Causes
There are many reasons for the development, the most common is the entry of viruses and bacteria into the organ of vision, which cause inflammation of the cornea. Other reasons are as follows:
- Injuries to the eye or the presence of foreign bodies in it.
- Violation of the rules for caring for contact lenses.
- Burns of various origins.
- Presence of immunodeficiency states.
- The eye disease keratitis develops due to vitamin A deficiency.
- Increased dryness of the eye.
- Problems with nerve conduction in this area. For example, with neuritis of the facial nerve, lagophthalmos develops, as a result of which the eyelids do not close completely, which facilitates the penetration of pathogens into this area.
- Keratitis is often a consequence of allergies.
- Concomitant endocrinological and autoimmune diseases.
- Pathology can also develop as a result of long-term use of hormonal and psychotropic drugs.
In case of chronic diseases of the organ of vision, there is a risk of the inflammatory process spreading to the cornea. In some cases, the cause of the pathology is parasitic infestations.
What are the dangers of wearing contact lenses for a long time?
Eye lenses are a foreign body located outside the cornea. Lenses are constantly exposed to adverse environmental influences and also interact with tear fluid. This leads to the formation of sediments and mineral deposits on the contact lenses. They form micro-roughness and irregularities that can cause injury to the cornea. This causes pain, irritation, and if infected, can lead to keratitis - inflammation of the cornea, which can result in loss of the eye.
In addition, the following factors have a negative impact:
- the risk of damage to the cornea if the lenses are put on and removed incorrectly;
- wearing lenses longer than expected;
- non-compliance with the rules for the use and storage of contact lenses;
- incorrectly selected lenses for the eyes.
If you use hard lenses for long periods of time, there is a certain danger (albeit small) of getting microtraumas during sports and sudden movements.
Symptoms and types
Symptoms of keratitis in humans are lacrimation, fear of light and blepharospasm. The latter term refers to the reflex closure of the eyelids; often patients cannot open their eyes at all during the acute period of the disease.
There are also complaints of pain of varying intensity, there is clouding of the cornea, and hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the organ of vision. Patients may describe the sensation as a feeling of a foreign body in the eye. During the period of illness there is a decrease in visual acuity.
Other symptoms of eye keratitis depend on the type of pathology. The variants of the disease are as follows:
- Allergic is characterized, in addition to the above symptoms, by the presence of a runny nose, swelling of the face, cough, itching and burning in the eyes.
- Bacterial keratitis often occurs due to injury or when wearing contact lenses, as this makes it easier for pathogens to enter the organ of vision. Patients have complaints of severe throbbing pain in the eye, swelling in this area, and the appearance of purulent discharge. Complications include ulcers and opacities.
- Viral keratitis has a corresponding etiology, spotty opacities on the membrane. With this type, more often than with others, a cataract forms. In most cases, herpetic (or dendritic) and adenoviral keratitis are diagnosed.
- Acanthamoeba . A simple organism, an amoeba, can get into the eye. This happens when rinsing lenses under running water. In such cases, acanthamoeba keratitis is formed. Its symptoms are severe pain, clouding of the cornea and ring-shaped ulcers on it.
- Fungal keratitis is characterized by the presence of diffuse pain in the eye, severe hyperemia, and when the cornea is irritated, the eyelids close. Complications include decreased visual acuity, formation of a cataract, and ulceration.
- Parenchymal keratitis is caused by Treponema pallidum, the causative agent of syphilis. Its signs are that the cornea gradually becomes matte, the sclera grows with vessels that give it an orange tint. In the case of this type of pathology, great importance is attached to the accompanying symptoms of syphilis.
- filamentous develops . The amount of tear fluid is significantly reduced, and the pathology often becomes chronic.
- If a foreign object gets in, the risk of ulceration is much higher. The ulcerative type of the disease is severe, often with breakthrough of pus into other structures of the eye, perforation of the membranes of the organ of vision.
