Waiting for the birth of a baby is not only a great joy in the family, but also a huge stress for a woman’s body. At this time, the balance of hormones, metabolism, and vision changes. Myopia is one of the problems that a woman faces during this period. If your vision was perfect, mild myopia may appear during pregnancy. Or existing myopia may become worse. There is also a possibility of developing complications. Therefore, expectant mothers need careful monitoring of eye health.
Why is myopia dangerous during pregnancy?
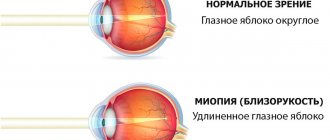
Myopia is a pathology of refraction in which distant objects appear blurry. This is due to the fact that the image of the object is projected not on the retina, but closer. Whether myopia is dangerous during pregnancy largely depends on the severity of this pathology.
Ophthalmologists distinguish three degrees of myopia:
- weak (up to 3 diopters),
- medium (3-6 diopters),
- high (more than 6 diopters).
The degree of myopia directly affects the likelihood of other pathological conditions of the organ of vision. For example, high myopia during pregnancy is fraught with complications on the retina, especially in the third trimester. Toxicosis can lead to increased myopia by up to 5 diopters. Myopia of the 3rd degree during pregnancy is also dangerous because childbirth in this situation also poses an increased risk for the retina, including its detachment, and this is a path to blindness.
But all of these risks relate mainly to severe myopia. Moderate and mild myopia during pregnancy carries significantly fewer risks, but observation by an ophthalmologist is strictly necessary for such women. The diagnosis and recommendations of the ophthalmologist must be taken into account by the doctor leading the pregnancy when choosing a method of childbirth. Of particular importance is the topic of birthright and myopia: the first birth in a woman’s life is a great stress for the body, and when choosing a method of delivery, it is necessary to take into account all health factors, including myopia.
For a specialist’s opinion on myopia during pregnancy, watch the following video:
What is myopia?
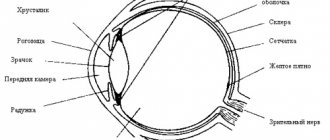
Myopia (myopia) is an eye disease in which the image is focused not on the retina, as it should be normally, but in front of it. That is, a person blurrily sees those small and large objects that are located far from him. Whereas when looking at objects located close to the eyes, there are no difficulties, they seem clear.
It is precisely because people with myopia can see everything close to them perfectly that the familiar Russian-language designation for the disease appeared - myopia.
As a result of the disease, the size and shape of the organs of vision may change, taking on a more oval and elongated shape. Due to the deformation of the eyeball, the image does not focus correctly on the retina.
With myopia, not only does visual acuity decrease (this is the most harmless symptom of all possible), in addition to this, pathologies of the retina arise, since due to the increase in the size of the organ of vision, it becomes stretched and strained.
Myopia can be congenital, hereditary, acquired and mixed. Congenital is characterized by an abnormal structure of the eyeball. It is often caused by infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy. This type cannot be cured completely, but you can at least stop the decrease in visual acuity.
The hereditary variant does not immediately manifest itself; it is usually transmitted from both parents, and not from one. In this case, only partial improvement of the condition is also possible; complete recovery remains unavailable. The acquired disease develops over the years as a result of excessive loads on the visual apparatus; it is most typical for schoolchildren and students who incorrectly distribute visual activity and do not follow a daily routine.
Myopia reduces a person’s quality of life and interferes with the full realization of the individual in society.
What complications can there be if left untreated?
Mild myopia in pregnant women is a condition that cannot be called rare. Even if the pregnant woman has had the disease before, she should contact an ophthalmologist to get practical advice.
It should be remembered that during the gestation period - carrying a child - the level of load on absolutely all systems and organs increases significantly. Already existing conditions can get worse, which also affects myopia.
Myopia, if left untreated, is quite capable of worsening and developing, its degree can become from mild to moderate, and then severe. If you let a woman with a serious illness go into labor on her own, there is a high risk of retinal detachment.
There are other dangerous conditions that are important for pregnant women to consider - these are lattice changes, retinoschisis, as well as swelling of the nerve disc, and retinal hemorrhages. All this is due to the fact that the female body will have to undergo serious tests, as well as increased stress during childbirth.
