Localization
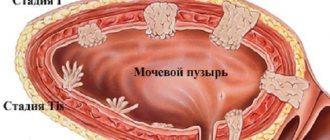
Bladder polyps in women have a clearer and more pronounced localization than in men. Unpleasant neoplasms are most often located:
- on the back wall of the organ. When small in size, they are characterized by an asymptomatic course and do not interfere with the outflow of urine. They become dangerous only with uncontrolled growth or multiple organ damage;
- at the site of narrowing of the bladder (neck). Such polyps quickly grow and block the excretory duct, causing stagnation of urine. If the ureter is completely blocked, the patient requires urgent medical attention;
- in the area of the ring sphincter (urethra). The most dangerous localization of a polyp, most often leading to cancer. Being in constant motion, the circular muscles irritate the formation, causing bleeding and infection.
The location of the polyp in the bladder largely determines the symptoms of the disease in women. Signs of cervical and urethral proliferation of mucous epithelium are especially pronounced. These may include:
- persistent urge to urinate in the absence of urine;
- blood in urine;
- frequent bowel movements in small portions;
- pain in the lower abdomen and along the excretory ducts.
Unfortunately, these symptoms appear only at an advanced stage of the disease.
Reasons for appearance
There is no single theory yet about the cause of polyps in men.
However, there are a number of factors predisposing to their development.
- Genetic predisposition. The occurrence of such a disease in family members and relatives, especially in men, significantly increases the risk of bladder polyps.
- Injuries to metabolic processes in the tissues that form the bladder.
- Chronic inflammatory diseases such as cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis. Delay in the treatment of acute inflammatory processes.
- Unfavorable environment and professional risks. This is especially true for men involved in construction, production, and repair work.
- Smoking. The substances contained in tobacco are a strong carcinogenic factor that can cause tumors.
- Hormonal disorders in the body. Most often they are associated with neoplasms in the prostate.
- Various types of damage, including mechanical. These include surgical procedures and diagnostic procedures. At the site of injury, the risk of polyp formation increases many times over.
- Prolonged urinary retention, less frequent urge to urinate. With age, men develop hyperplasia of prostate tissue, which impairs urinary drainage.
- Constant pressure.
- Alcohol consumption. Alcohol has a direct effect on the mucous membrane and causes functional disorders.
- Drug use.
- Eating errors, unbalanced diet, consumption of large amounts of salt, smoked, fried and spicy foods.
Symptoms
In most cases, polyps present on the bladder wall are not clinically evident in men. In these cases, they are detected by chance in diagnostic tests for prevention or in tests for other diseases.
Only in cases where the size of the polyp becomes significant, or it disintegrates or is damaged, the following symptoms occur:
- Urine is colored from light pink to red . The appearance of this sign indicates bleeding. Bleeding is localized either in the polyp itself when it disintegrates, or at the site of attachment of the polyp bone to the bladder.
- Delayed urination . Urinary retention occurs when polyps are located near the ureter and interfere with normal urination.
- Pain syndrome . The pain may be intermittent, gnawing, stringy, located in the lower abdomen, mainly over the chest, and radiating to the groin. If the polyp obstructs the flow of urine, pain when urinating increases. This leads to erectile dysfunction.
- General inflammatory disease of the bladder . Most of them have cystitis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing male polyps in the bladder is not difficult. The simplest and most accessible method is ultrasound diagnosis of the bladder. .
If a neoplasm is suspected, this study suggests additional research methods.
The next stage of diagnosis is cystoscopy. During this examination, the doctor uses an endoscope to visually examine the bladder cavity. If a tumor is detected, part of it is removed for histological examination. The biopsy results are used to assess the nature of the process.
Another way to obtain a complete picture of the disease is a contrast-enhanced . Thanks to the contrast, the bladder cavity is clearly colored, and the neoplasm is clearly visible in relation to the surrounding tissue.
Treatment
If a person has been diagnosed with bladder polyps after the necessary diagnosis, there are two options for treating the patient. In the first case, if the polyps are small and do not obstruct the flow of urine, they adhere to a waiting tactic.
The person is registered with a urologist and periodically undergoes control diagnostics. The doctor will monitor changes as the disease progresses. In another case, if the polyps reach a significant size, are complicated by bleeding or cause urinary retention, surgical treatment is performed.
