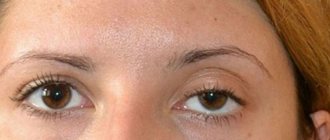
Coloboma of the iris
This disease has a congenital or acquired form. It manifests itself as complete or partial splitting of the structures of the iris. The word coloboma comes from Greek and means “missing part.” The disease is very rare. The congenital form can cause visual impairment in children and lead to blindness. Most often, the pathology occurs in residents of the following countries: China, America, France.
Causes
The causes of the disease depend on the type and its manifestations:
- Congenital form. The reason for the development of this type of pathology is hidden in the influence of negative factors during intrauterine development. Subsequently, the correct closure of the slits in the ocular structures is impaired. This leads to a change in their shape.
- Acquired appearance. Occurs as a result of injury to the eyeball, against the background of the development of necrosis. Rarely, it can develop in the postoperative period as complications.
Symptoms
The presence of such a pathology can be detected with the naked eye. The manifestation of symptoms depends on the type and location of the disease. In ophthalmology, coloboma of the choroid, lens, optic nerve, and eyelids occurs. It may occur in complete or partial form of the lesion.
The pathology affects one or both eyes. The damage usually appears in the lower part of the iris.
The defect is quite pronounced. Its shape resembles a pear. Normal or slightly reduced visual acuity leads to the fact that the patient is not able to independently control the influence of light rays in the retina. Against this background, light perception is disrupted.
If the entire thickness of the choroid is damaged, it is accompanied by the appearance of dark spots before the eyes. Bilateral pathology subsequently causes the development of nystagam. Rarely, symptoms include Ecardi and Charge syndromes.
Decreased visual acuity is one of the main symptoms. The degree of development depends on the lesion. If the pathology is accompanied by microphthalmia or damage to other structures, then there is a risk of complete blindness. Patients often complain of double objects in front of their eyes, dizziness, and blurred vision. In the congenital form, Down and Edwards syndromes can develop.
Photo
In the photo you can see the splitting of the iris.
Types of Kolobomas
There are three groups of optic nerve coloboma, which are caused by different exits of the central retinal vessels:
1. The first type is characterized by the emergence of a vascular bundle at the lower edge of the defect.
2. In the second type, the vessels are located in the center or closer to the upper region.
3. The third type is characterized by a uniform distribution of vessels along the entire edge.
The degree of influence on visual acuity in coloboma can be different (ranging from preserved to complete blindness). Undoubtedly, visual function depends on the size and location of the disease. Provided that the coloboma was localized in the projection area of the papillomacular bundle, then vision will be poor. But if the coloboma is localized in the nasal half of the disc, vision will be high, sometimes even up to 1.0.
The field of view is rarely affected by coloboma; if defects occur, they are usually localized in the upper half. Often optic nerve coloboma is diagnosed in a patient simultaneously with microphthalmos, choroidal coloboma and other eye anomalies.
Why does the defect develop?
An optic nerve defect (OND), as a rule, is detected immediately after the birth of a child, that is, it is caused by disturbances in the intrauterine development of the fetus. The rudiments of the visual organs appear in the embryo already in the second week after conception - these are the so-called bubbles, from which the eyes will later form. As the embryo develops, one of the walls of the bladder begins to bulge inward, forming a concave rudimentary eye structure with a slit.
Next, the edges of the gap begin to approach each other and join together around the fifth week of pregnancy. This point is very important: if the edges of the gap do not close completely, after 2-3 months defects in the iris and other elements of the organ of vision will be detected.
An unhealthy lifestyle, alcohol consumption, and especially cocaine, affect the intrauterine formation of the optic vesicle and the timely closure of the palpebral fissure, which can lead to the development of coloboma
Factors that provoke disruption of the optic fissure healing process may be:
- various infections during gestation, penetrating through the placenta to the fetus;
- serious medications that can cross the placental barrier;
- drinking alcohol during pregnancy and other drugs.
Underdevelopment of the optic nerve is most often observed against the background of systemic developmental defects in the child. Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, basal encephalocele, focal skin hypoplasia, trisomy are often accompanied by visual defects in the child.
Acquired coloboma becomes a complication of injuries to the organs of vision or a side effect of surgery. Both types of pathology can be distinguished by its typical manifestations.
