The process of removing urine from the body
Let us also consider in general terms the process of urine excretion in a healthy person.
- The liquid, in the mass of which waste products are removed from the body, travels a long way - through the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra.
- Urine accumulates in the bladder, a muscle sac whose volume is about 300-600 ml. As it accumulates, it is released by the body.
- The fluid is discharged through the urethra (urethra).
So why does urine smell strong? The most common reason is that one of the organs that we listed above has some problems in their work. But other things can also provoke an unpleasant odor.
Strong odor due to natural causes
The smell of urine is one of the natural aromas. However, in a healthy person who goes to the restroom on time, it practically does not occur. Urine with a pungent odor in the absence of pathologies or negative internal factors can only occur if a person has been holding back for a long time. For example, in the morning, after a long sleep, the liquid changes its smell to a more pronounced one. But how can anything cause a problem if it’s definitely not stagnant liquid?
A strange aroma in the area of the urinary system appears in both women and men. However, for representatives of the fairer sex it is more typical due to anatomical and physiological characteristics. The proximity of the genital organs to the excretory organs and the deep location of the urinary canal means that a repulsive odor can appear in just a few hours.
If the smell of urine has changed, first of all, it is worth checking whether this is caused by internal, non-pathogenic reasons. In a third of cases, the sweet smell of urine or rubber is the result of one of several minor factors:
- lack of personal hygiene;
- stale underwear;
- dehydration of the body;
- eating certain foods that increase urine and sweat odors;
- incontinence during sleep or stress.
All of these problems can be dealt with quickly and easily, but this does not mean that they do not need attention. It is important to find and eliminate the cause of the deviation.
Many women believe that to maintain healthy external genital and urinary organs, it is enough to take a shower once a day.
Lack of hygiene is a common problem even in the 21st century. It can lead not only to the appearance of an unpleasant odor, but also to the development of infection or inflammation. Many women believe that to maintain healthy external genitalia and urinary organs, it is enough to take a shower once a day. But gynecologists recommend washing yourself twice a day: morning and evening. Bacteria multiply quite quickly, especially in places like the perineum . Within 24 hours, they can create a sour or sweet odor that is not easy to remove. Therefore, hygiene must be ensured every 12 hours.
Another common internal cause is lack of fluid in the body. With it, the concentration of urea in the urine increases. The discharge becomes more brightly colored, thicker, and has a pungent odor. Such changes may appear if you drink less than 1.5-2 liters of water per day.
The last internal factor that leads to the appearance of fishy aroma is the consumption of certain foods. This is not necessarily junk food (fatty foods or fast food). Even seemingly harmless products can cause problems:
- red meat (if consumed in excess);
- asparagus (the smell remains for 3-4 hours from the moment of consumption);
- onion and garlic.
Sweets, as well as honey, juices, carbonated drinks and any other food containing sugar can also increase the odor. Sugar is excreted along with urine, and a small part of it remains in the perineum area. This environment is favorable for the development of bacteria. Reproducing quickly, they secrete foul-smelling waste products. At the same time, a woman may not notice their activity, since in the early stages of development, bacterial colonies do not yet cause pain, discomfort and inflammation.
Only a specialist can find out exactly what the unpleasant odor means. If you cannot get rid of it on your own, resorting to personal hygiene and improving nutrition, you should definitely visit a doctor.
The smell of urine often accompanies women infected with sexually transmitted infections
Certain foods
Why does urine smell - strong, pungent, unpleasant? The reason may lie in your recent lunch or dinner.
- Spices (particularly garlic) that emit a strong aroma. These seasonings can also give urine a distinct odor.
- Seafood. Especially if you have eaten them in large quantities. The statement applies most of all to mussels - both fresh and marinated.
