Pyelocystitis is a complication and consequence of ordinary cystitis. It is an inflammatory process localized on the mucous membranes covering the inside of the bladder and in the renal pelvis. The disease is painful, difficult to cure and easily becomes chronic.
Pyelocystitis is detected in men and women and is a complication and consequence of ordinary cystitis.
Forms and types
The term “pyelocystitis” is already outdated, and it is not in the latest edition of the International Classification of Diseases; accordingly, this disease does not have a code according to ICD-10. Two separate concepts are used: pyelitis and cystopyelonephritis.
If the primary focus of the infection is in the kidneys and the pathological process began from there, which then descended into the bladder, then this disease is called pyelitis.
If the bacteria initially occupied the bladder and then entered the renal pelvis, then the disease is classified as cystopyelonephritis.
There are 3 forms of pyelocystitis:
- spicy;
- chronic;
- candidiasis.
Spicy
The symptoms of the acute form are pronounced and appear rapidly. It often occurs in children as a complication of other pathological processes and as a result of previously administered incorrect therapy. Incorrect treatment can lead to a subsidence of the process for some time and subsequent outbreaks with increased unpleasant symptoms of the disease. Acute pyelocystitis is characterized by severe pain, which requires urgent hospitalization. In the hospital, a thorough diagnosis is carried out to prescribe adequate drug treatment.
Chronic
The chronic form of the disease has less pronounced symptoms, sometimes they may be completely absent. Inflammation worsens with decreased immunity or any stressful situation for the body (colds, hypothermia). This type of pyelocystitis is extremely difficult to treat. Treatment boils down to preventing relapses, which consists of increasing the body's protective functions, moderate physical activity, following dietary nutrition and personal hygiene rules.
Candida
When infected with the yeast fungus Candida, candidiasis develops, which serves as a factor provoking the development of candidal pyelocystitis. This inflammatory process often develops against the background of thrush and is its complication, as a result of which the kidneys and bladder are affected. The disease affects both sexes. Infection occurs during sexual intercourse, when bacteria enter the genitourinary system.
When infected with the yeast fungus Candida, candidiasis develops, which serves as a factor provoking the development of candidal pyelocystitis.
Prevention
To prevent pyelocystitis in children, it is necessary to regularly show the child to the pediatrician, provide the baby with a balanced diet, and keep the baby clean and warm. It is very important to dress your child according to the weather, avoiding hypothermia, and also to maintain the baby’s personal hygiene and wash him daily.
Prevention of pyelocystitis in adults consists of the following recommendations:
- It is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat healthy and balanced.
- It is recommended to avoid promiscuity and use condoms to avoid contracting STDs.
- It is very important to avoid hypothermia and dress appropriately for the weather.
- If signs of cystitis appear, you should be treated under the supervision of a doctor, and not on your own.
It is recommended to observe the rules of personal hygiene. You need to wash yourself in the morning and evening, and then change your underwear. During menstruation, the pad should be replaced every 3-4 hours, as bacteria multiply on its surface. You should use only a personal washcloth for washing, and wipe your genitals with a separate clean towel.
Causes of the disease
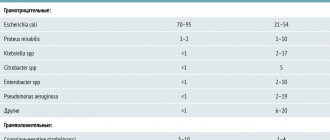
Pyelocystitis develops as a result of the ingestion of microorganisms such as:
- chlamydia;
- streptococci;
- gonococci;
- mycoplasma;
- staphylococci;
- viruses, etc.
Infection can enter the bladder in several ways:
- Ascending path. Initially occurring vaginitis or vulvovaginitis provokes infectious cystitis, because the infection rises along the urethra to the bladder. With a combination of circumstances and the presence of favorable factors, it goes further along the ureter and can cause inflammation of the kidney (pyelitis, nephritis, pyelonephritis). The pathological inflammatory process in the pelvis often begins due to advanced or untreated cystitis.
- Descending path. In this case, the infection from the kidneys goes down. Bacteria that appear in urine due to untreated pyelonephritis, entering a healthy bladder, cause an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane (cystitis). This path of development of pyelocystitis is much less common than the first option.
- With blood or lymph flow. The infection spreads from the diseased organ through the vascular system through the bloodstream. Any chronic infectious focus (bronchitis, prostate abscess, tonsillitis, endometritis, vaginitis, etc.) that remains untreated can lead to pyelocystitis.
The mucous membrane of the bladder copes with the penetration of infection quite easily. For inflammation to spread to the bladder and pelvis, predisposing factors must be present:
- disturbances of the circulatory process in the pelvic organs;
- disturbances and retention of urine outflow;
- hypothermia;
- defects in the structure of the urinary system;
- decreased immunity;
- hormonal imbalances;
- stress and anxiety;
- injuries;
- poor personal hygiene;
- unprotected sex.
