseases does it occur in?
Such a violation of visual perception is quite rare and can be observed in a number of diseases of various body systems.
central nervous system
Epilepsy. Especially often, distorted perception of objects occurs before or accompanies a seizure of temporal lobe epilepsy. Then vision gradually returns to normal.
Migraine. With this disease, impaired visual perception of the surrounding world is described as “Alice in Wonderland syndrome.” The shape and size of objects gradually change, foreshadowing the approach of a headache. Knowing these features, the patient can take the medications prescribed by the doctor, thereby interrupting the development of a pronounced pain symptom.
Pathology of the occipital lobe, where the central part of the visual analyzer is located. Also, objects can be perceived in a distorted, unrealistic form due to disorders or in areas of the brain where the occipital lobe borders the parietal and temporal regions. In this case, visual impairment may be associated with a brain tumor, cyst, previous traumatic brain injury, or severe atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels.
Psychovegetative syndrome with crises such as panic attacks in some cases may be accompanied by impaired visual perception. Encephalitis and meningitis can also cause a similar phenomenon.
One of the types of metamorphopsia is dysmorphopsia
Organs of vision
Quite rarely, such a disorder is caused by anomalies in the structure of the peripheral part of the visual analyzer and a violation of its receptor function. The patient should be screened for macular degeneration and ocular malformations.
Mental disorders
Schizophrenia. The patient complains of changes in the size of his own body parts and objects that surround his reality.
Hysteria. Metamorphopia in this case can be observed as part of a hysterical attack.
Alcohol abuse and drug use can also in some cases cause distorted visual perception of the world. After the intoxication is removed, everything should return to normal.
METAMORPHOPSIA
METAMORPHOPSIA
(Greek metamorpho[sis] transformation, transformation + opsis vision) - distorted visual perception of objects in the surrounding world. M. occurs when the peripheral part of the visual analyzer is irritated (see), representing a more or less curved, reduced (with micropsia) or enlarged (with macropsia) display of really existing objects of the surrounding world.
M.'s phenomena should be distinguished from subjective visual sensations noted by the patient in the eye in response to various influences (see Entoptic phenomena), as well as from real visual hallucinations (see).
All cases of M., depending on the origin, can be divided into refractive M., due to the optical features of the structure of the eye, and receptor M., the cut is based on certain anatomical changes on the part of the light-perceiving apparatus of the retina of the eye (see Retina).
M. in the form of micropsia is especially often observed with paresis or paralysis of accommodation. In these cases, in order to clearly perceive closely located objects, the patient has to strongly strain the ciliary muscle, as a result of which the fixed objects seem to be located closer to him than is actually the case. Accordingly, all objects seem smaller to him with the same angular dimensions. The occurrence of micropsia in some young people suffering from farsightedness can be explained in a similar way. The opposite phenomenon is observed in children with persistent spasm of accommodation. Under conditions of such a spasm, the child only needs the slightest additional tension of accommodation to clearly distinguish close objects, which is why they seem to be located further from the eye than they actually are, and therefore (for the same angular dimensions), larger than in reality.
A rapid change in the refraction of the eye, for example, with a traumatic rupture of the ligaments of Zinn (common tendon ring, T.) or with certain general intoxications, can lead to an incorrect judgment about the actual size of visible objects - to the occurrence of micropsia or macropsia in patients.
The receptor form of M. occurs in diseases of the retina. One of the most important symptoms of damage to the macula area is curvature, distortion of the shape and size of fixed objects. M.'s symptom in macular ulitis is most often observed in the stage of retinal scarring. Similar M. phenomena are sometimes observed with centrally located retinal detachments, certain exudative choroiditis, melanoblastomas of the macular or paramacular region.
Treatment of the underlying disease is carried out, the manifestation of which is M.
Bibliography:
Multi-volume guide to eye diseases, ed. V. N. Arkhangelsky, vol. 2, book. 2, p. 506, M., 1960; Lehrbuch und Atlas der Augenheilkunde, hrsg. v. H. Pau, Stuttgart, 1973.
A. Ya. Samoilov.
How to reduce the risk of infection
Prevention of acute respiratory diseases caused by coronavirus infection is not specific, and is carried out in the same volumes as for other viral etiologies. Its main element can rightfully be considered the prevention of the accumulation of large masses of people in closed, poorly ventilated rooms. Also, an important factor in the spread of infection is public transport, the use of which should be temporarily limited.
To reduce the risk of infection, you must follow certain rules:
- wear disposable medical masks;
- do not touch your face;
- regularly wash your hands with soap and water or use a disinfectant, especially after going outside;
- avoid crowded places (meetings, sports and other public events);
- limit handshakes when greeting;
- Ventilate the room you are in more often and be sure to wet clean it;
- Use only your own towel and toothbrush.
All of these tips are pretty simple. Naturally, following them will require some attention and forethought. But by observing the above preventive measures, you can seriously protect yourself. If everyone around you is infected, then you should stay home during the pandemic. In this case, the probability of becoming infected tends to zero.
As for whether the virus can be transmitted through objects such as coins and banknotes. The reality is that the risk of infection through contact with them is very low, but do not neglect the rules of hygiene and be sure to wash your hands with soap after shopping.
How to treat cough symptomatically?
Symptomatic treatment of cough of various etiologies is traditional, since it is not a separate disease that occurs independently. The main thing is to identify the underlying cause of this manifestation. Having determined the etiology of the symptom of the disease, the therapist will be able to prescribe a symptomatic treatment plan.
Further actions and recommendations from a specialist will be aimed at clarifying the productivity of the symptom. As is known, this criterion determines the presence or absence of sputum. It is known that a wet cough appears when phlegm descends into the respiratory organs. This is a common process for colds.