Important: congenital coloboma is inherited from parents to children as an autosomal dominant trait. If the father or mother has a genetic predisposition to this disease, the child has a greater than 50% chance of developing it.
Coloboma of the century
Coloboma of the eyelid is accompanied by damage to a certain area. Thinning of peripheral tissues occurs. In some cases, such a lesion may be accompanied by fusion of the skin of the eyelids with the mucous membrane of the eye. The pathology mainly develops in the upper eyelid. It can be complete or partial. Rarely, the lesion spreads to the upper and lower eyelids.
Causes
The reasons for the development of this form of the disease are hidden in congenital and acquired forms. Rarely occurs as a result of injury, chemical and alkaline burns. The closure of the eyelids is disrupted, which leads to the development of other ophthalmological diseases.
Symptoms
This type of pathology is accompanied by severe discomfort. Causes a pronounced cosmetic defect. The closure of the eyelids, the process of blinking, and the growth of eyelashes are disrupted. When the eyelid fuses with the mucous membrane of the eye, complete closure of the eyelids becomes impossible.
Photo
Photo of coloboma of the upper eyelid:
Types of Kolobom
Experts distinguish colobomas identified in the iris into the following forms:
- Congenital coloboma of the iris and acquired (depending on the cause of development).
- Unilateral and bilateral (one eye is affected, or both).
- Complete and incomplete (depending on how many layers of the iris are affected: with complete all layers are affected, with incomplete only part).
- Typical and atypical (depending on where the coloboma is localized: a typical coloboma is detected in the inferior nasal quadrant of the iris, all others are considered atypical).
Treatment of pathology
If coloboma is congenital and noted in a child, then no emergency treatment measures are usually taken. To begin with, the doctor will monitor the condition of the baby's eyes and conduct a series of studies - all of them are carried out during the first 6 months after the birth of the child. Preventive measures may be required.
Coloboma
Only after six months will the doctor be able to decide whether there are indications for surgery to eliminate the coloboma. For example, there is no point in surgical intervention if the coloboma is small in size and does not affect the health of the eyes and the quality of vision.
To reduce the amount of light entering the iris through the pupil and irritating the eye, use dark-colored contact lenses with a transparent center or glasses with mesh. These measures will help avoid blindness. The operation will be carried out only in case of special indications - such as serious impairment of visual functions.
Contact lenses are used during treatment
On a note! There are various types of operations to correct a defect such as coloboma. Among them there are both those that cause quite serious damage to the eye, and those that are considered less traumatic. But the doctor will most likely choose the technique depending on certain indications.
When treating coloboma surgically, the choice of a suitable medical institution is of great importance. It is worth contacting exactly the clinic where experienced doctors work, who can not only accurately diagnose and determine the condition of the eyes, but also, if necessary, perform the operation correctly and accurately.
Eye surgery
Video – Iris plastic surgery
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is carried out in several stages:
- Initially, you need to examine the eyeball and visual acuity. To detect a defect, a visual inspection is sufficient. With minor damage, the decrease in severity is insignificant or absent. It usually occurs when the choroid is damaged. If vision is greatly reduced, then most likely the patient is diagnosed with damage to the choroid or optic nerve.
- Ophthalmoscopy is used to examine the fundus of the eye. With this pathology, light spots are visible on it, which have clear boundaries.
- Biomicroscopy allows you to determine the presence of defects in the lens, retina, and iris. In these structures one can see changes characteristic of this pathology.
- Determination of reaction to light. This method is used to diagnose iris coloboma. If there is a complete lack of reaction, then the form of the disease is acquired, and if partial, it is congenital.
- Additionally, the visual axes can be checked.
- MRI, CT, and eye scanning are used to determine the location of the defect. Typically used when there are no visual signs.
After the examination results, the doctor can determine the etiology of this disease. Treatment is also prescribed to eliminate it.
Classification
Depending on what part of the eye is damaged, ophthalmology distinguishes several types of coloboma:
- Rainbow. This is the most common form of the disease, in which part of the iris is affected, most often in the lower part. Most often, one organ of vision is affected.