Causes of pyelocystitis
The main cause of pyelocystitis is the entry and spread of infection in the bladder and renal pelvis. Most often, the disease is provoked by streptococci, staphylococci, Klebsiella, STIs, etc. Bacteria and viruses enter the bladder through the urethra, but for inflammation to occur, the body must be affected by some negative factors:
- weak immunity;
- vitamin deficiency, poor unbalanced diet;
- hypothermia;
- frequent colds;
- stagnation of urine due to other pathologies of the urinary system;
- poor personal hygiene;
- diseases of the genital organs;
- injuries;
- congenital anomalies of the urinary system.
Young girls are most often susceptible to pyelocystitis, this is due to the structural features of the urinary system and children. In newborns, the renal pelvis pushes out urine poorly, so stagnation and inflammation may occur.
In adult women, pyelocystitis is a consequence of untreated cystitis, or occurs during exacerbation of chronic inflammation of the bladder. The likelihood of developing complications is especially high in case of weakened immunity and frequent acute respiratory infections, since the infection can spread to the bladder and kidneys even from the respiratory tract through the lymph and blood flow.
Symptoms of pyelocystitis
The symptoms of this disease are quite extensive, since inflammation affects two organs at once (bladder and kidneys). To prescribe complex treatment aimed at combating the pathology of both affected organs, both processes need to be diagnosed.
Pyelocystitis manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- elevated temperatures and chills;
- migraines and dizziness;
- lethargy;
- lethargy and weakness;
- deterioration or lack of appetite;
- weight loss;
- increased sweating;
- change in the color and odor of urine.
With pyelocystitis, the temperature rises.
The disease causes inflammatory processes occurring in the kidneys and bladder, so the pain syndrome with pyelocystitis is especially evident in the lower back and can radiate to the groin area. There is painful urination, sometimes accompanied by bloody discharge.
Laboratory urine tests reveal the following signs:
- leukocyturia (leukocytes in urine);
- proteinuria (protein in urine).
Symptoms
Acute pyelocystitis most often has the following symptoms:
- cloudy urine;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- feeling of discomfort during urination;
- frequent pain in the lumbar region;
- sharp pain when tapped in the projection of the kidneys;
- fever and chills;
- decreased appetite;
- dizziness and headaches.
The last three signs are common. The first relate to symptoms characteristic of damage to the genitourinary system. If you find any of them in yourself, you should consult a doctor. You should not self-medicate, since an advanced process can develop into cystopyelonephritis - damage to the kidney tissue.
Diagnostics
If pyelocystitis is suspected, it is necessary to carry out a thorough diagnosis.
A urologist deals with such diseases. The doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations that are required to make a diagnosis. The following studies are being carried out:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. The sizes of organs and qualitative changes that have occurred in their tissues are determined.
- Cystoscopy. Using a special catheter (endoscope), equipped with lighting and optics, the bladder is examined. The instrument is inserted through the urethra.
- MRI. All internal organs are examined.
- Contrast uropyelography. A special contrast agent is injected into the kidneys and the quality of urine outflow is assessed.
- Biopsy of the mucous membrane. To identify the inflammatory process and the presence of fungal infections, as well as to exclude oncology.
- General urine analysis. The number of leukocytes and proteins is determined.
- Blood analysis.
To determine the size of the organ and the qualitative changes that have occurred in their tissues, an ultrasound of the kidneys is prescribed.
Based on the results of tests and studies, the doctor prescribes a course of complex therapy. You will definitely need to consult a gynecologist and venereologist to rule out sexually transmitted diseases.
Treatment of pyelocystitis
Pyelocystitis can be cured in a hospital or under the supervision of a doctor. It is possible to begin therapy only after identifying the cause that provoked the disease. Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the factor that caused the pathology. To prescribe an antibacterial course, it is necessary to identify the strain of the virus and its resistance to antibiotics. Only after this does the doctor prescribe pharmacological agents.
Drugs
To treat pyelocystitis, complex therapy is used, which includes the following groups of drugs:
- antibiotics (Moxifloxacin, Lomefloxacin, Norfloxacin, Ofloxacin);
- antispasmodics and analgesics (Drotaverine, No-shpa, Ketonal, Tempalgin, etc.);
- antimicrobials (Furazolin, Urosulfan, Furadonin, Sulfalen);
- herbal medicines (Urocholum, Phytolysin);
- traditional medicine (bear ears, juniper, horsetail, bearberry, barberry, dill seeds, etc.).
