What is astigmatism
You will be interested in: Do colored lenses spoil vision: features of use, benefits and harms.
In Latin, the concept of “astigmatism” stands for lack of focus. Pathology can be acquired or congenital. Refractive error is characterized by the fact that the rays that enter the eye are located at several points. Because of this, images cannot focus on the retina, but only behind or in front of it. There is a distortion of the visible, blurriness, and double vision.
You may be interested in: Surgery for astigmatism: recommendations, contraindications, results
Astigmatism is a visual pathology that is very difficult to recognize at an early stage. This is its difference from myopia and farsightedness. The patient experiences uneven refraction of light rays in different parts of the lens and cornea. Therefore, correcting vision with such a diagnosis is much more difficult.
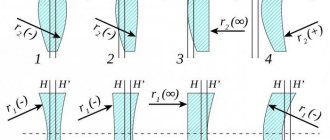
Types of lenses by design
Lenses or glasses - an individual choice
The design of modern glasses affects their cost. The more interesting the performance, the higher the price will be. In appearance, lenses can be:
- Spherical - most common. Their main difference is the equality of the radius of curvature at any selected point on the surface. To correct farsightedness, biconvex lenses are used, and to correct myopia, biconcave lenses are used. The simplicity of the design affects the appearance of the lenses - they do not look very attractive (they visually make the eyes smaller or larger). Another drawback is severe image distortion.
- Aspherical - one refractive surface is made in a shape different from a sphere. Thanks to this feature, aspherical lenses distort the image less. In addition, they do not affect the appearance of the face. Another advantage of such lenses is their lightness. Long visual loads are better tolerated in them. Aspheric lenses are recommended for severe visual impairment. The downside of the optics is glare due to the flat surface. To eliminate this drawback, an anti-reflective coating is applied to the lenses. Aspherical lenses cost more than spherical ones.
- Bi-aspheric - both surfaces differ in shape from a sphere. This allows you to maximize your field of view without distorting the image of surrounding objects. Bi-aspherical lenses are somewhat thinner and lighter than aspherical lenses.
Do I need to wear glasses all the time if I have astigmatism?
It depends on the degree of the disease and the presence/absence of concomitant pathologies. If astigmatism is mild up to 1D and is not accompanied by myopia or hypermetropia, then you do not need to wear glasses. The refractive error is dealt with by the accommodation apparatus, which compensates for the visual defect.
Glasses will have to be worn constantly if astigmatism is over 1.5 diopters. Deviations greater than 3D are difficult to correct with spectacle lenses. You have to select contact optics. Also, people who, in addition to astigmatism, have farsightedness or nearsightedness wear correction devices on a regular basis.
How to recalculate a recipe yourself?
Recalculation is carried out in 3 steps:
- We recalculate the sphere by summing the value of the sphere (Sph) and the cylinder (Cyl) in the recipe: Sph2=Sph+Cyl
- Change the sign of the cylinder (Cyl) to the opposite: Cyl2=Cyl*(-1)
- We change the value of the cylinder axis (Ax) to +90º or -90º, so that the resulting value remains in the range from 1º to 180º: Ax2=Ax±90º (12
If you want to learn how to recalculate lenses yourself, then we will study the transposition method.
This method allows you to select an equivalent lens, but with the condition that the lens will be installed at an angle changed to 90°.
What is recalculation using the transportation method?
The sphere power indicator (SPH) must be added to the cylindrical lens power indicator (CYL). The resulting number will be the new designation for the sphere's power. If the strength of the sphere is indicated by a minus, then it should be subtracted from the value of the cylinder.
The power value of a cylindrical lens should be changed so that it becomes inverse, for example: plus to minus.
90˚ should be added to the axis (AX). If the result of plus is more than 180˚, then the above figure should be subtracted. The resulting number is the new axis.
