- Causes of neurogenic bladder
- How to treat a neurogenic bladder?
- What diseases can it be associated with?
- Treatment of neurogenic bladder at home
- What medications are used to treat neurogenic bladder?
- Treatment of neurogenic bladder with traditional methods
- Treatment of neurogenic bladder during pregnancy
- Which doctors should you contact if you have a neurogenic bladder?
Causes of neurogenic bladder
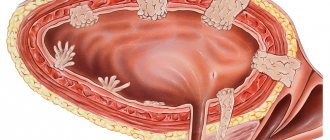
Neurogenic bladder is a group of urinary disorders manifested by impaired bladder emptying in individuals with a normal anatomical structure of the bladder and urethra.
Otherwise, neurogenic bladder is also called neurogenic voiding disorder or neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Neurogenic bladder is divided into two groups:
- caused by inorganic changes in the spinal cord or lower urinary tract,
- caused by organic damage to the terminal part of the spinal cord.
Seven clinical variants of nonorganic bladder dysfunction have been identified:
- subclinical (hidden) hyperreflex bladder - observed in 14-17% of patients with functional urination disorders; the disease is manifested by involuntary urination during sleep, urinary incontinence and a combination of similar symptoms;
- normoreflex bladder - observed in 4.5-5.5% of cases, combined with increased contractile activity of the urethral sphincter, manifested by involuntary urination during sleep, urinary incontinence, or a combination thereof;
- hyperreflexive non-adapted bladder - observed in 30-36% of patients with urination disorders of neurogenic origin; manifested by frequent (with an interval of 0-2.5 hours) urination in small portions of urine, urinary incontinence, and the presence of residual urine; characterized by intermittent intravesical hypertension during the entire period of bladder filling;
- hyperreflexive adapted bladder - observed in 29-31% of patients, characterized by the same symptoms as the non-adapted one, but less pronounced; the existing detrusor hyperreflexia is not accompanied by intermittent intravesical hypertension and the state of adaptation of the bladder to the filling phase is disturbed to a lesser extent;
- the fifth, sixth and seventh clinical variants of neurogenic dysfunction of the urinary tract are characterized by hyporeflexia of the muscles that push urine out; the differences lie in the fact that the presence of a hyperreflex bladder is combined with normal function (fifth clinical option), increased contractile activity (sixth option) and insufficiency (seventh option) of the urethral sphincter).
Clinically, all of these variants of the hyporeflex bladder are characterized by rare urination (2-3 times a day) and the release of large portions of urine (up to 500 ml or more), the presence of residual urine (up to 250 ml or more), as well as various types of urinary incontinence .
Neurogenic dysfunctions of the bladder of organic origin include all forms of neurogenic disorders of urination and urinary incontinence, united by a common etiological feature - separation of the bladder by the cortical centers of the brain, which ensure the controlled nature of urination. The most important and most common types of dysfunction of the bladder are those whose occurrence is caused by organic pathological changes in the spinal and peripheral conduction innervation. There are 4 main groups of spinal cord dysfunctions:
- I - with congenital malformations of the terminal part of the spinal cord and spinal column;
- II - with traumatic injuries of the spinal cord of extramedullary fibers of the cystic plexus;
- III - with inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the spinal cord and its membranes;
- IV - with damage to the intramural nervous system of the bladder.
Causes of neurogenic bladder include :
- congenital defects of the final part of the spinal column (spina bifida, agenesis and dysgenesis of the sacrum and coccyx);
- inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the spinal cord and its membranes, peripheral nerves and nerve plexuses, intravesical nerve endings (myelitis, poliomyelitis, meningitis, encephalomyelitis, syphilis, tuberculosis of the nervous system);
- damage to elements of the intravesical nervous system in obstructive uropathy in children;
- tumors and injuries of the spinal cord and spinal column, osteochondrosis;
- brain injury, cerebrovascular accident;
- damage to the nervous system by arsenic preparations, salts of heavy metals, endogenous and exogenous intoxication of the nervous system;
- long-term use of psychopharmacological and other drugs;
- denervation of the bladder due to massive surgical interventions in the pelvic organs.
The main role in the development of neurogenic urination disorders is played not so much by the nature of the cause as by the level of distribution and degree of damage to the nerve pathways and centers that provide the function of urination.
