Signs of the disease Causes of polyps Surgical removal techniques Preparation Indications Contraindications Recovery Prevention
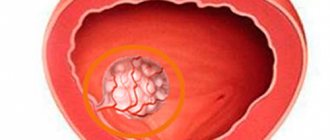
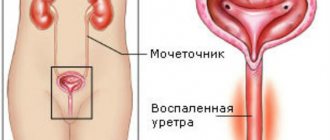
A urethral polyp is a benign formation located on the mucous membrane of the urethra. It must be removed because such a defect disrupts the flow of urine and can cause urine retention. Also, the danger of the disease lies in the fact that often (10-30% of cases) polyps become malignant.
Symptoms of the disease
At the initial stage, urination becomes more frequent and becomes painful because the mucous membrane is irritated due to the movement of urine. Other characteristic symptoms:
- difficulty urinating;
- bloody impurities in the urine;
- burning, sensation of a foreign body in the urethra;
- splashing stream of urine;
- feeling of constant fullness of the bladder;
- pain during sexual intercourse in women;
- painful urge to urinate without releasing urine.
In later stages, acute or chronic urinary retention appears because the lumen of the urethra is completely or partially blocked.
Transurethral resection with bipolar
General or local anesthesia
Operation time - 20-30 minutes
Recovery in hospital - 1-2 days
Cost of the operation: 25,000 rubles
Possible symptoms
Single and small polyps may not manifest themselves clinically and grow into the lumen of the bladder for a long time. In some cases, the appearance of dysuric syndrome is possible - a set of symptoms associated with impaired urination. These include:
- subjective discomfort during and after urination;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- pain when urinating.
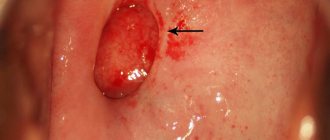
Large papillomas of the submersible type can cause hematuria - the appearance of blood in the urine. As a rule, microhematuria is observed (detected only in the laboratory by the presence of red blood cells in the urine), but sometimes macrohematuria is also found - an admixture of blood, determined visually. The urine has a purplish-scarlet tint.
Treatment of urethral polyps in women and men
It is extremely important to understand that at the first manifestations of the disease you need to consult a doctor. It is impossible to cure such a tumor with folk remedies or medications. Over time, the situation will only get worse. The only treatment method is surgery.
Preparing for surgery
Before the intervention, the patient needs to undergo urine and blood tests. Also, the doctor often prescribes diagnostic methods such as:
- urethroscopy;
- smear for sexually transmitted diseases;
- coagulogram.
Polypectomy techniques
The tactics for treating polyps of the urethra and bladder are removal of tumors with cleaning of the bed using an extremely gentle technique. The technique is selected taking into account the characteristics of the disease and the patient’s condition.
Preference is given to the TUR intervention technique - transurethral resection. Access to the tumor is carried out through the urethra - without punctures or incisions. To do this, microsurgical instruments and an endoscope are used - a device with a flexible cable, a miniature video camera and a light source. If, due to the location, size of the polyp, combined pathologies, and other factors, TUR is not possible, endoscopic access is used - without incisions, through punctures in the abdominal wall.
Anesthesia during surgery - local, epidural or general anesthesia (decided by the anesthesiologist after consultation and diagnosis). The duration of the intervention, depending on the volume, is 20-40 minutes. Open operations with opening of the abdominal cavity are rarely performed, in especially complex cases.
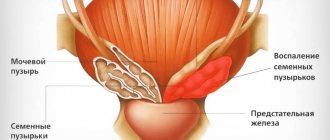
Features of the removal of urethral polyps in men and women
In women, polyps are more often localized outside the urethra or throughout the entire area of the urethra. In men - at the entrance of the urethra to the prostate and in the area of the seminal tubercle. When located in the lower parts of the urinary system in women, you can do without a urethroscope. In men and when urethral polyps are localized in the upper parts of women, TUR is used.