With modern capabilities, there is no need for cavity surgery; polyps are removed endoscopically . This is a kind of additional cystoscopy. After the tumor is removed, the man remains under medical supervision. Restorative treatment is prescribed, the purpose of which is to heal the mucosal defect left after polypectomy.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine is ineffective and should be agreed with a doctor so as not to aggravate the existing pathology. In folk medicine, they are used to treat polyps.
celandine, which is the basis for making tinctures. One of the most common medicines is a tincture of pure body with vodka in a ratio of 1:5. 10 drops twice a day, morning and evening.
Celandine decoction has a good effect. To prepare, pour a tablespoon of celandine into 0.5 liters of boiling water. The resulting decoction must be kept for one hour and then drunk three times throughout the day.
Loading…
Kinds
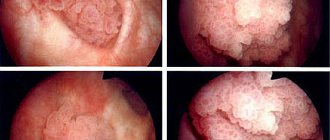
The morphological characteristics of the growths are of particular importance in determining the treatment regimen and further monitoring of the patient. Thus, it is customary to classify true neoplasms and pseudopolyps.
The first group includes all tumors arising from epithelial tissue and associated with it by the choroid plexus. This:
- fibrous polyps. They account for up to 70% of clinical cases. They do not have strict localization and rarely degenerate. They are formed from the internal epithelium of the bladder that has lost its functionality;
- villous polyps, or adenopapillomas. They have a dense spongy structure with many capillary plexuses, a stalk and a body covered with a large number of thin villi. Most often localized in the cervix and urethra.
Polypoid adenomas can be of several types:
- proliferative, i.e. inflammatory genesis;
- non-proliferative (simple);
- prone to malignancy.
If villous polyps are detected, it is necessary to constantly monitor their growth and extent of spread. If there is a risk of malignancy, they resort to urgent removal of the tumors.
False polyps are less dangerous in terms of degeneration. They can grow anywhere, layer and form entire colonies. They are often infectious in nature and lead to complications.
Causes
The reasons for the formation of polyps in the bladder in women are still unknown. There is an opinion that the disease is caused by a combination of unfavorable factors, among which the following are of particular importance:
- exposure to chemicals and radiation;
- industrial hazards;
- smoking;
- untreated chronic inflammation.
The risk of getting growths in the bladder increases in the presence of provoking factors:
- postmenopausal period;
- urolithiasis disease;
- long-term presence of the catheter in the urethra;
- hormonal disbalance;
- irradiation of the pelvic organs and taking Cytoxan;
- burdened heredity.
Women infected with the human papillomavirus often experience polypous growth in the bladder. Moreover, a relationship has been discovered between HPV and the rapid malignancy of even seemingly harmless growths.
Causes and treatment of polyps in the bladder in men
Polyps in the bladder are caused by all pathological processes occurring in the human body.
This disease occurs more often in men than in women. Patients do not have significant external symptoms and are usually unaware of their condition.
This pathology can only be detected with a thorough preventive medical examination. What are bladder polyps, what are their origins and how to treat them? Let's try to find out!
What are formations and why are they formed?
A bladder polyp is a benign new formation that grows from the transitional epithelium due to pathological tissue growth.
They usually form on the inner walls of the bladder. Rapid changes in metabolic processes in the body lead to active division of cells of the mucous membrane, which can follow the focal appearance of these formations.
There are no specific diseases or reasons for the appearance of polyps in the bladder in men, since the process of polyp formation can provoke absolutely any changes in the normal state of the body. The main risk group includes men who are monitored:
- Various diseases of the urinary tract (especially inflammatory ones) . In more than 90% of cases, polyps are found in patients suffering from cystitis, orchitis, folliculitis, and urethritis.
- Immunity . A weakened immune system is not able to completely renew the body's cells. As a result of active division, cells do not burn out, but accumulate in different places and form small tumors - polyps.
- Genetics . If a person from the family has patients suffering from all types of tumors (benign or malignant), then there is a high risk of polyps forming. Such people should be more attentive to their health status and, in case of chronic or severe viral diseases, undergo a thorough medical examination.
There are other factors that can influence the formation of polyps:
- Hormonal destabilization . This occurs due to pathological changes in the body or with the artificial administration of hormonal drugs. Bladder polyps are very common in men with diabetes who regularly undergo insulin therapy.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse . Polyps are most often transmitted sexually, and their formation cannot be concentrated only in the bladder.
