Normal vision in humans is determined by certain indicators of acuity and refraction in diopters. There are special tables and instruments to measure these parameters. Visual acuity is an indicator of vigilance that determines how well a person sees. How is normal vision measured and on what factors does it depend?
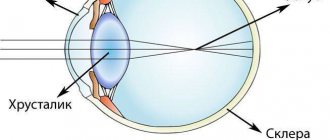
First of all, let us explain what eye refraction is; this is an important indicator for normal visual acuity. Our eyes consist of several refractive media at once: the vitreous body, the cornea, the lens, and, like any optical system, they have a focus. Its location relative to the retina is called the refraction of the eyes.
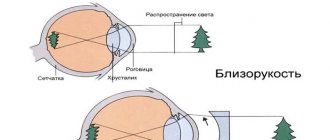
If the visual organs do not have pathologies, then the focus is clearly on the surface of the retina - this is called emmetropia, or normal vision, and the refraction in this case has a value of zero. With farsightedness, the focus is shifted behind the retina, and with myopia it is located in front of it.
What is normal vision?
This value is determined using special tables. The normal level of vision is considered to be visual acuity equal to one - 1.0 or 100%. In this case, there are cases when visual acuity (VA) exceeds the norm and is 1.5 or 2 units. If its value is less than one, this indicates the presence of various eye pathologies. Here are the most common ones.
- Myopia. Light rays entering the eye are collected in front of the retina. This change in visual acuity impairs visibility over long distances and leads to rapid eye fatigue.
- Hypermetropia. In this case, on the contrary, the light rays are focused in front of the retina, and the person has difficulty distinguishing nearby objects. Accommodation in farsightedness is impaired.
- Astigmatism. Irregular, pathological shape of the cornea or lens leads to decreased visual acuity. An astigmatist sees objects as distorted, bifurcated, with unclear contours.
- Glaucoma. A disease whose main symptom is increased intraocular pressure. In this case, deformation of the eye structures occurs and the optic nerve gradually dies, which leads to blindness.
- Cataract. The disease is characterized by clouding of the lens, and this significantly affects the decrease in visual acuity. Dark spots appear before the eyes, color perception and twilight vision deteriorate.
- Age-related macular degeneration. A disease of the central part of the retina - the macula, which is responsible for visual acuity. AMD leads to irreversible loss of central vision, although peripheral vision is preserved.
Inappropriate working conditions can also lead to deterioration of visual acuity: dusty or hazardous production, constant visual overload, hazardous working conditions. However, eye pathologies such as myopia, astigmatism, and hypermetropia are often diagnosed in children. Most often they are hereditary and acquired. In this case, all children are born farsighted, which is associated with a shortened size of the eyeball. Only after a few years, vision indicators return to normal in the absence of other pathologies.
Causes
The first main reason for the predisposition to poor vision is genetic inheritance. If both parents have problems with the visual system, then the child will develop similar diseases with a 70% probability.
Often deterioration occurs due to some disease. These may be diseases of the nervous system, respiratory system, diabetes, traumatic brain conditions, hepatitis. Doctors are confident that visual acuity is 0.3 - that this is a consequence of poor nutrition, alcohol abuse and smoking.
Young women suffering from low vision cite pregnancy and childbirth as one of the reasons. Indeed, due to these physiological processes, which entail a load on all systems of the body, a drop in visual acuity may be observed. Therefore, in the presence of diseases of the visual system, cesarean section is indicated for pregnant women.
Long-term regular watching of TV shows, working at a computer monitor and reading in low light can also cause vision of 0.3 in a child.
How is visual acuity tested?
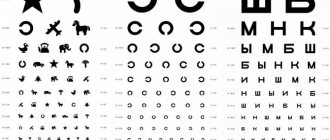
In Russia, the standard method is checking according to the Sivtsev table. Research is carried out alternately for both eyes. It consists of 12 rows of printed letters, and only seven of them from the alphabet are used: M, K, N, Sh, Y, I, B. Towards the bottom row, the letters gradually decrease in a certain pattern. On the left of each line is the D value, indicating the distance in meters from which a person with good vision should clearly recognize the letters in the table, and on the right is the V value, a conventional unit of visual acuity. If the patient is able to see the letters on the tenth line from five meters, this is considered normal, that is, V (visual acuity) is equal to one. If he cannot see them, then the table is gradually brought closer by 0.5 m until the person being tested names the letters of the top row. Depending on this, the doctor calculates the state of vision using the formula V = d/D, in which D is the distance at which a normal eye sees a given line in the table, d is the distance from which the study is carried out, and V is visual acuity. As a result, after calculations, V may turn out to be, for example, equal to 0.8 or 0.3 units.
