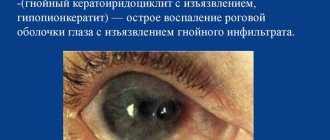
Perforation of the cornea occurs as a result of infection of the eye or its perforation during injury, burn or surgery. In this case, the patient experiences lacrimation, photophobia, pain in the eye and head, and the general well-being is significantly impaired. Pathology can be identified using ophthalmoscopy based on the presence of a characteristic clinical picture of eye damage in the patient.
Treatment of ulceration consists of eliminating the cause that provoked the pathology.
Recurrent corneal erosion
Recurrent corneal erosion is distinguished by the fact that its symptoms constantly return even with adequate therapy.
This disease can be diffuse and local. With repeated disease, scar areas appear on the cornea. Almost no light passes through them. As a result, a person’s vision drops sharply. Without treatment, erosions turn into ulcers. Unlike erosions, they affect the deep layers of the eye.
In severe cases of recurrent ulcers, erosions reach the anterior chamber of the eye. They are also the source of primary infection. If urgent measures are not taken, such a disease ends in blindness.
Complications
Severe inflammation can cause deep damage. They leave marks on the cornea. This may lead to the development of a cataract or stain. They can be distinguished based on the degree of damage. This affects the decrease in visual acuity. An ophthalmologist may see the spots during a routine examination. If they are present, vision deteriorates significantly. Therefore, it is important to start timely treatment. Severe chemical burns can also cause retinal detachment. In such cases, it is important to provide the victim with first aid in a timely manner.
Structure of the cornea
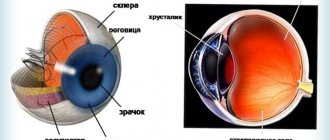
Corneal erosion is a condition in which the integrity of the outer epithelial layer of the eye is destroyed. Most often this occurs due to mechanical damage. The cornea consists of 5 separate layers:
- Epithelial is the surface protective layer of the cornea, which performs a protective function. It may recover on its own after some time. The epithelium on the cornea is responsible for the penetration of oxygen, as well as the control of the secreted tear fluid.
- Bowman's membrane is a layer that is responsible for protecting and nourishing the cornea. The anterior part of this shell is as smooth as possible, and the posterior part is ribbed, designed to smooth out the irregularities of the stroma. It is due to this that the cornea becomes transparent. Bowman's membrane is not able to regenerate, and opacities and scars may form on it. Over time, the cornea becomes cloudy and numerous abnormalities develop.
- The stroma is the part of the cornea that occupies 90% of this membrane. It consists of collagen plastics located horizontally to each other. The stroma contains cells that accelerate the regeneration process.
- Descemet's membrane is a thin plate located between the stroma and the endothelium. This layer accumulates collagen and glycoprotein, which maintain the transparency of the cornea.
- The endothelium is the deep layer of the cornea, the main activity of which is the outflow of excess fluid. This preserves the natural structure of the cornea and prevents the appearance of swelling. The endothelium is also responsible for the regeneration process and nutrition of the cornea.
Benefits and harms of home treatment
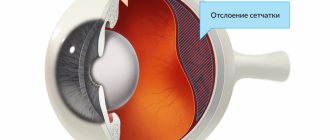
Sometimes patients may experience some improvement in their condition after sleep. If in the evening they tried to do any treatment at home - drop drops, rinse with tea, make compresses - they may mistakenly attribute the improvement to folk remedies. In fact, everything is simpler: in a horizontal position, the detached retina fits back, and the symptoms may partially go away or weaken. After the person gets up, the detached shell moves again.
Therefore, there is no benefit from poultices, compresses, drops and rinses. Retinal detachment cannot be treated not only with folk remedies, but also with medication: there is no way to stick the detached membrane back using medicinal methods. The only way to effectively treat is timely surgery.
But the harm from self-treatment is obvious: the process of retinal detachment progresses quite quickly. The longer you wait to see an ophthalmologist, making compresses and poultices, the more severe the damage to the retina. The photosensitive cells - rods and cones - that make up the retina begin to die over time. This process is irreversible - the doctor will not be able to revive the cells.
Therefore, the sooner you contact a specialist after detecting symptoms, the less destructive the consequences for the eye.
Causes of corneal erosion
Erosion of the cornea of the eye develops as a result of infection and the addition of traumatic factors. Causes of infectious corneal erosion:
- herpesvirus infection;
- fungal infection;
- chlamydia;
- bacterial conjunctivitis, which is provoked by different types of microorganisms.