- A separate group includes the tuberculosis type of disease, in which white nodules accumulate in the cornea and infiltrates form on the surface.
The classification of keratitis according to localization is as follows: superficial, involving the upper layer of the membrane, and deep, which affects the underlying structures. With the latter type of disease, scars form.
Acute keratitis of the eye is more often diagnosed, which usually ends without any consequences for the organ of vision. But the process can become chronic, occurring with exacerbations and remissions.
Also, according to localization, marginal keratitis is distinguished, which is a type of viral or bacterial. The pathological process is localized on the peripheral part of the cornea and is easily detected by visual examination.
Contact lenses and keratitis. Disease prevention
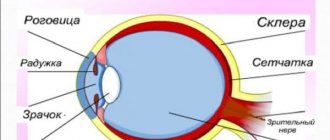
Keratitis is an inflammatory disease of the cornea - the most front, transparent part of the eye. The causative agents of keratitis are viruses and bacteria, less often fungi. The cause of the disease can be injuries, trophic disorders, decreased immunity, as well as wearing contact lenses.
Often inflammation of the cornea is combined with conjunctivitis. Due to the inflammatory process (keratitis), irreversible changes in the cornea can occur, which leads to a decrease in visual function, including blindness. Symptoms of keratitis are as follows: foreign body sensation or pain in the eye, photophobia, eyelid spasm, lacrimation, redness of the eye, and vision is often reduced.
Often, patients do not attach serious importance to redness of the eye and the feeling of a foreign body, mistaking corneal inflammation for banal conjunctivitis, do not consult a doctor and self-medicate. Keratitis is especially dangerous when the sensitivity of the cornea is reduced, since the disease can occur without obvious pain. The sensitivity of the cornea is often reduced in those who use contact lenses for vision correction for a long time. Often, the patient experiences redness and discomfort, which happens quite often among lens users due to malnutrition of the cornea and tear production of the eye. However, he continues to wear contact lenses. If you do not consult a doctor in time and do not undergo appropriate treatment, you may develop a dangerous form of keratitis, which can lead to noticeable loss of vision.
When the cornea becomes inflamed, clouding occurs , which is explained by the accumulation of various cellular elements (leukocytes, lymphocytes, etc.) in the corneal tissue. This accumulation of cells is called infiltrate. Infiltrates can be single or multiple, of different shapes, sizes and colors.
Superficial infiltrates may resolve without a trace or leave slight clouding on the cornea. With deeper damage, after the inflammatory phenomena subside, scar changes of varying degrees of severity remain on the cornea, which explain the low visual functions.
Also, with keratitis, vascularization of the cornea occurs - the ingrowth of blood vessels into it. The appearance of vessels in the cornea has a positive effect on the resorption of the infiltrate and is a compensatory, protective phenomenon, but on the other hand, it causes a decrease in the transparency of the cornea, since normally the cornea does not have vessels, which is one of the explanations for its transparency.
The clinical picture of keratitis is characterized by the so-called corneal syndrome - lacrimation, photophobia, blepharospasm (the palpebral fissure is sharply narrowed, the patient practically cannot open the eye). Worries about severe pain, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, redness of the eyeball. The inflammatory process may spread to the iris, ciliary body and sclera. An inflammatory focus on the cornea can ulcerate; if the course is unfavorable, perforation of the cornea and penetration of infection into the eye with the development of endophthalmitis can occur.
The clinical picture of individual forms of keratitis has its own characteristics and can also vary depending on age, general condition of the body, properties of the pathogen, etc. If symptoms of keratitis appear, you should definitely contact an ophthalmologist. Depending on the form of keratitis, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, healing gels, immunostimulants, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Widespread and deep forms of keratitis require treatment in a hospital setting.
For keratitis, medications are used in the form of eye drops, ointments, and drugs are administered as injections under the conjunctiva. Tablet forms, intramuscular and even intravenous injections are also prescribed. Products that promote corneal epithelization are widely used, usually in the form of gels and ointments. Biogenic stimulants are also prescribed to accelerate healing and increase local immunity.