- Exposure of the body to toxic or aggressive chemicals . When a person inhales the fumes of paint, gasoline and other similar substances for a long time, their mucous membranes are deformed and provoke their active division, leading to the formation.
- Irradiation, irradiation . Each radiation disease is accompanied by pathological disorders in the structure of the body.
- Nervous system disorders . These include diseases such as epilepsy, akinesia, neurasthenia, neuritis, myelitis, fibromyalgia. Normal stress, emotional tension or depression can cause neoplasia.
- Bad diet . Polyps are nothing more than a tumor. Large amounts of fatty, fried and spicy foods often lead to tumors of various internal organs.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking . Alcohol and tobacco significantly increase the risk of new cases of growth.
You may be interested in: Glandular fibrous polyp: what it is, treatment and removal
Various types of tumors, including bladder polyps, are caused by hypothermia. With a sharp drop in body temperature, inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs throughout the body, contributing to the development of various neoplasms in the form of tumors, papillomas and polyps.
Main manifestations of the disease
Polyps that are small in size have absolutely no external manifestations, so the patient can live with the disease for several years or even his entire life without knowing about its presence. As the pathology develops, neoplasms can degenerate and increase in size. Bladder polyps have the following symptoms:
- Presence of blood contamination and pus in the urine . Tumors that are too large stretch the inner wall of the bladder and rupture the surface layer of the epithelium. Pus occurs as a result of the inflammatory process of urea, accompanied by pain and heaviness.
- Increased urge to urinate . Proliferation in the bladder blocks the urethral meatus. The person constantly feels the need, and urination is accompanied by a severe cut in the bladder. The symptom of pain appears gradually, from mild discomfort to the absolute impossibility of emptying urea.
The symptoms are very similar to prostate inflammation. Men often treat themselves without further examination, but painful bladder symptoms do not go away and only get worse.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
To identify the disease and make an accurate diagnosis, doctors prescribe the following types of tests:
Complete blood test for antibodies.- General urine analysis.
- Ultrasound test of the bladder.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the bladder.
- If cancer is suspected, your doctor may order an additional biopsy.
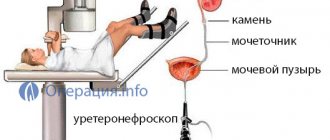
After a series of tests, if the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe a cystoscopy. This examination is carried out using a special device - a cytoscope.
This is a very uncomfortable procedure in which a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted through the penis and into the bladder. This procedure makes it possible to examine the type and size of nodules.
How is polyposis treated?
Only after basic and additional studies of polyps in the bladder can a doctor prescribe individually effective treatment. There are three main methods for removing polyps:
. In small foci of tumor growth, anti-inflammatory drugs, for example: Omeprazole, prednisolone, ciprofloxcin, dexamethasone, aviation, lycomycin, cipran and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be effective. The drug itself and the dosage prescribed by the doctor, depending on the individual characteristics of the body.
Medical treatment- Surgical removal. At the time of diagnosis, partial surgery is performed using a cystoscope. If the polyps are small, the cystoscope cuts the stalk of the foreign calf, which is then excreted in the urine under the influence of diuretics. If large growths are found, complete surgery must be performed.
- Chemotherapy In cases where polyps develop into malignant nodes and there is a high risk of developing cancer, the doctor prescribes chemotherapy.
After successful removal of polyps, the patient is prescribed restorative treatment aimed at normalizing all functions of the urinary system.
Traditional methods of treating pathology
Conservative treatment with folk remedies cannot eliminate polyps in the bladder, but it is an excellent way to prevent this disease in men and prevent its recurrence. There are two medically approved popular prescriptions against polyposis:
The first preparation is based on egg yolk, vegetable oil and pumpkin seeds. To prepare, you need 5 fresh egg yolks, powdered pumpkin seeds (5 pcs. L.) and 200 ml of vegetable oil. All this needs to be mixed, cooked and cold, one tablespoon at a time before bed.- The herbal infusion is pure. Pour 1 liter of boiling water over about 20g of pure herb and let it brew for 3-4 hours. The resulting drink is filtered and taken three times a day, 100 ml, half an hour before meals. Pure herbs have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and diuretic properties.