No-spa as a pain reliever for pyelocystitis.
If necessary, if there are abnormalities in the urinary system (for example, stones), surgery is performed to correct the problem.
Nutrition for pyelocystitis
The effectiveness of the therapy directly depends on proper nutrition and diet during the treatment of pyelocystitis. It is necessary to drink more fluid (at least 2.5 liters per day), and also greatly reduce salt intake or completely eliminate it from the diet. Smoked, salted, fatty, spicy foods and alcohol are prohibited. It is recommended to give preference to plant foods and dairy products. Meals should be frequent (4-6 times a day) and in small portions.
Treatment
Treatment of pyelocystitis is conservative. It assumes:
- Use of medications.
- Proper nutrition.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Maintain rest during therapy.
- Physiotherapy (blood irradiation with ultraviolet light, electrophoresis, UHF therapy). Effective during the period of remission after pain has been eliminated.
- Local thermal procedures (applying a heating pad to the abdomen, dry compresses, sitz baths).
In case of acute urinary retention, a catheter is inserted. If obstructive pyelocystitis develops, nephrostomy may be required.
In case of purulent complications, decapsulation of the kidney (dissection of the capsule) is performed.
This helps normalize blood pressure and reduce tissue swelling.
Treatment of pyelocystitis is conservative. It involves the use of medications.
Drugs
For inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs, including pyelocystitis, the following groups of medications are used:
- Antibiotics (fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, protected penicillins, drugs based on phosphonic acid). If the kidneys and bladder are inflamed, then the following may be prescribed: Palin, Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Suprax, Monural, Fosfomycin and Nolicin. Antibiotics are used for 10-14 days. They are best administered by injection, since in this case the bioavailability of the drug increases and the onset of the effect is accelerated.
- Nitrofuran derivatives (Furadonin-Lect, Furagin-Lect).
- Immunocorrectors.
- NSAIDs (Ibuprofen).
- Antispasmodics (Spazmalgon, Drotaverine).
- Antiseptics (Miramistin).
Phytotherapy
Auxiliary agents for pyelocystitis are: Canephron N, Cyston and Fitolysin. They contain herbal components and are therefore well tolerated by patients and rarely lead to undesirable reactions. Cyston contains plant extracts (doublecarp, madder, saxifrage, vernonia, onosma, etc.). This herbal medicine is approved for use during pregnancy. The medicine is not recommended for use for acute pain.
Effective for pyelocystitis Canephron N, containing lovage, centaury and rosemary leaves.
Canephron N, containing lovage, centaury and rosemary leaves, is no less effective for pyelocystitis. The drug is prescribed after the symptoms of the disease subside. Canephron N should not be taken in case of individual intolerance to the components of the drug, lactase and sucrase deficiency, stomach ulcers and children under 6 years of age.
Along with ready-made herbal remedies for pyelocystitis, you can drink decoctions and infusions based on herbs (lingonberry leaves, rose hips, St. John's wort, echinacea, eucalyptus, thyme, dill, parsley). Eleutherococcus and ginseng are used to enhance immunity.
Nutrition
If pyelocystitis develops, you must adhere to a healthy diet. Patients need:
- drink 2-2.5 liters of clean water per day (in the absence of acute urinary retention);
- adhere to a dairy-vegetable diet;
- eat more vegetables and fruits;
- reduce salt intake;
- enrich the menu with products containing easily digestible proteins;
- eat melons and watermelons;
- drink fruit drinks and fresh juices.
Complications
In the absence of treatment or the wrong treatment tactics for pyelocystitis, the process intensifies and can develop into a chronic stage, which is difficult to cure and can haunt a person for the rest of his life. Against the background of a weakened immune system, other infections (chlamydia, E. coli, gonococci) can appear in the body. This pathology has a complicated course.
Scheme of urolithiasis.
Due to improper functioning of the organs, various salts settle on the walls of the bladder, which leads to urolithiasis. Other complications are possible in the form of kidney damage, leading to organ failure.
Features of the disease in different categories of patients
This inflammatory process has some characteristics in different categories of patients, although the symptoms are similar and the treatment is the same
In men
Men suffer from pyelocystitis much less often than the fair sex. It often occurs as a complication of other inflammatory processes occurring in nearby organs (inflammation of the testicles, prostate, etc.).
Among women
The disease most often affects women. This is due to the structure of the genitourinary system. The short and wide urethral canal allows infections and pathological microorganisms to easily penetrate into the overlying organs. Fluctuations in hormone levels, which can trigger the disease, also play a role in this.