Depending on the level of damage to the innervation of the bladder and changes in the tone of its muscles, central, spinal and peripheral (inside and outside the organs) forms of urination disorders are distinguished, as well as hypo- and atonic neurogenic bladder.
There are also reflex, hypo-, hyper- and are-reflex, sclerotic neurogenic urination disorders.
Patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction complain of:
- feeling of heaviness in the pubic area;
- urinary disturbance
- inability to completely empty the bladder,
- paradoxical urinary retention (ischuria) when the bladder is full, involuntary urination;
- weak stream of urine even when pressing on a full bladder;
Overactive Bladder
Sign up for a consultation by phone
Or fill out the form online
Make an appointment Neurogenic bladder dysfunction cannot be considered as an independent disease in the generally accepted sense of the word. This is a collective syndrome that combines conditions that arise in connection with congenital or acquired lesions at various levels of the nerve pathways and centers that innervate the bladder and provide the function of voluntary urination. All forms of neurogenic dysfunction are united by the fact that the bladder as a working system is disconnected from the cortical centers that ensure the voluntary nature of urination in humans.
Classification of neurogenic bladder dysfunctions:
- Uninhibited cortical bladder;
- Reflex spinal bladder;
- Unadapted bladder;
- Areflex bladder;
- Mixed (areflex-non-adapted) bladder;
- Shriveled bladder.
Symptoms of Neurogenic Bladder:
A typical manifestation of urination disorders when brain lesions are localized above the micturition center located in the pons of the brain is detrusor hyperactivity. Frequent urination at short intervals, urge urinary incontinence, strangury are typical symptoms of detrusor overactivity. Occurring at any time and often in an inconvenient place, these symptoms bring significant anxiety to patients. The mechanism of occurrence of these symptoms is a decrease or loss of voluntary control over the act of urination and a decrease in the adaptive ability of the detrusor. At the same time, the reflex arc, including the center located in the sacral region and the center of urination in the area of the cerebral pons, remains intact. In other words, with detrusor overactivity, despite the preservation of the independent act of urination, the accumulation of a sufficient amount of urine in the bladder becomes impossible.
When the suprasacral region is affected, patients may experience a lack of supraspinal suppression of autonomic contractions of the bladder, which is accompanied by detrusor overactivity up to urge urinary incontinence, as in the case of cerebral disorders. At the same time, spinal injuries also have their own characteristic features in the form of damage to the reticulospinal tracts coming from the pons and participating in the synergistic integration of the activity of the urethral sphincter and detrusor. In addition to involuntary contractions of the detrusor, at the same time there is a contraction of the striated urethral sphincter, which causes urinary retention and is accompanied by an increase in intravesical pressure. This condition is called detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia.
Clinical manifestations of suprasacral spinal cord lesions consist of irritative (frequent, imperative urination, sometimes to the point of imperative urinary incontinence, combined with strangury) and obstructive (interruption of the urine stream, often to the point of complete retention of urination, which may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and perineum) symptoms . Detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia is characterized by incomplete emptying of the bladder with the appearance of residual urine, which increases the possibility of developing inflammatory complications of the bladder and upper urinary tract, as well as urolithiasis. In addition, at this level of damage, incomplete relaxation of the striated sphincter and its paralysis may be observed, which is manifested by a severe form of urinary incontinence (sphincteric incontinence).
Damage to the sacral region causes loss of reflex contraction of the detrusor (detrusor areflexia) and loss of contractility of the striated urethral sphincter. In this situation, patients complain of a lack of urge to urinate. In the absence of normal bladder emptying, patients subsequently develop urinary incontinence due to bladder overflow. Another option for urinary dysfunction in sacral injuries is a decrease in the contractility of the detrusor, which causes impaired bladder emptying and is manifested by difficulty urinating with a sluggish stream with a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. All of the above symptoms from the lower urinary tract can lead to various disorders of the upper urinary tract - vesicoureteral reflux, dilation of the ureters and pelvis, pyelonephritis and chronic renal failure.