Thus, the difference in visual acuity lies in the distance from which people clearly distinguish the same object. Let's give an example. A person with normal vision equal to 1.0 is able to see the license plate of a car located at a distance of 40 meters in daylight. If this vision is below one, then the distance from which he can see the number will also be less. So, with a HP value of 0.4 units, it will be 16 meters. Another example: a person with a visual acuity of 1.0 can read the top line of Sivtsev’s table at a distance of 50 meters, and with a visual acuity of 0.1 - no further than five meters.
What is visual acuity
Visual acuity is the ability of the visual organs to recognize two separate bright points at the smallest visual angle. This angle in normal condition should be equal to a minute. The procedure for checking the quality of vision is visometry.
Visual acuity is checked in the same way in a child and an adult. For this purpose certain tables are used. There are several types of special diagnostic tables:
- Sivtseva is the most common among ophthalmologists. Contains lines with printed Russian letters. On a poster, the higher the letter lines are placed, the larger the symbols. Indicator 1.0 is set if the 10th line of the poster is clearly recognized from 5 meters.
- Snellen. This is a prototype of the previous table. It is actively used in those parts of the world where the population is English-speaking. There are only 11 lines in it, at the very top there is only one large letter, then they become smaller. Vision is tested at a distance of 6 meters.
- Orlova. It is used to test the vision of young children. Here the letters are replaced with pictures of various objects; the lower the lines, the smaller the images. Normally, a child should clearly see line 10 when sitting about five meters away.
- Golovin. It includes rings of various diameters, which have breaks on different sides.
An ophthalmologist must check the quality of vision in compliance with certain rules, otherwise the results will be unreliable and it will not be possible to correctly prescribe treatment.
A distance of about 5 meters should be maintained between the place where the person being tested sits and the poster with the symbols. It is important that line 10 is located approximately at the level of the patient’s eye sockets.
Peculiarities of children's vision testing and exceeding the norm
To study children's visual acuity, the Orlova table is used. It depicts animal figures and other simple objects that children who still know their letters can name. The calculation principle in this case is similar to Sivtsev’s table. When checking, it is unacceptable to make mistakes from the first to the third line, from 4 to 6 lines - only one error is possible, from the seventh to tenth - only a couple of inaccuracies. The last two lines are intended to identify people with telescopic vision of 150% and 200%, or V=2.0. Such individuals are able to read inscriptions on very distant road signs, and some of them even see the rings of Saturn. There are people with so-called microscopic vision, who are able to distinguish very small objects without special optical instruments.
Different ages have their own vision standards. So, it is lower for older people, but at birth all babies have some degree of farsightedness.
Congenital farsightedness in newborns
One of the main causes of farsightedness is the shortened size of the eyeball along the anteroposterior axis. A baby's eye at birth has a diameter of 17-18 mm, while in an adult it is already 23-25 mm. Light rays passing through a child's eye are not focused on the retina due to the insufficient size of the eyeball, but enter the area behind it. This is why a child’s vision up close is not as clear and contrasting as at longer distances. The amount of farsightedness in young children is approximately 2.5-3 diopters. As the body grows, the diameter of the eyeball increases. Normally, by 12 months of life, the value of hypermetropia should be no more than 2-2.5D, and by approximately 14-18 years the eye reaches a size of 23-25 mm, and farsightedness disappears.
Correction of mild myopia
Glasses are one of the standard methods of maintaining visual functions. For mild myopia (such as -1.5 diopters), doctors usually prescribe patients to wear spectacles or contact lenses.
The selection of correction means is carried out in accordance with the percentage of visual functions lost. In this way, the focusing of the rays can be returned to the center of the retina. This will help to avoid overstrain of the eye muscles, prevent further deformation of the eyeball (its elongation), which will thereby serve as a good prevention of the progression of the pathology. Surgery at -1.5 diopters is not prescribed. Firstly, after diagnosing myopia, it is necessary to monitor the state of the visual apparatus for some time to exclude the possibility of complications. The main task of a specialist is to identify the type of myopia. If the disease is stationary (non-progressive), then there is no point in doing laser correction or resorting to other methods of eliminating the symptoms of refractive error.