Non-infectious eye lesions are possible due to decreased immune defense or exposure to a traumatic factor. The causes of non-infectious damage to the cornea of the eye are:
- improper dressing and wearing of lenses;
- xerophthalmia;
- ingress of foreign objects, chemical reagents;
- consequences of unsuccessful surgical interventions;
- injuries;
- influence of high temperature and ultraviolet radiation.
Erosion of the cornea of the eye sometimes accompanies the following diseases:
- atopic dermatitis;
- rheumatoid joint damage;
- diabetes;
- neoplasms;
- demodicosis;
- pathologies that lead to disruption of normal eyelash growth.
The risk group includes people who work with chemicals or whose activities involve exposure to hazardous factors. The main symptoms of recurrent corneal erosion:
- severe burning sensation;
- increased secretion of tear fluid;
- redness.
Causes
Causes of corneal erosion:
- Mechanical injuries, for example, when hit by a foreign object or impact.
- Adverse effects of chemicals. This can be household products and harmful production factors.
- Damage due to thermal effects. Welding burns often result in more severe damage to the outer layer of the cornea.
- Accompanying illnesses. Diseases of the eye apparatus can provoke damage of this nature. In this case, an additional inflammatory process often occurs.
- Incorrect eyelash growth. This phenomenon is quite rare, but sometimes the upper or lower eyelashes can “roll” inward, causing discomfort and injury to the eye.
Damage can be caused by poor hygiene or improper care of contact lenses. In addition to external damage, an inflammatory process also develops.
The outer shell no longer keeps the inner part from getting infected, which can lead to infection of the entire eye apparatus.
Prevention
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Strengthening the body's defenses.
- Timely contact an ophthalmologist if you receive an eye injury or develop inflammatory processes.
- Regular treatment for chronic diseases, endocrine pathologies, metabolic disorders.
- Compliance with all medical recommendations when treating with ophthalmic agents.
- Use of protective equipment (masks, goggles) in professional activities and when working at home to reduce the risk of traumatic eye injury.
Romanovskaya Tatyana Vladimirovna
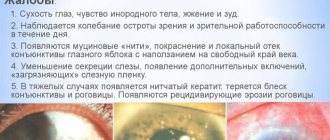
Symptoms of corneal erosion
Clinical symptoms of corneal erosion are specific. Sometimes a diagnosis can be made after an initial examination of a person. The main sign of pathology is extremely acute, sometimes unbearable pain in the eyes. It is similar to the one that occurs due to a foreign object entering the eye.
A few days after the onset of erosion of the cornea, copious discharge of tear fluid appears. The patient's eyelids swell. In the vast majority of cases, blepharospasm occurs: the patient cannot open his eyes and blink them. Erosion of infectious origin is characterized by the appearance of additional signs:
- redness, swelling of the mucous membranes of the eye;
- discharge of a large amount of pus;
- photophobia when trying to look at a bright light source;
- decreased visual acuity (if microbes begin to infect the central part of the cornea).
Corneal dystrophies
- congenital (primary)
- acquired (secondary)
Congenital (primary) dystrophies are hereditary in nature, most often appear in early childhood and have a progressive course and can be caused, including by disorders during pregnancy.
Acquired (secondary) dystrophies can develop as a result of: collagenosis, congenital glaucoma, progression of keratoconus, vitamin deficiency, burns of the conjunctiva and sclera, insufficiency of tear fluid, etc.
Types and classification of retinal erosion
There are 2 types of the disease. Ophthalmologists distinguish:
Traumatic appearance
- Traumatic erosion.
- And recurrent.
Traumatic – damage to the epithelium
Traumatic – occurs as a result of external influence. That is, a foreign body got into the eye, there was contact with chemical reagents, exposure to high temperatures, etc. In this case, the damage does not affect the deep layers of the cornea of the eye. Only the epithelium is damaged.
You can check your visual acuity at home using this link.
Recurrent
Recurrent erosion also occurs due to damage, but only in this case the deeper layers of the cornea are damaged. If during the exposure process the basement membrane (the layer of the cornea that supports epithelial cells) was affected, then the disease will become recurrent.
Since the basement membrane is a denser layer of cells, changes in its structure will lead to damage to the epithelium - as a result, relapse of erosion.
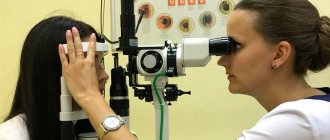
Diagnosis of pathology and its classification takes place during an ophthalmological examination using a slit lamp. But if the areas of erosion are not common and it is difficult for the doctor to determine their location, then medical dyes are used.
With their help, the ophthalmologist “stains” the cornea, which makes it possible to detect even minor damage to the surface of the epithelium.
These manipulations are usually sufficient to differentiate the disease. But in some cases, an ultrasound of the eyeball is performed.