Polyps in the bladder in men: removal, causes, symptoms and diagnosis
Proliferation on the mucous surface of the bladder is called a polyp. The formations rise above the surface of the bladder cavity and are benign.
However, in men, in the presence of undesirable factors and various concomitant pathologies, bladder polyps can develop into a malignant form, which can lead to serious complications.
What causes the growth of bladder polyps in men and how they can be dealt with is explained in detail in the material below.
Causes and symptoms of polyps in the bladder
Benign growths on the walls of the bladder are formed under the influence of certain factors and causes. Including:
- Genetic predisposition;
- The presence of chronic inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- Disorders in the metabolic processes of the bladder;
- Poor environment and smoking.
Important: Men who have had similar cases should pay special attention to their health. And the connection with age is directly related. This means that if a relative is overgrown at 45 years old, then the descendant at this age should pay special attention to himself.
It is worth understanding that the initial stage of the pathology is asymptomatic. In this case, height is determined by chance during external examinations. When the polyp has already reached an impressive size and is probably injured, the clinical picture of the growth of polyps in the bladder is as follows:
- The color of the urine changes from the usual straw yellow to pale pink. This indicates bleeding in the bladder.
- Pain when urinating when a growth has formed in the area of the ureter, obstructing the flow of urine.
- Frequent chronic inflammatory processes in the bladder in the form of cystitis.
Diagnosis of polypous neoplasm
Bladder polyps in men are diagnosed using modern hardware. Such methods include:
- General urine analysis. Allows you to detect blood, protein and leukocytes in the urine, which indicates inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system.
- Ultrasound of the bladder. Allows you to see the tumors themselves, assess their size and structure.
- Cystoscopy. The procedure is performed by injecting a cystoscope into the bladder cavity through the urethral canal. A mini camera is used to assess the condition of polyps and their appearance. Using the device, you can also take tissue samples for histological analysis (detection of malignant polyp degeneration).
- Cystography. X-ray examination of the bladder using X-ray contrast agent. The substance colors tumors a certain color if they are benign or malignant.
You may be interested in: Glandular polyp of the rectum: what is it, symptoms and treatment
Important: The absence of polyps means that they are born into a malignant tumor.
Treatment methods for bladder polyps
To overcome bladder polyps in men, either popular methods, conservative therapy or surgery can be used. However, in any case, treatment tactics are prescribed by a urologist or andrologist.
Traditional methods
In the popular treatment of growths of the bladder walls, the use of the following agents is recommended:
- Fresh parsley and dill in sufficient quantity.
- Purity in the form of tinctures. The tincture is made from herb and water. The ratio is 1 tablespoon per 500 ml of boiling water. Everything was mixed and poured within an hour. The finished infusion is drunk in three servings throughout the day.
- Herbal potion. Here you need to mix the leaves of horsetail and birch (4 parts each), calendula, celandine and sage (3 parts each) and wheat (roots 2 parts). Mix them all and collect 3 tablespoons. Pour them into boiling water (1 liter) and let them soak in the steam bath for another 45 minutes. Ready for peeling and drink up to 75 ml 3-4 times a day.
- Pumpkin seeds and egg yolk. Here you should mix 3 tablespoons of dried pumpkin seeds and 3 chicken yolks. All this should be carefully filled with vegetable oil (0.25 l) and kept in a water bath for 20 minutes. The finished product should be placed in a container and refrigerated. Take 1 spoon of the product 30 minutes before breakfast in the dining room. The duration of treatment is 10 days.
Medication methods
There is no cure per se for bladder growth. Only in rare cases, endoscopic injection of medicinal solutions into the cavity of the affected organ can be used to fight cancer.
Surgical intervention
In such cases, surgical removal of polyps in the bladder in men is indicated:
- Rapid growth in education;
- polyps on the wall of the bladder (polyposis);
- The presence of blood in the urine and permanent damage to the formation;
- Anatomical localization of a polyp obstructing the flow of urine (growth of a formation at the entrance to the ureter);
- Risk of growth into a malignant tumor.
