- What kind of farsightedness can there be at different degrees of its development, symptoms and causes;
- Symptoms of farsightedness;
- Causes of farsightedness;
- Which makes things worse and makes you more vulnerable;
- Correction of farsightedness (hypermetropia);
- Diagnosis of farsightedness.
What is hypermetropia (farsightedness)?
Hypermetropia (farsightedness) is one of the types of clinical refraction of the organ of vision, in which light rays entering the eye, which is in a state of resting accommodation, are focused behind the retina.
In the “Norm”, the human eye, in a calm state, is able to provide a clear image of distant objects on the retina and, therefore, normal vision, this eye condition is called emmetropia (normal), with hypermetropia the image is not on the retina, but in the plane behind it, which and leads to a blurred image perceived by the retina.
Hypermetropia
is confused with presbyopia - a natural state of the visual system for every person, which occurs after 40 years, manifests itself as a decrease in the accommodative ability of the eyes. Due to the development of presbyopia after 40 years, patients with hypermetropic refraction are identified due to previously existing hidden farsightedness. The influence of the accommodative apparatus of the eye mitigates partially or even completely the negative effect of hyperopia (farsightedness) on the visual system.
The patient's age, degree of hypermetropia, the presence of astigmatism, the eye's ability to accommodate, and the presence of amblyopia reduce the resistance of the visual apparatus.
Farsightedness in very young children and the presence of hypermetropia is physiological.
Most full-term newborns have a hyperopic form of eye refraction and range from +2 to +3 diopters, a very small number of infants have hyperopia of more than +3.23 diopters. By the age of 5, most children's eye refraction approaches normal. The accompanying high degrees of astigmatism and farsightedness also tend to decrease by this age. In childhood, only an experienced ophthalmologist can identify a predisposition to childhood farsightedness when conducting a thorough diagnostic examination.
Ophthalmologists distinguish 3 degrees of hypermetropia (farsightedness):
- Weak (refraction up to +3.5 diopters);
- Average (refraction up to +6.0 diopters);
- High (refraction more than +6.0 diopters).
What are the types of ametropia?
There are several forms of ametropia, namely:
Myopia (myopia).
Farsightedness (hypermetropia).
Presbyopia (i.e., age-related farsightedness).
Astigmatism.
Myopia causes difficulty focusing on objects at a far distance. In most cases, a person does not have problems viewing nearby objects. This disease is not uncommon among teenagers. As a rule, at a young age, its symptoms arise due to non-compliance with the rules of labor and visual hygiene.
Farsightedness is fundamentally different from myopia, according to the characteristics of refraction. Thus, with hypermetropia, the patient does not encounter problems in perceiving distant objects, while he experiences discomfort and difficulties when working with objects located next to him. Similar symptoms appear in patients with presbyopia, with the difference that the pathology occurs in people over 40 years of age. Presbyopia is a consequence of decreased elasticity of the lens. As a result, it does not change the curvature of the refracted rays, which leads to unclear focusing. When a doctor puts “astigmatism” in the diagnosis line, it means that light rays enter the organs of vision along different meridians, which is why they are refracted with unequal strength. As a result, a person not only sees objects poorly, but also notices the deformation of their contours. Refractive errors and the degree of ametropia are usually calculated in diopters. As part of the diagnosis of myopia or farsightedness, the doctor determines by how many diopters the refractive power needs to be increased or decreased in order to normalize the focusing of the rays on the patient’s retina. The forms of these diseases are considered advanced when the corresponding indicator is 6 diopters or higher. Average values are 3-6 diopters, weak - up to 3.
The degrees of determination of astigmatism vary significantly from those described above. Thus, for a strong manifestation of the disease, indicators of more than 4 diopters are typical, for a weak manifestation - up to 2 diopters. Values between 2 and 4 diopters are classified as average.
What kind of farsightedness can there be at different degrees of its development, symptoms and causes
- With weak degrees of hypermetropia, high visual acuity is maintained both at distance and near. This occurs due to the constant tension of accommodation. But there may be complaints of fatigue, headache, dizziness, especially when working at close and medium distances.
