Fear of urination after childbirth
Often the first attempts to urinate are accompanied by pain, burning and fear of tearing the stitches, which keeps the woman from trying. Despite the troubles, women are advised to urinate no later than 8 hours after giving birth to prevent urinary tract infections .
Flushing with tap water or trying to urinate while showering may help. If this does not help within 8 hours after birth, the woman will have a catheter inserted.
How to speed up recovery of bladder function
- Try to empty your bladder as quickly as possible after giving birth - this will stimulate the uterus to contract and protect the urinary organs from infection.
If you have difficulty getting up, use a bedpan, not a cold one, but a preheated one. Urination can be caused reflexively - by the sound of pouring water. If you are unable to go to the toilet on your own, tell the nurse who will insert the catheter.
- Train your bladder: do not reduce the amount of fluid you consume, especially if you are breastfeeding.
- Force your bladder to work: In the first days after giving birth, go to the toilet every two hours, even if you don’t feel the urge.
- Walk more: this stimulates normal bowel and bladder function.
- Perform special exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles - Kegel exercises.
While lying down or sitting, tighten the muscles of the vagina and anus as if you were holding back urination, hold in this position for a few seconds, and then completely relax the muscles. When performing exercises, do not tense your stomach and buttocks or move your legs together. It is recommended to do Kegel exercises at least 3 times a day, and preferably more often. It is optimal to perform 8–10 muscle contractions in one approach.
- Avoid drinking drinks and foods that irritate the bladder - coffee, spicy seasonings, pickles, smoked meats.
Restoring normal functioning of the bladder can take from several days to one to one and a half months. If incontinence does not go away during this time, you need to inform your gynecologist about this at a routine examination, which usually occurs six weeks after birth.
- after healing of tears or cuts in the perineum, you still experience pain or burning in the urethra or in the bladder area;
- the urge to urinate is frequent, but the amount of urine produced is scanty;
- urine is cloudy and has a sharp, unpleasant odor;
- body temperature is increased, even slightly.
The listed symptoms may be a sign of the development of a urinary tract infection, which without proper treatment will cause pyelonephritis. Treatment today can be successfully combined with breastfeeding, so do not be afraid to seek medical help if your bladder does not work like a charm after childbirth.
For 80% of women, pain when urinating after cesarean section (CS) becomes a real problem. If in the last stages of pregnancy you are tormented by the urge to go to the toilet every half hour, then after childbirth the situation changes dramatically. Young mothers experience many negative sensations: pain, stinging, burning, nagging pain in the scar area, etc. All these unpleasant feelings are mainly natural consequences of surgery and should go away within a few days. However, such symptoms may indicate serious complications, so you should additionally consult your doctor.
Stress urinary incontinence
Pregnancy is most often associated with stress urinary incontinence. This is the leakage of urine when pressure is applied to the bladder during physical activity. They can be caused by coughing, laughing, lifting heavy objects, or running.
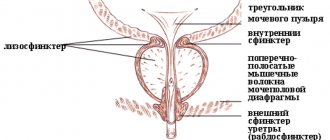
The pressure then forces urine out of the bladder because the sphincter muscles responsible for closing the bladder are not doing their job. Injuries to the pelvis during childbirth can damage the bladder sphincter.
Normally, the nerves, ligaments, and muscles of the pelvis work together to support and support the bladder and prevent leakage through the urethra.
If a woman suffers from stress urinary incontinence before or during pregnancy, she is more likely to experience discomfort after childbirth . Only a small number of women see it for the first time after giving birth.
Women who have given birth vaginally are more likely to experience this problem than women who have had a caesarean section. However, stress urinary incontinence sometimes occurs even after surgical childbirth.
Treatment of urinary incontinence after childbirth
Today, there are many ways to treat urinary incontinence after childbirth. To eliminate this pathology, surgical and non-surgical treatment methods are used.
Non-surgical treatment involves performing various exercises. Surgical treatment of urinary incontinence after childbirth is considered the most effective way to combat this pathology. Since surgical treatment methods are invasive and can cause complications in the postoperative period, doctors suggest their patients use laser therapy.
Laser treatment is a painless method for treating urinary incontinence in postpartum women. Laser therapy is a safe method of eliminating weakness of the pelvic floor muscles, thereby helping a woman avoid surgery and improve her quality of life.
How does the method work?
The principle of operation of the laser is based on changing the structure of collagen, a fibrillar protein that is part of vaginal tissue. Thus, in patients with urinary incontinence, the amount of fibrillar protein in the pelvic tissues is reduced. Under the influence of a laser beam, collagen fibers contract, which leads to a change in the muscle tone of the pelvic organs.