For diagnosis, corneal keratotopography is also prescribed, which is described in detail here.
Classification of corneal ulcers
Based on the depth of the lesion and the nature of the course, corneal ulcers are divided into perforated and non-perforated, superficial and deep, chronic and acute. Depending on the location of the ulcerative defect, central, paracentral and marginal (peripheral) forms of the disease are distinguished.
To classify a corneal ulcer, it is important to take into account the direction of the spread of the pathological process.
So, if an ulcer grows towards one of the edges and epithelializes on the opposite side, then it is called creeping. Usually, not only the superficial, but also the deeper layers of the cornea, up to the iris, are affected, which leads to the formation of hypopyon. The causative agents of creeping ulcers are most often Pseudomonas aeruginosa, diplococci or pneumococci.
There is also a corrosive ulcer of the cornea. Its etiology, that is, the causes of its occurrence, is currently unknown. With this course of the disease, several defects are formed simultaneously on the cornea, located along its edges. They increase in size and merge with each other to form a single ulcer, shaped like a crescent. Healing is accompanied by scar formation.
Diagnosis of corneal erosion
The diagnosis of corneal erosion is made by a thorough examination of the eye. External examination and assessment of the surface of the cornea is carried out using a slit lamp. This technique allows you to detect an area of irregularities in the endothelium of the cornea. Small foci appear after staining with fluorescein. He visualizes even the smallest flaws well.
It is necessary to study the nature of eyelash growth on the eyelids. The doctor examines the eyelash line and the inner surfaces of the eyelids. Here, abnormal growth zones of individual eyelashes may appear, which are directed towards the eyeball. This anomaly leads to inflammation of the eyeball and erosion of the cornea.
Features of keratoplasty
Keratoplasty is a cornea transplant. This procedure is recommended for patients in the following cases:
- with impaired transparency of the stratum corneum;
- if astigmatism is diagnosed;
- for various injuries, keratitis, acute keratoconus;
- to strengthen retinal tissue.
Keratoplasty is divided into 2 types:
- Layered
. It is prescribed for superficial opacities. The upper part is cut off and donor tissue is transplanted. The lower layers are preserved and are not touched. - Through
. Consists of excision and replacement of all layers. Excision can be partial - when the area does not exceed 4 mm, subtotal - when the size is more than 5 mm, and also be a total operation on the entire cornea.
Treatment of corneal erosion
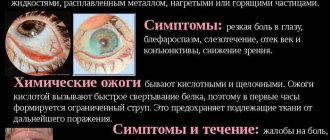
When the first signs of damage to the cornea appear, first aid measures should be provided:
- You should rinse your eyes with saline solution. If not, boiled water will do. Rinsing should be done carefully so as not to damage the eyes.
- Cool compresses can relieve swelling and reduce pain. Procedures should be done several times a day until the unpleasant symptoms disappear.
- Using artificial tears, you can disinfect the surface of the cornea and restore its normal moisture. At the same time, the intensity of unpleasant sensations is significantly reduced.
In order for the affected cornea to heal as quickly as possible, the doctor prescribes keratoprotectors. These are medicinal substances that not only restore the integrity of the cornea, but also strengthen it and prevent relapses. The most commonly used means are:
- Kerakol.
It accelerates the healing of the epithelium, strengthens blood vessels and maintains the transparency of the cornea. - Dacrolux
or hypromellose softens and moisturizes the surface of the organ of vision, improves its refractive ability. The medicine quickly and effectively relieves signs of inflammation of the conjunctiva. - Visitil
forms a protective film on the surface of the eye and prevents it from drying out. The drug prevents swelling of the cornea.
It is imperative to use medications to moisturize the cornea of the eye:
- Corneocomfort;
- View-dresser;
- Visine;
- Biosoft Active;
- Oksial;
- Renu MultiPlus;
- Lacrisin.
Thanks to these funds, it is possible to moisturize the cornea of the eye and get rid of unpleasant sensations - irritation, pain and stinging. These medications need to be used for as long as it takes to restore moisture to the membranes of the eye.
For the purpose of prevention, the eye doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs of the tetracycline or cephalosporin series. Thanks to the use of antibacterial drugs, it is possible to suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms developing in the eye. Such drugs should be used only as prescribed by a doctor and only in the recommended concentration. Self-use of antibiotics can cause damage to the organ of vision.
If drug treatment for corneal erosion does not bring results, the doctor prescribes surgery. In the process of keratoplasty, the affected epithelium is removed using modern laser technologies.
You should not rely on traditional methods of getting rid of clouding of the cornea. They do not replace medication, much less surgical treatment. However, they complement well the treatment prescribed by the doctor and serve as a preventive measure against a decrease in visual acuity. Here are a few folk recipes for treating clouding of the cornea:
- Pour a tablespoon of eyebright herb with a glass of boiling water and use it as a compress.