Prognosis and prevention of keratitis The prognosis for keratitis primarily depends on the location and depth of damage to the cornea. With timely treatment, superficial infiltrates completely resolve or slight opacities remain, which have virtually no effect on visual acuity. Deep keratitis, ulcers , especially if they are localized in the central and paracentral zone of the cornea, can lead to a significant decrease in visual acuity due to the development of intense opacities and the formation of rough scars.
Prevention of keratitis consists in preventing injuries and microtraumas of the eye , which includes the use of safety glasses, safety precautions in production and construction. It is important to avoid contact with the eyes of various chemicals that lead to the development of burns of the cornea and mucous membrane of the eye, as well as to promptly identify and treat chronic blepharitis and conjunctivitis.
In order to prevent keratitis, it is necessary to carefully follow the rules of wearing and care when using contact lenses, and their careful hygiene. Timely contact with an ophthalmologist at the initial manifestations of the disease is the key to successful treatment and preservation of vision.
Be healthy!
How to treat keratitis
It is important to note that keratitis in children and adults occurs in the same way, and treatment methods are no different from each other. It is important to start treatment for the disease as early as possible. Treatment is complex, includes various areas, depending on the etiology of the disease.
Some patients have a question about how to treat eye keratitis at home. Hospitalization to an ophthalmology department is usually required; only the superficial, uncomplicated form can be treated on an outpatient basis.
Anti-infective therapy
This type of therapy depends on the pathogen. For bacterial etiology, Ofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Sulfacyl drops are used. If necessary, apply antibacterial ointment to the organ of vision (for example, Tetracycline). In case of severe intoxication, antibiotics are taken in the form of injections or tablets.
Treatment of herpetic keratitis of the eye includes the mandatory use of Acyclovir in the form of tablets and eye drops. Ganciclovir can be used and is more effective in severe cases. Arborescent keratitis often requires surgical correction, including corneal transplantation.
Also, for viral etiology, drugs containing interferon are used, and special ointments are placed in the organ of vision (for example, Florenal ointment).
To eliminate allergic reactions, special eye drops are used for keratitis of a similar etiology - Allergodil, Opatanol.
If a patient has syphilis or tuberculosis, drugs specifically directed against these pathogens are used for treatment.
Symptomatic treatment
The symptoms and treatment of keratitis are inextricably linked. To improve the patient's condition, mydriatics are prescribed that stimulate the outflow of tear fluid (Atropine, Cyclomed), artificial tears, and antiseptics (Albucid, Vitabact).
Agents are used that promote epithelization of the organ of vision - Solcoseryl, Cytochrome, Retinol. Vitamin eye drops - Taufon, Quinax, Katachrom - are also prescribed as symptomatic remedies.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of eye keratitis is required for the formation of scars, ulcerative lesions, deeper penetration of the pathological process, and severe herpetic lesions. Laser or thermal coagulation and keratoplasty are used (if this layer is destroyed). In some cases, treatment for keratitis in people may require a cornea transplant or laser vision correction. In very advanced cases, the question of complete removal of the affected eye may arise.
Is it appropriate to use folk remedies?
According to ophthalmologists, treating keratitis with folk remedies is inappropriate and even dangerous. The use of these techniques can worsen the course of the disease and increase the risk of complications, including the most serious ones (more on them below). Therefore, you should abandon traditional medicine and, at the first signs of illness, consult an ophthalmologist.
Allergy
The negative consequences of wearing lenses can manifest themselves in the form of an allergic reaction that occurs to the material from which the lens itself is made, as well as to the components of the solution in which it is processed.
In the latter case, ophthalmologists recommend replacing this solution with one that is made without the use of preservatives.
Deposits that form on the surface of the lens can also cause eye allergies. In this case, a transition from allergy to conjunctivitis often occurs.
