general characteristics
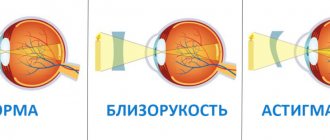
With ear congestion, patients report a feeling of discomfort, fullness in the external auditory canal, and decreased hearing, accompanied by a constant hum or ringing.
Some people compare the sensation to the ear canal filling with water. With short-term physiological congestion, bilateral symptoms are more often detected; inflammation and other pathological causes can cause unilateral manifestations. Congestion can last from several minutes to several weeks. Patients often notice a connection between discomfort in the ear and acute bacterial or viral infections, injuries to the auricle or head in the temporal region. If congestion bothers you constantly or occurs periodically over several days, this is an indication for a visit to a specialist. It is also necessary to visit a doctor when the symptom is combined with other manifestations - headaches or pain in the ear canal, dizziness, increased body temperature.
Causes of ear congestion
Changes in atmospheric pressure
Congestion in both ears is a typical symptom that most people experience during air travel. Unpleasant sensations are associated with the difference in pressure inside the middle ear and outside. A person feels pressure on the eardrums, which is accompanied by decreased hearing, noise or ringing in the ears. The same symptoms are observed when jumping into water and quickly diving to great depths (swimmer's ear). Usually, the discomfort disappears after the pressure levels are equalized; if congestion persists for a long time, you should visit a doctor.
Otitis
The most common causes of congestion are inflammatory processes of bacterial or viral etiology. Patients experience pressure in the ear, which is combined with unilateral hearing loss and increased perception of their own voice (autophony). The symptom is constantly disturbing, sometimes an unpleasant feeling in the area of the external auditory canal causes intense headaches. With external otitis, there is sharp pain when pressing on the auricle, and purulent or serous discharge from the ear canal is possible.
Severe ear congestion occurs due to inflammation in the tympanic cavity - otitis media. Patients complain of a feeling of fullness and pressure, and hearing on the affected side is sharply reduced. In addition to a stuffy ear, the patient is bothered by sharp pain in the temples. Pathological discharge is uncharacteristic. When the process is started, congestion often turns into temporary hearing loss, which is associated with damage to the eardrum. Self-medication of otitis media is fraught with neurological complications, so you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
Eustachian tube lesion
Normally, the Eustachian (auditory) tube provides communication between the oropharynx and the middle ear cavity, which is necessary to equalize external and internal pressure. Some reasons provoke swelling and closure of the lumen of the organ, while patients feel congestion, bloating and discomfort. In inflammatory processes, the lesion is often bilateral. Depending on the etiological factor, eustachitis is accompanied by a runny nose, sore throat, headache, and fever. Closure of the lumen of the auditory tube is caused by:
- ARVI
: influenza, rhinovirus and adenovirus infection. - Diseases of the nasopharynx
: chronic rhinitis and sinusitis, deviated nasal septum, choanal atresia. - Childhood infections
: measles, scarlet fever, whooping cough. - Allergic pathology, hay fever
. - Complications after nasal tamponade
.
Sulfur plug
When wax accumulates in the outer ear canal, congestion develops gradually. First, there is a feeling of discomfort and a sensation of a foreign body in the ear, then on the affected side the hearing progressively worsens. Patients note constant distension and pressure in the ear canal. Some patients, to eliminate unpleasant sensations, try to rinse the ear themselves, which causes a worsening of the condition, since upon contact with water, the wax plug swells and completely closes the lumen of the external ear canal.
Inner ear diseases
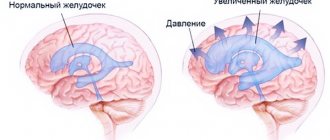
Ear congestion, which is combined with severe dizziness, can be caused by labyrinthitis. Patients associate the onset of discomfort in the ear canal with a viral or bacterial infection or head injury. With moderate severity of the disease, pressure and ringing in the ears occur periodically; as the condition worsens, the symptoms become permanent. Against the background of congestion, hearing loss progresses. Characteristic complaints are imbalance, staggering when walking, nausea and vomiting, which are caused by damage to the vestibular apparatus.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Most often, pressure and discomfort in the outer ear area appear after taking medications to treat bacterial infections for 2 weeks or more. Along with congestion, patients note progressive unilateral or bilateral hearing loss. After the cause ceases, the unpleasant manifestations may disappear on their own, but if the neurosensory cells responsible for the perception and recognition of sounds are damaged, persistent hearing loss is observed. An unpleasant feeling of pressure and fullness in the ear is provoked by:
- Aminoglycoside antibiotics
: gentamicin, kanamycin, amikacin. - Loop diuretics
: furosemide, ethacrynic acid. - NSAIDs in high doses
: aspirin, indomethacin, diclofenac sodium. - Psychotropic drugs
: amitriptyline, phenazepam, carbmazepine. - Cytostatics
: cisplatin, vincristine, methotrexate. - Anti-tuberculosis drugs
: streptomycin, florimycin, capreomycin.