Procedure progress during laser treatment
Laser therapy consists of 2 phases. The first phase involves inserting a laser imager into the woman's vagina, after thoroughly cleaning it with an antiseptic solution. Under the influence of laser irradiation of vaginal tissue, collagen fibers contract.
The principle of operation of phase 2 of laser therapy is the effect of the beam on the vestibule of the vagina. During therapy, a woman may experience slight tingling in the vaginal mucosa, or a burning sensation, but this procedure does not require pain relief.
Unpleasant sensations disappear immediately after the end of laser therapy; the procedure takes no more than 25 minutes. After laser treatment is completed, the woman can begin her work and do her usual activities.
Preparation for laser therapy
Before starting laser treatment for urinary incontinence after childbirth, a woman must undergo an examination by a gynecologist, which includes smears for oncology, the level of vaginal cleanliness and scraping from the cervix.
It is very important to contact a gynecologist immediately after the occurrence of this pathology. You should not be ashamed of this, since the success of treatment depends on the neglect of the pathology. If you consult a specialist in a timely manner, a woman will forever forget about the problem of urinary incontinence.
Exercises for urinary incontinence
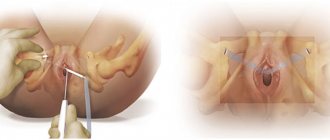
For this type of urinary incontinence, Kegel exercises can help restore the strength of the sphincter muscles. If exercise is not enough, the bladder can be supported by an operatively implanted device that acts like a brace.
To train your pelvic muscles, you can:
- sitting on the toilet, you can keep the stream of urine moderate;
- contract your muscles as if you were trying to stop the flow of gas from the rectum;
- lie down and insert your finger into the vagina, and then squeeze the muscles, as if the woman was trying to stop the flow of urine.
In addition, if a woman has urinary incontinence, she should use tampons that absorb urine and prevent it from leaking out.
Overactive Bladder
Another type of urinary incontinence is overactive bladder. The bladder is leaky because it contracts and contracts when it shouldn't. It usually shrinks when allowed to do so and remains empty.
An overactive bladder tries to empty itself without the body's permission, causing a woman to experience an uncontrollable urge to urinate. This type of urinary incontinence is more common in older women, but can occur at any age.
If you have an overactive bladder, you can exercise it by going to the toilet regularly. In this case, the woman should not completely empty her bladder every time she feels the need to urinate.
Try to empty it every 3-4 hours. A woman can start by going to the toilet every two hours if she wishes, and then increase the time in between. Bladder training involves going to the toilet by the hour rather than as needed.
Pharmacological agents are intended to support training by relaxing muscles while abstaining from urination.
Methods for treating urinary incontinence
Another way to treat urinary incontinence is to drink the right amount of fluid, not too little or too much. If there is not enough fluid, urine concentrates, which can irritate the walls of the bladder, and if there is too much, it can aggravate bladder problems.
Caffeinated drinks, acidic juices and fruits, and alcoholic beverages can irritate the bladder and increase the need to urinate. The body needs six to eight glasses of liquid a day.
Of course, their amount should be adjusted if there are factors such as diarrhea, fever, exercise, fever and breastfeeding.
Urethral abrasion
A few days after giving birth, a woman may feel discomfort when urinating. Difficulty urinating may also be due to chafing around the urethra during childbirth.
If a woman experiences a tingling or burning sensation when urinating, pour water from a bottle or jug over her perineum or urinate in the shower.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of urinary incontinence after childbirth
- Spontaneous release of a small amount of urine during physical exertion;
- During sexual intercourse;
- When sneezing, coughing, laughing;
- Feeling of a false urge to urinate;
- Feeling of bladder fullness;
- Spontaneous leakage of urine after taking small doses of alcohol.
In this case, the amount of urine released involuntarily can range from a few drops for the above reasons of exposure to constant release throughout the day.
Causes
The main cause of urinary incontinence after childbirth is weakening of the muscles of the pelvic organs. Since during pregnancy there is increased pressure on the walls of the bladder from the baby’s head, as it grows, the muscles of the pelvic day weaken due to disruption of normal blood supply. In addition, during childbirth, the pelvic muscles also experience a lack of blood supply.
Predisposing factors
Urinary incontinence after childbirth can occur in the following cases:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Birth of a large fetus (over 3600 grams);
- Application of obstetric forceps during childbirth;
- Repeated births;
- Episiotomy.
The influence of these factors leads to weakening of the pelvic floor muscles, which can lead to involuntary urination after childbirth. Predisposing factors to the appearance of urinary incontinence after childbirth can also be excess weight, hormonal imbalance in the body, previous surgical interventions on the pelvic organs and genital infections.