If a head injury occurs, it is important to immediately begin rehabilitation measures at home, which will help prevent serious complications - intracranial hemorrhages, swelling and dislocation of brain structures. If a person falls and hits their head hard, the consequences can range from a mild concussion to coma and death. Statistics show that the prevalence of head injuries is about 200 cases per 100 thousand population annually. For 30% of patients, brain damage is fatal. Every year, severe head injuries and associated disorders of vital and brain functions lead to the death of 1.5 million people in the world. Another 2.5 million people become disabled.
Definition
A head injury occurs when a person falls or hits the skull with a hard object; the condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.
Even weak blows to the skull area lead to an increase in the permeability of the blood-brain barrier, the development of autoimmune reactions in the tissues of the central nervous system, and neurodegenerative changes.
If you hit the back of the head, forehead, or temple hard, the tissues of the brain and skull will be damaged, which can be hidden from view during a visual inspection when there are no violations of the integrity of the skin. A fracture of the bone structures of the skull is a life-threatening disorder, which is always accompanied by a change in the morphological structure of the brain matter.
A dent on the forehead, crown or back of the head after a blow is a reason to suspect a fracture of the cranial bones. Other signs to look out for include softening of the bone structures of the skull, progressive loss of motor coordination and other reactions. If you shake your head, it is important not to make sudden movements, which can aggravate the dysfunction of the brain.
If struck, a person may be seriously injured. As a result of a skull fracture, pneumocephalus (air entering the cranial cavity) often develops. A common complication of head injury is damage to the cranial nerves. The condition is accompanied by paresis of the facial muscles and visual impairment.
Often the pathology is combined with damage to the spinal column in the cervical region. Airway obstruction (obstruction) is a common cause of early death in TBI. Head injuries in 90% of cases are accompanied by loss of consciousness, which correlates with a decrease in the tone of the muscles located in the pharynx. A decrease in tone leads to a displacement of the tongue and soft palate, which causes a violation of the patency of the respiratory system.
Types of injuries
Taking into account the nature of the damage, concussion, contusion of brain tissue or compression of the brain are distinguished. Considering the severity of the injuries received, a distinction is made between concussion of the brain (mild contusion), moderate contusion of brain tissue, and severe trauma. A wound that appears on the head when you fall, get knocked, or are attacked occurs:
- Open (damaged skin).
- Closed (skin without damage; subcutaneous soft tissues, bone and medulla undergo pathological changes in morphological structure).
- Penetrating (characterized by a violation of the integrity of the meninges).
Depending on the location of the pathological focus, contusion of the occipital area, frontal, temporal, parietal lobe is distinguished.
Features of head injury in childhood
The bone tissue of a child under 12 years of age contains a large amount of water, has a fibrous structure, and is characterized by a low content of calcium salts. The bones of the skull in childhood are soft and flexible. After a blow, a dent may appear on the child’s head; the brain matter is damaged more often due to strong mechanical impact on the skull than in adult patients.
If a child falls and hits his head, he may have a headache, an increase in body temperature, and vomiting, which suggests the need to urgently take the following actions: lay the child in a horizontal position and call a doctor. Even if the baby remains conscious, it is important to pay attention to changes in his behavior.
Affected children usually lose their appetite. They become inactive and complain of double vision. If a child feels sick after hitting his head, and signs such as apathy, lethargy, weakness, drowsiness and dizziness appear, he needs urgent medical attention.
Features of bruises in children
A bump on the head after a blow in a child is a very common occurrence. After all, children love a mobile and active lifestyle. Babies have delicate scalp, so a hematoma can form even with a minor blow.
However, head injuries in children are often accompanied by concussion and other unpleasant consequences. Therefore, you need to pay attention to the baby’s well-being. Many children cry a lot when they are bruised, but most often this is due to fear rather than pain. You need to let the baby calm down, and then take a closer look at his condition. If you have the slightest doubt, you should contact a pediatric traumatologist.
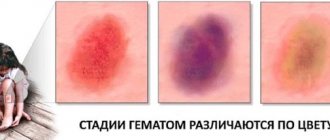
The size of the hematoma does not always indicate the danger of injury. For example, with forehead bruises, huge bumps always form. However, the frontal bone is the strongest and protects the brain well, so unpleasant consequences from bruises in this area are rare.
Causes
If you have a headache after a fight, it is better to immediately seek medical help. Contusion of the brain and bone structures of the skull occurs due to a direct blow to the skull area, mechanical impact with acceleration, and compression of the cranial structures. Common situations associated with injury:
- Road accidents.
- Falling from height.
- Industrial injuries.
- Traumatic injuries as a result of a fight or attack.
- Sports activities.
