Electrocoagulation of urethral polyp
Posted at 16:44h in Services by doctor
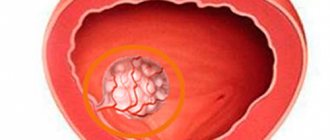
A urethral polyp is a benign neoplasm located on the epithelial layer of the wall of the urethra. The disease is diagnosed in 4% of urological patients who seek help from a doctor.
A polyp is a rounded growth on a stalk. In women, this pathology occurs much more often than in men, due to the structural features of the genitourinary system.
The risk of developing the disease increases with age. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in women over fifty years of age. This is facilitated by past infections, impaired blood supply to the walls of the urethra and changes in hormonal levels after menopause.
Causes of urethral polyp formation
1. In case of violation of the vaginal microflora in women, due to dysbacteriosis, decreased hormonal levels
2. Mechanical trauma during sexual intercourse, when the external opening of the urethra is located close to the vagina
3. Inflammatory diseases of the urethra
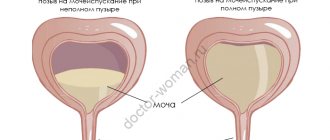
Urethral polyp
should be distinguished from prolapse (loss) of the urethral mucosa, urethral papilloma, paraurethral cyst, urethral diverticulum.
Urethral polyp photo in women is one of the causes of the occurrence and periodic exacerbation of chronic cystitis; symptoms appear in the form of a burning sensation in the urethra, after urination, sometimes constantly. For large urethral polyps
There is difficulty urinating, up to acute urinary retention. Bleeding is also possible if the urethral polyp is injured.
Classification
Depending on the reasons for the development of pathology, tissue structure and the number of neoplasms, they are classified as follows:
These are nodular growths consisting of glandular tissue into which blood vessels grow. Most often, this type of neoplasm occurs due to hormonal imbalances. Polyps of this type grow very quickly and can penetrate into the lower layers of the urethral tissue. During histological examination, patients are also often found to have cysts (cavities that are filled with secretion or serous fluid)
This type of growth consists of fairly dense connective tissue with a minimal number of vessels and interspersed with glandular cells. The cause of their appearance in most cases is infectious diseases or a violation of the cellular nutrition of urethral tissue. Usually a single polyp is diagnosed, which grows slowly and practically does not affect the neighboring layers. Such formations very rarely degenerate into malignant tumors
In women, in most cases, the formation of polyps occurs on the back wall of the urethra. They often spread to the vaginal tissue. Neoplasms can reach large sizes - up to a centimeter in diameter.
Causes
The inflammatory response leads to a decrease in local immunity and cell damage. The result of this is increased carcinogenesis and tumor formation
Formations can occur as a result of trauma to the urethra as a result of surgical operations in the genitourinary system, during abortion or difficult childbirth, as well as when kidney stones pass through the ureters and bladder
Most often, pathology develops in women during menopause, when the level of estrogen in the body decreases. People with diabetes and hypothyroidism are also susceptible to the disease.
The pathology can be inherited, so the risk of the disease in children whose parents have neoplasms increases
There are also provoking factors that contribute to the development of the disease. These include:
- bad habits;
- stress;
- poor nutrition;
- excessive physical activity;
- age-related changes.
A polyp has appeared in the urethra - how to treat?
Any inflammation in the urinary system should be treated immediately. It develops without obvious symptoms, but can lead to complications that affect the health of the entire body.
The result is often a urethral polyp, an elongated growth growing from cells in the lining of the urethra.
Despite the fact that it is a benign tumor, it is at risk of severe pain, bleeding and diseases of the reproductive organs.
Causes of polyps in the urethra
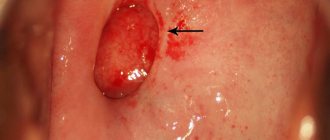
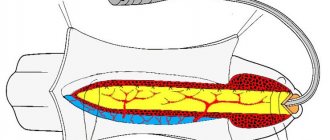
The tumor is a neoplasm on the urethral mucosa. It has an elongated shape, a short stem and a fungal cap. The polyp develops over several months or even years and is often detected during a routine ultrasound examination of the urinary tract. Most often it is one piece no larger than 1 cm in size; less often several pieces are diagnosed at a distance from each other.