All the situations described can become complicated if a woman is diagnosed with anemia, which is not uncommon. That is why you should not neglect the doctor’s advice and skip visits to the ophthalmologist. Strict adherence to the prescribed measures allows you to preserve your vision and carry out a normal pregnancy, and then give birth to a baby.
Treatment and correction
Treatment and correction of myopia is carried out to control metabolic processes and microcirculation in the retina.
To choose a method of preventive treatment, you need to apply the following rules:
- block all retinal breaks (without a tendency to self-limit);
- block areas of lattice dystrophies in combination with retinal detachment.
The most effective and not very traumatic method of preventing detachment is laser coagulation. Timely laser coagulation minimizes the possibility of retinal detachment. Natural childbirth is possible if after laser coagulation there are no negative changes in the fundus.
It is advisable to choose argon laser coagulation, which ensures stabilization of pathological processes for a long time.
A few months after the operation (scleroplasty, laser coagulation), medication treatment begins:
- nicergoline;
- pentoxifylline;
- riboflavin;
- taurine;
- trimetazidine.
Does pregnancy affect myopia?
How does the vision of an expectant mother change and how does existing myopia behave if a woman becomes pregnant? Since serious changes occur in the body as a whole, the state of vision may also deteriorate. This is usually due to several main reasons:
- swelling of the inner lens of the eye - the lens, which because of this changes shape, and this leads to increased myopia;
- complications on the retina: retinal dystrophy, etc.;
- increase in myopia values due to exposure to toxicosis;
- risk of retinal detachment and vitreous hemorrhage during childbirth.
The above-mentioned difficulties are associated rather with high values of myopia. Myopia of 1 or 2 degrees during pregnancy is less dangerous.
Any degree of myopia requires mandatory supervision by a specialist throughout the entire pregnancy. This is necessary in order to track the possible progression of myopia and the occurrence of complications.
Causes
Myopia can be diagnosed for people of different ages, but, as a rule, it most often occurs between the ages of 7 and 12 years. After approximately 25 and up to 35 years, the condition becomes stable, myopia stops progressing. For what reasons it occurs is not fully understood scientifically.
It has long been established that myopia appears in people whose main work involves eye strain, for example, those who write or read a lot. Reasons that adversely affect visual abilities:
- insufficient amount of light;
- prolonged focusing of the gaze on closely spaced images;
- eye strain;
- uncomfortable working postures.
Scientists have found that such unnatural visual tension provokes atrophy of the muscles of accommodation (ciliary or ciliary), which is the cause of the disease.
Myopia is often inherited, which is most likely due to inherited characteristics of the eyeball:
If both parents are diagnosed with myopia, then there is a 50% chance that myopia will occur in children under 18 years of age. At the same time, if mom and dad have good vision, then the likelihood of their children developing myopia is low - up to 10%. Individuals who are genetically predisposed, if they are negligent in their eye health, will experience rapid development of the disease.
Complications
In the absence of proper treatment, myopia during pregnancy can lead to a number of serious problems, which will be expressed in the following factors:
- sharp progression of the disease against the background of acute late toxicosis;
- during the third trimester during pregnancy, complications with the retina may occur, which will begin to peel off;
- Increased eye pressure during childbirth can lead to hemorrhages, which will cause a sharp deterioration in vision.
Therefore, it is so important to pay special attention to eye health and, in case of complications, undergo the necessary course of treatment to stop the further development of the disease.
If you have problems with your vision, you should visit your doctor at least three times during pregnancy:
- 1 time - at 12-14 weeks;
- 2 times - at 32 weeks;
- 3 times - at 34 weeks.
This is necessary in order to monitor possible changes in the fundus of the eye and promptly identify unfavorable trends that may occur with it, as well as, if necessary, begin treatment.
During the last visit to the ophthalmologist immediately before childbirth, a verdict is made based on the tests and diagnostics performed, and the recommended delivery tactics are prescribed. If serious vision problems arise with unfavorable development dynamics, the doctor recommends a cesarean section, and in rare cases, prescribes the use of obstetric forceps.
