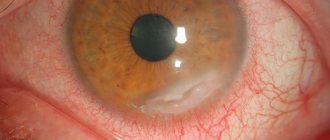
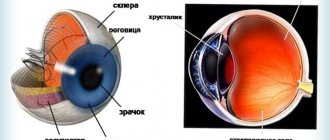
Classification of corneal ulcers
Corneal ulcers have multiple classifications. According to the flow, the defect is divided into the following stages:
- acute – severe pain with rapid damage to the membranes of the eye;
- chronic - the presence of an eyesore, indicating gradual damage; visual acuity does not drop immediately.
Classification by depth of damage:
- perforated - the defect is localized deeper than the surface epithelium:
- non-perforated – superficial lesion.
Division of ulcers by type of defect:
- central;
- paracentral;
- peripheral.
There are 2 main types of the disease depending on the degree of progression of the defect:
- Creeping ulcer.
From the area of damage, defective cells spread to the edges. Gradually, new layers from the cornea to the iris are involved in the pathological process. The most common cause is bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, pneumococcus). - Corrosive.
The process is formed for unknown reasons. 2-3 peripheral ulcers appear, merging into one area of damage. They become scarred, leading to blindness.
Depending on the etiological factor, 2 types of disease are distinguished:
- Infectious.
Damage is caused by fungi, viruses, and bacteria. - Non-infectious.
The cause is allergies, chronic dry eyes, impaired nutrition of the cornea through blood vessels (dystrophy), and erosion.
After collecting anamnesis and conducting research, the doctor makes a diagnosis. In the medical history, he must indicate the full classification, since the method of therapy depends on its type.
Classification of pathology
Depending on the nature and severity of the course, the pathology can be acute and chronic, deep and superficial, non-perforated and perforated. Also in ophthalmology they are classified according to the location of the defect - peripheral (marginal), paracentral, central. The division of the disease into groups is also based on the tendency to increase the size of the crateo-shaped defect:
- creeping. The spread of such an ulcer occurs only to one edge, and at its opposite end epithelization of the defect is observed. A pathological accumulation of purulent exudate in the anterior chamber of the eye is detected. The ulcer gradually deepens, affecting the underlying tissue. The cause of the formation of a defect is almost always tissue infection with pneumococci, diplobacillus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- corrosive. This type of pathology is characterized by the formation of several small defects at once. Slowly but steadily they increase in size until they merge into one crescent-shaped formation. The factors that provoke the development of the destructive-degenerative process have not yet been established.
There are infectious forms of the disease - herpetic, bacterial, parasitic, fungal, chlamydial. Non-infectious varieties include pathologies occurring against the background of allergic conjunctivitis, systemic autoimmune lesions, and dry eye syndrome.
When carrying out diagnostic measures, the form of the corneal ulcer must be determined. This factor becomes one of the determining factors for the choice of therapeutic tactics.
Causes of corneal ulcers
There are 2 main reasons for the development of corneal ulcers:
- penetration of infection, which includes the herpes virus, fungi, bacteria, parasites;
- non-infectious factors, for example, autoimmune diseases, dry eye syndrome, corneal dystrophy.
Not every person develops a corneal ulcer under the influence of negative factors. Patients are often affected by the following negative factors that increase the risk of pathology:
- constant wearing of contact lenses, including violation of hygiene rules;
- use of medications for other purposes than their intended purpose, excessively high course or dosage (hormones, antibiotics);
- carrying out ophthalmological procedures that cause complications;
- eye burn of any kind;
- damage to the eyeball due to a foreign body, exposure to excessively bright light, or injury;
- surgical operations on the eyeball (vision restoration, cataract removal).
Risk factors include frequent ophthalmic diseases. For example, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, trichiasis. Since the ulcer appears on the cornea, chronic keratitis is the most dangerous.
Chronic, systemic diseases can lead to pathology. Among them are diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, vitamin deficiency, and immunodeficiency. Pathologies lead to disruption of eye trophism. Autoimmune diseases cause the accumulation of leukocytes in the organ of vision, which begin to destroy its tissue.
Causes of the problem
All disease provocateurs are divided into two categories:
- Infectious;
- Non-infectious.
The causes of ulcerative keratitis of an infectious nature are as follows:
- Infection of viral origin;
- Fungal infection;
- Parasitic infection;
- Infection of bactericidal origin.
Due to the influence of pathogenic microorganisms, keratitis develops, followed by a corneal ulcer.