Today, growths can be removed through the urinary tract by endoscopic insertion into the bladder cavity using a special cystoscopic device. Or better said, a diathermocoagulator is introduced into the organ cavity.
Using a special belt, they caught the knot and electrocuted his leg. In this case, the wound surface is cauterized.
Using a special mini-camera, the doctor observes the process.
Important: The operation is performed under general anesthesia. This operation is not dangerous for the patient.
It is worth knowing that the postoperative time with this procedure is short. The patient recovers within a short time. After 3-4 days the patient can return to their normal lifestyle. It is important to monitor every six months to prevent relapses or detect them early. If the pathology does not reappear within the next two years, an examination can be performed once a year.
Prognosis and prevention
As for the prognosis for polyps in the bladder, in 10% of cases the growth degenerates into a malignant tumor. This can be avoided with early diagnosis.
In other cases, the patient's prognosis is good. However, it should be borne in mind that in 9% of cases growth can be repeated.
Among the preventive measures to prevent the growth of polyps, the following stand out:
- Balanced diet;
- Quit smoking;
- Optimal drinking conditions;
- Timely and high-quality treatment of infections and inflammations of the genitourinary system.
Everyone should understand that false shame, due to which the patient does not rush to see a urologist even with obvious symptoms of pathology, plays a bad role for the patient.
All doubts should be clarified as soon as possible, and if the clinical picture is suspicious, a doctor should be consulted. Only a specialist in the field of genitourinary medicine can properly treat problems of the genitourinary system.
Remember that delays can be expensive.
Rating for this publication: ( 2
Methods for removing urethral polyps in women and men
Radio wave technique
Used when the size of the formations is small. It is performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. First, the bladder is emptied, then a radiosurgical scalpel is inserted into the urethra. The tumor is exposed to radio wave radiation, which destroys pathological tissue. During such an intervention there is no risk of damaging healthy tissues, there are no scars left after it, and purulent complications are excluded.
Cryodestruction
The formation is affected by low temperature, the procedure is done under local anesthesia and lasts about 10 minutes. The liquid inside the polyp turns into ice, causing harmful cells to die.
Electrocoagulation
An electric current is applied to the polyp; the procedure is performed under local anesthesia and is painless. Contraindications to it are: blood clotting disorders, the malignant nature of the formation and/or its large size.
Wedge excision
This type of surgery is performed when a large urethral polyp needs to be removed. During this procedure, general anesthesia is used. The operation lasts about 20 minutes and requires further hospitalization for a short period. The purpose of the intervention is to remove a triangular section of the external opening of the urethra. The polyp is also removed along with it. Stitches are placed and daily drainage is installed.
The removed biomaterial is sent for histological examination.
Prevention
- Quitting bad habits, mainly smoking.
- Consume at least 2 liters of water per day.
- Ensure maximum safety when working in hazardous conditions.
- Do not endure when the urge arises, but immediately visit the toilet. Otherwise, urine will accumulate and harmful effects of toxins on the bladder walls will occur.
- At the first signs of a bladder infection, consult a doctor and get treatment.
- Avoid injury to the bladder area.
- Avoid STDs.
If there is a hereditary factor, then you need to regularly visit a urologist and have an ultrasound scan.
How to treat polyps in the bladder in men?
Bladder polyps in men appear on the mucous membrane and are benign tumors.
To stop the disease, you need to know its symptoms and causes.
What is it?
A polyp is a benign tumor, but can become cancerous if left untreated.
polyps block the urinary tract, leading to bladder failure 8 . Urination becomes problematic.
ICD-10 code: D 30.3.
Reasons for appearance
There is a disease for the following reasons :
- Genetic predisposition.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Damage to the bladder.
- Stagnation of urine in the urinary tract.
- Stress.
- Smoking.
- Alcohol consumption.
- Metabolic disorder.
- Diabetes.
- Cystitis.
- Hypothermia.
- Cystitis.
- Denial of hygiene.