- Mycoplasma;
- Chlamydia;
- Trichomonas;
- Ureaplasma.
Polyposis is often a complication of the internal form of herpes. It will provoke inflammation of the uterus and bladder, leaving behind inflamed areas. Doctors have established a connection between the disease and long-term stressful situations, neurosis and dysbacteriosis. A polyp in the urethra can appear after injury to the pubic bone, which can easily be caused by sports or accidents.
A painful polyp in the urethra also occurs in women after disabling contractions that have led to high blood pressure in the pelvis, multiple lacerations and other problems. This often happens after 40-45 years, when the weaker sex begins to reduce hormone levels.
There is a high risk of such pathology in diabetes mellitus or other endocrine disorders.
You might be interested in: Polyp in the duodenum, what to do?
How to recognize polyps in the urethra
- Patients complain of frequent calls to urinate due to heaviness and discomfort;
- Urine leakage occurs unevenly and intermittently;
- itching and burning occur in the urethra;
- pressure on the anus and lacerations in the pelvis increase;
- intimacy only causes acute pain.
A person immediately notices changes in the outgoing urinary flow. His pain is concentrated in the prostate area. If the polyp grows strongly, blood is added to the fluid, swelling may occur and blood pressure may increase.
These formations tend to spread and block the urinary tract. A person is faced with urination problems; in some cases, waste products practically do not end.
As a result, there is a danger of poisoning the entire body, which manifests itself in a sharp increase in temperature, skin rashes and weakness.
Sometimes the polyp reaches incredible sizes, and the patient experiences thickening in the pubic area.
Urethral polyps cause inflammation of the bladder or reproductive organs. They block the release of urine and harmful compounds, causing an increase in infections. This patient often has inflammation of the bladder and ureter, as well as problems with the prostate gland. Without treatment, the kidneys and the entire excretory system are involved in this process, and the composition of the blood deteriorates.
Visual examination is not enough to make a diagnosis. The polyp may be so small that it is difficult for an experienced ultrasound technician to see. The specialist collects various tests and recommends urethroscopy. A miniature pen is inserted into the urinary tract and helps identify the problem and distinguish it from a wart or boil.
It is important to correctly determine the cause of inflammation, for which a series of tests are performed for sexually transmitted diseases, diabetes mellitus and ureaplasma.
Methods for removing urethral polyps
Modern technologies make it possible to remove a urethral polyp with minimal discomfort. The choice depends on the diameter and location of the process:
- standard cutting with a scalpel. It is performed only under general anesthesia and helps to get rid of fused formations. The surgeon can perform urethroplasty and correct the mucous membrane. Despite the long and painful recovery, the procedure is irreplaceable if cancer is suspected.
- destruction by electricity. The electrocoagulation method is considered quite gentle and allows you to remove several cones in the urethra at once.
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen. Another technique for small polyps that does not require incisions or stitches. It is used at the initial stage and practically does not lead to dangerous complications, which significantly reduces the risk of wound infection.
- Safe treatment of polyps with radio waves of a certain frequency. Recommended for patients who are allergic to certain types of anesthesia. The only drawback is the need for several procedures when the tumor has already reached a very impressive size.
After the operation, the patient must not only recover, but also undergo comprehensive treatment of the disease that led to the development of a dangerous pathology. In the future, the patient should repeat the urinary system examination every year. This will help to promptly detect the appearance of new polyps and prevent their malignancy.
After surgery, you can use popular methods that have a good effect on the mucous membrane and make urination easier and relieve inflammation in the urethra.
Herbal teas and collections containing dried St. John's wort stems, bay leaves and sage should be drunk daily. For treatment or
Eliminates irritation and stress caused by sessile husks by boiling flax and horsetail seeds from the field.
In the initial phase, you can remove the urethral polyp with the juice of a celandine plant. To do this, the stems are crushed and the resulting liquid is mixed with vodka or purified alcohol.
The solution is placed in water and taken daily before meals. The course of treatment lasts at least 4-6 weeks, after which a break is taken.
However, since this drug contains aggressive substances, it is prohibited during pregnancy, breastfeeding and any form of epilepsy.