- In the same way, prepare an infusion of chamomile flowers. Use it for eye baths.
- Twice a day it is necessary to lubricate the sore eye with sea buckthorn or hemp oil.
- Bagged tea can be used as a lotion.
General information
The eyes are the most important human organ, providing up to 90% of information coming from the outside world. Impaired visual perception significantly complicates a person’s life, making him, in fact, disabled. Today, there is a clear trend of rapid deterioration of vision in people of different ages and social groups. The rapid development of technology and the expansion of visual information carriers (television, laptops, tablets, smartphones, computer games, etc.) significantly increase the load on the organ of vision and largely contribute to its impairment.
The most common are refractive errors of the eye (defined as eye refraction - a group of diseases that appear as a decrease in visual acuity, caused by a disruption in the process of focusing the incoming image on the retina). Types of refractive error (i.e., refractive error in the optical system of the eye) are represented by myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia.
Along with refractive errors, there are many other eye diseases: diseases of the conjunctiva, sclera, cornea, retina, lens, iris, vitreous body, optic nerve, oculomotor system, which limit a person’s ability to see. Let's consider just one of them - destruction of the vitreous body and especially, why is destruction of the vitreous body of the eye dangerous?
Destruction of the vitreous body is a pathological process manifested by disturbances in its structure, caused by thickening of individual fibers and changes in the chemical/physical characteristics of the colloidal gel of the vitreous body with loss of its transparency (turbidity).
First of all, what is the vitreous? The vitreous body (VH) is an avascular transparent gelatinous (gel-like) formation that occupies most of the volume of the eyeball. The vitreous body, due to its inherent transparency, is the main light-refracting medium of the eye, ensuring the passage of light rays to the retina. It is the constancy of the chemical composition of the vitreous body and the absence of any inclusions that ensures its transparency and the implementation of its optical function.
The mass of the vitreous body varies within 4 g, and the volume is 4 ml. The gel-like substance consists of a fibrous framework and a substance of loose consistency that fills the gaps, including whey proteins, ascorbic/hyaluronic acids, salts and other components and is supported by a framework of protein fibrils (fibers) arranged in layers. There are three types of fibers: precollagen fibers, glial fibers and gel fibers. The vitreous is bounded anteriorly by the lens, ciliary body/fibers of the ligament of zinn, and the retina peripherally and posteriorly (Figure below).
The absolute transparency of the vitreous body is achieved due to the special structure and composition of the molecules that form it. Due to various reasons and the influence of unfavorable factors, these even layers of fibrils first begin to mix with each other, and then stick together with the appearance of floating threads in the field (filamentous destruction). In unfavorable situations, the resulting threads can stick together, forming floating and coarser film formations (film destruction).
As one reaches old age, a qualitative change occurs in the volume and structure of the vitreous body, due to the release of cholesterol, calcium salts, phosphate/carbon dioxide salts of calcium, and magnesium into it. Such inclusions resemble grains (granular destruction), which in most cases is barely noticeable by the patient and cannot be treated. The most often destructive processes of ST are observed in the central sections of the colloidal gel.
Treatment
Treatment of corneal erosion is based on two principles:
- restoration of epithelium;
- moisturizing its surface.
Medicines
During treatment, doctors usually prescribe the following drugs:
- Keratoprotectors: ointments (at night) and drops (during the day).
- Antibacterial drugs in the form of gels and drops (so that another infection does not occur).
- Antihistamines and hormonal drugs.
- Medicines aimed at improving metabolic processes.
- Preparations based on natural tears for the prevention of relapses.
The treatment process takes from five to fifteen days, depending on the extent of the lesion.
How to provide first aid?
Since the main cause of erosion is the entry of a foreign body into the eye, you need to know how to give yourself first aid. If there is no possibility of urgent medical assistance, the patient must:
- Rinse the eye with plenty of saline, saline, or clean water. For rinsing, you can make a bath or use a glass.
- Blink your eyes several times to remove any remaining foreign body.
In this case, it is absolutely forbidden to:
- Rub your eye with your hand.
- Try to independently remove a large foreign body that prevents the eye from closing.
- Touch the eyeball with any objects (tweezers, cotton swab, corner of a handkerchief).
- Carry out treatment yourself.
Eye medications should only be prescribed by your doctor. Even saline drops have their contraindications: for some eye diseases this drug cannot be used.
If epithelial healing does not occur, the patient will require the assistance of an eye surgeon. Keratoplasty involves removing the corneal epithelium using an excimer laser and targeting Bowman's membrane.