Symptoms of polyps
May be different for each gender.
In men
In the male population, the disease manifests itself as follows:
- stomach ache.
- Burns when urinating.
- Urinary retention.
- Weakness.
- Drying of the urethra.
- Decreased erection. Male face
decreased performance, fatigue, dizziness. Gradually, the pain under the abdomen becomes strong and throbbing.
Among women
Women also suffer from this disease. Symptoms include:
- stomach ache.
- Frequent calls for urination.
- When urinating there is a burning sensation and pain, small urine comes out. She stagnates.
- Improvement of external genitalia.
- Unhealthy looking.
- Dizziness, weakness.
- Decreased sexual desire.
- Itching in the genital area.
The pathology causes severe pain in women in the lower abdomen. There is drowsiness, lethargy, and possibly the appearance of tear fluid. Modern medicine
Diagnostics
Modern medicine successfully diagnoses polyps . Effective diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the bladder.
- cytoscopy.
- Biopsy.
- Urine test.
- Cystography.
Read our article about bladder cystography.
These methods help diagnose . Only after they are completed, the doctor prescribes treatment for the patient.
Treatment of the disease
It is impossible to get rid of polyps with the help of drugs.
They can only relieve pain and alleviate the patient's condition , but the tumors do not disappear. Painkillers include:
- Analgin.
- No-Spa.
- aspirin.
Medicines are taken one tablet at a time to relieve pain. The maximum dose is 4 tablets per day .
Polyps can only be treated surgically . Performed under general anesthesia. Before the operation, the patient undergoes a blood test, a urine test, and a test for allergic reactions to anesthetics.
The operation is performed using a cytoscope. It is inserted into the urethra, the polyp is carefully removed by diathermocoagulation: the polyp is placed in a loop, heated to a high temperature, and the polyp is removed. In this case, the likelihood of bleeding is very low, there are no stitches.
The patient recovers quickly . After the polyp is removed, the patient is washed with antiseptics to prevent infection.
If the polyps have reached large sizes, then open resection is performed. In this case, the polyps are removed through the abdominal wall. Not only the polyps are removed, but also part of the bladder wall.
To prevent recurrence of polyps, the patient should visit the doctor frequently, treat inflammatory processes in a timely manner, follow a healthy diet and avoid drinking cigarettes and alcohol.
Advantages of SM-Clinic
Our medical center employs some of the best doctors in St. Petersburg, and also has advanced diagnostic and treatment equipment. Preference is given to minimally invasive methods with a short rehabilitation period. In cases where a surgical operation with hospitalization is required, we provide comfortable double rooms and provide round-the-clock monitoring of the patient’s condition. To consult a urologist, undergo expert diagnostics and remove polyps in the urethra and bladder if they are detected, make an appointment with us by phone.
Causes
The exact causes of bladder papillomas remain unknown, but there are risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease. These include:
- elderly and senile age;
- decreased local immunity of the mucous membrane;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- disturbance of urine passage;
- congenital and acquired immunodeficiency conditions.
Recently, the influence of cytopathogenic viruses on the mucous membrane of the bladder has been actively studied: papillomavirus infection, herpes simplex viruses, cytomegalovirus infection, Epstein-Barr virus. The presence of these pathogens in the body goes unnoticed for a long time; they reveal themselves with a persistent decrease in the body’s immune resistance, one of the manifestations of which may be increased tissue proliferation and the growth of tumors.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) | In installments (RUB) |
| Consultation with a surgeon for surgery (ACTION) | 0 | — |
| Online doctor’s opinion on surgery (SPECIAL) | 0 | — |
| Endoscopic removal of neoplasms of the bladder mucosa, stones, foreign bodies, category II. difficulties | 25000 | from 2498 |
| Endoscopic removal of neoplasms of the bladder mucosa, stones, foreign bodies, category III. difficulties | 35000 | from 3498 |
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments.
Our doctors
Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
35 years of experience
Make an appointment
Mukhin Vitaly Borisovich
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment