Causes of epispadias
The causes of epispadias, like hypospadias and many other congenital anomalies, cannot be accurately determined. This may be either a genetic predisposition, or the unfavorable influence of the environmental situation also plays a certain role.
Matar Asaad Akhmadovich
Head of the center, professor, pediatric surgeon, urologist-andrologist
The main principle of our center is high professionalism, dedication to their profession, human participation and mutual understanding between specialists, young patients and their parents!
Go to doctor's page
Prevention
Recommendations for the prevention of developmental anomalies can only be general. They are known to any expectant mother, which does not prevent many from not doing them. All women during pregnancy should follow the following recommendations:
- infections are very dangerous for a pregnant woman. Moreover, the danger comes both from the pathogen itself and from the drug used for treatment. The expectant mother should monitor her health very carefully;
- it is necessary to give up bad habits - alcohol, drugs, smoking, at least during pregnancy and lactation;
- You can’t give up physical activity. This not only promotes good health, but also facilitates the course of toxicosis, and the latter is one of the possible causes of pathology;
- If the work of the expectant mother is associated with toxic production or involves ionizing radiation, it is necessary to refuse it. The risk of pathological development of the fetus is very high.
Epispadias is a severe developmental defect that leads to disruption of normal urination, and in men, also to disturbances in reproductive function. The pathology can only be cured surgically and does not require therapeutic treatment.
Since the reasons for the development of such an anomaly remain unknown, there are no specific preventive measures. However, female representatives during pregnancy need to:
- completely give up bad habits;
- eat properly and balanced;
- avoid stress if possible;
- take precautions, and it is best to completely refuse work that involves occupational hazards;
- seek qualified help in cases of the slightest change in health status.
Thanks to the possibility of early detection and surgery, it is often possible to achieve a favorable prognosis, which consists of restoring and controlling urination, as well as preventing psychological disorders.
It is worth noting that those patients who underwent surgery to eliminate epispadias in childhood should be constantly monitored by a urologist (for males) or a gynecologist (for females).
Like any developmental defect, prevention of epispadias involves proper management of pregnancy, compliance with the timing of ultrasound to monitor fetal development, and elimination of the influence of teratogenic factors.
Since it was not possible to find out the exact causes of the defect in the structure of the urethra, preventive measures include general rules. All women during pregnancy should:
- give up smoking, alcohol and other bad habits that can harm the child’s health;
- avoid colds and treat infections promptly;
- do not take medications without consulting a doctor;
- eat a balanced and healthy diet;
- completely exclude work that involves contact with occupational hazards;
- If there are any changes in your health, seek medical help.
Classification of epispadias
Depending on the level of splitting of the anterior wall of the urethra (starting from the head of the penis), epispadias is distinguished:
- Heads
- Stem
- Total
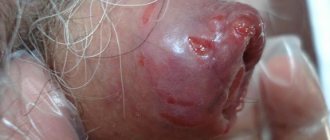
The glanular form of epispadias is characterized by clefting of the urethra to the coronal groove of the penis. With this form of epispadias, the penis is somewhat curved and raised upward towards the anterior abdominal wall. Urination is usually not impaired. The erection of the penis is also not impaired. Sexual life with this form of epispadias is possible.
With trunk epispadias, the splitting of the urethra reaches the pubic angle. This form is also accompanied by splitting of the bones of the pubic symphysis, and sometimes separation of the abdominal muscles. The penis in such patients is pulled towards the stomach and slightly shortened. The opening of the urethra has the shape of a funnel. With this form of epispadias, the child cannot urinate normally, as urine splashes, resulting in wet clothes. The penis is deformed during erection, making sexual activity impossible.
With total epispadias, the sphincter of the bladder is also split. The urethra has the shape of a funnel and is located just below the pubis. Due to the fact that in this form the sphincter of the bladder, the muscle responsible for opening and closing the urethra, also suffers, urine is constantly released in such patients. This causes maceration (corrosion) of the skin, dermatitis of the perineum, scrotum, and inner thighs. Constant wetness and the smell of urine deprives the child of the opportunity to attend kindergarten and school, or play with peers. The scrotum and penis are underdeveloped, their size is reduced. The concomitant divergence of the pubic bones in such patients leads to the fact that they have a so-called “duck gait”. With this form of epispadias, other anomalies of the genitourinary system are also noted, for example, cryptorchidism.
Pathogenesis
The process of epispadias formation is a violation of the formation and laying of the groove and platform of the urethra, the transformation of the groove itself into the urethral tube, and the development of the cavernous body of the urethra.
To date, the reasons for the formation of this type of anomaly in the development of the genitourinary system remain unknown. Theories have been put forward that such a pathology occurs against the background of a violation of embryogenesis in the interval between the seventh and fourteenth week of intrauterine development of the fetus.