- With an average degree of hypermetropia , distance vision remains good or is partially reduced, but near vision worsens significantly, silhouettes are blurry - one’s own accommodation is not enough for a clear vision.
- A high degree of farsightedness is accompanied by poor vision both far and near. Distant objects are not focused on the retina, since all the eye’s ability to accommodate and focus has been exhausted.
Any treatment for farsightedness , be it optical correction (glasses and lenses for farsightedness), contact correction, hardware techniques or surgery, is aimed at increasing the refractive power of the eye.
It is necessary for the image to arrive at a certain area of the retina. Farsightedness correction aims to focus light rays where they focus during normal vision!
Symptoms of farsightedness
It is very important to promptly identify hypermetropia at a young age. Because it is at this age that the human eye is able to compensate for a weak degree of hypermetropia due to accommodation reserves and provide a clear image on the retina, without the development of asthenopia. However, such an eye is prone to rapid visual fatigue.
With medium and high degrees of development of farsightedness, it can provoke the occurrence of blurred vision, asthenopia, impaired accommodation, impaired binocular vision, amblyopia and strabismus. All these symptoms are accompanied by blurred images, especially close up!
Causes of farsightedness:
- Irregular eye shape. The length of the anterior axis of the eye is less than normal, light rays are focused beyond the retina;
- Relatively flat corneal curvature;
- Insufficient refractive power of the eye lens;
- Increased density of the eye lens;
- Hereditary factors. Those at risk are those who have at least one parent with hyperopia (farsightedness). Ophthalmologists believe that poor vision is not inherited, but a physiological predisposition to it is inherited;
- Refusal from optical correction of hypermetropia from an early age.
What makes the situation worse and makes you more vulnerable:
- Eye strain
- Excessive eye strain
- Insufficient lighting
- Incorrect sitting position while reading
- Sitting for many hours at a computer, tablet, telephone, smartphone, game console
- Reading paper books in moving vehicles and in a lying position, as well as from the screens of smartphones, phones and tablets.
Clinical refraction - concept and its role for vision
Good vision in humans is due to several factors.
The transparency of the refractive media of the eye and the absence of pathological phenomena in them are the main factors in the formation of a clear image on the retina. The normal operation of the neuro-visual apparatus strives to correctly convey the image to the cortical analyzer. Despite the complex scheme for constructing a clear image, the main role belongs to the optical function of the refractive system of the eye, its refraction. Refraction is the unique property of the eye to refract visual rays at rest and bring them to a single point on the retina.
The cornea, lens, anterior chamber humor and vitreous body constitute a single refractive system of the eyeball. It is similar to a set of complex optical lenses of the eye, the refractive power of which is usually measured in diopters. This is a physical quantity and in total it equals 60 diopters.
In life, we encounter clinical refraction - the ratio of the dioptric power of the optical “set” of the eye to the length of the axis, that is, its horizontal size. Clear vision is achieved when all visual rays merge in the area of the macula of the retinal membrane. The visual rays may not reach the main spot or, conversely, converge into a single line behind the retina.
In these cases, a person will see, but the contours of the object and its image will be blurred. It turns out that the optical power of the refractive media of the eye changes if the visual rays are either longer or shorter than the optical axis of the eye.
Physical refraction and the anterior-posterior size of the eyeball, which is equal to the length of the optical axis, are purely individual, like any human personality. These differences determine one or another clinical refraction - emmetropia, myopia and hypermetropia.
Correction of farsightedness (hyperopia)
Types of hypermetropia correction:
- Spectacle correction;
- Contact correction
- Hardware techniques
- Surgical methods of treatment
regimen for hyperopia (farsightedness) must be planned taking into account the needs of the patient. The degree of hypermetropia, the presence of astigmatism or amblyopia, the state of accommodation and convergence, and the planned visual load should be taken into account.
Treatment is aimed at reducing the accommodative load, ensuring clear and comfortable vision, creating conditions for binocular vision, alleviating the symptoms of asthenopia, reducing the risk of developing amblyopia and strabismus.
Doctors at OPTICS-RADUGA actively use hardware methods for the treatment of hyperopia in childhood, together with spectacle correction of farsightedness and visual exercises.