The causes of non-infectious corneal ulcers are:
- The influence of high temperatures;
- The influence of chemicals that are caustic and aggressive;
- Mechanical eye injuries, including burns;
- Prolonged and uncontrolled use of aggressive drugs with antifungal effects;
- Lack of minerals and vitamins in the body;
- Ignoring hygiene standards when caring for the eyes;
- An ulcer can be caused by eye diseases and their improper treatment, as well as various diseases of the body, in particular diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency;
- Dry eye syndrome;
- Improper use and storage of contact lenses. This is one of the most common causes of the development of keratitis, due to the impact of which the development of a corneal ulcer begins. Of course, this does not mean that you need to wear horn-rimmed glasses, but the lenses need to be properly cared for and stored;
- Use of ointments, gels, and other preparations made according to organic recipes;
Why does pathology occur?
Poor nutrition leads to a lack of microelements and vitamins, which negatively affects the cornea.
An ulcer on the cornea occurs as a result of destructive processes in which a defect in the form of a crater is formed on Bowman's membrane. There are several types of pathology, but the most severe is considered to be a marginal creeping corneal ulcer. It is characterized by a deepening in one of its borders and capture of the iris tissue. The disease is provoked by the following factors:
- burns and eye injuries;
- infection with pathogenic microorganisms (streptococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, herpesviruses, gibi, acanthamoeba);
- incorrect use of contact lenses and improper care of them;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- development of dry eye syndrome;
- unnatural direction of eyelash growth;
- chronic ENT diseases;
- infectious diseases of the organs of vision (conjunctivitis, keratitis, trachoma);
- diabetes;
- arthritis;
- decreased immunity;
- use of non-sterile equipment for ophthalmic or aesthetic manipulations in beauty salons.
Symptoms of a corneal ulcer
When a corneal defect appears, it gradually increases. Therefore, over time, the patient develops new clinical symptoms:
- in the early stages of the pathology, a sensation of a foreign body is formed, then pain in the eyes;
- as the ulceration increases, the pain syndrome progresses, which leads to photophobia and constant lacrimation;
- the eyelids swell, blepharospasm is observed;
- the eyes turn red, the vascular network is visible.
Further, the symptoms of a corneal ulcer vary depending on the location of the pathology. If it is located centrally, the following signs are distinguished:
- significant decrease in vision, which gradually leads to blindness;
- a cataract or scar on the central part of the eye of varying sizes.
The following signs are characteristic of an ulcer of infectious origin:
- cutting pain accompanied by lacrimation;
- discharge of pus from the eyes due to the accumulation of pathogenic microflora;
- first, an infiltrate is formed, which gradually disintegrates to form a crater on the cornea;
- the defect penetrates into the eye, which leads to various pathologies of the cornea (iritis, iridocyclitis).
The tuberculosis form differs from all pathologies of infectious origin. Initially, mycobacteria are localized in the lungs, kidneys and other organs. When they move onto the eyes, a rim-shaped infiltrate is formed. Gradually it becomes round. The ulcer may gradually fade, then form again. It's getting deeper.
Symptoms
Immediately after the appearance of corneal erosion, the patient experiences pain in the eye. This is due to the fact that there is irritation of the nerve fibers of the cornea. The pain is accompanied by profuse lacrimation. At the same time, patients note:
- photophobia;
- redness of the eye, which is manifested by the reaction of local vessels to irritation of nerve endings;
- When the cornea is located in the central zone, there may be a significant decrease in vision due to tissue swelling and clouding.
With an ulcer, the corneal stroma is often deformed and when it is restored, a scar is formed, which can be invisible or very pronounced (until the formation of a cataract).
Often, with extensive and deep ulcers and the simultaneous manifestation of the infectious process, intraocular structures are affected - the ciliary body and the iris. Ulcerative keratitis develops, which leads to loss of vision.
Diagnosis of corneal ulcer
An ophthalmologist diagnoses a patient's corneal ulcer. It includes the following laboratory and instrumental tests:
- General inspection.
It is performed with a slit lamp. With its help, changes in the structure of the cornea can be seen. Often the patient develops an eyesore. If the process is started, the ulcer is visible to the naked eye. - Ultrasound.
The condition of internal structures is revealed. Determine how deep the damage is. - Gonioscopy.
The anterior chamber of the eyeball is examined. - Diaphanoscopy.
Translucent eye tissue in a dark room. Determine the quality of the lens and retina. Foreign bodies, tumors, and iris defects are found. - Fluorescence test.
A fluorescent liquid is added to the tear fluid. If there is an ulcer on the cornea, it turns green. Assess its vastness and depth. - Laboratory research.