Nevertheless, clinicians identify a large number of predisposing factors that cause the appearance of this disease:
- a wide range of viral infections that a woman can suffer during pregnancy;
- addiction to bad habits - not all female representatives consider it necessary to give up alcohol, nicotine and drugs just because they will soon become mothers;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- early or severe toxicosis;
- prolonged influence of stressful situations and nervous overstrain;
- abdominal injury;
- exposure to ionizing radiation on the body;
- the presence of endocrine disorders in pregnant women;
- the impact on the fetus of harmful effects from the place of work of the expectant mother.
The influence of other factors cannot be excluded.
The occurrence of epispadias is associated with a violation of the embryonic development of the embryo, which occurs in the 3rd - 4th week and consists in the displacement of the primary paired rudiment of the genital tubercle in the caudal direction, while the urogenital sinus remains in its usual place. Such displacement and delayed formation of the genital tubercle are accompanied by disruption of the formation of the mesodermal plate, which leads to resorption of the ecto- and endodermal plates of the urogenital sinus.
In the future, this causes the absence of the anterior wall of the urethra and the muscular layer of the anterior wall of the bladder in the area of its neck with the formation of a submucosal fissure. If the pathology of the primary genital tubercle is not accompanied by a disturbance in the course of the mesodermal anlage, the process of non-closure is limited to the urethra.
Epispadias of girls
This is a rare malformation of the urethra, in which there is a splitting of its anterior wall, a splitting of the clitoris and a divergence towards the labia.
In girls, this anomaly occurs in three forms:
- clitoral form of epispadias - with this form, only the clitoris is split, and the external opening of the urethra opens above it, which is shifted upward. Urination is not impaired;
- subsymphyseal form - there is not only a splitting of the clitoris, but also the labia;
- complete epispadias - in this case, both the clitoris and labia are split, the external opening of the urethra is located behind the pubic symphysis. In this case, there is also a splitting of the symphysis pubis and the sphincter of the bladder.
Diagnosis of epispadias in a child
To make a diagnosis, doctors use the following diagnostic methods:
- examination of the genital organs: visual and instrumental;
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the kidneys and bladder is performed;
- conducting an X-ray examination of the urinary tract using intravenous contrast. This research method is based on the ability of the kidneys to remove X-ray contrast agent;
- filling the bladder with an x-ray contrast agent, followed by a series of x-rays. With this research method, malformations, diverticula, tumors, stones, and injuries are assessed;
- the urethra is examined with the introduction of contrast into the urethra and a subsequent series of x-rays of the urethra;
- X-ray of the symphysis pubis;
- carry out a diagnostic procedure to determine bladder dysfunction;
- a method for diagnosing the closure apparatus of the bladder is used;
- a study of bioelectric potentials arising during muscle excitation is carried out;
- In girls, ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs is performed. In boys, ultrasound diagnostics of the scrotum.
Treatment of epispadias
As with hypospadias, the treatment of epispadias is surgical.
The clitoral form of epispadias in girls and the cephalic form in boys do not require surgical treatment if they are not accompanied by urinary incontinence.
Currently, operations are performed on children aged 4–5 years. As with hypospadias, until recently, operations for epispadias were carried out in several stages. Typically, at the first stage, the narrowed external opening of the urethra was corrected, at the second stage, the notochord (a connective tissue cord leading to curvature of the penis) was excised and the penis was straightened, and at the third stage, plastic surgery of the urethra was performed.
Currently, one-stage operations are becoming increasingly popular.
The purpose of surgery for epispadias is:
- Correction of penile curvature
- Restoration of the missing part of the urethra
- Restoring the normal appearance of the external genitalia
- If necessary, reconstruction of the anterior wall of the bladder
Depending on the degree of complexity of the defect, the surgical technique has its own characteristics.
The surgical technique for epispadias is similar to the surgical technique for hypospadias, with the only difference being that with epispadias the anterior wall of the urethra is restored.
Typically, foreskin tissue is used to recreate the anterior wall of the urethra. The distal part of the urethra along with its external opening is excised. To determine the degree of curvature of the penis, a saline solution is injected into its cavernous bodies, after which it takes the shape of an erection. This makes it easier for the surgeon to perform the operation. To form a new wall of the urethra, a plastic or silicone catheter is inserted into the bladder for 8 to 10 days.
Causes
The following factors lead to the occurrence of hypospadias: genetic, endocrine and environmental.
Genetic factors. Among monozygotic twins, the incidence of hypospadias is 8 times higher than in the general population. This situation may arise due to insufficient production of human chorionic gonadotropin by the placenta during critical periods of urethral development.