- The most common food cause of strong urine odor is asparagus. No matter what form you use this plant, it will cause a sharp, unpleasant odor in your discharge. However, this kind of deficiency can be easily eliminated - add a little sea salt to the dish with asparagus before eating.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on the cause. Often the most effective way is to reduce your coffee intake. People who drink more than 4 cups of coffee per day should drink more water to balance their caffeine intake.
If other foods and drinks affect the smell of urine, it is recommended to avoid or limit their consumption.
Some diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and bladder infections, can change the smell of your urine. Call your doctor if your coffee-smelling urine is accompanied by:
- pain, burning or discharge when urinating;
- increased frequency of urination;
- decreased rate of urination;
- swelling and pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the lower back;
- nausea, vomiting and diarrhea;
- fever or chills;
- flu-like symptoms lasting longer than two weeks.
Systemic disturbances in the functioning of organs
Why does human urine smell very strong? As we discussed above, this may be due to a systemic dysfunction of organs. Especially those systems through which urine passes.
The most common causes are the following diseases:
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process occurring in the kidneys. It can be either a primary form (the disease affects healthy kidneys) or a secondary form (pyelonephritis is a consequence of another kidney disease). A change in the smell of urine will not be the only sign here. The patient will complain of sharp, nagging pain in the lower back. The disease is quite serious - you need to seek help from a doctor as soon as possible!
- Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder. The disease can be either infectious or non-infectious in nature. The mucous membrane of the muscle sac becomes inflamed, which leads to disruption of its functioning - the patient’s urine will become cloudy and have sediment. An unpleasant ammonia odor will also be felt from freshly collected urine. Sometimes “medicinal” cystitis occurs - the disease is caused by long-term use of large doses of medications that irritate the bladder mucosa. In particular, these are “Urotropin”, “Phenacetin”. The urine will have a sharp “pharmacy” or “hospital” smell.
- Urethritis is an inflammation of the walls of the urethra (urethra). A disease of bacteriological, viral nature. In addition to the strong smell of urine, the patient will notice noticeable pain when urinating, purulent, bloody spots in the urine. Moreover, the smell of this disease appears as the very first of all symptoms.
- UTI (urinary tract infection). Due to the anatomical proximity of the organs, diseases of these systems are in some cases interrelated. Vaginosis, chlamydia, gardnerellosis are the causes of the sharp unpleasant odor of urine. The collected urine here will also be cloudy when held up to light.
Causes of olfactory hallucinations
Olfactory hallucinations are found in people with mental disorders, neurological diseases, alcoholism or drug addiction. The main causes are acute psychotic states and organic brain damage. In both cases, there is a pathological activation of the brain structures responsible for processing olfactory stimuli and forming the corresponding image of perception. Therefore, people who smell imaginary aromas may describe them in detail and react with loss of appetite, a feeling of nausea, or increased salivation.
Neurological diseases
Organic damage to the brain structures responsible for olfactory perception is the most common cause of hallucinations. Observed in local traumatic and tumor processes, neurodegenerative pathologies, epileptic foci. The possibility of forming a critical attitude of patients towards imaginary odors depends on the severity and nature of the disease; the hallucinatory origin is recognized by patients with reversible forms of pathologies (injuries, regressing tumors). The following are considered possible causes of olfactory hallucinations:
- Epilepsy.
Olfactory hallucinations are often diagnosed in people with epilepsy. The causes of this symptom continue to be studied. According to one of the confirmed theories, the basis is increased ictal activity in the anterior parts of the piriform cortex (a region of the olfactory system). Its forced stimulation leads to the development of convulsive seizures. Approximately 1% of patients experience olfactory auras, which are characterized by the smell of sulfur, burnt rubber, and feces. - Traumatic brain injuries.
Olfactory hallucinations and impaired odor recognition are observed with damage to the cortical olfactory cortex in the temporal and frontal mediobasal regions. With severe injuries, these disorders occur during the recovery period in 48% of patients, with moderate injuries – in 15%. Typically the perception of smoke, hydrogen sulfide, burning - neutral or unpleasant imaginary stimuli. - Alzheimer's disease.