Due to the fact that denervation of the bladder, at whatever level it occurs, leads to pronounced trophic disorders, the course of the disease is often complicated by interstitial cystitis, causing sclerosis and shrinkage of the bladder (microcysts). This severe complication increases the risk to the kidneys and in some cases requires special surgical interventions to increase bladder capacity.
Causes of Neurogenic Bladder:
In the etiology of neurogenic bladder dysfunctions, the level and extent of damage to the nervous system are of primary importance. Thus, trauma, tumors, inflammatory-degenerative diseases that cause transverse dissociation of the spinal cord in the region of the lumbosacral segments or higher will lead to fundamentally the same, although having specific shades, urination disorders.
The causes that directly reproduce denervation can be combined into several groups:
- Inflammatory-degenerative diseases and tumors of the brain and spinal cord and their membranes, extraspinal and intramural centers of the bladder and pathways (particular forms - encephalitis, diabetic and post-vaccination neuritis, cholesteatomas, tuberculomas, demyelinating diseases, etc.).
- Traumatic injuries to these same formations in the broadest sense (stroke, ruptures, compression, destruction, including injury to the peri-vesical nerve formations during difficult childbirth or surgical interventions on the pelvic organs).
- Congenital defects of the terminal spine and spinal cord.
- Damage to the intramural nervous system of the bladder in obstructive uropathy and congenital underdevelopment of the cystic ganglia of the brain (megalocysts).
Treatment of Neurogenic Bladder:
Treatment of neurogenic bladder dysfunction continues to be a complex and largely unsolved problem. The disease affects the most complex mechanisms of the relationship between the detrusor-sphincter systems and disrupts all three functions of the bladder - accumulation, retention and expulsion of urine.
Until recently, the task was not even set to provide a treatment regimen based on pathogenetic principles and approaches. It still has a pronounced symptomatic orientation.
There are three main areas of symptomatic treatment: medication, electrical stimulation and symptomatic surgery. However, the main type of treatment for urological disorders in patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction is the use of pharmacological agents. It depends on disturbances in the urodynamics of the lower urinary tract, leading to difficulty in storing urine in the bladder or emptying the bladder.
Recently, positive effects have been noted when using low-intensity laser irradiation.
However, neither drug treatment and stimulation, nor symptomatic operations provide satisfactory lasting results. Therefore, in the last 20 years, persistent attempts have been made to develop treatment methods based on the pathogenetic principles of restoring the innervation of the bladder. The variety of forms of neurogenic dysfunctions does not allow us to successfully solve all issues of pathogenetic therapy using one method. The entire complex of pathogenetic therapy must be applied as early as possible, before secondary complications occur in other organs and systems, as well as degeneration of local neuromuscular structures.
Benefits of the service
Convenient work schedule
We work until late in the evening to make it convenient for you to take care of your health after work
No queues
The patient registration system has been debugged over many years of work and works in such a way that you will be seen exactly at the chosen time
Cozy interior
It is important to us that patients feel comfortable within the walls of the clinic, and we have done everything to make you feel comfortable
Attention to the patient
At your service there are attentive staff who will answer any question and help you navigate
How to treat a neurogenic bladder?
Treatment of a neurogenic bladder is a complex set of procedures. Treatment consists of restoring urination, maintaining sufficient bladder capacity and addressing the inflammatory process. Treatment of a neurogenic bladder of nonorganic origin should be comprehensive, aimed at correcting all identified disorders, and multi-stage. Its purpose is usually:
- maintaining normal kidney function,
- preventing (or treating) infection,
- ensuring urinary continence.
Treatment is based on periodic catheterizations under sterile conditions along with selective use of anticholinergic drugs. This helps reduce pressure in the bladder and prevents uninhibited bladder contractions.
The following areas of treatment for neurogenic bladder are distinguished:
- medicinal effects on the nervous system of the bladder with pharmacological drugs of directed mediator action + electrical stimulation;
- surgical palliative treatment;
- surgical palliative-symptomatic treatment.