The recipe SPH-2 CYL-3 AX 60˚ is recalculated differently: after subtracting the value of the cylinder from the sphere, it turns out - 1D. Now we need to change the value of the cylinder -3D. You need to add 90˚ to the axis. The result will be 150˚. Now the recipe looks like this: SPH-1D CYL-3D AX 150˚
Rules for selecting astigmatic glasses
Astigmatism is corrected with glasses and contact lenses. You can also correct the curvature of the cornea during laser surgery. The correction method is determined by medical indications and a number of other factors. The selection procedure for astigmatic glasses is considered difficult. It is not always possible to select suitable optical products the first time. Moreover, it is difficult to create a base for such optics. It is individual and made to order according to specific parameters identified during the examination.
Astigmatic glasses are very different from regular spherical lenses. The latter have a uniform structure. Their thickness is the same at different points. Glasses for correcting astigmatism have an uneven shape. At one point the lens may be thickened. It's like there's an extra bulge on it. This is the optical power of the cylinder, which provides correction along one of the meridians. The spherical component of the optical product compensates for the refractive error along another meridian. In other words, astigmatic glasses are completely prescription glasses. If, when selecting lenses for nearsighted or farsighted people, optics may have a model with the required parameters, then optical products for astigmatism are made to order, since they have a very complex geometry. To form a database of such lenses, thousands of different models will have to be manufactured.
In the prescription for astigmatic glasses you can see the following designations:
Sph—diopter for the right (OD) and left (OS) eyes;
DP—interpupillary distance;
Cyl is the optical power of the cylinder;
Ax is the cylinder tilt axis.
What does a prescription for glasses for astigmatism say?
After collecting all the necessary information, the ophthalmologist writes a prescription for astigmatic glasses. Here is the information that will be included in it:
- Sph (sphere) - value in diopters for the right (OD) and left (OS) eyes;
- DP is the distance between the centers of the pupils;
- Cyl is the optical power of the cylinder;
- Ax is the cylinder tilt axis.
It is these parameters that the master optician will be guided by, producing astigmatic cylindrical glasses to individual order. What are they? Their difference from simple spherical lenses is that light rays falling into a plane parallel to the glass axis are not refracted, but rays in a perpendicular plane, on the contrary, tend to be refracted. To do this, the recipe indicates Ax - the axis of inclination of the cylinder in degrees up to 180°.
Glasses for astigmatism are an affordable and easy way to correct this visual impairment. However, it is advisable to use spectacle optics only for mild pathology up to –3 diopters. For moderate and severe degrees, toric contact lenses are suitable or surgery is prescribed. The fact is that astigmatic glasses noticeably limit peripheral vision, while distorting the size and proportions of the image, especially with a strong degree of complex myopic or mixed astigmatism. Not all users can adapt to glasses when choosing contact lenses.
Decoding medical abbreviations
Abbreviations of medical terms were invented in order to save time and paper. When reading a prescription, the patient does not always understand the meaning of what is written, and therefore it does not hurt anyone to know what this or that medical abbreviation means. So, the decryption:
- OD - in Latin means nothing more than the right eye;
- OS – left eye, respectively (Oculus Sinister);
- OU is short for Oculus Dexter, which in Latin means both eyes.
The following information follows:
- D – it denotes the number of diopters, that is, it is an indicator of strength. If a person is farsighted, then the number next to the abbreviation is marked with a plus sign, if nearsightedness, a minus sign;
- SPH – spherical lens power (flat). Indicated in diopters (see above);
- CYL is an abbreviation for a cylindrical lens (cylinder). Measured and indicated in diopters.
There are other indicators:
- AX is the inclination (axis) at which only the cylindrical lens is installed, the degree is indicated in degrees;
- DP is the distance between the pupils and is indicated in millimeters.
We should also talk about addition: it is abbreviated ADD and is not always indicated in recipes. Addition is the amount of diopter gain + or - at the top or bottom of a spherical lens when needed. It is found only in the most modern models of glasses or lenses. Appears in recipes quite rarely.
Astigmatism - visual impairment
Astigmatism is a visual impairment that results in blurry and unclear vision of surrounding objects. Quite often, astigmatism is accompanied by such types of visual impairment as myopia or farsightedness.