Patients are diagnosed with olfactory disorders, the most common of which are impaired identification and discrimination of odors. Olfactory hallucinations are detected in 1.2% of patients. They often become the basis of persecutory delusions, such as ideas about spilled poison or poisonous gas released by neighbors. The reason is atrophic changes in the cerebral cortex, which affect the primary olfactory cortex, areas of the hippocampus, thalamus and hypothalamus. The degree of impairment of the sense of smell directly correlates with the severity of the decline in speech and intelligence. - Brain tumors.
Hallucinations of various types develop with neoplasms in the area of the temporal lobes of the cortex or the bottom of the third ventricle. Olfactory phenomena are represented by the smells of burning, rotten eggs, and smoke. Their localization is determined near the nose, from the mouth, from the body. With tumors of the left hemisphere, long-term anxious depression increases, which is replaced by euphoria when the tumor spreads to the frontal region of the right hemisphere. - Parkinson's disease.
The causes of olfactory disturbances in Parkinson's disease continue to be studied. According to recent studies, disorders are associated with atrophic processes in the structures of the limbic system - in the piriform cortex, amygdala nuclei. Many patients have a reduced ability to recognize odors. Olfactory hallucinations are much less common.
Mental disorders
Olfactory hallucinations are characteristic of the acute phase of mental illness. For some pathologies, for example, for bipolar affective disorder, they are specific markers of an impending exacerbation. With a sluggish process, changes in the olfactory function are hardly noticeable. In the prodromal period, they serve as harbingers of severe psychotic states and behavioral disorders. The following mental illnesses are the causes of olfactory hallucinatory symptoms:
- Schizophrenia.
In schizophrenia, disruption of the olfactory system is associated with pathological changes in the cortical and peripheral areas of the analyzer. There is a decrease in innervation and distortion in the regulation of intracellular nerve signal transmission. Most patients experience odor recognition disorders, and approximately 35% have olfactory hallucinations. Patients perceive odors of a different nature, the origin of which is often interpreted as delusional ideas. - Bipolar disorder
. The brain cortical areas responsible for emotions and the perception of smells overlap each other. Studies of olfactory function in depressed patients have revealed a decrease in response to odors that provoke an emotional response. Many patients found it difficult to determine the location of the source, felt unpleasant odors more strongly, and almost did not feel pleasant ones. Severe depressive episodes with psychotic symptoms are often accompanied by delusions, olfactory hallucinations, and depressive stupor. Typical smells are of rotting flesh and dirt. - Stimulant psychosis
. Psychotic disorders caused by taking psychostimulants are acute, with paranoid ideas, hallucinations, and disorganization of behavior. The causes of olfactory hallucinations are the use of large doses of the drug, chronic drug addiction. For example, olfactory perceptual deceptions with relational delusions often occur during the development of methamphetamine psychosis. In rare cases, hallucinatory symptoms occur when taking therapeutic doses of psychostimulants under medical supervision. - Alcoholic psychoses
. Olfactory hallucinations can occur as part of alcoholic delirium - a state of clouded consciousness during the period of alcohol withdrawal after prolonged continuous use. Most often, they are accompanied by delusions of poisoning: a person smells poisonous gas or poison, is alarmed, hides at home, or seeks protection from others. The causes of hallucinosis are acute alcoholic psychosis, which develops at the height of intoxication or with a hangover, as well as subacute meta-alcoholic psychosis, lasting several months.
In men and women
The characteristic putrefactive smell of urine can indicate diseases of the genital area. This is a cause for concern for both women and men. This means that inflammatory foci have formed somewhere in the genitourinary system, surrounded by suppuration. This may also speak about rectal fistulas - rectal, vesical fistulas.
The sharp unpleasant smell of urine in men is one of the symptoms of prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland). The patient also notes pain in the perineum, sexual dysfunction, and difficulty urinating.