Drug therapy is carried out in cases where lesions of the sympathetic or parasympathetic innervation predominate. The prescription of pharmacotherapeutic agents is combined with intraanal electrical stimulation. For its implementation, special devices “Tonus-1”, “Tonus-2”, “Bion-3” and the like are usually used. Direct electrical stimulation is carried out using a catheter-electrode, which is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. The electrode contacts the wall of the bladder through an electrolyte introduced into its cavity or directly. During neurotropic stimulation, platinum needle electrodes are inserted percutaneously into the area of the nerve roots at the level of the third segment of the spinal cord. If electrical stimulation produces a positive effect with this technique, implantation of electrodes in the cauda equina area is carried out surgically.
All methods of treating neurogenic bladder in this group of patients can be combined into 4 groups:
Influencing the effective parts of the autonomic nervous system at the segmental level or directly on the muscle that pushes urine out and the sphincter of the urethra. The goal is to restore the normal detrusor-sphincter ratio, reservoir function of the bladder and controlled urination by reducing or increasing the tone, contractile activity and reflex excitability of the muscle that pushes urine out, and to normalize the closing functions of the sphincter. They use - M-anticholinergics, M-cholinomimetics, anticholinesterase drugs and antiprostaglandin drugs, α-adrenolytics, α-adrenostimulants, calcium ion antagonists.
Influencing the efferent parts of the autonomic nervous system through the influence of pharmacological drugs against the background of preliminary activation of metabolic processes. Adrenergic agonists and antagonists of potassium ions (ephedrine hydrochloride and isoptin), as well as coenzymes and cholinomimetics (cytochrome C for injection, riboflavin mononucleotides, aceclidine) are used simultaneously.
Causing activation of detrusor-stabilizing reflexes in their effective link and restoring the normal detrusor-sphincter ratio. Various forms of electrical stimulation of the anal sphincter, perineal muscles and bladder are used.
Influencing the higher centers of autonomic regulation through the use of neurotropic antidepressants, tranquilizers, and metabolic therapy.
Treatment of neurogenic bladder of organic origin is ineffective. It is mainly aimed at prolonging the patient’s life. The cause of death of the patient may most likely be not so much dysfunction of the bladder as complications that occur in the upper urinary tract and kidneys, which leads to pyelonephritis, urosepsis and chronic kidney failure.
When conservative treatment is ineffective, it becomes necessary to choose a surgical treatment method.
In the final stage of the disease, therapy is aimed at saving the patient and prolonging his life. In such cases, a permanent catheter with a Monroe system is often installed.
For reflex bladder caused by transverse dissociation of the spinal cord above the lumbar region, tidal drainage of the bladder with Monroe has become widespread. The purpose of drainage is to develop and consolidate the reflex state of the bladder. With strict adherence to asepsis and an individual regimen, this method is safe and effective. The catheter must be changed after 3-4 days; to rest the urethra, it is necessary to periodically interrupt drainage for 2-3 days.
Pathogenetically based operations include:
- ileovesicopexy,
- ileorectovesicopexy,
- rectovesicopexy,
- reinnervation of the bladder by the rectus abdominis muscles
Intestinal plastic surgery for a neurogenic bladder is justified only in cases where the bladder is able to serve as a reservoir and provide outflow from the upper urinary tract. In practice, this is observed with an autonomous bladder due to damage to the spinal cord, with denervation of the bladder, which is observed after massive operations in the pelvic cavity.
After surgery, conservative treatment methods are used to strengthen the mechanisms of active urination, including active physiotherapy, physical therapy, and electrical stimulation of the bladder.
Contraindications to radical surgical treatment are:
- spinal cord injuries in the cervical and thoracic regions with bladder automaticity;
- severe bilateral ureterohydronephrosis, which developed as a result of vesicoureteral reflux in the presence of severe renal failure;
- massive narrowing of the urethra;
- dysfunction of the sphincters, accompanied by urinary and fecal incontinence.
The prognosis depends on the form and stage of the disease, the timeliness and correctness of the choice of a pathogenetically based method of treating neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
Diet for overactive bladder
What is included in lifestyle changes?
Medicines prescribed by a doctor are not the only component of treatment. Much attention is paid to behavioral therapy. [1] This method aims to help the patient restore the storage capacity of the bladder. If drugs cannot be used, or they do not fully help, it is behavioral changes that help the patient restore a normal standard of living.