Symptoms
Initial
At the initial stage of the disease, there may be no symptoms. Some women report slight discomfort when urinating or a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. These symptoms resemble cystitis or urethritis, so in most cases these diseases are treated.
Over time, the formation increases, and the signs appear more clearly. The main symptoms of the pathology include:
- pain and burning when urinating;
- discomfort in the urethral area when walking or during sexual intercourse;
- feeling of bladder fullness after urination;
- urinary incontinence: initially during sneezing, coughing or physical stress, later, when the polyp reaches a large size, urine can leak constantly, causing discomfort to the woman;
- blood in urine. This disorder occurs in cases where a polyp grows in the tissue under the mucous membrane of the urethra.
If the tumor is not eliminated in time, a bacterial infection may occur, resulting in the development of:
- pyelonephritis : inflammation of the kidneys;
- cystitis : inflammatory process in the bladder area.
When an infection occurs, pain occurs in the lumbar region or lower abdomen, frequent urge to urinate, swelling and purulent discharge.
Acute
If the growth quickly increases and narrows the lumen of the urethra, this becomes the cause of acute urinary retention. This problem is most often observed in men. This is due to anatomical features (long and narrow urethra). But in some cases, women also face this.
- the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies when pressing this area;
- inability to empty the bladder despite a strong urge to urinate;
- appearance of anxiety: a person cannot sit in one place, moves in a half-bent position.
Acute symptoms develop very quickly, sometimes within a few hours. In this case, the outflow of urine can only be restored using catheterization.
How are polyps in a man's bladder treated?
A bladder polyp is a benign tumor that develops from the transitional epithelium of the bladder wall. The polyp is not prone to persistent malignancy, but this possibility increases with age. A polyp can go undetected for a long time and can only be discovered after an abnormality or when it has grown significantly.
You may be interested in: Fibrous polyp of the rectum: first symptoms, surgery and consequences
A bladder polyp may develop into a malignant tumor with increasing age.
Causes
Modern self-defense equipment is an impressive list of items that are mostly different from each other. The most popular are those that do not require a license or permission to purchase and use. In the Tesakov.com online store you can buy self-defense equipment without a license.
The exact mechanism of tumors is unknown, because the trigger can be anything - from simple stress to long-term illnesses. The risk group also includes men with a tumor:
- Bad inheritance . If at birth a man suffered from malignant and benign formations, then the risk of their occurrence among the heirs increases.
- Persistent inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system - cystitis, orchitis, colliculitis, urethritis. It is important not to start with such diseases and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
- Weak immunity . Weak immunity is one of the causes of tumors in general. The immune system does not destroy cells in time, the genetic apparatus of which has ceased to function normally - tumors develop, including polyps.
Factors that can contribute to the formation and development of polyps, like other types of benign tumors:
The exact causes of polyps are unknown
- hormonal dysfunctions and imbalances, improper hormonal treatment;
- promiscuity, unprotected sexual intercourse;
- bad habits - alcoholism, smoking, drug use (especially strong ones);
- prolonged contact with toxic and toxic substances - paint products, industrial antiseptics, etc.;
- irradiation, radiation sickness;
- frequent and severe stress, constant depression;
- poor diet - large amounts of fatty foods and meats, foods with strong additives, small amounts of fruits and vitamins
Clinical manifestations
A small tumor may not appear for a long time - without pain, and also without urinary tract diseases. There are several situations that may indicate a tumor in the bladder:
- A polyp blocks the entrance to the urethra . This leads to frequent urination, urinary retention, and pain in the bladder. These symptoms appear gradually, from an increasingly frequent need to urinate to severe pain and inability to empty the bladder.
- Large polyp . When the tumor becomes large, pain may occur when the walls of the bladder are stretched, visits to the toilet become more frequent (the tumor occupies a large volume), and in many cases it also blocks access to the bladder.
- Presence of blood and pus in the urine . The epithelium of the bladder wall tends to stretch, and with strong stretching, the polyp can rupture with subsequent inflammation. Clinically, this manifests itself in severe pain, blood and purulent dirt in the urine.
Diagnostics
New tumors of this type are detected using ultrasound. However, for an accurate diagnosis, it is usually necessary to perform a cystoscopy to find out the exact location, presence/absence of a leg and exact dimensions.