- Coloboma of the choroid. Damage to the choroid occurs, most often the defect forms in the lower part. Coloboma of the choroid is a common type of disease that cannot be cured.
- Eyelash. Part of the ciliary body is missing, and there is a disturbance in the accommodation of the eye.
- Coloboma of the lens. A rare form of pathology in which the lens is deformed and the process of refraction of light rays is disrupted. Sometimes accompanied by strabismus and heterochromia.
- Coloboma of the optic nerve. One of the rarest forms in which deformation of the nerve occurs; its nipple takes on an irregular shape, and depressions and notches are observed in the affected area.
- Coloboma of the eyelids . With this form, part of the eyelid is missing. The defect usually has the shape of a triangle or a month; its size can vary. In most cases, only the upper eyelid of one eye is affected.
Read in a separate article: False myopia (myopia): what it is and how to treat it
Taking into account the degree of spread of the pathological process, the following types of disease can be distinguished:
- unilateral - only one organ of vision is affected;
- bilateral – coloboma is diagnosed in both eyes;
- isolated - a separate part of the shell is affected, no additional defects are observed;
- combined - the defect spreads to several membranes at once (iris and retina);
- complete – all layers of the eye are affected.
Based on the location, they also distinguish between typical (the defect is located in the lower quadrant on the side of the nose) and atypical (any other part is affected) coloboma of the pupil.
Coloboma of the membrane in children
Diagnosis is carried out in the same way as for iris defects in adults. The child's eyes are examined by an ophthalmologist to determine the extent of the damage. The patient's individual complaints are taken into account.
When checking visual acuity, a decision is made to perform surgical treatment. If the deviation is mild and does not significantly affect the quality of vision, then the operation is not performed.
In newborns
At an early age, congenital forms that arise during gestation are diagnosed. This pathology does not always lead to deterioration of vision, so a comprehensive examination is carried out later.
Typically, a decrease in visual acuity occurs with simultaneous damage to other structures of the eye. If they are not involved in the pathological process, then there is a possibility that the child will see well in the future despite the presence of a defect. In any case, surgery or any other therapeutic measures cannot be performed due to early age.
Diagnosis and treatment of coloboma
Confirming the diagnosis of coloboma in some cases is not difficult. So, in case of coloboma of the pupil or eyelid, a visual examination is enough for a specialist. The doctor will ask about whether the disease was detected in the patient’s relatives, how long ago the first symptoms appeared, and what they are.
Further research may require methods such as ultrasound, ophthalmic and biomicroscopy, perimetry, optical tomography, CT or MRI, and histology analysis.
Conservative treatment methods are used to a limited extent. They can only give an effect when used in newborns: fortification, keratoprotectors and antiseptics can improve the situation, but the cosmetic effect will remain.
In most cases, surgery is indicated to treat coloboma. Doctors can “sew” the edges of the gap, implant a collagen insert that will serve as a frame, and coagulate some areas. These techniques are used when the patient’s condition worsens and there is a threat of losing vision. If we are talking only about a cosmetic defect of the pupil, surgical operations are not indicated.
Treatment
There are several methods for treating this pathology. They should be determined by a doctor after a full examination.
Surgery
The following types of surgical intervention are used:
- plastic;
- photocoagulation is performed when the optic nerve is damaged;
- lens replacement;
- eyelid surgery;
- blepharoplasty.
Drug treatment
This treatment is relevant in the early stages of development of such pathology:
- moisturizing drops;
- for glaucoma, medications are used to reduce intraocular pressure;
- decreased visual acuity requires wearing contact lenses or glasses;
- Vitamin complexes are prescribed for auxiliary therapy.
Collagenoplasty
This is a modern method of treating such pathology. A special frame is made from collagen. It prevents the development of the eyeball and the spread of the lesion.
Causes
The anomaly forms in the fetus during the prenatal period. This can happen under the influence of cytomegalovirus, which has infected the body of the expectant mother. In some cases, the fetus closes the palpebral fissure early, resulting in underdevelopment of the eyeball. Among the provoking factors of coloboma are also called:
- use of alcohol and drugs by the expectant mother while carrying a child;
- gene mutation in an autosomal dominant manner.
The acquired form of the disease can be diagnosed as a result of mechanical damage to the lens. In some cases, coloboma is provoked by pressure on the lens of neighboring neoplasms of various types: tumors or cysts.