They include an immunological test to determine the amount of immunoglobulins in the tear fluid serum. The study is used for autoimmune pathologies. If the presence of an infectious agent is suspected, a bacteriological culture is taken.
During therapy, examinations may be repeated to check the quality of the drugs used. If they do not help, radical treatment is prescribed.
Diagnostics
If you suspect a corneal ulcer, a person should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor confirms or denies the suspicion during the initial examination using a slit lamp. In addition, in order not to miss small formations, the cornea is additionally stained with a special dye. A fluorescein solution helps to identify even the smallest affected areas, their extent and depth.
In addition, the doctor may additionally prescribe an examination using the following methods:
- ultrasound of the eye organ;
- diaphanoscopy;
- gonioscopy;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- tonometry.
Important: Extensive ulcerative lesions with infection often affect the deepest structures of the eye. This provokes the formation of ulcerative keratitis with subsequent loss of vision.
Also, to determine the root cause that caused the ulcerative formation on the cornea from the membrane, a smear is taken for cytological and microbiological examination. Such an examination allows you to identify the provocateur of the disease and prescribe adequate therapy aimed at eliminating the root cause and consequences.
Treatment of corneal ulcers
Patients are prescribed medications and physiotherapy under the supervision of a doctor. If the condition is severe, surgery is performed. Let's take a closer look at the methods of treating corneal ulcers:
- Procedural methods.
Pathology tends to expand. To prevent this, it is treated with an alcohol solution of brilliant green. Instead, you can use iodine tincture and laser coagulation. If the patient has dacryocystitis, lavage or dacryocystorhinostomy is used in the area of the nasolacrimal duct. Eliminate the infectious source. - Medicines.
Antiviral, antibacterial, antiparasitic, antifungal drugs are used. The use of non-steroidal or hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs may be required. To relieve swelling and inflammation, drops based on antihistamines help. For elevated intraocular pressure, antihypertensive drugs are used. Most medications are used only topically to achieve greater effect. - Physiotherapy.
Electrophoresis during drug administration, magnetic therapy, and ultraphonophoresis help. With their help, they stimulate metabolism, which triggers natural tissue regeneration. - Operation.
Keratoplasty is used. It is made using the through or layer-by-layer method. If a scar has formed that makes vision difficult, laser removal of the surface tissue of the cornea is used.
In many patients, the pathology is prone to relapse. Therefore, after completing therapy, you need to contact your doctor again. If the ulcer recurs, the use of medications together with physical therapy is started again.
How is the treatment carried out?
Drug therapy
Medicines must be prescribed by a doctor; self-medication is dangerous. Comprehensive treatment of creeping corneal ulcers includes drops and ointments shown in the table:
| Pharmgroup | Name of the drug |
| Antibiotics | "Ciloxan" |
| "Floxal" | |
| "Tobradex" | |
| "Vigamox" | |
| "Levomecitin" | |
| "Tobrex" | |
| "Signitsef" | |
| "Tsipropharm" | |
| Anti-inflammatory | "Diclofenac" |
| "Indocollier" | |
| "Dexamethasone" | |
| "Diklo-F" | |
| To prevent dry eyes | "Artelak" |
| "Vizimax" | |
| "Hypromellose" | |
| "Lipoflavone" | |
| "Sikapos" | |
| Vitamins | Vitamin complexes containing vitamins A, C, E, PP |
Physiotherapy
The procedure speeds up the effect of the drug. Changes in the structures lead to the formation of scars, so treatment of corneal ulcers includes physiotherapeutic methods, such as:
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- UHF therapy;
- diadynamic therapy;
- exposure to ultrasound;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- diathermocoagulation.
The initial stage of an eye ulcer is successfully treated, since the methods have the following effect:
- relieve pain and inflammation;
- promote tissue regeneration;
- normalizes blood circulation;
- eliminates the consequences of the inflammatory process;
- stops vision loss.
Surgical intervention
If a bacterial corneal ulcer cannot be cured conservatively, surgery is required. The following types of surgical intervention are used:
- Keratoplasty. The cornea is removed and replaced with a graft.
- Excimer laser scar removal. Laser scraping of the upper layers of the membrane along with the resulting scars is carried out.
Diagnostic measures
Laboratory diagnostics will help determine the nature of the lesion.
Keratitis and corneal ulcers are identified and treated by an ophthalmologist. The doctor performs the following diagnostic procedures:
- examination of the cornea with a slit lamp;
- instillation test using fluorescein solution;
- gonioscopy to visualize the anterior chamber;
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- diaphanoscopy;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- ultrasound examination of ocular structures;
- bacterial culture of purulent discharge from the eyes;
- microscopy;
- blood chemistry.