Workout
. Doctors prescribe so-called Kegel exercises to patients with overactive bladder. [1, 3, 4] Their essence is in training the pelvic floor muscles. Exercise can help you regain some control of your bladder. The patient must alternately tense and relax these muscles and repeat the exercises throughout the day. Such treatment is more effective if the patient constantly communicates with the doctor, is motivated to continue training and is informed about the correct technique. [3] Sometimes, instead of independent exercises, doctors prescribe electrical stimulation: muscles contract and unclench under the influence of current pulses. [3]
Urinary control.
One of the measures aimed at restoring bladder control. The idea is to “train” your bladder to respond at certain times. [1, 3] To do this, urination is prescribed on a schedule at predetermined intervals. At first they are small, then gradually increase. Patients are sometimes advised to keep a diary to have clear information about the frequency and nature of urination. In addition to going to the toilet every hour, relaxation practices are used: exercises that help control the irresistible urge. [3]
Thoughtful drinking regime.
Patients are advised to be more careful about their fluid intake. It is believed that people with OAB need to drink about 1500–2000 ml of water per day. [3] Larger amounts will cause the urge to become even more frequent. Less will make the urine concentrated, and in this form it will irritate the walls of the bladder more. Therefore, drinking too little water is not a good idea as it may worsen your symptoms. It is also recommended for patients to: [3, 4]
- limit the amount of liquid you drink in the evening or before a walk;
- Be sure to empty your bladder before going to bed;
- drink large amounts of water only if you have access to a toilet nearby within the next few hours;
- reschedule taking medications that may affect urination until the first half of the day.
Diet
. The diet for an overactive bladder is aimed at eliminating unnecessary irritation of the walls of this organ. [3] If the bladder becomes irritated, the urge becomes stronger and more frequent, and the patient's condition worsens. Therefore, you need to avoid products that:
- have a diuretic effect;
- have an effect on the mucous membrane of the urinary tract.
If you cannot completely give up some foods, you should reduce their consumption. You should stop eating such food 3 hours before bedtime and do not eat it shortly before leaving the house.
What diseases can it be associated with?
Bladder dysfunction is only the primary link in the pathogenesis of the disease; it gradually leads to a change in the anatomical structure of the organ, which significantly aggravates the functional disorders that already exist. Often the course of this pathology follows a “vicious circle” type. All this over time leads to profound changes in the ureter, upper urinary tract and kidneys, which are the main ones in the clinic of neurogenic bladder dysfunction and ultimately determine its consequences.
In some cases, patients with a neurogenic bladder are diagnosed with spina bifida, cleft sacral canal, etc.
The infection that occurs in such cases leads to the development of pyelonephritis, chronic renal failure, and urosepsis. Often, in its symptoms, a neurogenic bladder is similar to acute cystitis or pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Treatment of bladder cancer with folk remedies
Any cancer is a great misfortune for a person and for his relatives. Therefore, it is absolutely natural that people are looking for any ways that will help them recover from this terrible disease. Patients are driven by the desire to be cured without surgery and strong medications, so they resort to traditional recipes for cancer. Of course, doctors are skeptical about such aspirations and about the possibility of curing anything with the help of herbs or roots. Oncologists warn that any independent treatment may not only not give positive results, but will most likely lead to the loss of precious time, which should not be allowed under any circumstances. However, no one is in a hurry to completely discount folk remedies. The main thing they give the patient is hope for recovery. A positive attitude during cancer treatment is extremely important. Also, with the help of folk remedies, you can remove harmful and toxic substances from the body, cleanse it and saturate it with useful substances, because their shortage during cancer is very serious. Regarding the diagnosis of bladder cancer, traditional treatment for this disease involves drinking plenty of fluids, and in this sense, consuming decoctions of beneficial herbs can provide good support to the body. For bladder cancer, folk remedies also suggest the use of poisonous plants. You should definitely notify your doctor if you are taking such medications. The main thing is that the treatment of the disease does not turn into poisoning of the body. Traditional treatment suggests using fly agaric for bladder cancer, as well as henbane, hemlock, celandine and many other strong plants. You should carefully consider the advisability of taking such drugs, because they cause serious side effects with questionable effectiveness. For example, if you take fly agaric for bladder cancer, you may experience hallucinations, hysterical attacks and other mental disorders. Unfortunately, many people are ready to resort to such dangerous means, but are afraid of chemotherapy, considering it extremely harmful. This is a fundamentally wrong approach, and doctors strongly recommend consulting with them before deciding to take fly agaric for bladder cancer, or another dubious remedy that can cause irreparable harm to health.