Prevention
At the moment, there are no specific methods to prevent the development of this pathology. To avoid the development of light perception disorders, it is necessary to use glasses and special darkened contact lenses. They are selected by the doctor taking into account the degree of damage individually for each patient.
As an auxiliary therapy, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes. The patient must adhere to a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and nutritiously. You should also give up bad habits.
Symptoms
Lens coloboma refers to a partial form of this type of anomaly. As a rule, it is localized in the lower part of the eye; this is a typical case. In atypical forms of the anomaly, the coloboma is located in other parts. Patients may experience a sensation of double vision of the observed objects, and sometimes dizziness is also noted. In case of injury, pain and rapid eye fatigue during exercise are noted. Sometimes, against the background of lens coloboma, strabismus, amblyopia, and myopia develop. Patients often have astigmatism with myopic refractive error. In this case, a significant decrease in the quality of vision and distortion of perceived objects are diagnosed.
Strabismus may develop against the background of coloboma.
With large colobomas of the lens, its splitting may occur. Because of this, the refractive index varies in different areas, and the quality of vision suffers greatly. There may be distortion of the picture or loss of some parts of the image.
Symptoms of coloboma by location
Vascular coloboma or choroidal coloboma is characterized by a malnutrition of the ocular structures. If the entire thickness of the retina is affected, the pathology causes scotoma (the appearance of a blind spot). In the incomplete absence of the vascular lining, color perception is impaired. With coloboma of the ciliary body, farsightedness occurs.
This type of anomaly cannot be treated and occurs along with other facial pathologies. And in the most difficult cases it leads to complete blindness.
Retinal coloboma is the absence of retinal tissue, which leads to the appearance of a blind spot (affects the missing retina), and in more complex cases, retinal detachment occurs due to malnutrition of the eye structures. Detachment is treated with a coagulator (photocoagulation), as if soldering the detached part to the fundus. Coloboma itself cannot yet be treated.
Coloboma of the optic nerve is a complex pathology, which in its isolated form manifests itself as a slight decrease in vision, but in combination with other pathologies can provoke significant impairments and lead to complete loss of vision.
Very rarely, disc coloboma occurs, which manifests itself in several types: defects of the optic disc itself (very rarely) or cystic ectasia of the sclera in the area of the optic disc. This pathology cannot be treated.
Coloboma of the iris is one of the most visually noticeable pathologies. In this case, the iris of the eye takes the shape of a castle or a drop, turned down. This type of anomaly with a slight coloboma does not affect vision, and the cosmetic defect is corrected with the help of colored lenses. If a significant amount of tissue is missing, this affects light perception: the patient is unable to regulate the flow of light to the retina. With such an anomaly, surgical treatment is performed: the edges of the coloboma are excised and then stitched (a ring is formed), healing occurs quite quickly, but the operation is complex.
Coloboma of the eyelid is the most noticeable visual anomaly, which can be easily corrected with surgery. This pathology usually does not cause visual impairment, but can cause drying of the cornea. With prolonged disruption of tear production, cracks and ulcers appear on the cornea. Coloboma of the upper eyelid is diagnosed much more often than pathology of the lower eyelid.
With coloboma of the lens, it cannot contract, which leads to visual impairment similar to astigmatism and myopia. In this case, a peculiar notch is revealed along the edge of the equator, and the absence of a ciliary band. This type of anomaly is the most difficult to diagnose. With minor pathology, vision may not suffer, but with large colobomas or when they are combined with colobomas of the iris, choroid or microphthalmos, surgical intervention will be required. Treatment in this case is the same as for other diseases of the lens - replacement with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). This pathology can be cured almost completely.
Diagnosis of pathology
An examination of the newborn by an ophthalmologist is often sufficient to diagnose the anomaly. During an external examination, a doctor can detect pathology; in addition, ophthalmologists also use for diagnosis:
- Ophthalmoscopy (helps detect defects of the fundus, choroid, optic disc, optic nerve).
- Biomicroscopy with a slit lamp (microscopic colobomas of the iris and lens are detected)
CT and MRI for a more detailed study of the pathology, determining the size of the coloboma and its dislocation.