Unambiguously answer the question: “which method of correcting hypermetropia is most suitable?” - impossible. Much depends on the individual structure of the eye and the general condition of the visual system.
But diagnosing the eye for farsightedness will provide a starting point.
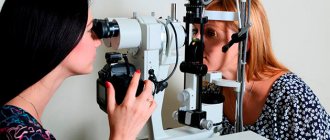
Diagnosis of farsightedness
To determine the degree of farsightedness and select the most appropriate treatment method, an ophthalmologist at OPTICS-RADUGA, using modern diagnostic equipment, will conduct the necessary vision diagnostics.
Diagnosis of hypermetropia includes:
- assessment of refraction and skiascopy (in childhood it is mandatory in conditions of paralysis of the ciliary muscle of the eye - cyclopegia);
- study of eyeball movement;
- presence of binocular vision;
- determination of the nearest point of view, convergence and study of the reserve of accommodation.
How to treat farsightedness?
The main principle of treating farsightedness is to achieve maximum improvement of vision, as a result, improve the quality of visual perception and prevent the occurrence of complications in the development of the eyeball.
For the proper development of the human body, good vision is important. Treatment of hypermetropia should include full correction and be combined with other therapeutic measures.
Correction with glasses
This method is the main one and should be used as early as possible. Hypermetropia detected in a child over three years of age must be corrected by selecting glasses. This is necessary for the full development of the eyeball, a special rate of which is observed between the ages of 12 and 14 years.
The correction should be selected so that the strength of the “plus” glasses is as close as possible to the natural degree of hypermetropia. Considering that this method involves an increase in clinical refraction, serious problems may arise that will be caused by individual intolerance to spectacle correction. Overcorrection can cause dizziness, headaches and refusal to wear glasses.
It is especially problematic to choose glasses for a child. Only with complete mutual understanding between the child and the doctor can proper correction be achieved. Sometimes wearing glasses causes a negative reaction from patients associated with their psycho-emotional mood.
Despite the inconvenience, spectacle correction is the only treatment method for children over 2 years of age.
Contact correction
This type of correction is convenient because it can “correct” any degree of hyperopia up to 100% of visual acuity. Moreover, contact lenses are always the same thickness, which cannot be said about glasses. Of course, young people and children leading an active lifestyle would like to use lenses. With this correction, good vision is ensured throughout the day and does not limit possibilities.
Considering that therapeutic correction begins to be used in children from 2 to 3 years old, and lenses can be used by children from 12, this type of treatment is not the main one. “Night” lenses are allowed for use from the age of 6, but usually, having already started wearing glasses and noting positive dynamics, parents and children do not change the chosen treatment path.
Treatment with devices and methods of physiotherapy
The use of hardware treatment for eyes suffering from refractive error has long been widespread and has lived up to expectations. Exposure to these methods improves blood supply to the ciliary body and its muscles, which are the main “workers” in constructing a clear image.
These methods, of course, will not get rid of farsightedness, but will only become good assistants in complex treatment. With a high degree of hypermetropia, hardware treatment is aimed at preventing complications such as amblyopia, strabismus, and impaired binocular vision. This type of treatment should be prescribed only by an ophthalmologist and carried out directly under his supervision.
Treatment with drugs
Drug treatment is used as one of the auxiliary methods in the complex treatment of farsightedness. Its principle is to improve the blood supply to the eyeball, eye muscles, and increase the adaptation of the eye to visual stress. It is allowed to use vitamin complexes in full from 7 years of age. The frequency and frequency of administration is determined by the doctor.
It should be noted that the ophthalmologist does not always prescribe medications, but is limited to the selection of glasses and hardware treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to adhere to exactly the treatment tactics that your doctor has chosen for you.
Laser correction
Currently, the use of a laser for correction is the only method that can restore vision. Every year the laser method is improved, reducing the recovery period to a minimum and the result to a maximum. Patients who agree to this treatment receive, in most cases, 100% vision for the rest of their lives.