Myopia 1.5 - can it be treated?
In medical circles, ophthalmologists involved in the treatment of myopia have ambivalent answers to the question of whether correction is advisable for mild myopia. Some believe that since a slight decrease in visual function does not affect the quality of life, there is no reason for concern. Others, on the contrary, based on experience and fears of worsening the patient’s condition, prefer to do everything possible to cure myopia: they prescribe prescriptions for corrective agents, prescribe additional eye medications and even physiotherapy.
There is a myth that with regular use of optics, the eyes get used to working in tandem with it, so over time they completely stop “fighting” the onset of myopia. However, during research it was experimentally revealed that this is not the case. In any case, doctors are unanimous in their opinion that it is absolutely not worthwhile to self-medicate myopia, as well as completely ignore the changes that have occurred.
Features of vision in old age
At the age of 40-45 years, aging mechanisms begin to work in the body, including the visual organs. Even in the absence of eye pathologies and general diseases, the quality of vision gradually decreases. This phenomenon is explained by deterioration of blood circulation and inhibition of metabolic processes in the retina and optic nerve in older people, the development of cataracts, age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma and other reasons.
According to medical statistics, by the age of 60, normal visual acuity remains in approximately 70% of people, and after 80 years - only in 45-47%. Most older people experience a decrease in central vision and a narrowing of peripheral vision, as well as deterioration in color vision. With age, the quality of vision at close distances becomes worse and worse: it becomes difficult to see details or font when writing, reading, or small needlework. This is due to presbyopia - age-related farsightedness. Over time, the lens loses its elasticity, its core hardens and it loses the ability to accommodate when looking at close objects. When trying to see their eyes, they quickly get tired and headaches occur. You have to resort to correction means - glasses or contact lenses, even if before that your vision was 1.0 or 100%. Older people may also undergo eye surgery to restore lost visual acuity, for example, a lensectomy - replacing a clouded lens with an artificial one in case of cataracts. A high-quality intraocular lens will allow you to maintain good vision for the rest of your life.
Features of vision treatment 0.5 in children
Features of treatment are related to the development of children's vision. In the first six months, most of them have farsightedness; in one and a half years the situation changes, visual acuity is 0.6–0.8, but this is considered a normal process.
Indicators are normalized at the age of 5–7 years. If this does not happen, then the pediatrician should prescribe special procedures for correction.
Treatment tactics and glasses are selected only after a complete examination; special attention is paid to children whose parents have vision problems.
If improvements are not observed with age, then glasses are most often prescribed. Only an ophthalmologist should select them; you should not skimp on the quality of glasses and lenses.
Important. It is strictly not recommended to wear contact lenses for children.
In most cases, doctors do not prescribe drug treatment until the age of twelve; before this time, the eyes are still developing. Farsightedness of 2.0 does not disappear until two years of age; this is the norm for this age.
Accurate refractive indexes can only be determined by completely relaxing the eye muscles with drops. But if this indicator is higher than normal, then spectacle correction is required.
Otherwise, there is a high risk of developing amblyopia, which is formed as a result of a long-term optical defect. Another problem is that strabismus may appear.
Courses of hardware treatment are prescribed from the age of two, but only under the constant supervision of a doctor. As visual acuity increases, lens diopters are adjusted.
At this age, glasses should be worn constantly; they have a pronounced therapeutic effect.
As for childhood astigmatism, it is, unfortunately, a congenital defect. With it, the cornea changes the direction of light rays along one axis more than along the other.
Glasses are not required if correction requires lenses of no more than 1D and there are no signs of amblyopia. In all other cases, the earlier spectacle therapy is started, the better the final results will be.
At the same time, vitamin support and various eye exercises are provided. Only a complete ophthalmological examination can provide a picture of the disease, on the basis of which the doctor makes decisions.
Often parents take their child to an ophthalmologist. The reason for this is the baby’s visual impairment. The number of such children is steadily growing every year. But you shouldn’t completely rely on doctors in this matter.