Many people, faced with this disease, practically do not feel any inconvenience or discomfort. However, we are talking only about a weak degree of astigmatism, which does not require urgent medical intervention and is practically not felt.
However, patients who have a high degree of the disease very often complain of rapid eye fatigue, a sharp decrease in visual acuity, frequent headaches, and double vision.
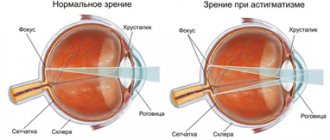
Astigmatism is a form of visual acuity impairment in which a point object is not reflected on the retina and, accordingly, is not perceived by us as an image of a point. With such a visual impairment, a person sees all objects unclearly, as if in a distorting mirror.
Actually, the word astigmatism itself, translated from Greek, means the absence of point focusing (a - negation, stigma - spot, point), and the word “toric” is equal in meaning to the word “astigmatic”, but is most often used specifically in relation to soft contact lenses.
Spectacle correction with cylindrical lenses is possible, but toric contact lenses are more preferable.
In addition to impaired visual acuity, uncorrected astigmatism inevitably causes such unpleasant symptoms as double vision, constant need to squint, fatigue, a feeling of pressure in the eyeballs and frequent severe headaches of “unexplained origin.”
In addition, people with uncorrected astigmatism face additional visual problems in conditions of insufficient visibility, which, for example, when driving in the evening or at night, can lead to tragic consequences.
In most cases, the correct selection of astigmatic glasses or toric contact lenses quickly, within a few days (or even hours), relieves the patient of all these troubles.
Degrees of the disease
Doctors distinguish three degrees of the disease: weak (up to 3 diopters), medium (from 3 to 6 diopters) and high (more than 6 diopters). In the first case, the disease is easily correctable, which can be done with laser therapy, correction with glasses or lenses.
In the second case - with a moderate degree of astigmatism - you need to seek help from glasses, contact lenses or surgery. With a high degree of astigmatism, severe changes occur in the cornea, so hard contact lenses should be used.
Diagnostics - Jackson method
As you know, accurate timely diagnosis is the key to health. The earlier a problem is identified, the easier it is to avoid its most undesirable consequences.
In modern ophthalmology, several methods are used to diagnose the pathology in question. Today, the crossed cylinder diagnostic method is widely used.
This technique was first proposed in 1907 by the American ophthalmologist Edward Jackson. Initially, the crossed cylinder was intended to determine the accuracy of the force and position of the axis of the correction cylinder.
These cylinders are also used in cases where the patient’s reaction to small gradations in the force of the corrective cylinder or changes in the position of the axis is recorded.
Clarification of the degree of violation
During the test, the patient is asked to wear a trial frame. A special astigmatic lens is placed in front of the eye in a trial frame. A crossed cylinder is installed alternately in several positions in front of the lens socket and the trial frame.
- The position in which the axes of the correcting cylinder and the cylindrical lens coincide.
- The axis of the correcting cylinder coincides with the opposite axis of the crossed cylinder.
Before starting the test, the handle of the crossed cylinder is set to 45 degrees. Subsequently, using this handle, alternate rotation is carried out from one position to another.
There is a special table in front of the examinee at the time of the test (table for checking visual acuity). The patient is tasked with noticing at what position of the cylinder his vision is best focused.
In the second case, the axis is weakened by the same number of diopters. Subsequently, the test must be repeated as many times as necessary to obtain an informative result.
The degree of astigmatism is determined depending on the option when the cylinder gave an uncertain result.