When a person is diagnosed with advanced bladder cancer, alternative treatment can help, but no one guarantees the effectiveness of this method. Folk recipes involve the use of alcoholic tinctures and decoctions using a variety of plants that have been used for centuries for healing purposes.
When diagnosing bladder cancer, folk remedies suggest the use of rather poisonous herbs, such as spotted hemlock, etc. In cases of bladder cancer, folk treatment sometimes offers very strange recipes. One of them involves infusing young, milky walnuts in aviation kerosene and then using this tincture a few drops per day. It is unclear what motivates people who use such recipes. After all, science has long proven that contact with petroleum products is one of the factors that causes bladder cancer. Treatment with folk remedies can also help with inflammation that accompanies malignant tumors.
One of the serious problems of people suffering from cancer is a depressed state of mind. For bladder cancer, folk remedies use certain properties of plants. They have the ability to restore strength, give vitality, remove toxins and cleanse the blood and much more.
When diagnosed with bladder cancer, treatment with folk remedies can help the main treatment, but the methods of traditional medicine cannot be neglected. Moreover, you cannot arbitrarily decide to take any potent, poisonous drugs. The best thing anyone can do for themselves is to strengthen their immune system. Research in the field of immunology and oncology has shown that the body's natural defense - immunity - is able to protect a person from cancerous tumors. Also, restoring immune functions can cure existing bladder cancer. The fact is that immune cells constantly scan the body for the presence of enemy microorganisms, pathological cells and other dangers, and when they find them, they destroy and dispose of them. If the cells of the immune system are not strong enough, or, more often, not sufficiently informed about how to identify enemy cells, then it will not be able to protect the body from aggressors.
Immune cells receive information from peptide compounds - transfer factors, which store a huge amount of data about a wide variety of microorganisms and pathological cells that must be destroyed. Transfer factors have the function of teaching immune cells by transmitting information to them. It turns out that to strengthen the immune system and organize its effective fight against cancer cells, the body needs transfer factors. These compounds are included in large quantities in the drug of the same name. Transfer factor is currently the only immune drug that can configure the immune system to independently fight cancer.
This drug has proven effectiveness in the complex treatment of malignant tumors. Doctors also recommend it for the prevention of cancer of the bladder and other organs. Transfer factor during rehabilitation can significantly speed up the process and avoid relapse of the disease. The high efficiency and complete safety of the drug are explained by its natural origin and principle of action, which does not interfere with the physiological processes of the human body. Transfer factor can be used at all stages of treatment, regardless of age and diagnosis.
What medications are used to treat neurogenic bladder?
A wide variety of pharmaceuticals are used to treat neurogenic bladder
- M-anticholinergics - atropine sulfate, beladonna,
- M-cholinomimetics - aceclidine, carbacholine,
- anticholinesterase drugs - prozerin,
- antiprostaglandin drugs - acetylsalicylic acid, indomethacin,
- α-adrenolytics - phenoxybenzamine,
- α-adrenergic stimulants - ephedrine hydrochloride,
- calcium ion antagonists - isoptin, finoptin,
- coenzymes and cholinomimetics - cytochrome C, riboflavin mononucleotides,
- antidepressants - melipramine, amitriptyline,
- tranquilizers - seduxen,
- means of metabolic therapy - pantogam.
The dosage of medications, as well as the duration of the course, and the combination of the above drugs are determined by the attending physician, taking into account the origin of the dysfunction, the characteristics of its course and the results of individual diagnostics.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - n
| Drug addiction treatment |
| Treatment of neurasthenia |
| Treatment of obsessive-compulsive neuroses |
| Treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia |
| Treatment of Anorexia Nervosa |
| Treatment of diabetes insipidus |
| Treatment of ulcerative colitis |
| Treatment of unstable angina |
| Treatment of nephrogenic hypertension |
| Treatment of nephropathy |
| Treatment of nephroptosis |
| Treatment of nephrotic syndrome |
| Treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.