This is an unpleasant procedure, so many men choose not to undergo it and continue to live with the polyp.
In some cases, this is the best solution - it can stop its growth and does not affect a person’s life, and unnecessary operations are always harmful to the body.
Cystoscopy helps make an accurate diagnosis
However, doctors recommend regularly monitoring such a benign tumor as it can become malignant. The sooner it is detected, the more likely it is that it will be removed rather than metastasizing to other organs.
Treatment
polyps are treated surgically. For this there must be appropriate indications - a large area, scars, tears, inflammation. It is better to leave small formations “as they are” and not remove them, but simply observe them regularly.
The modern surgical method used to remove polyps is called diathermocoagulation .
A surgical cystoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder, at the end of which there is a loop - this loop is placed on the polyp, the loop is heated and the polyp is ruptured.
The operation is performed quickly, under general anesthesia, and healing usually occurs quickly and without complications. After surgery, the polyp tissue is examined for malignancy.
Complications
Stages of polyp growth and transformation
If the polyp is not examined or is not removed with a delay, complications may arise:
- malignant tumor with subsequent possible metastasis to other parts of the body;
- lacerations and inflammation, which can spread to other organs of the genitourinary system;
- necrosis, which can lead to extensive purulent inflammation of the bladder wall;
- bleeding from lacerations, which may worsen over time.
All these complications can be avoided if you regularly (at least twice a year) visit a urologist and regularly examine already identified polyps.
Prevention
If you have a family member with tumors, there are several rules that should be followed to reduce the risk of developing tumors. The same applies to all those who care about their health:
- Timely treatment. If you suspect diseases of the genitourinary system, you should immediately contact a urologist and undergo an examination. All of the pelvic organs are connected in some way, and inflammation or swelling in one part of the pelvis can affect another.
- Healthy lifestyle . The development of tumors is most strongly influenced by smoking - tobacco smoke contains the most carcinogenic substances.
- Good food . Less fried and fatty foods, more fruits and vegetables, dairy products.
- Rest . Chronic stress negatively affects the body and reduces immunity, so breaks and rest are necessary. This is especially true for those whose work is associated with nervous tension and difficult decisions.
- Is your beard not growing? Or is it not as thick and chic as we would like? He's not lost yet.
- Cosmetics and accessories for proper care of your beard and mustache. Come in!
Diagnostics
A small polyp on the urethra in women is usually discovered by chance at a preventive appointment or during examination for other diseases.
- laboratory methods : general blood and urine analysis, collection of biomaterial from the urethra and vagina, histology;
- ultrasound examination of the urinary system : the simplest, painless and effective way to identify a formation, as well as the ability to evaluate the microstructure of the growth;
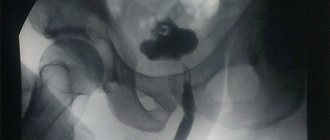
- urethrography : one of the modern methods of x-ray examination, which makes it possible to determine the location and size of polyps (they can be seen in the photo), as well as the diameter of the lumen of different parts of the urethra. With ascending urethrography, imaging the female urethra is technically more difficult than that of men.
Diagnosis of urethral polyps
The localization of polyps mainly in the area of the external opening of the urethra determines the clinical picture of the disease in women:
- Burning and cutting during urination;
- Pollakiuria (the need for repeated urination during the day or night, subject to the release of a normal or reduced daily volume of urine);
- Strangury (difficulty urinating);
- Postcoital urethrorrhagia (discharge of blood from the urethra after sexual intercourse).
Symptoms of urethral polyp in women include episodes of acute urinary retention, initial hematuria (blood discharge from the urethra outside the act of urination).
The examination scheme for patients suffering from urethral polyps at the Yusupov Hospital includes the examination of scrapings from the urethra and cervical canal for urogenital infection using the culture method and PCR (polymerase chain reaction). Laboratory technicians determine the content of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-4 in blood serum using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
To study the microcirculation system of the mucous membrane of the urethra with a polyp, a laser blood microcirculation analyzer is used. The average blood flow, or microcirculation index, standard deviation, amplitude-frequency characteristics in various ranges of blood flow fluctuations are determined, on the basis of which the fluxmotion index was calculated, which reflects the effectiveness of microcirculation regulation.