Prices for diagnostic services and consultation with an ophthalmologist
| Type of medical service | Service price in rubles |
| Complete ophthalmological examination | 1000 |
| Complete ophthalmological examination of children | 1100 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye disease in an adult | 500 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye diseases in children over 3 years of age | 700 |
| Selection of simple glasses with a prescription | 500 |
| Selection of glasses for astigmatism with a prescription | 700 |
| Selection of progressive, office glasses with prescription | 700 |
| Selection of contact lenses with training and prescription | 1000 |
| Training in the use of contact lenses | 400 |
Treatment methods
Complete ophthalmological examination
Has your visual acuity decreased or are you experiencing increased eye fatigue? Do you suffer from watery or dry eyes? Do you have chronic eye diseases? Our clinic specialists will conduct a full examination and identify the presence/absence of eye pathologies.
Hardware treatment of eyes in children
Treatment with ophthalmological devices makes it possible to achieve a lasting therapeutic effect in young patients. In some cases, it is possible to completely get rid of pathologies such as amblyopia, impaired binocular vision, and false myopia.
Presbyopia or vision after 40
Presbyopia occurs after 40 years of age and is characterized by decreased vision at close distances. In order not to aggravate the situation, you should follow your doctor’s recommendations and use modern vision correction devices.
Selection of glasses
The selection of glasses is a necessary measure that will ensure the owner is able to see clearly. Experienced doctors select spectacle lenses taking into account many measured parameters and taking into account the slightest deviation from the norm.
Varilux progressive lenses
Varilux lenses are an excellent tool for correcting age-related changes that occur in the organs of vision after 40 years. They provide excellent, clear images regardless of the distance to the subject in question.
This is interesting
Blue light and optical coatings that reduce its transmission
What diseases can be diagnosed based on the condition of the eyes?
Preserving vision and eye health with Crizal Eyezen lenses
Protect your eyes from the sun with UV filter contact lenses
Which spectacle lenses should I choose? Choose your glasses with Crizal Corner
Prevention of farsightedness
Unfortunately, hypermetropia is a consequence of a violation of the anatomical dimensions of the eyeball . Therefore, prevention of this disease should begin long before the birth of the child. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and the absence of bad habits will contribute to the proper development of the visual organ.
If at least one of the parents has farsightedness, then their children will also have a similar vision defect.
An important preventive measure is a mandatory visit to an ophthalmologist. Preventive examinations are carried out regularly, starting when the child reaches one month of age. Observation by an ophthalmologist for detection of farsightedness should be 2 times a year. It is necessary to start treatment in a timely manner to avoid further progression of hypermetropia and the occurrence of complications. Wearing glasses has a direct purpose - therapeutic.
Constant use of spectacle correction from the age of 2 in most cases prevents the further development of farsightedness, and in some cases eliminates it, affecting delayed refractogenesis. “Plus” correction prevents the second stage of increased hypermetropia - the divergence of rays when the object in question approaches.
Which contact lenses to choose for farsightedness?
There are several reasons on which ophthalmic products are classified. One of them is the replacement schedule. According to this parameter, lenses are divided into:
- 1-Day Acuvue TruEye from Johnson & Johnson, Dailies AquaComfort Plus from Alcon, 1-Day and 1-Day Premium from Ochkov.Net.
- PremiO (Menicon) and AQUAMAX (Pegavision).
- Monthly Comfort - examples of monthly ophthalmic products with increased comfort. Optima FW, Sea Clear Vial are high-quality quarter lenses that can correct varying degrees of hyperopia.
Contact optics are also divided for other reasons. Lenses can be clear or colored. There are models that can correct farsightedness and change eye color. Such ophthalmic products are selected in the same way as regular ones - in the ophthalmologist's office.
Therapy for the disease
Source: myshared.ru The doctor’s main task is to create mechanisms that will allow the main focus of the eye and retina to be combined.
The standard method remains the creation of an additional optical system in front of the eye - glasses. There is also a surgical treatment method that helps change the refractive power of one of the anatomical structures of the eye. Correction with glasses consists of the use of the following types of lenses:
- spherical lenses mainly have a positive effect in the treatment of presbyopia;
- cylindrical lenses are prescribed for regular use in cases where the correct form of astigmatism is detected;
- prismatic elements correct heterophoria, the effect of double vision in pathologies of the muscular system and strabismus;
- hypermetropia therapy is carried out by correction with collective positive lenses;
- treatment of myopia includes prescribing diverging lenses;
People with the correct form of this disease need to wear lenses or glasses for astigmatism.
Types of lenses:
- soft lenses are used with a corrective effect to compensate for spherical ametropia, anisotropy, and presbyopia;
- lenses used for aesthetic effect.
Spectacle correction for ametropia
Spectacle correction - glasses are a special medical optical device consisting of lenses and frames. Depending on the type of refractive error (the process of refraction of light rays in the optical system of the eye), different types of lenses are chosen; for ametropia of varying degrees, the optical power of the lens also changes.
With hyperopia or farsightedness, and beyond it - a person sees unclearly, blurry near, and with a high degree of hyperopia both near and far) they use collective (positive) lenses, passing through which the light is focused on the retina.
For myopia or myopia (a form of refractive error in which light rays are focused in front of the retina; a nearsighted person typically sees well near and blurry at a distance), diverging (negative) lenses are used to help focus light correctly on the retina.
For mild myopia (up to -3 diopters (a unit of measurement for the otic power of a lens)), glasses are prescribed only for distance, i.e. a person puts them on when he needs to look far enough away from himself.
At higher degrees of myopia, glasses are prescribed for constant wear, while complete correction of myopia is not performed due to the possibility of overcorrection and deterioration of visual acuity. In some cases, for myopia, two types of glasses are prescribed - for near and for distance, with different optical powers of the lenses.
The selection of spectacle correction for astigmatism (a form of refraction in which there is a combination in the eye of varying degrees of the same refraction (myopic or hyperopic) or different types of it (mixed astigmatism)) is quite complicated - cylindrical and spherical lenses can be used.
Without proper correction, visual function with astigmatism is significantly reduced. Anisometropia (the presence of different types of refraction or different degrees of one type of refraction in the same person) is corrected with glasses if the difference between the optical powers of the eyes does not exceed 2 diopters.
Reference
If the difference is greater, it is recommended to wear contact lenses or special glasses with two lenses.
Today, spectacle correction is the most common and accessible type of correction due to its relative cheapness and ease of use. But there are situations when only spectacle correction is recommended or, conversely, they are advised to choose another type of correction.
Indications for spectacle vision correction:
- high degree of myopia;
- high degree of hypermetropia;
- astigmatism from -6 to +6 diopters;
- presbyopia - a decrease in near visual acuity that occurs after 40-45 years, is considered a natural sign of aging;
- childhood;
- intolerance to contact lenses;
- impossibility of surgical (laser) correction of ametropia.
Contraindications to spectacle correction:
- risk of possible eye injury (sports, outdoor games);
- professions that require a fairly large field of view, such as pilots or firefighters;
- anisometropia (with a difference of more than 2 diopters between the eyes);
- individual intolerance to glasses.
Contact (lens) vision correction is a change in refraction using contact lenses. They are called contact because they are in direct contact with the cornea - the transparent membrane of the eye.
A contact lens is a small, cup-shaped lens that is inserted behind the lower eyelid and rests against the cornea.
Currently, contact correction has become very widespread, because it freely allows you to engage in active sports, does not limit the field of view, and does not put pressure on the bridge of the nose and ears, unlike glasses.
There is an opinion that lens correction is only suitable for myopia, but this is not true. Any refractive error can be corrected with contact lenses. It’s just that for some disorders, for example, presbyopia, their use is inappropriate, because patients suffering from presbyopia wear glasses only for near work or for reading.
Currently, lenses are made from high-quality material (silicone hydrogel), which freely passes oxygen to the cornea of the eye.
The patient can choose lenses that are suitable specifically for him: hard or soft (mostly soft ones are used), and lenses are also divided depending on the period of wear (two weeks, 3 months, etc.). One-day lenses are widely used, which a person takes off in the evening, throws away, and puts on other lenses the next day.
A person chooses a convenient mode for wearing lenses: daytime wear (the lenses are removed at the end of the day), flexible wear (if necessary, you can leave the lenses on for 1-2 nights), extended wear (the lenses are not removed for several days in a row), continuous wear (the lenses are used within 30 days).