Rare causes
- Autoimmune diseases
: systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), scleroderma. - Congenital diseases
: aplasia of the cochlea of the inner ear, cholesteatoma, fetal alcohol syndrome. - Oncological pathology
: tumors of the tympanic cavity, neoplasms of the nasopharynx. - Otosclerosis
. - Occupational hazards
: long-term vibration and noise exposure.
Causes of ear congestion
Often many people feel as if something is pressing on the ears and feel dizzy, creating a feeling of general malaise and problems with well-being. As a rule, the most common cause of this pathology is considered to be osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (mainly 1 and 3 vertebrae).
Another cause of malaise in the ear apparatus may be otitis media, which is just beginning to develop. Because of this, increased ear pressure occurs, creating some discomfort. Damage to the skull, trauma and ear infections can provoke the appearance of such ailment.
If we talk about infectious diseases in the ears, then the pathology is additionally accompanied by loss of coordination, imbalance and a feeling of general discomfort.
Analyzing situations that occur in practice, deterioration in well-being in the form of dizziness and temporary partial deafness occurs for the following reasons:
- During pregnancy, when blood volume increases.
- After suffering stress or fright, the nerve endings in the head become inflamed, which provokes additional pain.
- Due to chronic lack of sleep.
- Due to narrowing of blood vessels in the brain.
- As a result of taking medications, since in certain cases dizziness is included in the list of possible adverse reactions.
- With a long-term unbalanced and incorrectly selected diet, the general state of health and well-being worsens.
- Anemia, characterized by a decrease in blood hemoglobin.
The reasons for blocked ears and dizziness can be very different, so it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner for a detailed examination and an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Ear congestion is an indication for visiting an otolaryngologist, who conducts a full examination of the hearing analyzer in order to determine the cause of the unpleasant symptoms. Laboratory and instrumental studies are aimed at studying the degree of hearing impairment and morphofunctional changes in various parts of the ear. The following have the greatest diagnostic value:
- Instrumental examination of the external ear
. During otoscopy, inflammatory changes, pathological discharge, cracks or ruptures of the eardrum are detected. To clarify the cause of congestion, microotoscopy is additionally prescribed. - Audiometry
. The degree of dysfunction of the auditory analyzer is assessed using a special device that produces sounds of varying frequencies and volumes. To detect damage to the middle and inner ear, impedance audiometry and tuning fork tests are used. - Assessment of patency of the auditory tube
. Excluding eustachitis involves performing special tests: with an empty throat, Toynbee maneuver or Valsalva maneuver. To objectively study the patency of the Eustachian tube, it is blown through, followed by otoscopy or audiometry. - Laboratory methods
. Discharge from the external auditory canal is collected for bacteriological culture and identification of pathogenic microorganisms. A general blood test is indicative of identifying signs of inflammation. In the presence of a general infectious syndrome, serological diagnostics (ELISA, RIF, PCR) can be used.
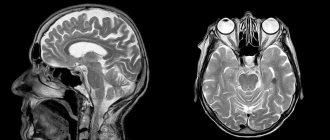
For suspected vascular disorders in the organ of hearing, Dopplerography and rheoencephalography are recommended. The presence of neurological symptoms serves as the basis for a CT scan of the skull, MRI of the head, and electroencephalography. If an allergic nature of the disorder is suspected, allergy tests are performed. Patients are also referred for a comprehensive examination to a neurologist and for consultations with other specialists.
Otoscopy for ear congestion
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Ear congestion that occurs when the pressure changes can be eliminated on your own - to do this you need to make several swallowing movements and blow your nose. To open the lumen of the Eustachian tube, you need to close your nose and try to exhale intensely. If the discomfort is caused by a runny nose, it is recommended to drip vasoconstrictor nasal drops into the nostril on the side where the congestion is felt, then lie on your side. To identify the cause of discomfort in the ear and select a treatment regimen, you should contact a specialized specialist.