Cylinder transposition
There are often cases when patients are faced with a phenomenon that is incomprehensible to them. When ordering glasses from a workshop, the customer can change the lens parameters. For example, an optician wrote the following prescription: OD sph - cyl +0.5 ax 180 OS sph - cyl +0.5 ax 0 DP=52mm In the workshop, the following entry may appear on the order form: OD sph +0.5 cyl −0.5 ax 90 OS sph +0.5 cyl −0.5 ax 90 DP=52mm
Don't worry - this is a normal phenomenon, a purely technical issue without any deception. An astigmatic lens always corresponds to two equivalent entries: one with a plus cylinder, and the other with a minus cylinder. The transition from one record to another is called cylinder transposition. Its principle is as follows: 1. Add the force of the sphere and the cylinder, taking into account the sign, to obtain a new value of the sphere force: In this case, 0 + 0.5 gives a value of sph +0.5 2. Change the sign of the cylinder force to obtain a new value of the cylinder force : +0.5 we replace + with - and we get cyl −0.5 3. Change the position of the axis by 90 degrees: 180 degrees turns into 90, the same as 0 into 90.
This is how two outwardly different entries can appear, but essentially meaning the same parameters of lenses for glasses.
Current version of the page so far
not checked
Current version of the page so far
not checked
experienced participants and may differ significantly from
Glasses prescription
- a form containing the data necessary for the correct manufacture or purchase of finished glasses.
Treatment
Of course, astigmatism in children and adults is very bad and needs to be corrected or eliminated permanently using the methods listed below.
Laser correction
Alignment of the cornea under the influence of laser beams. Allows you to get rid of the defect in 15-30 minutes.
Implantation of an intraocular lens
This is a complex surgical operation that involves inserting a toric intraocular lens into the eye. The latter should be in front of the cornea.
Night contact lens
They have a special shape and align the cornea during night sleep, after which vision is normalized. The effect of this correction lasts 24 hours.
Still, there are times when these methods are contraindicated, for example, children aged 3-5 years. If the cornea is thin, which is the case in all children, laser correction is contraindicated. Implantation of an intraocular lens is prohibited in case of uevitis and cataracts. Refractive therapy is contraindicated for dry eye syndrome and its internal pathologies, including corneal defects, as well as for inflammatory diseases of the eyelids. And finally, the price of correction is of no small importance. This is why many people wear glasses or contact lenses.
Lens recounting is not a calculation of their number, as it might seem at first glance, but a necessary procedure that allows you to quickly select glasses or contact lenses if this cannot be done according to the prescription. The peculiarity of the procedure is to add or subtract (sometimes) the values of the sphere and cylinder. During the recalculation, the cylinder axis also changes. A lens made according to a recipe modified by recalculation will refract light in the same way as the one prescribed by the ophthalmologist.
After an examination and the necessary diagnostic tests, the doctor may prescribe you to wear glasses. The entry in the recipe will look something like this: OD Sph −3.0D, Cyl −1.0D ax 180 OS Sph −3.0D, Cyl −2.0D ax 175 Dp 68 (33.5/34.5) Let's try to figure it out, What do these strange letters and numbers mean?
OD (oculus dexter) is the designation of the right eye, OS (oculus sinister) is the name of the left eye. In some cases, it may be indicated - OU (oculus uterque), which means “both eyes”. In ophthalmology, to avoid confusion, it is customary to always indicate the right eye first, then the left.
Sph (sphere) - denotes a spherical lens. These lenses are used to correct nearsightedness (myopia) and farsightedness (hypermetropia).
The number (in our example 3.0) indicates the optical power of the lens, expressed in dioptres - D (dioptria). In the case of collective lenses (for hyperopia), a “+” sign is placed in front of its value, in the case of diverging lenses (for myopia) - “-”; In our example, the “-” sign is used, which indicates the need to correct myopia.
Cyl (cylinder) - designation of a cylindrical lens. These lenses are used to correct astigmatism. By analogy with a spherical lens, it is not difficult to guess that 1.0, as in our example, is the optical power.
The cylinder value can be minus to correct myopic (nearsighted) astigmatism and positive to correct hypermetropic (farsighted) astigmatism.
A mandatory parameter of a cylindrical lens is such an indicator as Ax (axis) - the axis of the cylinder. It is measured in degrees from 0 to 180. This is due to the characteristics of the refraction of light passing through a cylindrical lens. Rays going perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder are refracted. And axes running parallel do not change their direction. Such properties allow us to “correct” the refraction of light in the specific meridian we need.