Depending on the strength of the traumatic impact, damage of varying degrees of severity occurs - reversible disorders (concussions of the brain) and irreversible (foci of crushed brain structures). The crush site is a variable area of the cerebral hemispheres, in the area of which the meninges are ruptured and particles of alternative brain matter are present.
The crush site is characterized by a functional and structural change in the nervous tissue (neurons, gliocytes, nerve fibers, synapses) and elements of the vascular system, in the area of which multiple hematomas appear. Bruises of the skull are usually accompanied by the formation of foci of hemorrhage.
The crush site in the acute period of TBI manifests itself clinically as an intracranial space-occupying process (hematoma, tumor) and contributes to the progression of hypertensive-dislocation syndrome. As a result, life-threatening conditions associated with pinching and compression of the brain stem may develop.
Causes
Contusion of the soft tissues of the head occurs as a result of mechanical impact . This could be a fall and bruise on the ground, a deliberate or accidental hit with a certain object.
Most often, such injuries occur as a result of sports training, combined with a fall, in ice, as a result of a fight, etc.
Symptoms
Injuries in the skull area are differentiated based on severity. In accordance with this classification, they are divided into mild, moderate and severe forms. Symptoms depend on the severity of the damage. A mild form, known as a concussion, is accompanied by symptoms:
- Darkness, loss of consciousness (lasts several seconds, minutes).
- Disorientation in space and time, confusion of thoughts.
- Amnesia (memory loss) of retrograde or anterograde type.
- Pain in the head area (intense, bursting, acute), dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Noise, buzzing in the ears.
- Pain in the eye orbits.
Neurological deficit of focal type is absent or mildly expressed. A strong blow to the back of the head during a fall or as a result of mechanical impact from the outside in adults and children is associated with serious consequences. Moderate injuries are accompanied by symptoms:
- Prolonged loss of consciousness (lasts several minutes or hours).
- Lethargy, inability to adequately navigate time and space.
- Amnesia of retrograde and anterograde type.
- Diffuse type headache.
- Meningeal symptoms (muscle rigidity in the occipital region, pathological reflexes of Brudzinsky, Kernig, state of stupor, stupor, paresis and paralysis, paresthesia - sensitivity disorder, numbness, tingling in the area of the limbs, face).
- Psychomotor agitation.
Additional signs of damage to nervous tissue depend on the localization of the site of impact during a head injury; taking into account the focal symptoms, the doctor decides what to do. Focal symptoms include impaired motor coordination, pyramidal signs (pathological foot and hand reflexes, reactions of oral automatism, clonus - rapid, involuntary contractions of muscle groups, synkinesis - involuntary friendly contraction of a limb in response to voluntary movement of a symmetrical limb).
Some patients experience damage to the bone structures of the skull - most often the vault and base, which is accompanied by the appearance of subgaleal hematomas (accumulation of blood in the space located between the periosteum and the aponeurosis - a tendon plate formed from collagen fibers). Bleeding from the wound often occurs.
In the absence of a violation of the integrity of the cranial bones and soft tissues of the head, sometimes there is a leakage of a mixture of blood and cerebrospinal fluid from the physiological openings of the head - the nasal and auditory passages, from the pharynx. If a TBI is accompanied by liquorrhea (random leakage of cerebrospinal fluid), it is considered open.
After a strong blow, which provokes severe damage to the nervous tissue, an acute, debilitating headache appears and dizziness occurs. The patient does not regain consciousness for a long time. Signs noted: severe impairment of respiratory function and cardiac activity. Other symptoms:
- Heart rhythm disturbances (tachycardia, bradycardia).
- Increased blood pressure values.
- Difficulty breathing associated with obstruction of the respiratory system.
In the acute period, primary brainstem symptoms develop - horizontal, slow, unassociated movement of the eyeballs, dilation or contraction of the diameter of the bilateral pupils, unstable changes in muscle tone, decerebrate rigidity (increased tone of the extensor muscles, decreased tone of the flexor muscles).
Primary brainstem symptoms that develop with a strong blow to the head include a decrease in deep reflexes (tendon, articular, periosteal), which correlates with the serious condition of the victim and necessitates the need to correct vital functions.
Neurological deficit is manifested by general cerebral signs - severe depression of consciousness up to coma. In victims who have developed an intracranial hematoma as a consequence of a blow to the head, there is a short-term clear interval (temporary improvement in condition), after which a sharp deterioration occurs.
In addition to severe bradycardia (less than 40-50 beats per minute), symptoms such as unilateral mydriasis (pupil dilation), hemiparesis of collateral (lateral) localization, convulsive attacks of local (local) or generalized (widespread) type are detected. After a strong blow to the head, the body temperature may rise, which is due to various reasons:
- Stressful effects on the body.