Drug therapy
Therapeutic measures for a stuffy ear are primarily aimed at eliminating the cause of the symptom. To increase the effectiveness of therapy, several drugs are combined that affect different parts of the mechanism of development of the disorder. Etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy involves the use of the following groups of drugs:
- Antibiotics
. Medicines are prescribed for purulent processes in the middle and inner ear. The otolaryngologist selects medications that do not have ototoxic properties. For mycoses, specific antifungal agents are used. - Anti-inflammatory drugs
. Usually, medications from the NSAID group are recommended, which effectively relieve swelling of the mucous membrane and eliminate congestion. The drugs have an analgesic effect, therefore they are also indicated as symptomatic therapy for severe pain. - Antihistamines
. _ Prescribed for proven allergic causes of discomfort in the outer ear. In addition, antihistamines, which relieve swelling and restore the patency of the auditory tube, are included in the treatment regimen for eustachitis. - Immunomodulators
. They are used to increase local and general protective functions of the body, accelerate regenerative processes in the epithelial cells of the hearing organ. Immunostimulants are especially effective for otitis of a bacterial and viral nature.
Physiotherapy
As a rule, the treatment plan for congestion and other unpleasant symptoms of the hearing organ includes physiotherapeutic techniques. Blowing the auditory tube according to Politzer is effective, aimed at improving the outflow of exudate from the tympanic cavity and reducing discomfort in the patient. To stimulate blood circulation and reparative processes, pneumomassage of the eardrum is performed. Complex treatment involves the use of UHF, laser effects, and microwave therapy.
Surgery
In some situations, effective therapy for ear congestion is possible only after surgical elimination of the cause. For massive purulent otitis, drainage operations are indicated to facilitate the outflow of pus and speed up the recovery period. In cases of significant enlargement of the adenoids, a tonsillectomy is performed. According to indications, correction of nasopharyngeal pathologies is prescribed - septoplasty, removal of polyps and other benign tumors, conchotomy for hypertrophic rhinitis. In some cases, reconstructive interventions in the inner and middle ear are required.
Stuffed ears and dizziness reasons, what to do
Migraine. With this disease, persistent and prolonged headaches occur, covering half the head or some part of it (in Greek the disease is called “hemicrania”, that is, half the head). The pain can be weak and increase to unbearable, when a sick person is literally afraid to make an extra movement, because it will respond with a blinding attack of pain.
Diseases that are in one way or another associated with vascular dysfunction. This large group includes the most common causes of headaches and ear pressure: high and low blood pressure, vegetative-vascular dystonia, severe vascular spasms, atherosclerosis and many other diseases. A particular danger to health is arterial hypertension, which causes aching pain in the back of the head, and with a sharp change in pressure, dizziness occurs and the ears become blocked.
Patients with atherosclerosis note the presence of intrusive sounds in the ears, ringing, ticking, “clicking grasshoppers” and other repetitive and monotonous noises. Some people, who usually have weak blood vessels and a tendency to low or high blood pressure, may experience high weather sensitivity.
In this condition, about an hour to an hour and a half before the weather changes (mainly before precipitation, the onset of a strong thunderstorm or blizzard, or the appearance of powerful gusts of wind), a person notices a deterioration in health, which is accompanied by compression of the head, noise in it and in the ears, pain and weakness. A short time after the start of rain or snow, the patient Fr.
The condition is provoked by high sensitivity to changes in external atmospheric pressure and practically does not require treatment. In some cases, pain in the ears and head, noise, ringing and other extraneous sounds, as well as nausea, vomiting, foggy consciousness and loss of consciousness, delirium may be signs of severe head injury, hematoma or stroke. Often it is a micro-stroke that is masked by the appearance of a severe local headache and aching in the ears.
Some diseases, the symptoms of which are headaches and discomfort in the ears, can threaten the patient’s health, and in the absence of proper and timely treatment can lead to serious consequences.
What to do if both your head and ear hurt? If these 2 symptoms appear, you should seek help from a specialist, as severe pain may indicate a serious illness. In some cases, the person himself is to blame for the fact that he began to suffer from unpleasant sensations.
The feeling of stuffy ears and dizziness can occur frequently or periodically, and last from a couple of seconds to several hours. It is necessary to find out what this is connected with, since the problem can be quite serious.