If a woman, especially after recent sexual intercourse, diagnoses urine with an unpleasant odor, this may be evidence of the presence of a sexually transmitted infection in the body, an imbalance of the vaginal microflora. For the same reason, some women note this symptom after childbirth.
Diagnosis and which doctor to contact
An accurate diagnosis can only be made after a comprehensive examination of the patient. To get diagnosed correctly, you need to know which doctor to see.
Depending on the accompanying symptoms, you will need to undergo examinations by the following specialists:
An accurate diagnosis can only be made after a comprehensive examination of the patient.
- endocrinologist;
- urologist;
- gynecologist;
- venereologist;
- ultrasound specialist;
- infectious disease specialist
First of all, you need to see a therapist. He will collect a history of the disease and refer the patient to doctors who, in his opinion, can identify the disease. What determines the list of specialists who need to be visited? Whether there are signs of inflammation, fever, infection, endocrine changes or diabetes.
If you suspect an STD, the patient must visit a gynecologist and venereologist. A specialist will need to take a smear and also conduct a visual examination of the genitals. If a virus is suspected, a biochemical blood test may be needed.
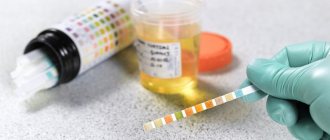
If inflammation of the bladder or kidneys is suspected, an ultrasound examination is performed. It will show whether these organs are enlarged and whether there are any negative changes in them: cysts, darkened areas. If an infection is suspected, urine tests are also taken for bacteriological culture, and a smear is taken from a gynecologist.
An endocrinologist should be visited if you have symptoms of diabetes. In this case, blood is also donated for sugar. Based on the results of this analysis, the use of insulin may be prescribed.
Dehydration
Why does urine smell? The pronounced ammonia smell of urine is a rather alarming sign. It may indicate total dehydration of the body! The reason is that water imbalance makes the urine more concentrated than normal.
Dehydration is not always caused by a critical situation or serious illness. It can even affect a completely healthy person. If we are carried away by work or other occupation (and even more so physically), on a hot and stuffy day we forget to drink the required amount of water. Let us remind you that the minimum norm for a person per day is 1.5 liters.
Measures to prevent the appearance of acetone odor
At the end of the article, a few words about what to do to prevent and protect the body from the appearance of acetone in the urine. The most important thing is to maintain an active and healthy lifestyle.
These include moderate physical activity, swimming and contrast showers as ways to harden the body, adequate sleep for at least 7-8 hours a day, walks in the fresh air to improve immunity and prevent anemia, proper drinking regimen, and avoid stressful situations. If acetone reappears in the urine, it is recommended to undergo diagnostics of the whole body at least 2 times a year.
Starvation
The consequence of fasting is acidosis with all the sad consequences that flow from it. The human body needs a certain amount of carbohydrates every day. When there is a shortage, the deficiency begins to be compensated from preliminary reserves of fatty acids.
Hypoglycemia (insufficient blood glucose) develops. The blood mass becomes acidic, which leads to acidosis. The consequence is that ketone bodies are excreted in the urine. They will give the urine a strong smell of acetone.
Other diseases
Why does urine have a strong smell? The reason may also be diseases that, at first glance, have nothing to do with the urinary tract:
- Diabetes. A symptom of diabetes is dehydration, which causes urine to smell. If the form of the disease is severe enough, then a certain sweetish smell emanates from the urine, somewhat reminiscent of apple. This indicates an increased content of ketone bodies. The most dangerous signal is when a diabetic’s urine begins to characteristically smell like acetone. Here the level of ketone bodies went beyond the maximum norm, and acidosis began in the body. If emergency measures are not taken in this case, the patient may fall into a diabetic coma.
- Liver failure. Serious disorders affecting the functions of the organ, which can occur with viral acute hepatitis, toxic, alcoholic, drug and other lesions. The efficiency of the liver system is also reflected in urine. With the so-called jaundice, the urine has an atypical thick odor and becomes the color of dark beer or even a brownish, greenish hue.