Treatment of myopia during pregnancy
Pregnancy and myopia are a combination that requires mandatory follow-up by an ophthalmologist. Any visual symptoms experienced by the expectant mother should be referred to a specialist. Deterioration in the quality of vision, flickering of spots before the eyes, double vision of objects and any other unusual sensations should be described at the appointment, so that the doctor, if necessary, conducts an in-depth diagnosis and prescribes treatment appropriate for pregnancy.
Observation by an ophthalmologist
A woman usually undergoes her first examination by an ophthalmologist at the very beginning of pregnancy, when registering. The doctor records the condition of the visual organs in the medical record so that during subsequent examinations he can compare the data and draw conclusions about possible changes in the patient’s vision.
In total, during pregnancy it is necessary to undergo at least two examinations by an ophthalmologist: the second appointment is scheduled at 30-32 weeks to give recommendations on the method of delivery. The doctor will check the condition of the visual organs, evaluate the fundus, refraction and intraocular pressure. Based on the results of the study, he will write a conclusion in which he will indicate the recommended method of childbirth: natural or artificial.
Laser coagulation
The retina of the eye is most vulnerable during pregnancy and childbirth. It is her condition that the ophthalmologist especially closely monitors if the patient has myopia, since the development of dystrophy is possible. The degree of myopia is not always directly related to emerging retinal pathologies. Focal dystrophy can appear with both severe and slight myopia.
If foci of dystrophic changes in the retina are identified, laser coagulation can be prescribed: this type of correction will prevent its detachment. This eye surgery will help minimize the risk of abruption during childbirth and eliminate the need for a caesarean section delivery.
Effect on pregnancy
The risk group for visual impairment during pregnancy includes women with preeclampsia. At this time, toxicosis develops in the later stages, increasing intraocular and blood pressure. These processes contribute to impaired blood flow in the eye area, degeneration of the retina and optic nerve.
Women at risk should be periodically examined by an ophthalmologist. The definitive diagnostic test is fundus examination. The doctor periodically evaluates the condition of the retina and microcirculation vessels. If a significant or severe deviation is detected, the ophthalmologist will recommend a cesarean section.
What is myopia
Myopia, or myopia, is a visual impairment in which distant objects are seen blurry.
With normal vision, light rays passing through the eyeball are focused on the retina, and a person sees objects clearly, without distortion. With myopia, the shape of the eyeball changes, becoming elongated, which causes focusing to occur in front of the retina, and the image of distant objects appears blurry. The greater the degree of myopia, the more objects lose their clear outlines.
The disease occurs in every third person and first appears between the ages of 7 and 18 years. At an older age, the disease can progress or remain at the same level.
The causes of myopia can be:
- hereditary predisposition. It has been proven that if the mother or father has myopia, in most cases it is transmitted genetically;
- eye damage, traumatic brain injury;
- constant overwork of the visual apparatus, poor visual hygiene (prolonged work at a PC, improper lighting while reading, etc.);
- eye infections that can lead to disruption of refractive media;
- some chronic pathologies (rheumatism);
- lack of vitamins, poor nutrition;
- untimely or inadequate correction of visual impairments.
Myopia can affect bearing a child, so even with slight myopia, a woman needs to consult an ophthalmologist.
The essence of myopia
Myopia or, scientifically, myopia is one of the most common eye diseases. About 1/3 of the planet's population are its victims, and, apparently, it is not going to give up. Let's look at the essence of myopia in more detail. The physiological essence of myopia consists of changes in the shape of the eyeball and increased refraction of light rays by the eye lens and cornea.
Due to this visual specificity, the focusing of images occurs not on the retina, as it should be normally, but in front of it. It turns out that the eye seems to be “adjusted” to viewing images up close—the lens remains convex. To adjust the eye to see objects in the distance, the lens must become flat. This function does not work well for those suffering from myopia; they need to squint their eyes to see objects further than 5 meters.
How to give birth with myopia
Myopia and childbirth are compatible things, if you follow all the recommendations of specialists. A possible risk during childbirth with myopia is associated with the severity of this refractive error, as well as with its accompanying complications: pathologies of the retina, optic nerve, and lens. Depending on the combination of these factors, doctors make a conclusion about whether the patient should give birth herself or whether it is better to prescribe a cesarean section.
For a long time it was believed that childbirth with high myopia carries a risk of retinal detachment, which leads to complete blindness, so women in labor with high minus refractive values were sent for cesarean section. However, modern research shows that not everything is so simple, and high myopia does not pose a direct risk for a woman in labor: it all depends on complications.
Is it possible to give birth on your own if you are myopic?
Uncomplicated mild or moderate myopia does not impose any restrictions on the method of delivery. A more serious factor is the condition of the fundus, blood vessels, intraocular pressure. This is why a thorough examination by an ophthalmologist in the third trimester of pregnancy is so important. If no pathologies are detected, the doctor, for his part, will give the green light to natural childbirth, but with high myopia complicated by other pathologies, they may be in question.
When is a caesarean section necessary?
Childbirth with high myopia, complicated by pronounced focal degenerative changes in the retina, most often cannot be natural. The risk of detachment during pushing is too high, when intraocular pressure increases sharply. In this situation, doctors usually conclude that it is better to prescribe surgery than to risk the future mother's vision.
A direct indication for a cesarean section is a retinal detachment that has developed during pregnancy and has been operated on, and a similar operation in the patient’s history, if vision is then present in only one eye.
Caesarean section for myopia: pros and cons
It is precisely because of the danger of retinal detachment that a high degree of myopia has long been considered a contraindication to natural childbirth, and patients with such a pathology were prescribed a cesarean section. Such a conclusion was usually made during an examination by an ophthalmologist in a local clinic; a referral for surgical delivery was given based on the presence of the disease.
However, there are both pros and cons to having a caesarean section.
Among the disadvantages:
The need for anesthesia, which has side effects on the body of both mother and child:
- Significant blood loss.
- The appearance of seams.
- Formation of adhesions in the abdominal cavity.
- Long-term bed rest necessary for recovery after abdominal surgery.
- The baby, who was born very quickly, lacks adaptation to environmental conditions.
The advantages of a cesarean section include the following:
- The planned nature of the operation allows for the necessary preparation, ensuring a predictable outcome, which is especially important if the woman in labor has serious diseases, which include high myopia.
- The short period of labor - the operation takes up to half an hour - does not create stress and does not tire the woman in labor.
- The presence of anesthesia relieves pain and tension.
- Removing the baby through the incision preserves the integrity of the perineum and eliminates the possibility of deformation of the baby's head.
It is difficult to talk about which method is better: natural childbirth or caesarean section. It is necessary to understand that doctors, when prescribing a caesarean section for a woman in labor who has a high degree of myopia, care primarily about preserving the patient’s vision.
However, if in the 70s women with this disease had practically no choice and were prescribed surgical delivery via cesarean section, today the situation has changed dramatically.
What are the risks for pregnant women
How does labor affect the functioning of the visual apparatus? This question cannot be answered definitely. When deciding on the method of delivery, the gynecologist must take into account all factors that can affect the organs of vision:
- general health of the patient;
- condition of the inner lining of the eye and the fundus of the eye;
- age of the woman in labor;
- the course of pregnancy;
- stage of myopia.
However, even in this case, it is difficult to predict the course of the birth process and its consequences.
Uncomplicated pregnancy most often does not affect eye refraction. However, with natural childbirth, the likelihood of increased intracranial pressure, optic disc edema, and hemorrhage in the retinal tissue increases.
There are some pathologies that can reduce vision by 1-2 diopters. These include early toxicosis and gestosis. Retinal degeneration can also become a serious complication: changes in intraocular pressure during contractions and pushing often lead to retinal detachment.
That is why the expectant mother needs to see an ophthalmologist again immediately before giving birth: this will allow the specialist to identify dystrophic changes in the retina and fundus of the eye, and also give a recommendation for a cesarean section.
Symptoms to watch out for in pregnant women with myopia
There are many signs, the appearance of which should alert myopic expectant mothers. These include:
- rapid deterioration of distant vision (when myopia gradually changes from low to medium and then to high);
- periodic appearance of spots and “gnats” before the eyes;
- decreased clarity of object contours (images and objects become blurred and distorted);
- sharp narrowing of the visual field;
- the appearance of discomfort when wearing glasses or lenses (this signals the transition of the disease to the next stage).
If at least one of the listed symptoms occurs, you should immediately seek ophthalmological help. It is possible that such a phenomenon will require urgent visual correction.
For this purpose, special physiotherapy procedures may be prescribed, or perhaps laser correction, depending on the severity of the symptoms of the pathology.
Myopia after childbirth
Both pre-existing myopia and myopia that has appeared or intensified after childbirth requires special attention. After the baby is born, the woman needs to undergo another examination by an ophthalmologist to determine the condition of her eyes and, if necessary, prescribe or change the treatment method.
If myopia appears or worsens after pregnancy and childbirth, you need to choose a method of optical correction (glasses or contact lenses). You can also talk to your doctor about the possibility of laser vision correction to eliminate the need for optics.
It is also important to clarify the diagnosis: perhaps during pregnancy the patient developed not true, but false myopia - a spasm of accommodation. This is due to increased load on the eye muscles, which leads to their spasm and disruption of the clarity of distant objects. By relieving the spasm with the help of medications and exercises, imaginary myopia will also go away.
Rules of conduct for a pregnant woman
To prevent possible eye complications during pregnancy and childbirth, it is necessary to determine in advance the state of the pregnant woman’s visual organ.
Therefore, regardless of the type of refraction and the presence or absence of vision complaints, all pregnant women should be examined by an ophthalmologist at 10-14 weeks of pregnancy. In addition to the usual examination, it is necessary to examine the fundus after pupil dilation. If no changes are detected, a repeat control examination is carried out four weeks before the expected due date of delivery and a conclusion is given about the nature of delivery based on the condition of the eyes.
If, at the first examination, breaks and thinning of the retina are detected, they are separated as gently as possible by laser - the so-called preventive laser coagulation, in which the retina is, as it were, “welded” to the underlying choroid. In these cases, patients are observed monthly before birth, and at the last examination 4 weeks before birth, with reliable blockade of ruptures, they are given a conclusion about the possibility of independent delivery. If new retinal breaks occur, repeated laser coagulation is performed, and if retinal detachment develops, surgical intervention is performed. For swelling and hemorrhages in the retina in its central parts, decongestant, hemostatic (hemostatic) and resorption therapy is carried out.
If you experience symptoms such as flickering, light flashes, floating opacities before the eye, distortion of the shape of objects, loss of vision or its narrowing, in the form of a so-called “curtain”, which may indicate the development of complications of myopic disease, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. If changes are detected, the doctor will recommend medication, laser or surgical treatment, after which most pregnant women are allowed to give birth on their own.
Main reasons
The appearance of myopia can have various causes, but there are a number of indicators that contribute to the development of the disease:
- hereditary factor;
- constant loads on the organs of vision over a long period of time;
- metabolic failures;
- the result of incorrectly performed vision correction;
- lack of balanced nutrition.
In addition, the reason for deterioration of vision is that during pregnancy a woman is exposed to significant stress and frequent shocks, all this, together with an unbalanced diet and lack of a daily routine, can lead to problems.
Therefore, if you have any symptoms confirming a deterioration in visual acuity or if you already have myopia at the initial stage of pregnancy, you should visit an ophthalmologist so that he can prescribe special preventive measures or treatment. And it will also not be superfluous to carry out special exercises for the organs of vision or include tea from fruits and berries in the diet, in agreement with the doctor.
Effect on the fetus and future vision of the child
A woman’s body is designed in such a way that when pregnancy occurs, a placenta is formed. It is well supplied with blood, through it the necessary nutrients, trace elements and minerals are supplied. The woman’s body will be deficient in these substances, but they will be supplied to the fetus in sufficient quantities.
If a woman has hereditary myopia, the risk of developing such a disease in her child increases. Most often, such children are born with well-functioning vision. If hereditary myopia is passed on to him, it develops at school age. This is provoked by the following factors:
- increased load on the visual organs due to the large amount of time spent in lessons;
- using a computer, phone, tablet, TV at irregular times;
- the beginning of curvature of the spine, especially in the cervical region, as the child begins to sit at a desk for many hours and wears a heavy backpack.
A child develops myopia more often if both parents suffer from this disease. Therefore, he is at risk and should be periodically examined by an ophthalmologist.
Prevention of myopia in pregnant women
It is quite possible to reduce the risk of developing or increasing myopia during pregnancy. The main methods of preventing the disease in pregnant women are:
- regular ophthalmological examinations;
- visual hygiene, reducing visual stress;
- for dry cornea - use moisturizing drops prescribed by a doctor;
- attending childbirth preparation courses, where they teach how to breathe correctly and push so as not to damage the eyes;
- proper nutrition, walks in the fresh air.
Uncomplicated myopia does not interfere with natural childbirth, even if it reaches high levels. However, it is necessary to carefully ensure that the expectant mother does not develop complications associated with the condition of the retina. Therefore, at the first symptoms of visual impairment during pregnancy, it is necessary to come for an additional consultation with a specialist.
Perhaps your eyes not only need medical attention, but also require urgent attention. If everything is in order, then slight myopia does not pose any risk during natural childbirth.
Share the article on social networks so that more expectant mothers learn about myopia during pregnancy. All the best!
How is moderate, mild, and severe myopia diagnosed?
Often a woman knows about the pathological condition of her vision organs even before registering with the antenatal clinic during pregnancy. The doctor will need to assess the severity of the disease and send the patient for a vision test by an ophthalmologist. He will assess the health of the visual organs using several diagnostic techniques:
- Ophthalmoscopy is a process that will allow you to assess the condition of the retina, blood vessels, nerves, and fundus of the eye;
- Analysis of visual acuity – allows you to assess the severity of myopia;
- The study of refraction is carried out using special equipment that allows you to check the refractive ability of the living optical system of the eye;
- Ultrasound of the eyeballs is a process that will allow you to evaluate the characteristics of blood flow in the organ.
Other diagnostic methods can be used, including biomicroscopy, when a Goldmann lens is also connected to the process. The technique will allow you to find out everything about the condition of the retina, etc.
Often, one examination by an ophthalmologist is not enough to give a conclusion about the need to allow a woman to have a natural birth or to send her for a caesarean section. To obtain a final conclusion, three visits to the ophthalmologist will be required, the last of which is planned for 35–36 weeks.
Myopia symptoms
If a woman did not suffer from myopia before pregnancy, she should be aware of the nature of the manifestation of deviations in the visual apparatus. This includes:
- the appearance of regular headaches;
- the appearance of dark or bright spots before the eyes;
- unclear visualization of objects (contours blur);
- the eyes get tired even with small visual loads.
Women who suffered from myopia before pregnancy note a deterioration in the condition of the visual system. Sometimes vision can be so impaired that it is impossible to clearly visualize objects at arm's length.
Symptoms may change over time. In the first and third trimester, the symptoms are more pronounced; in the middle of pregnancy, the manifestation of myopia is reduced.
Hardware diagnostics
A pregnant woman should inform her gynecologist about all changes occurring in her body. Vision is no exception, as it can be greatly affected during gestation. The gynecologist will write a referral to an ophthalmologist for a thorough examination. Diagnostics in an ophthalmology office is nothing scary. First, the doctor will check visual acuity using tables (letters of different sizes), then conduct hardware diagnostics:
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye);
- tonometry (checking intraocular pressure);
- skiascopy (examination of pupil functionality);
- rheoophthalmography (examination of intraocular circulation);
- other types of examination.
Along the way, the doctor identifies congenital pathologies of the visual system.
Diagnosis of myopia during pregnancy
Pregnant girls are examined by highly specialized doctors at the tenth week. To analyze the condition of the pregnant woman and identify any abnormalities, a full examination is carried out, including a number of procedures.
Anamnesis
When visiting an ophthalmologist, first of all, you need to tell about all the unpleasant symptoms that you have noticed in yourself. Do not forget to report any operations you have had on your visual system (if any).
Laboratory research
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is recommended to donate blood for a general analysis and conduct a coagulogram (a mandatory procedure for all pregnant women).
Instrumental studies
Using special devices and medical equipment, the ophthalmologist performs the following procedures:
- Visometry. Visual acuity testing;
- Ophthalmoscopy. Study of the condition of the fundus;
- Skiascopy. Used to determine the functionality of the pupil when light is refracted;
- Tonometry. Measurement of intraocular pressure;
- Biomicroscopy. It is carried out using a slit lamp, the essence of the procedure is to examine the anterior segment of the eye;
- Rheoophthalmography. It is carried out to analyze the blood supply to the tissues of the organ of vision.
Also, all of the above procedures help detect congenital eye abnormalities.
Differential diagnosis
A method of examining patients that excludes pathologies that are not suitable for the symptoms that are possible in a pregnant woman. In simple words, the doctor rules out some diseases and as a result, one anomaly remains, which matches all the signs the woman has.
| For example, with myopia, the development of glaucoma or cataracts is automatically excluded. |
Indications for consultation with other specialists
If a pregnant woman’s health worsens, it is recommended to visit a specialized doctor. After all, even a minor disruption in the functioning of the body negatively affects the development of the fetus. During examination, in addition to myopia, a woman may be diagnosed with increased blood sugar levels or problems with the vascular system.
Diagnostics
The baby's eyes are initially examined in the maternity hospital. Such an examination allows you to establish the fact of gross congenital malformations of the visual organs, such as glaucoma. But it is not possible to establish a predisposition to myopia or its very fact at this first examination.
Myopia, if it is not associated with congenital defects of the visual analyzer, is characterized by gradual development, and therefore it is so important to show the child to an ophthalmologist within the allotted time frame. Scheduled visits should be carried out every month, every six months and every year.
Premature babies are recommended to visit an ophthalmologist at 3 months.
Visual and test inspection
Diagnosis begins with an external examination. In both infants and older children, the doctor evaluates the position and size parameters of the eyeballs and their shape. After this, the doctor establishes the baby’s ability to carefully monitor a fixed and moving object, fix his gaze on a bright toy, gradually moving away from the toddler, and assessing at what distance the baby ceases to perceive the toy.
For children from one and a half years old, use the Orlova table. There are no letters in it that a preschool child does not yet know, and there are no complex images. It consists of familiar and simple symbols - an elephant, a horse, a duck, a car, an airplane, a mushroom, and an asterisk.
Normal vision is considered if the child sees the pictures in the tenth line from the top from a distance of 5 meters. A decrease in this distance may indicate myopia. The shorter the distance from the child’s eyes to the sheet of paper at which he sees and names the pictures, the stronger and more pronounced the myopia.
You can check your vision using Orlova’s table at home; to do this, just print it out on an A4 sheet of paper and hang it at the baby’s eye level in a room with good lighting. Before conducting testing or going to an appointment with an ophthalmologist, you should definitely show your child this table and tell him the names of all the objects depicted on it, so that the child can easily name in words what he sees.
He will carefully examine the condition of the cornea and anterior chamber of the eyeball, as well as the lens, vitreous body, and fundus. Many forms of myopia are characterized by certain visual changes in the anatomy of the eye; the doctor will definitely notice them.
Separately, it is necessary to say about. Myopia is often accompanied by such a clearly visible pathology as divergent strabismus. A slight strabismus may be a variant of the physiological norm in young children, but if the symptoms have not gone away by six months, the child should definitely be examined by an eye doctor for myopia.
Samples and ultrasound
Skiascopy or shadow test is carried out using the main instrument of the ophthalmologist - the ophthalmoscope. The doctor is placed at a distance of one meter from the small patient and, using a device, illuminates his pupil with a red beam. As the ophthalmoscope moves, a shadow appears on the pupil illuminated by red light. By examining lenses with different optical properties, the doctor accurately determines the presence, nature and severity of myopia.
Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) allows you to take all the necessary measurements - the length of the eyeball, anteroposterior size, and also determine whether there are retinal detachments and other complicating pathologies.
Cases in which myopia can affect a woman’s pregnancy
To find the relationship between a woman's vision and pregnancy, it is not necessary to involve any additional equipment to detect the connection. During pregnancy, a woman’s body begins to rebuild and prepare for further childbirth, as well as for the lactation period.
It is quite natural that restructuring for bearing a fetus is nothing more than stress for the body. Therefore, some organs begin to undergo changes, and vision is no exception.