Complications
If any eye damage occurs, consult a doctor immediately. Undiagnosed corneal erosion can lead to serious vision problems.
Erosion is often accompanied by a complication such as corneal neovascularization. It can occur due to infection of the eyes, which often accompanies erosion, as well as due to improper or uncontrolled use of contact lenses.
Which daily lenses are considered the best, read this link.
If treatment is not started on time, destructive processes are almost impossible to stop.
Neovascularization of the cornea is accompanied by pathological proliferation of its vessels. A person’s vision deteriorates and visual interference appears. In the initial stages, the complication can be stopped if keroplastic therapy is effectively carried out, which can prevent corneal opacification . The severity of damage to the eyeball is not immediately visible. It is almost impossible to predict in the first days what the outcome will be. Sometimes a corneal transplant is required.
In case of such a complication, the most effective treatment for corneal erosion is keratoplasty. Cloudiness of the cornea caused by erosion contributes to poor vision. This pathology is divided by size and intensity into spots, cataracts and clouds. Clouds are gray clouds that have limitations. They are barely visible upon inspection.
Cloudiness of the cornea that occurs due to erosion can cause loss of vision if not treated in a timely manner. In such cases, you need to act immediately. And the only solution is keratoplasty - corneal transplantation. This surgical operation involves replacing a damaged area of the cornea with a donor one. This treatment method helps restore damage and improve vision. If corneal clouding is caused by an infection or chemical burn, then a transplant will help stop the process of vision loss.
The causes of such a disease as night blindness in humans will be explained in this material.
Prevention
Corneal erosion can be avoided by maintaining eye safety at all times. Prevention is the best way to prevent any disease. If a person wants to preserve his vision, he must avoid any eye injuries when working with chemicals and strictly follow safety precautions.
It is also worth learning in detail about retinal detachment.
To prevent secondary inflammation, antibacterial drugs are used topically: chloramphenicol 0.25% and sodium sulfacyl 10-20%.
After restoration of the corneal epithelium, drops based on natural tears are prescribed for a long time to prevent the occurrence of recurrent corneal erosion.
Optic nerve atrophy can lead to blindness. So, recognize the symptoms and treat this disease promptly. How mild myopia is expressed is indicated in this article.
Causes of strabismus in children: https://eyesdocs.ru/zabolevaniya/kosoglazie/detej-pochemu-voznikaet-i-kakim-obrazom-lechitsya.html
Treatment options
To stop the destruction of the cornea, the doctor uses brilliant green.
To prevent the defect from spreading on the cornea, it must be treated with a brilliant green solution, as well as diathermo- and laser coagulation. It is also recommended to rinse the nasolacrimal canal. When sowing an infection of bacterial origin, the use of antibacterial drugs is recommended, and for fungal infection, fungicidal agents are used. Also shown are eye drops with a mydriatic effect, agents that improve the metabolism of the tissues of the visual analyzer.
To relieve inflammation, anti-inflammatory, antihistamine, antiallergic, and immunomodulatory drugs are used. Local antihypertensive drops will help reduce pain in the visual analyzer. Physiotherapy methods in the form of magnetic therapy, phonophoresis, electrophoresis and eyeball massage will be useful. In severe cases, surgical intervention is performed with keratoplasty using a laser. Excimer laser resurfacing of superficial corneal scars will help improve vision after the defect has healed.
Without proper treatment, corneal perforations can cause complete loss of vision.
Complications of corneal erosion
Untimely treatment of corneal erosion or a complete lack of treatment measures leads to dangerous complications. One of them is corneal neovascularization. In this case, capillary vessels grow into the cornea. Because of this, the patient's vision deteriorates sharply. Vascularization of the cornea can be quickly corrected if keratoplasty is performed effectively. This surgical intervention prevents clouding of the cornea.
Another, no less dangerous complication of corneal erosion is its clouding. It goes through several stages in its development:
- "Cloud". A slight cloudiness is visible, which is detected only after instrumental examination.
- The stain is clearly visible without the use of special diagnostic instruments. Significant damage to visual acuity becomes noticeable.
- When a cataract develops, the outer shell of the eye is completely or partially matte. Sometimes it can resemble porcelain.
With timely treatment, the prognosis for erosive lesions of the cornea is favorable. It worsens when there is an ulcer in this part of the organ of vision. With an uncomplicated form of the disease, a person recovers in about three to four days.
All about thinning of the cornea and its deformation
The term keratoconus is a combination of two words, “kerato” and “konos,” which are Greek for “cornea” and “cone.” The name of the pathology best characterizes its essence. Keratoconus of the eye is characterized by thinning of the cornea and its deformation. Let's look at why this happens.