If you are allergic to the material from which the lenses are made, you should simply replace them with a different type.
The consequences of wearing lenses for a long time can manifest themselves in the form of allergic conjunctivitis. It is accompanied by itching, lacrimation, fear of light, swelling and general discomfort. In this case, it is necessary to use anti-allergenic drugs in the form of drops, which are injected onto the cornea of the eye before placing the lens in it.
Complications and consequences
One of the complications is ulceration of the cornea, which can lead to the penetration of pathogens deeper into the underlying and nearby structures of the organ of vision. In severe cases, this process can cause significant reduction or complete loss of vision.
Complications also include scars on the cornea, which remain after recovery from the inflammatory process. The consequence of the disease can be glaucoma, cataracts, and cataracts. In some cases, inflammation (neuritis) of the optic nerve develops.
Protein deposits
These consequences of wearing lenses are very popular, but harmless.
Fats, calcium and proteins that are on the tear surface begin to come into contact with the surface of the contact lens. Subsequently, an uneven and rough film appears on it. It is almost invisible to the human eye; you can only pay attention to the greasy structure of the surface. But under a microscope everything is clearly visible.
Thus, these deposits accumulate and cause eye irritation. They begin to itch and turn red. In this case, you need to wear lenses for less time. If nothing is done, an infection may develop, which will lead to more severe consequences.
A multi-purpose solution that contains enzymes can help in this situation. And in order to control the consequences of wearing contact lenses, such as protein deposits, it is recommended to use disposable devices for some time.
In cases where such problems appear very often and in large quantities, it is recommended to use lenses that are made of material using crofilcon A or netrafilcon A. They are most resistant to such complications.
It is worth remembering that such protein deposits can be dangerous to the eyes, as they are potential carriers of germs and infections. In addition, the rough and uneven surface of the lens can scratch and injure the cornea.
Is it possible to wear lenses after keratitis?
This issue is always resolved by the doctor individually. If the process is complete, then wearing lenses is allowed after some time from the moment of recovery. The type of lenses must be selected by a doctor, the duration of use is gradually increased. The rules of care must be strictly followed, otherwise re-infection cannot be avoided.
If complications in the outcome of keratitis could not be avoided or the disease has become chronic, then wearing lenses is contraindicated. They can further injure the eye, which will only worsen the patient’s condition.
Acanthamoeba keratitis
This disease can be found quite rarely, but it is the most dangerous, since if treatment is not started in time, you can lose not only your vision, but also your eye.
The cause of this disease is Acanthamoeba, which lives and easily moves in soil, water, even drinking water. It can appear on the surface of any type of contact lenses.
Therefore, while wearing lenses, you should not swim in the pool, in ponds, or even in the bath. Also, avoid washing or rinsing lens cases in tap water.
Prevention
Complications of keratitis can be easily prevented by timely consultation with a doctor at the first symptoms and full treatment of the disease. As for other methods, doctors do not recommend prolonged exposure to the sun in cloudless weather. It is important to follow all rules for hygienic care of contact lenses.
For any disease of the organ of vision, it is important to start treating it on time to prevent the process from becoming chronic and the inflammation spreading further. Any concomitant pathologies should be transferred to the stage of decompensation; it is important to sanitize all sources of chronic infections in the body.
Traumatic keratitis is easily avoided if all necessary requirements in the workplace are met - wearing masks and other protective items, following safety regulations.
Consequences of wearing lenses at night
The risk of infectious diseases when wearing lenses at night increases, so you should give your eyes a break from them. If you use special ones, then such consequences arise much less frequently, but these devices are much more expensive and do not always justify themselves. It should be remembered that any lenses must be properly cared for and changed periodically.
Of course, it is not recommended to sleep in regular lenses that are not intended for nighttime use. Due to the release of proteins and lipids, plaque can form on their inner surface, which can damage the cornea.