Corneal ulcers in cats and dogs
Corneal ulcers in cats and dogs can also be of an infectious or non-infectious nature. However, the damaging factors of the second cause are more extensive:
- predisposition to the disease in breeds (Pekingese, pugs);
- foreign bodies in the third eyelid;
- entropion of the eyelid;
- abnormal eyelash growth or excessive hair that constantly injures the cornea;
- violation of limbal division of diseased stem cells;
- suppression of local immunity.
Animals are characterized by pain in the eye, increased lacrimation, and photophobia. They find it difficult to keep their eyes open, so they squint. If you look closely at the eyes, you can see that they are red, the cornea is cloudy and swollen.
To diagnose the disease, contact a veterinarian. The determining factor is fluorescent staining, in which the area of the ulcer becomes bright green. Antiviral, antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal drops are used for therapy. If this does not help, surgical operations to restore the cornea are used.
Complications of corneal ulcers
The following are typical complications that occur as a result of corneal ulcers:
- deepening of the defect, accompanied by a protrusion like a hernia;
- perforation of the cornea;
- a scar that impedes vision function if it is located opposite the pupil;
- difficulty in the outflow of intraocular fluid, which leads to glaucoma;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- phlegmon, orbital abscess;
- proliferation of purulent infection, which penetrates the vitreous body with the formation of endophthalmitis, panophthalmitis;
- spread of infection from the eyeball to the vascular bed with the development of sepsis (if bacteria pass through the blood-brain membrane, meningitis is formed).
Due to the risk of complications, timely cleansing of the corneal surface is required. Without treatment, the patient may completely lose vision or die from infectious complications.
Complications
The most common complications are infectious ulcers accompanied by a purulent process. But the prognosis of the disease largely depends on the stage at which the patient seeks ophthalmological help. Any pain in the eye is a reason to visit a doctor.
Common complications of a purulent corneal ulcer are:
- excessive expansion, deepening of the ulcerative defect;
- the formation of a hernia-like protrusion;
- perforation of the cornea;
- formation of rough scars;
- development of secondary glaucoma and blindness;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- phlegmon of the orbit;
- brain abscess;
- blood poisoning.
If the course is unfavorable, a purulent infection can spread to the vitreous body, causing the development of phlegmon, brain abscess, meningitis and blood poisoning. The outcome of the disease is clouding of the stratum corneum. This complication is accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity and occupies a leading place among all causes of blindness. To prevent the formation of a cataract, it is necessary to promptly treat injuries that patients often receive at home and during the performance of professional duties.
Cloudiness of the stratum corneum requires surgical treatment. The doctor must replace the affected area with an implant. Such reconstructive operations are quite complex and dangerous, accompanied by a high risk of rejection of the material used and bleeding.
A significant decrease in vision is characteristic of a corneal ulcer, which is located in the central zone. It leads to a large cataract and significant scarring of the formed defect.
Eyesore
Symptoms: how does the disease manifest itself?
The growth of a bacterial infection provokes the appearance of purulent discharge.
Most often, a purulent corneal ulcer appears at stage 2 of keratitis due to tissue death. The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- photophobia;
- pain and stinging in the eye;
- foreign body sensation;
- lacrimation;
- involuntary blinking of the eyelids;
- swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva;
- formation of infiltrate from particles of cells, lymph and blood;
- the appearance of purulent discharge;
- clouding of the cornea;
- blurred vision;
- redness of the sclera.
Prevention of corneal ulcers
To prevent corneal ulcers, use the following rules:
- compliance with hygiene rules, especially when wearing contact lenses;
- avoid microtrauma to the eyes, but if this happens, it is important to use antiseptic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory agents;
- promptly consult a doctor if there is any damage to the eye or eyelid.
A corneal ulcer is a dangerous pathology. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, it will spread in depth and width. Self-medication is prohibited; this will cause complications including loss of vision or sepsis. Conservative therapy in the form of local medications is more often used. In severe cases, a surgical operation is prescribed that completely stops the formation of the ulcer, restoring its tissue.
Prevention and prognosis
Ulcerative lesions of the cornea always lead to deterioration of vision, so the prognosis is unfavorable.
The prognosis is also influenced by the addition of complications, the state of a person’s immunity, and age. However, with timely treatment, it is possible to restore visual function with keratoplasty. To prevent the disease from occurring, you should avoid injuries, do not touch your eyes with dirty hands, and use and install contact lenses correctly. It is recommended to treat all systemic infectious foci in a timely manner. It is also recommended not to visit beauty salons if the sanitary situation is alarming.