It should be remembered that folk remedies can be used as additional or preventive measures, but not as the main treatment.
Possible complications
In many cases, bladder polyps do not appear, and the person does not even know about their existence. However, there are cases when polyps begin to actively grow and be born again due to various pathological changes in the body. This can lead to a number of complications such as
- inflammation of the bladder and the entire urinary system;
- chronic cystitis and cholecystitis;
- persistent prostatitis;
- necrosis of the bladder as a result of inflammation;
- Polyps have the property of developing into malignant tumors (cancer cells) without treatment.
All this can be avoided. It is necessary to undergo a medical examination on time, including from a urologist, control diet, physical activity and give up bad habits. Rest plays an important role. In order for the body to fully recover, it is necessary to maintain a sleep schedule.
We recommend additional articles on this topic
Is it possible for a polyp to resolve on its own?
As a rule, neoplasms in the bladder do not go away on their own. The reason for fantastic stories about the disappearance of large growths visible on ultrasound or CT is incorrect diagnosis, when salt deposits due to urolithiasis are mistaken for polyps.
Formations on a thin base, located in the lumen of the ureter or on the neck, can come off when the leg is twisted or pinched. In this case, there is also no need to talk about the resorption of the growth. The patient after amputation experiences severe pain and bleeding from the urethra. In addition, the separation is most often incomplete and requires the intervention of surgeons.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) | In installments (RUB) |
| Consultation with a surgeon for surgery (ACTION) | 0 | — |
| Online doctor’s opinion on surgery (SPECIAL) | 0 | — |
| Endoscopic removal of neoplasms of the bladder mucosa, stones, foreign bodies, category II. difficulties | 25000 | from 2498 |
| Endoscopic removal of neoplasms of the bladder mucosa, stones, foreign bodies, category III. difficulties | 35000 | from 3498 |
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments.
Diagnostics
Detection of a polyp in the bladder comes down to instrumental and laboratory tests. The most indicative in this regard is an ultrasound examination. Additionally, computed tomography is used, which makes it possible to detect even very small formations and cytoscopy.
In addition to instrumental studies, the patient is prescribed laboratory tests: general and biochemical blood tests, urinalysis. If an infectious nature of the polyp is suspected, a bacteriological examination of urine is performed.
To rule out cancer suspicion, a biopsy is performed by removing a small piece of material during cystoscopy. Histology is complemented by cytology and urine analysis for tumor markers.
Methods for removing urethral polyps in women and men
Radio wave technique
Used when the size of the formations is small. It is performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. First, the bladder is emptied, then a radiosurgical scalpel is inserted into the urethra. The tumor is exposed to radio wave radiation, which destroys pathological tissue. During such an intervention there is no risk of damaging healthy tissues, there are no scars left after it, and purulent complications are excluded.
Cryodestruction
The formation is affected by low temperature, the procedure is done under local anesthesia and lasts about 10 minutes. The liquid inside the polyp turns into ice, causing harmful cells to die.
Electrocoagulation
An electric current is applied to the polyp; the procedure is performed under local anesthesia and is painless. Contraindications to it are: blood clotting disorders, the malignant nature of the formation and/or its large size.
Wedge excision
This type of surgery is performed when a large urethral polyp needs to be removed. During this procedure, general anesthesia is used. The operation lasts about 20 minutes and requires further hospitalization for a short period. The purpose of the intervention is to remove a triangular section of the external opening of the urethra. The polyp is also removed along with it. Stitches are placed and daily drainage is installed.
The removed biomaterial is sent for histological examination.
Treatment
If a polyp in a woman’s bladder does not show signs of malignancy and does not worsen her health, no treatment is prescribed. The tumor is monitored - if the growth actively increases over the course of a year, surgery is recommended. This helps to avoid degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
Photo from the site russdoc.ru
Removal of a bladder polyp is usually performed by transurethral (closed) resection using a cystoscope. A wire loop or laser beam is used to tear off the build-up. If the tumor turns out to be malignant and has metastasized, a complete cystectomy is performed. The uterus and ovaries are amputated along with the bladder.
How is the operation performed?
The surgical technique is selected by the surgeon individually depending on the clinical characteristics. The intervention is performed under general or spinal (epidural) anesthesia. The urologist carefully inserts a flexible cystoresectoscope equipped with a miniature video camera into the cavity of the bladder through the urethral canal. Next, the bladder is filled with sterile saline solution to provide the specialist with maximum visibility of the surgical field.