Keratoconus: the main causes of the disease
The nature of this disease is directly related to the fact that the fibers that form the structure of the cornea gradually lose their strength. As a result, the cornea protrudes forward and takes on a cone shape under the influence of intraocular pressure. The exact causes of a disease such as keratoconus have not been studied. Many experts believe that the problem is associated with a violation of the mechanical properties of the underlying substance of the cornea. Presumably, several factors contribute to this: disruption of the endocrine system, viral infections (including hepatitis B), corneal injuries, genetic predisposition, allergic reactions, constant stress, as well as adverse environmental influences (bad ecology). Each of them can serve as a kind of trigger for the start of the development of pathology.
The cornea of a healthy eye has a spherical shape, which allows for correct refraction and precise focusing of rays. With keratoconus, due to structural changes, it gradually takes on a cone-shaped appearance. This causes distortion of the rays, inaccurate focusing and blurred vision. As a rule, the disease develops in both eyes at once. It usually occurs in adolescence and middle age (up to 30 years).
Keratoconus is a degenerative, non-inflammatory eye disease. It is characterized by slow progression - the change in the shape of the cornea occurs in stages, over several years. However, in some cases, patients experience a fairly rapid deterioration in their condition, so it is necessary to state the individual characteristics of the course of the disease in each specific case.
Why does keratoconus disease occur?
There are several reasons, including:
• genetic predisposition; • disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system; • viral infections (eg hepatitis B); • allergic reactions; • constant stress; • adverse environmental impacts.
Many experts argue that one of the most significant factors influencing the appearance of this pathology is genetic predisposition. Therefore, people whose relatives have been diagnosed with keratoconus are at a certain risk group. They need to visit the ophthalmologist regularly, starting in early childhood. In the last decade, ophthalmologists have noted an increase in cases of the disease, which is associated with deteriorating environmental conditions.
Keratoconus: main symptoms
At the initial stage of the disease, its symptoms are practically no different from the signs of myopia, farsightedness or astigmatism. The patient complains of blurred vision; he sees objects unclearly, blurred and, in some cases, distorted. This is due to the fact that at different points of the shell, light rays are refracted unevenly due to its cone-shaped shape. The main difference is that this progressive corneal disease cannot be corrected with glasses or soft contact lenses. In some cases, in the early stages, keratoconus is mistaken for other refractive errors due to similar symptoms. Only a qualified ophthalmologist can reliably identify the cause of visual impairment when conducting a thorough examination of the visual system using modern diagnostic equipment.
Over time, as the deformity increases, the patient experiences various phantom images. Ophthalmologists characterize this phenomenon as monocular polyopia. This effect is most often observed when the patient looks at objects with high contrast for a long time, for example, while looking at dark dots on a light background. Instead of one point, a person observes a picture with various chaotic images. In the evening and at night, halos and glare may appear, which causes discomfort. In the final stages, the pathology of the eye with keratoconus becomes visually noticeable: a cone-shaped protrusion of the cornea is formed.
Keratoconus of the cornea: main signs:
• impaired vision clarity (similar to myopia and farsightedness); • distorted image perception (similar to astigmatism); • ineffectiveness of using standard optical aids (glasses and soft contact lenses); • progressive decrease in visual acuity; • glare and halos in the evening; • photophobia and double vision; • phantom images when looking at contrasting objects for a long time; • cone-shaped protrusion of the cornea, visible to the naked eye (in the final stages).
Why is the eye disease keratoconus dangerous?
This disease is non-inflammatory in nature, but it is extremely dangerous. In the last stages of keratoconus, there is a progression of thinning of the cornea, up to its rupture. This is accompanied by severe pain and complete loss of vision. If the disease is not diagnosed in a timely manner and urgent measures are not taken to treat it, powerful pathological processes in the body will inevitably start, which will lead to serious and sometimes irreversible disorders of the visual system.
Only competent and timely treatment can stop this process.
What can this disease lead to if left untreated:
• Hydrocele of the cornea. • Corneal rupture • Complete loss of vision without the possibility of recovery.
Keratoconus: what are the stages?
Currently, there are various classifications of this disease, but the most popular among ophthalmologists is the M. Amsler method. It is based on ophthalmometric changes in the cornea from the point of view of the biomicroscopy picture.