Dp (distantio pupillorum) - the distance between the centers of the pupils in millimeters (can be indicated in brackets for each eye separately).
So, let's summarize this information and read the recipe given. Myopia correction is required for the right eye using a lens with a power of 3.0 diopters. Correction of astigmatism is also necessary using a cylindrical lens with a power of 1.0 diopter and a cylinder axis of 180 degrees. For the left eye, the correction of myopia is the same as for the right, but to correct astigmatism, a cylindrical lens with a power of 2.0 diopters and an axis of 175 degrees is required. The interpupillary distance is 68 millimeters.
There are differences in issuing prescriptions for glasses abroad. There the number of characters is minimized and the recipe looks like this: −2.00 +1.50×80
Wearing Features
So, the man turned to an ophthalmologist, and he, in turn, after conducting a series of studies, established an accurate diagnosis and determined a number of parameters that allowed him to find out what lenses the patient would need to correct the quality of vision. But lenses that are effective for both myopia and astigmatism have their own specific characteristics. So, having become the proud owner of this correction tool, it is worth remembering that putting on toric lenses is somewhat more difficult than ordinary soft ones. The fact is that they must be in the correct position on the cornea - the so-called meridians of the eye must coincide with a number of meridians of the products themselves. A lens, when put on correctly and in its intended place, will not move or interfere with the eye.
Rules for wearing lenses
Also, at first, you should not hope that wearing lenses will be possible without discomfort, especially if a correction device (at least glasses) has not been used since childhood. You will have to get used to it gradually, that is, start wearing it for a short time at first, increasing the period of wear every day. Usually addiction lasts about a week.
Contact lenses are the best option for vision correction. They are ideal for those people who do not like to wear glasses, they have a big “minus”
The main disadvantages of TCL
Most patients prefer to use CL for vision correction, as it is more convenient, effective and aesthetically pleasing than using classic glasses. However, toric lenses have a number of features that make them not suitable for everyone. Many users leave negative reviews about them and prefer, if necessary, to wear regular contact lenses, without astigmatism correction, or continue to use glasses. The main reason is the difficult and lengthy adaptation due to the thickness of the CL.
If a patient has never used contact methods of vision correction, it will be easier for him to adapt to thickened TCLs - he will not be able to compare their use with others. But if the patient previously wore soft regular CLs and then switched to TCLs, he will feel the difference and will suffer from discomfort.
So, if you decide to try toric contact lenses, you should prepare for the following possible complications and side effects:
Since toric CLs are thicker than regular ones, when worn they can cause discomfort and the sensation of a foreign body in the eye: even after several weeks, adaptation does not occur. The additional cylinder on the lens puts a strain on the visual organs; eyes in such lenses get tired faster than in regular ones
This is important for those who work at a computer all day or drive. TCLs do not allow air to pass through well, so the cornea does not receive enough oxygen. This can lead to a change in its shape, which is why ophthalmologists recommend not using TCL continuously, but removing it at night
For many patients, this wearing mode is uncomfortable. If the diopters are different on the right and left eyes, optical distortions may occur when wearing a TCL. With long-term, constant wearing of cylindrical lenses in patients, the shape of the cornea changes, which leads to the formation of keratotonus. Keratotonus is a contraindication to laser vision correction; the patient should definitely be aware of this if he plans to correct the defect using this method in the future. Since cylindrical lenses are denser, if used carelessly, it is easy to injure the surface of the eye when removing or putting on contact lenses. TCLs have a significant mechanical effect on the eyes, therefore, if the patient uses decorative cosmetics, special hypoallergenic products should be selected. This reduces the likelihood of developing irritation. Those patients who regularly use TCL are more often diagnosed with conjunctivitis, dry eye syndrome, swelling and irritation of the cornea, ulcers and erosions
This can lead to a change in its shape, which is why ophthalmologists recommend not using TCL continuously, but removing it at night. For many patients, this wearing mode is uncomfortable. If the diopters are different on the right and left eyes, optical distortions may occur when wearing a TCL. With long-term, constant wearing of cylindrical lenses in patients, the shape of the cornea changes, which leads to the formation of keratotonus. Keratotonus is a contraindication to laser vision correction; the patient should definitely be aware of this if he plans to correct the defect using this method in the future. Since cylindrical lenses are denser, if used carelessly, it is easy to injure the surface of the eye when removing or putting on contact lenses. TCLs have a significant mechanical effect on the eyes, therefore, if the patient uses decorative cosmetics, special hypoallergenic products should be selected. This reduces the likelihood of developing irritation. Those patients who regularly use TCL are more often diagnosed with conjunctivitis, dry eye syndrome, swelling and irritation of the cornea, ulcers and erosions.