- The development of the inflammatory process due to pathogens (bacteria, viruses) entering the wound.
- Shock due to injuries.
- Intoxication of the body as a result of the formation of decay products of damaged tissue.
If after a blow you have a headache and your body temperature has risen, you need to consult a doctor and do a comprehensive examination, which will help to find out the exact causes of the disorders.
First aid
Immediately after the impact, carefully place the child on the bed and carefully examine his head. At the same time, there is no need to rush and fuss so that the baby does not become even more frightened. After all, hysteria can increase intracranial pressure or increase bleeding from a wound.
When a lump forms, apply ice wrapped in a piece of cloth to it. A cold water bottle or a bag of frozen food wrapped in a towel will do. A cooling compress will help relieve swelling and prevent the development of a hematoma. But you need to hold it for no more than five minutes.
If you find a wound, treat its edges with hydrogen peroxide and apply a gauze or cloth swab to absorb the blood. If bleeding does not stop within 10 minutes, call a doctor.
If there is no damage at the site of impact, the child's condition should be closely monitored for at least a week. Moreover, in the first few hours it is better not to put the baby to bed, since the main symptoms of a concussion appear precisely at this time.
Children of the first year of life cannot talk about their health. Consult a doctor if you notice prolonged crying, refusal to eat, restless sleep, or vomiting.
An older child needs to be asked in detail how he fell and where the pain is felt. If the impact is muffled by the carpet, and the fall itself was not dangerous, medical attention is not required. But it doesn’t hurt to watch the baby for a few days to make sure there are no dangerous consequences.
Diagnostics
Timely, correct diagnosis significantly improves the prognosis for severe head injuries; the doctor identifies the nature and extent of the damage and determines what to do. Priority methods of instrumental diagnostics are CT and MRI. During neuroimaging, the exact localization of the pathological focus, the presence of intracranial hematomas, and the extent of the pathological process are detected.
To assess the state of consciousness, the criteria of the Glasgow scale are used. In a hospital setting, a blood test is done to determine the concentration of glucose and electrolytes, blood clotting indicators. In some cases, lumbar puncture is indicated (confirmation of the presence of intracranial bleeding, exclusion of infectious lesions of the central nervous system).
Treatment methods
In case of a mild concussion, the patient is advised to rest in bed. If you hit the back of your head or any other part of your head, the first thing to do is call an ambulance. The doctor will assess the severity of the condition and, if necessary, carry out rehabilitation measures, which include:
- Tracheal intubation.
- Air duct insertion.
- Connection to a ventilator.
- Administration of plasma replacement solutions.
- Dehydration therapy.
If necessary, surgical intervention is performed, during which intracerebral and meningeal hematomas are removed and impaired blood flow is restored.
Prevention
A blow to the temple can have life-threatening consequences. In this area, the brain is most vulnerable, since the temporal bone is quite thin (two millimeters). Doctors recommend taking precautions. Do not get into fights, avoid extreme hobbies. Children need to be monitored especially closely, as they are the ones most susceptible to head injuries.
If a bruise does occur, you must immediately call an ambulance. The consequences of a bruise may not appear immediately, but after several days, so it is important to undergo prompt diagnosis and begin therapy to reduce the risk of developing dangerous consequences.
Consequences of a head injury
The consequences of a strong blow to the back of the head can be expressed in sleep disturbances, visual dysfunction, deterioration in performance and cognitive abilities, and the development of depression. A simple hit to the head with a ball can lead to serious consequences:
- Chronic headaches.
- Hydrocephalic syndrome, persistent increase in intracranial pressure.
- Paresis, paralysis.
- Brain abscess.
- Epileptic seizures, convulsive syndrome.
The consequences of strong blows to the head with a fist often manifest themselves in the form of intracranial bleeding, swelling of brain tissue, dislocation of brain structures, which can ultimately lead to disability or death.
A head injury, regardless of severity, can have serious health consequences. For any head injury, it is necessary to undergo a diagnostic examination and receive adequate treatment.
519
When a doctor's help is needed
It is necessary to consult a doctor if the bump on the head after the blow does not go away within a week. If swelling does not disappear for a long time, this may indicate trauma to the bone tissue.
Seek immediate medical attention if a child or adult experiences the following symptoms:
- pain in the head and neck area;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blurred vision;
- strabismus;
- discharge of blood or clear fluid from the nose or ears;
- increase in pain syndrome;
- disorders of speech and consciousness;
- pain that increases when turning the head;
- seizures;
- bleeding from the wound that does not stop for more than 10 - 15 minutes.
These warning signs may indicate a severe head injury. It is necessary to put the patient to bed, call an ambulance and monitor his consciousness and breathing until the doctors arrive.