Familial inheritance of hypospadias also occurs. The probability of having a child with this pathology from a father with hypospadias is about 8%. Inheritance is most likely polygenic.
Endocrine factors. Decreasing androgen concentrations during pregnancy or blocking their effects on tissue can lead to hypospadias. In 1997, Aaronson et al. it was found that 66% of boys with distal hypospadias and 40% with proximal forms had a defect in testosterone biosynthesis.
Mutations in the gene responsible for the production of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into its active metabolite dihydrotestosterone, have been associated with the occurrence of this pathology. A report published in 1999 by Silver et al. showed that nearly 10% of boys with isolated hypospadias had at least one affected allele for the production of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. Despite the fact that androgen deficiency leads to hypospadias, there are other causes that lead to impaired formation of the penis and urethra.
Some authors have noted that in countries with cold climates, the incidence of children with hypospadias is higher. Theoretically, this may be due to the effect of daylight and sun on pituitary function, which in turn affects the hormonal milieu of the mother and fetus. However, other authors have not noticed this connection.
With in vitro fertilization (IVF), there is a fivefold increased risk of having a child with an anomaly of the genital organs compared to the control group. This is due to the effects of progesterone, which is used in IVF protocols. Progesterone is a substrate for 5-alpha reductase and acts as a competitive inhibitor of the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone. Other endocrinopathies or fetal endocrine abnormalities also play a role.
Environmental factors. In many animal studies, estrogens have been implicated as the cause of this defect. Chemicals with significant estrogenic activity are observed throughout industrialized societies. Found in pesticides used on fruits and vegetables, endogenous plant estrogens through animal milk, plastic linings on metal cans, and pharmaceuticals.
The Hadziselimovic study reported increased estradiol concentrations in placental basal syncytiotrophoblasts in boys with undescended testes compared to the healthy population. Undescended testes and hypospadias are likely related, but increased estradiol concentrations have not been shown to cause hypospadias.
Combined theory. A growing body of evidence suggests that hypospadias is a multietiological disorder involving genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
Complications after surgery
As with any other surgical operation, complications may occur. Most often this is bleeding, infection in the area of the surgical wound, dehiscence of the wound edges with subsequent formation of urethral fistulas and swelling. The percentage of formation of fistulas and urethral strictures (narrowings after surgery) averages 10%.
If it is not possible to come for an in-person consultation, then you can send photographs of the penis from different sides so that the external opening of the urethra is clearly visible via E-mail, WhatsApp or Viber
Complications
Early complications include bleeding, inflammation, dehiscence, skin flap necrosis, and swelling. Late complications - urethral fistula, narrowing of the urethra, secondary curvature of the penis. The number of complications in the treatment of proximal forms of hypospadias is higher than with distal ones. Postoperative bleeding rarely occurs and is usually controlled by a compression bandage on the penis.
Urethral fistulas are long-term complications and are most often detected after removal of the catheter draining the urinary tract. The probability of fistula formation for most one-stage operations is about 10% according to world literature. When reconstructing proximal forms of hypospadias, the probability of fistula formation approaches 40%. Fistulas rarely close spontaneously and most often require reoperation after 6 months. The probability of fistula recurrence is about 10%.
Another complication is meatal stenosis, or narrowing of the urethra. Urethral strictures can occur in the long term and require bougienage; if ineffective, surgical treatment. Urethral diverticula may appear after urethral reconstruction using preputial skin. The created urethra does not have a frame base, therefore, when resistance to the flow of urine appears in the distal sections, a diverticulum-like expansion of the urethra occurs. This complication usually requires removal of excess skin tissue and suturing of the urethral tube onto an age-appropriate catheter. It is optimal to create the same diameter throughout.
One of the complications is the growth of hair in the urethra when using skin bearing hair follicles. As a result, stones appeared in the urethra, which required multiple repeated operations. Despite the fact that skin flaps with hair follicles have ceased to be used, such patients are still encountered in urologist practice.
Consultation with an endocrinologist
If a violation of sex formation is suspected in a patient with hypospadias, or if hypospadias is combined with cryptorchidism or micropenia, consultation with an endocrinologist is indicated.
Cost and price of epispadias surgery in children:
| Service | Price |
| Epispadias surgery of 1st category of complexity | 85000 |
| Epispadias surgery of 2nd category of complexity | 140000 |
| Epispadias surgery, category 3 complexity | 220000 |
The price list published on the website is not a public offer agreement. The provision of services is carried out on the basis of an agreement for the provision of medical services. You can find out the cost of the service during the consultation.
Our advantages
Experienced surgeons
Individual approach
Without pain and fear
Comfortable conditions