The surgeon identifies and excises the polyp along with the germ zone (submucosal layer), a special loop, laser or radio wave scalpel, while coagulating the vessels. We use modern equipment that ensures targeted precision of intervention with minimal surgical trauma. The removed tissue is removed through a cystoscope and sent for histological analysis. After removing the equipment, catheterization of the bladder is performed to restore normal urine flow.
You have questions? We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Tatyana
Traditional methods
With a stable size of polyps, classical medicine allows the use of folk remedies. Celandine has a particularly good effect in the fight against uncontrolled cell division. The anti-inflammatory properties of the plant prevent the development of complications and further growth of the tumor, and reduce the risk of new formations.
There are several recipes for using celandine to treat polyps in urology:
- Three teaspoons of dry herb are poured into ½ liter of boiling water, infused, filtered and taken half a glass 4 times a day. The course of treatment is 1 month.
- A collection of 4 tsp has a good anti-inflammatory effect. celandine, 2 tsp. chopped rosehip root, 3 tsp. knotweed and horsetail. A mixture of herbs (3 tsp) is poured into a liter of boiling liquid, heated for 20 minutes in a water bath and taken 1/3 cup three times a day. Duration of therapy is 2–3 weeks.
- For pain and streaks of blood in the urine, it is recommended to prepare an infusion of celandine (3 tsp) and knotweed (2 tsp). The herbs are poured into a thermos and 500 ml of boiling water is poured. Leave for 6–8 hours. Then filter and drink 100 ml 4-5 times a day for a week. After a break, the course is repeated.
Celandine for polyps in the urethral canal and bladder in women can be used in the form of an alcohol solution. It is prepared from fresh grass, which is tightly packed into a jar and filled with 70% alcohol. Leave for 2 weeks, filter and take 30 drops three times a day after meals. The course of therapy is 1–1.5 months. After 14 days, treatment can be repeated.
Rehabilitation and treatment after surgery
In the early postoperative period, men and women wear a Foley catheter to ensure normal urine flow and prevent the development of strictures and infectious inflammation.
After transurethral resection, a catheter is only needed for the first 3 hours, and then you can return to natural urination.
You should take certain medications at the same time:
- Uroseptic agents for urine disinfection : Furadonin, Furamag, Nitroxoline;
- Antibacterial drugs to stop the infectious process - the choice of antibiotics is carried out according to individual indications;
- Antispasmodics when pain occurs : No-Shpa, Drotaverine;
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs : Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Diclofenac.
After the operation, moderate physical activity, careful hygiene of the intimate area, and sexual rest for up to 1 month should be observed.
After removal of polyps, it is recommended to undergo regular examinations, at least 2 times a year. Unfortunately, no operation can guarantee the complete absence of relapse in the distant future.
Prevention
Prevention of polyps in the bladder involves reducing the negative impact of provoking factors. The patient’s lifestyle has a great influence on the development of tumors.
Measures to prevent polypous growth:
- constant monitoring of the condition of the bladder epithelium in women with a family history;
- prevention of urine stagnation;
- sufficient consumption of clean water;
- to give up smoking;
- good nutrition;
- avoiding stress.
An essential element in the prevention of polyps in the urethral canal and bladder is timely treatment of inflammation of the urinary system.
The outcome of the disease largely depends on the location and type of growths. By taking good care of her health, a woman most often manages to coexist peacefully with an unpleasant neighbor. If necessary, cystectomy is performed, which, as a rule, completely solves the problem of malignancy.
Author: Elena Medvedeva, doctor, especially for Nefrologiya.pro
Useful video about bladder polyps
List of sources:
- Vorobyov A.V. Classification and diagnosis of bladder cancer. Research Institute of Oncology named after. prof. N. N. Petrova, 2003.
- Radical cystectomy: choice of method of urine diversion and long-term results / A.V. Sergeev // St. Petersburg, 2014.
- Radical cystectomy as the main treatment method for muscle-invasive bladder cancer / gr. authors // w. Practical Oncology, No. 4.2003.
- Complete encyclopedia of health improvement / G.P. Malakhov. - Saint Petersburg. Krylov, 2008.