- Leucinosis. Another name is “maple syrup disease.” This is a hereditary pathology, which is characterized by a violation of the metabolism of amino acids in the body - valine, leucine, isoleucine. The second name of the disease was given precisely by the characteristics of urine. The urine begins to smell somewhat like maple syrup. It is caused by the presence of a substance in the urine that appears from leucine.
- Trimethylaminuria. A rather rare disease characterized by a “fishy” smell of urine. What is the reason? The human body accumulates the substance trimethylamine, which is characterized by the shade of rotten fish.
- Phenylketonuria. The urine here will have a "mouse" smell. A genetic disease in which a person has difficulty metabolizing phenylalanine (one of the amino acids) in the body. The concentration of the substance in the urine gives the characteristic odor.
Smell of fish
While the properties of urine after eating asparagus were a natural consequence of metabolism, urine that has a fishy odor, although physically harmless, may be a more burdensome illness.
Trimethylaminuria (TMA), also known as fish odor syndrome, is a rare metabolic disorder in which the body lacks the FMO3 enzyme. This compound is involved in the conversion of trimethylamine, which is found, for example, in fish. When FMO3 is deficient or impaired, the body cannot break down TMA. Excess substance is excreted in the urine and then found in saliva.
Fish odor syndrome
Although the first diagnosed and medically documented case of this disease dates back to 1970, there are many references to this unpleasant disease in the literature. The Mahabharata, an ancient Hindu poem, describes a beautiful girl who exuded a fishy smell. Also in Shakespeare’s comedy “The Tempest,” one of the characters comments on Caliban’s illness: “What do we have here, a man or a fish? Alive or dead? It’s fish, it smells like fish!”
For unknown reasons, the disease is more common in women. Scientists suspect that female sex hormones such as progesterone and estrogen worsen symptoms.
Although there is no effective treatment for trimethylaminuria, patients are not doomed to social marginalization. By maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding legumes, certain fish, meats and foods containing nitrogen, carnitine and sulfur, you can reduce the amount of odor produced. In addition, antibiotics that reduce the concentration of bacteria in the digestive system and the use of acidic skin products with a pH of 6.5 will help.
Why is my baby's urine smelly?
Let's look separately at cases involving children:
- Only newborns will have no odor in their urine. As you grow older, your urine will take on characteristics characteristic of adult urine.
- An unpleasant odor of urine in infants is one of the signs that the child has a genetic disease.
- For example, why does the urine of a 5-year-old boy smell sharp? This may indicate a genitourinary disease in the child.
- Urine in children acquires a pungent odor at high temperatures and dehydration (often these factors are related). In such cases it becomes more concentrated. This will be the cause of the smell. Try to give your baby as much fluid as possible.
- If a baby is breastfed, the smell of his urine often reflects what the mother ate. We have already said which products give urine a pungent odor.
Even if the reason seems too banal to you, it would not be a bad idea to take your child for a consultation with a pediatrician.
Why does my cat have stinky urine?
In conclusion, about our little brothers. Reasons why a cat has smelly urine:
- Just like in humans, the strong smell of ammonia from urine will indicate dehydration.
- The animal has entered the period of puberty and hunting. The smell is caused by increased activity of the sex glands.
- The cat's diet is incorrect. The reason is a protein imbalance.
- Disease of a genitourinary nature. Everything here repeats the human situation.
- Hormonal diseases, cancer. An alarming sign is a putrid smell. Often he alone can speak about a serious pathology.
- Severe stress. A pungent odor in this case is a disruption in metabolic processes.
If an unusual smell appears for no apparent reason and does not go away within 2 weeks, this is a reason to take the animal to the veterinarian.
So we have figured out all the reasons for the strong smell of urine. Even if some of them are harmless, this is still a sufficient reason to consult a doctor.