How to restore a child’s vision if he does not want to do long and boring exercises? To do this, you should take a certain course of classes with him.
READ MORE: Visual acuity 1.0: what does it mean?
Preventive measures
Naturally acute vision is a precious gift, and you need to take care of it, avoiding overload on the eyes. Unfortunately, modern society is too dependent on gadgets and computers, and this especially affects children's vision. Parents should monitor the quality of their child’s vision, starting from the moment of birth, and pay attention to signs indicating the development of any visual pathology. It is especially important to monitor his behavior when he starts school - it is during this period that vision most often begins to deteriorate due to sharply increased loads. If a schoolchild has been prescribed glasses, then one should not neglect to wear them in order to avoid irreparable consequences.
Adults should also be careful about their health. If you experience discomfort in your eyes, you should visit an ophthalmologist to find out the cause. Many eye pathologies do not manifest themselves at all at the initial stage and are detected already at a critical stage. After 40 years, regular visits to an ophthalmologist to check visual acuity are recommended. General advice for people of all ages is simple but effective: maintain a daily routine, spend more time in the fresh air, eat foods rich in vitamins that are good for the eyes, and avoid visual overload.
CDC specialists will check your visual acuity using the most modern instruments, measure your eye refraction, and help you decide on the choice of contact or spectacle optics, if necessary. Our Center for Contact Vision Correction is open seven days a week from 9.00 to 21.00 at the address: metro station. Tverskaya, Pushkinskaya, Chekhovskaya (1 minute from the metro), Maly Palashevsky lane, 6. You can make an appointment by calling +7 (495) 587 95 95,.
Prevention
Every person should follow rules that will prevent vision deterioration.
- Stick to a work and rest schedule.
- Read in a sitting position, in good lighting.
- Spend more time outdoors.
- Limit the time you use gadgets.
- Avoid excessive physical activity.
- Eat properly.
- Set up your workplace correctly.
It is worth remembering that the diagnosis of myopia is not a death sentence. The main thing is to see a doctor in time. Compliance with all the specialist’s recommendations, conscientious exercise, daily routine and medication will help restore your former visual acuity. Or at least stop the progression of the disease.
If the appearance of myopia cannot be avoided, care must be taken to ensure that the disease does not continue to progress.
Prevention in a child:
- provide good lighting in the room;
- teach you to write and read exclusively at the table;
- use books with large letters and pictures for reading;
- monitor the baby’s posture;
- maintain the optimal distance to the book (30-35 cm);
- do not allow using a computer, gadgets or watching TV for more than 30 minutes at a time.
Two key factors in the prevention of myopia in children and adults are regular examinations by an ophthalmologist and reducing the load on the visual system.
The diagnosis of myopia should not be neglected, even if the disease is mild. Human vision undergoes a number of changes over time. Therefore, no one can guarantee that mild myopia will remain static and will not develop into a moderate or even high degree.
Children and young people often encounter the problem of myopia. Most often due to the fact that they perform monotonous work for a long time close to them (writing, working on a computer, etc.). When a vision problem is already present, it is very important to prevent it from developing further. To do this, it is necessary to prevent the progression of myopia.
- When performing near work for a long time, you need to periodically (every 15-20 minutes) exercise your eyes into the distance. For example: when working at a computer, look outside the window or to the far wall, try to look at small details.
- Perform a set of eye exercises daily. Different authors describe exercises with slight differences in the order of execution, frequency of repetitions, etc. But in general, the exercises are similar and are aimed at training the extraocular muscles.
- Observe work and rest schedules, spend more time in the fresh air. It has already been proven that spending children with myopia in the fresh air slows down and prevents further development of myopia.
- Stick to a diet. In this case, diet means increasing the amount of vitamin-rich vegetables and fruits in the diet. And also, taking vitamin complexes in the winter and spring periods.
To ensure that eye problems affect you as late as possible and to a lesser extent, you must follow simple rules:
- always read in sufficient lighting, thereby significantly reducing the load on the visual apparatus;
- When working at a computer, take fifteen-minute breaks every hour, try to spend less time at the monitor, it is advisable to use special glasses;
- reduce or completely eliminate alcohol, caffeine, starch and flour from your diet;
- do not neglect sunglasses on clear days;
- Eat more healthy foods that are high in vitamins A, K and zinc (grapefruit, carrots and especially blueberries).