At the very first examination of a pregnant woman, a specialist in the field of gynecology collects data on absolutely all the diseases that the expectant mother has suffered.
However, if a vision problem previously arose and was successfully eliminated, this does not mean that this pathology can no longer develop. Myopia can occur during pregnancy in women due to prolonged wearing of incorrectly fitted or uncomfortable contact lenses.
Myopia can cause the following complications in a woman:
- Myopia can aggravate myopia in a pregnant woman due to swelling of the lens of the eye, as a result of which it can become deformed.
- Complications associated with the retina of the eyeball (usually can occur in the final stages of pregnancy).
- Retinal detachment during childbirth. As a rule, this leads to hemorrhage into the glassy tissue of the eye, which can lead to significant deterioration or complete loss of vision.
Based on this information, a woman with myopia during pregnancy needs to constantly monitor the condition of her body and listen to the advice of experienced doctors.
Experts in the field of ophthalmology classify 3 degrees of pathology such as myopia:
- Up to three diopters (usually does not in any way affect the course of labor and childbearing of a pregnant woman).
- From three to six diopters (during pregnancy, a woman with myopia needs constant examination by a qualified ophthalmologist).
- More than six diopters (considered the most dangerous degree of myopia, therefore the decision on whether to give birth to a child naturally or through a special operation is made at a consultation of doctors).
Even if a pregnant woman with such a high-grade disease constantly consults a highly qualified ophthalmologist, she should in any case undergo a thorough diagnosis.
In addition, after the examination, it is advisable for her to register.
This is necessary so that if any complications arise that can provoke high myopia associated with this disease, experienced specialists can quickly take certain measures to prevent the development of this pathology.
It is necessary to start monitoring especially closely for moderate myopia from 25-30 weeks from the moment of pregnancy.
Moderate myopia during pregnancy does not pose a particular threat to a woman’s body. However, when diagnosed with a moderate disease, a woman should undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist.
This measure is necessary in order to timely diagnose the progression of the disease and the deterioration of the woman’s condition.
With a higher degree of pathology, specialists may resort to additional treatment or artificial birth.
How does pathology affect the way childbirth is managed?
Pathology affects the process of labor and can lead to complications. The method of labor management depends on its presence.
Is it possible to give birth through natural means?
With a mild degree of the disease, ophthalmologists do not give contraindications for natural childbirth, since the internal structures of the eye are minimally changed. A woman will be able to give birth on her own without any problems. A healed retinal tear or laser vision correction performed before pregnancy are not considered an obstacle to natural childbirth.
With an average degree of pathology, the situation becomes more complicated. When myopia does not progress, natural childbirth is allowed. During the entire pregnancy, the expectant mother will have to visit the ophthalmologist at least 3 times to identify all possible risks.
Reference. If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with moderate or severe myopia, and there is also a threat of retinal detachment, then a caesarean section is recommended. Natural childbirth significantly increases the load on the body and the visual apparatus in particular. There are high risks of serious injury or even blindness. Under such circumstances, doctors recommend a caesarean section.
Pregnant women with visual impairments especially need to take courses in preparation for childbirth. You can learn to breathe properly and relax between contractions. If you push incorrectly, it will only make your eye problems worse. Severe tension contributes to retinal detachment. With competent behavior during labor, the load on the visual organs is significantly reduced, and the risk of vascular injury is reduced.
Useful video
Myopia and pregnancy, what are the consequences?
Indications for surgical delivery
There are a number of indications for surgical intervention during childbirth:
- myopia progresses (i.e. visual acuity worsens by at least 2 diopters per year);
- moderate or high degree of pathology, accompanied by significant changes in the fundus;
- the retina of the eye is torn during pregnancy;
- severe degenerative changes occur in the retina;
- retinal detachment was operated on (it does not matter at what point in life the operation was performed, even if long before pregnancy; the sutures and scars made may come apart);
- they did scleroplasty and keratotomy (also does not depend on the time of the intervention);
- a combination of visual impairment with diabetes mellitus (it leads to impaired blood circulation and hemorrhages in the retina, which can cause it to detach during natural childbirth).