In addition, there are a number of patient conditions when the use of contact lenses of this type is strictly prohibited. These include:
- contraindications to refractive correction;
- presbyopia (senile farsightedness) of any degree;
- astigmatism 6 diopters and above, myopia up to 30 diopters or farsightedness up to ten diopters.
In case of individual intolerance to conventional contact lenses, toric lenses are not prescribed.
It’s worth knowing: despite the contraindications and a rather long list of disadvantages, modern, improved TLCs have become a real salvation for many patients. People got the opportunity to continue playing their favorite sport, work and relax fully. It is absolutely not necessary for adaptation to be difficult, and for the lenses themselves to cause eye irritation. If you follow all recommendations for care and use, no side effects will occur.
Varieties
The selection process for astigmatism is complicated by the fact that conventional lenses are contraindicated for the patient. They are specially selected, since simple ones will constantly shift and distort the image. Recalculation of astigmatic lenses allows them to take the desired position, thereby attaching to the surface of the cornea. There are the following types of this optics:
- Soft. It appeared not very long ago. It looks like a film that follows the shape of the cornea. This lens is invisible to the eye and provides comfortable wearing. Due to these qualities, patients prefer this type to rigid optics.
- Tough. It consists of polymers that allow air to freely penetrate to the cornea. It maintains its shape well and is suitable for long-term wear. However, due to the rigid structure of the device, the eye takes a long time to adapt to new sensations. It has a number of contraindications for use.
Soft astigmatic lenses belong to the category of modern developments. Recently, more patients have preferred them. Unfortunately, when wearing these lenses, astigmatism will be felt more strongly due to the fact that they are thin, tightly attached to the cornea and follow all the irregularities.
In order to choose the appropriate type of optics, you need to take into account individual indicators and doctor’s advice. In some cases, it is recommended to simply try both varieties to see which one is most comfortable. Both hard and soft lenses need to be properly maintained and disinfected. Special drops are prescribed for the eyes to prevent inflammation from constantly wearing optics.
What is eye astigmatism
“Doctor, I was informed that I have eye astigmatism, but what is it? Is astigmatism treatable? Is it possible to correct it?”
These are the questions most often asked when visiting an ophthalmologist. Considering that astigmatism of the lens or cornea of the eye is a fairly common phenomenon, and a small degree of astigmatism is present in most people, in this article we are going to understand in detail what ocular astigmatism is, whether it can be treated, how to correct it, and discuss the types of astigmatism.
Astigmatism - a disease, its causes
Astigmatism is not a disease, the essence of astigmatism is an error of refraction, which can be translated from Latin as “lack of sphericity.”
Normally, the human eye, cornea and lens have a shape close to a sphere. Rays of light (images of objects) pass through the smooth, spherical cornea and lens and create a clear image of the objects in question on the retina of the eye.
If the shape of the cornea or lens is uneven, not spherical, then the light rays will not evenly hit the retina, some of the rays will not reach the retina and will form an image in front of it, and some of the rays will fall behind the retina. In such cases, circles of light scattering are formed on the retina and the image of the object in question will be unclear, blurry, doubled and distorted.
Types of astigmatism
Ocular astigmatism can be:
- simple - in combination with emetropia (emetrope - a person with good vision).