According to this classification, there are 4 stages of keratoconus:
• First. The minimum radius of curvature of the cornea is more than 7.2 mm, and visual acuity ranges from 0.1 to 0.5. There is the possibility of correction using cylindrical glasses. • Second: The minimum radius of curvature decreases to 7.19-7.1 mm, and visual acuity ranges from 0.1-0.4. The disease at this stage can also be corrected with the help of astigmatic (cylindrical) glasses. There may be an initial manifestation of corneal thinning. • Third: visual acuity ranges from 0.02-0.12, and the radius of curvature of the cornea decreases to 7.09-7.0 mm. There is a noticeable protrusion of the membrane and its thinning. Opacities in Bowman's membrane are also possible. Correction is made exclusively with hard lenses. • Fourth. At this stage, opacities of the corneal stroma and lesions of Descemet's membrane are observed. In this case, the radius of curvature is no more than 6.9 mm, and visual acuity ranges from 0.01-0.02, but can no longer be corrected.
Also, in some cases, a different classification of keratoconus disease is used. Thus, there are anterior (true), acute and posterior types of pathology. In the first case, pathological processes occurring in Bowman's membrane are observed. The acute form of the disease, also known as hydrops of the cornea, is accompanied by the entry of intraocular moisture into the inner layers of the cornea, which is associated with a change in its barrier function due to damage to the Descemet membrane. Posterior keratoconus is caused by abnormalities of the mesoderm. It is characterized by a centrally formed thinning, sometimes presented in the shape of a saucer.
How is eye disease such as keratoconus treated?
In the early stages of the disease, distortion of objects can be eliminated using cylindrical glasses. As the disease progresses, patients are advised to constantly wear contact lenses to improve clarity of vision. The selection of these optical products is strictly individual, since there is no single design suitable for all types and stages of keratoconus. The use of soft means of contact correction is limited, since they adapt to the distorted shape of the corneal surface and are therefore ineffective. In this case, ophthalmologists recommend using rigid gas-permeable lenses that are securely fixed and do not deform during use. This allows you to restore clarity of vision in case of this disease of the cornea of the eye.
Popular methods of treating the disease in the initial stages include cross-linking. It involves simultaneous instillation of riboflavin and exposure of the cornea to a special device (Seiler lamps). As a result, additional chemical bonds are created between its collagen fibers, forming a new structural framework. Another popular method, implantation of stromal rings, is a surgical approach to the treatment of keratoconus, aimed at introducing small arc-shaped elements from a material biocompatible with the structures of the eye into the cornea, creating a dense frame and helping to reduce intraocular pressure.
If the cornea is severely deformed, keratoplasty may be indicated. This is an operation during which sections of the shell are replaced with a special graft, which is located on its front layers or replaces them. For this purpose, special materials with increased survival rate are used. In addition, the treatment method using a femtosecond laser has become widespread. During this surgical intervention, a laser effect is applied to the structure of the cornea and its shape is changed. This method is considered one of the most gentle and effective, since it allows taking into account the slightest individual characteristics of the patient’s visual system.
The main methods of treating keratoconus:
• cross-linking (exposure to a Seiler lamp); • keratoplasty; • implantation of stromal rings; • use of femtosecond laser; • correction using rigid gas-permeable lenses (in the early stages).
Come for a diagnosis at the Kazakh Research Institute of Eye Diseases at the address: Almaty, Tole bi street, 95a (corner of Baitursynov street).
Telephone ;.
More news in the Telegram channel “zakon.kz”. Subscribe!
Symptoms
The very first sign of erosion is the appearance of pain , which is associated with irritation of nerve receptors. The pain may increase with blinking, especially if the erosion is caused by a foreign body.
Then lacrimation appears . Its severity usually depends on the area of the damaged area. If a secondary infection of the eye occurs, purulent discharge appears from the eyes. Along with this, there is increased sensitivity to bright light (photophobia).
With large erosions, hyperemia (redness) of the conjunctiva appears . Some patients may complain of a feeling of grit in the eyes and a burning sensation. This may indicate involvement of the mucous membrane in the inflammatory process and the development of secondary conjunctivitis.
If erosion of the eye shell is localized in the central areas, the possibility of decreased visual acuity cannot be ruled out.
Symptoms of the disease
In the first stages of the disease, the pathological changes occurring in the tissues of the eye are invisible to the patient, but over time the functioning of the visual system begins to deteriorate.
At the initial stage, a morning improvement in vision is characteristic, which occurs due to the partial disappearance of fluid during sleep.
During this period, people attribute the symptoms that appear to fatigue and do not turn to specialized specialists, as a result of which the condition of the eyes worsens.
The main signs of the disease include:
- the appearance of a shadow in the image;
- flashing black dots before the eyes;
- “flashes” and “sparks” in the field of view.
When the retina is damaged, complete or partial dysfunction of the organs of the visual system is observed.
Attention! In advanced stages, detachment of the membrane of the eye can lead to blindness
When identifying the first signs of the disease, it is important to immediately consult an ophthalmologist
There is also deformation of the lines and configurations of objects.