Histologists conduct electron microscopic examination of semi-thin and ultra-thin sections of tissue. Light-optical examination and morphometric analysis were carried out using a universal microscope and a digital camera. If there is a urethral polyp in women, the photo is discussed by specialists of various profiles.
During endoscopic examination, urethral polyps in women are tumor-like formations in the area of the posterior lip of the external opening of the urethra, ranging in size from 2 mm to 1–2 cm, pedunculated or broad-based. They have a smooth, sometimes bleeding surface.
Treatment
Surgery is necessary in cases where the polyp causes unpleasant symptoms, bleeds, or causes an obstruction in the flow of urine.
- physical destruction . Polyps can be removed using electrocoagulation, laser or cryodestruction. The procedure is performed under general or local anesthesia. In this case, the formation is eliminated, strictly adhering to its boundaries and without damaging healthy tissue;
- surgical excision . This method of removal is used if the formation reaches a large size or is potentially malignant. Manipulations are carried out under general anesthesia followed by suturing.
If the size of the neoplasm is small and there are no symptoms of the disease, and also if the pathology is detected in an elderly person, removal is not carried out, limiting itself to therapy of the inflammatory process and observation.
Treatment with traditional methods
To treat pathology, folk remedies are used, which, according to patients, in some cases help get rid of the problem:
- recipe No. 1: celandine grass is crushed and the juice is squeezed out, which is mixed in equal proportions with 70% medical alcohol. The finished product is taken 20 drops three times a day, half an hour before meals. Treatment is continued for a month, then a two-week break is taken and, if necessary, it is resumed;
- recipe No. 2: 6 tablespoons of dry, hullless pumpkin seeds are ground into flour and mixed with six yolks from hard-boiled chicken eggs. At the next stage, add 500 ml of refined olive oil and place in a water bath for 20 minutes. Take one teaspoon on an empty stomach once a day. Treatment is carried out for a week, then take a break for five days. The finished medicine is stored in a tightly sealed glass container in the refrigerator;
- recipe No. 3: mix 2 parts of birch buds, 3 parts of horsetail and 4 parts of bearberry. 2 tablespoons of dry raw materials are poured into 400 ml of boiling water and left for an hour. Strain and take 100 ml 4 times a day. The duration of treatment is one month. This remedy helps stop the growth of polyps.
Before using folk remedies to treat tumors in the urethra, you should consult your doctor.
Treatment of urethral polyp
For surgical treatment of the urethral polyp, local infiltration anesthesia with a 2% lidocaine solution administered paraurethrally in an amount of 2-5 ml was used. 40 patients underwent resection of the urethral polyp with the Surgitron apparatus, followed by suturing of the bed with single atraumatic catgut sutures, dissection of the external urethral opening for stenosis - in 8 patients, dissection of urethro-hymenal adhesions - in 2 patients. Patients with urethral dystopia refused surgical treatment and were given long-term antibiotic therapy. Patients had a Foley catheter installed for 24 hours. The next day, everyone was examined at the Central Hospital, the catheter was removed, and baths with a manganese solution were prescribed twice a day.
Three weeks after surgical treatment of the urethral polyp, 20 ml of colloidal silver solution was instilled into the bladder every other day (10 manipulations). When flora was detected in urine culture, antibacterial therapy was carried out according to sensitivity to antibiotics. After treatment, cystoscopy performed 3 months later revealed no signs of cystitis. According to histological examination, all urethral polyps were benign.
Complications
- malignancy (transformation of a benign tumor into a malignant neoplasm);
- chronic cystitis, pyelonephritis or urethritis;
- violation of the integrity of the urethral mucosa, resulting in frequent bleeding, leading to the development of iron deficiency anemia.
Removal of polyps must be carried out regardless of their type, since there is a risk of degeneration into a malignant form, especially if the growth grows quickly and reaches a large size.
After removal of a urethral polyp
After surgery to remove a urethral polyp, drug treatment is prescribed, treatment of the external opening of the urethra with octenisept, and levomikol ointment on the urethra. No dressings are required, just wear and change a disposable pad. The postoperative period after treatment of a urethral polyp takes 2 weeks until the urethral mucosa is completely restored. Hospitalization is not required to remove a urethral polyp.