- complex myopic – in combination with myopia (myopia)
- complex hyperopic – combined with hyperopia (farsightedness)
- mixed astigmatism – in combination with myopia and hypermetropia simultaneously in different meridians
Astigmatism is congenital and acquired
Most children are born with an astigmatic cornea - this is congenital astigmatism, after a year the degree of congenital astigmatism decreases and an adult remains with a small degree of astigmatism of 0.5 - 0.75 diopters, the so-called physiological astigmatism, due to the fact that it does not cause a significant reduction sight, it is usually not noticeable. In approximately 40% of cases, congenital astigmatism will be greater than 1.0 diopters. Such astigmatism must be identified as early as possible and must be corrected with glasses or toric contact lenses to avoid complications. Read more about this in the article Astigmatism in children. Congenital astigmatism does not progress and usually remains constant throughout life.
Acquired astigmatism occurs as a result of injury to the cornea or lens, as well as after eye surgery. This type of astigmatism is difficult to correct with correction.
Astigmatism in keratoconus should be noted.
Keratoconus is a disease of the cornea of complex nature. As a rule, astigmatism in keratoconus is of a high degree and progresses, and is poorly corrected.
Degrees of astigmatism
There are three degrees:
- Weak - up to 3 diopters. occurs most often)
- Average - from 3 to 6 diopters
- High – over 6 diopters (most often with keratoconus)
Symptoms of astigmatism
The following symptoms may be signs of astigmatism. Complaints about decreased visual acuity, double vision of objects, distortion, for example, letters on a vision test table are not seen straight, but at an angle. With uncorrected astigmatism, due to the fact that the ciliary muscle contracts unevenly, there is rapid fatigue and eye strain when working close (asthenopic symptoms), and headaches may occur, which also more often appear when working at close distances (reading or computer). When looking at objects in the distance, it becomes necessary to constantly squint. The eyes are most often red and irritated.
How to select lenses
Many patients with this pathology are interested in whether it is possible to use lenses for astigmatism. Ophthalmologists answer this question positively, emphasizing the advantages of contact devices over astigmatic spectacle lenses. For this disease, special toric optics are used. It is highly accurate and suitable for people of all ages. However, in order to achieve a positive effect, you need to choose the right optics.
When selecting lenses, the ophthalmologist must take into account various nuances of a person’s lifestyle, which include:
- driving a vehicle;
- field of activity;
- presence of any kind of sport;
- degree of activity.
You may be interested in: Bates Method for Vision Restoration
The patient's activity is of great importance. If every day he has to work at a computer, putting enormous strain on his eyes, this must be taken into account when selecting and quickly recalculating the diameter of the lenses. These optical devices come in several varieties.
Advantages
An indicator of the correct selection of astigmatic lenses is the absence of discomfort during their use. Most patients see only benefits while wearing optics. The advantages of such lenses include:
If the blurriness of the picture completely disappears after using the optics, then the lenses are selected correctly.
Contraindications to wearing contact lenses
- acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the anterior segment of the eye,
- acute inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs,
- allergic diseases of the conjunctiva and ENT organs,
- abnormalities in the position of the eyelids and lacrimal apparatus,
- pterygium.
When examining, it is better to use the minimum brightness of the light so that you do not have to wait until the patient recovers from blindness.
In addition to the symptoms of dystrophic and inflammatory diseases of the ocular surface, you should pay attention to the size of the palpebral fissure, sensitivity to touch, the tone of the eyelids (a narrow palpebral fissure and increased tone of the eyelids make it difficult for the patient to select and independently use lenses), sensitivity of the cornea (the opportunity to check it will be later - in moment of lens installation; with increased sensitivity of the cornea, intolerance is possible; with decreased sensitivity, there is a high risk of corneal erosion). Children's age is not a contraindication to the use of contact lenses
If manipulating the lenses does not cause difficulties for the child or his parents, then they can be used in the same mode as for adults.
Children's age is not a contraindication to the use of contact lenses. If manipulating the lenses does not cause difficulties for the child or his parents, then they can be used in the same mode as for adults.