Prevention of corneal erosion
To minimize the risk of developing corneal erosion, you must adhere to these simple preventive measures:
- wear sunglasses to minimize exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- avoid eye injuries by complying with all safety regulations;
- undergo regular medical examinations with an eye doctor;
- if a foreign object gets into the eye, it is important to provide first aid promptly and correctly;
- follow simple hygiene rules;
- do not visit solariums and observe moderation when sunbathing.
If a foreign object enters the eye, it is necessary to rinse it with water and blink. In some cases, it is recommended to use eye drops. You should never rub your eyes: this can injure it. If, after rinsing, a foreign body remains in the eye, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
You should not try to remove a large foreign body yourself using tweezers, a cotton swab, the edge of a handkerchief, or other methods. This can injure the cornea of the organ of vision and introduce an infection into it.
During the treatment of corneal erosion, it is necessary to minimize visual stress, especially working at a computer.
If timely measures are taken to treat erosion of the cornea, a person’s vision is quickly restored. Otherwise, the disease will steadily progress and lead to serious complications, including blindness.
Developmental anomalies subject to correction
A large cornea or megalocornea is found in babies at birth. The norm is considered to be a shell diameter of 10 mm. If it exceeds by at least 1 mm, then this is a corneal symptom. The refraction of the eye is impaired - the larger the radius of curvature of the lens, the lower the refractive power.
The defect is dangerous for a number of complications - glaucoma, cataracts, problems with the retina. Megalocornea is often a symptom of complex genetic diseases (Markesani syndrome, Marfan syndrome, etc.). The disease has no cure. To improve vision, corrective glasses and lenses are prescribed.
Microcornea or small cornea. The opposite case. The shell, on the contrary, is less than 10 mm in diameter. The pupil appears unnaturally small. The consequence of microcornea is farsightedness. Glaucoma, cataracts, etc. develop against the background of the disease. If the cornea remains transparent, the doctor will prescribe symptomatic treatment and telescopic devices for vision correction.
Both cases (macro-, microcornea) are of genetic origin and are inherited.
Diagnostics
Detailed imaging techniques are used to diagnose erosive corneal damage. Examining the eyes using special instruments helps determine the cause of the ailment:
- detect foreign objects in the conjunctival sac;
- see tumor changes in the mucous membranes;
- visualize exudate in infectious eye diseases.
After a simple visual examination, biomicroscopy of the eye is performed - a detailed examination of the cornea using a special optical device. The procedure helps to visualize the erosion, determine its size and the degree of penetration into the cornea.
Good to know! If the doctor sees external signs of erosion, but cannot detect the pathological focus due to its small size, he uses fluorescein - a special dye that “highlights” even microscopic damage on the cornea of the eye.
Additional studies are used to identify the causes of the disease:
- diaphanoscopy or measurement of intraocular pressure;
- ophthalmoscopy and ultrasound diagnostics to identify intraocular pathologies;
- bacteriological and cytological analyzes of a smear from the conjunctiva.
Patients who wear contact lenses will have to have them examined under a microscope. The fact is that they may have microscopic cracks and roughness that can damage the cornea. Based on the data obtained during the diagnostic process, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Diagnosis of corneal pathologies
Any disease can be treated only after diagnosis. Diseases of the cornea are usually detected using high-precision equipment. In ophthalmology, the following diagnostic methods are used when examining the cornea:
- Pachymetry;
- Biomicroscopy of the eye;
- Confocal microscopy of the eye;
- Keratotopography.
Pachymetry is a diagnostic method that allows you to measure the thickness of the cornea over its entire area.
For the procedure, the patient is asked to lie down on a couch, after which local anesthesia is given to the eye being examined. When pain relief occurs, a special device is used to touch the eyes, lightly pressing the cornea. The equipment automatically calculates the thickness of the shell and displays the obtained data on the screen. To prevent the slightest damage from causing an infection, drops with an antibacterial effect are instilled into the patient. Biomicroscopy is an ultrasound examination that allows visualization of the intraocular structures of the anterior part of the eyeball.
The method allows you to assess the condition of not only the cornea, but also the lens, iris and the angle of the anterior chamber. Confocal microscopy is a method of studying the cornea, making it possible to visualize its structure at the cellular level. Diagnosis is made using a microscope with high resolution. The patient's living tissues are examined. As a result, the ophthalmologist receives information about the thickness of each layer of the membrane and the degree of their morphological changes.
Keratotopography is a method that results in a topographic map of the ocular cornea. The thickness of the shell, its curvature, uniformity and unevenness are examined. Keratotopography is one of the most effective ways to diagnose a rare congenital anomaly - a flat cornea.
In case of iridocyclitis, iridodiagnosis is additionally performed to identify the condition of the iris.