Urinalysis is one of the most common forms of primary diagnosis in children. With its help, you can recognize the disease at an early stage and prescribe proper treatment.
Children are often prescribed a general analysis. But other types of studies are carried out for detailed diagnosis. The appropriateness of their implementation is determined by the doctor.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko in children is one of the most reliable research methods.
Features of the method
Analysis using the Nechiporenko method is a study of urine, in which microscopy of its sediment is performed to determine the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes and cylinders in 1 ml of volume. It is recommended in situations where changes in the overall analysis have been detected. It can be used to confirm or exclude renal pathologies. You can return it for free.
Indications for use
If dangerous changes are observed in a clinical study, an accurate diagnosis can be made through the Nechiporenko study.
Why it is carried out:
- To identify inflammatory processes in the urinary system (urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis).
- To assess kidney damage in a number of systemic diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus).
- For a more accurate diagnosis of diseases of the urinary system.
- To monitor the treatment of pathologies of the urinary organs.
In what cases is it indicated:
- For symptoms of diseases of the urinary system (changes in color, clarity of urine, pain during urination).
- If there are deviations in the overall analysis.
- For systemic diseases in which there is a risk of kidney damage.
- As a preventive measure.
- It is not prescribed to absolutely everyone. If the general examination does not reveal any deviations, there is no point in carrying out additional procedures.
Preparing children for testing
In order for the results of a urine test to be reliable, it is necessary to properly prepare the child.
- The day before passing urine, it is recommended to remove foods from your diet that can change the color of urine.
- You should not undergo the examination while taking medications that may affect the results.
- Before the examination, you should avoid physical activity.
- It is not recommended to collect urine according to Nechiporenko for children who have flu symptoms.
- Teenage girls should not collect a sample during their period.
Rules for collecting urine in children
Parents are required to know how to properly collect a sample from their child.
- Before you start collecting urine, you should wash your baby. Girls should wash not only their labia, but also their anus.
- Urine needs to be collected in the morning.
- Not the entire portion of urine is used for study. To get what you need, you should ask the baby to urinate a little, and only after that start collecting. If the baby is a newborn, you should just wait until the first portion of urine passes.
- The resulting sample should be submitted for examination no later than two hours after collection.
What the analysis shows
What the analysis collected from children shows is that the Nechiporenko study allows you to determine the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes, as well as cylinders per 1 ml of urine.
Decoding
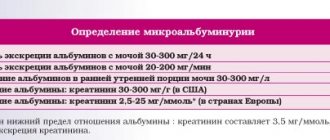
The Nechiporenko urine test in children is interpreted by a doctor. Normal indicators are presented in the table in the photo:
Each element speaks to a specific type of problem. If hematuria is observed, this indicates the development of cystitis or urolithiasis. An increased level of leukocytes indicates the development of pyelonephritis or nephrolithiasis.
Norm of leukocytes in children
White blood cells are cells that circulate throughout the circulatory system and control the functioning of the immune system. If there is a danger of an infectious lesion, they accumulate at the source of this lesion and try to destroy the microbes.
The norm of leukocytes for children of different ages is up to 2000 per 1 ml of urine.
Norm of red blood cells in children
Erythrocytes are red blood cells that circulate throughout the vascular bed. Red blood cells in a child’s urine should not exceed 1000 per 1 ml. This indicator is the same for both infants and older children. Most often, there are no red blood cells at all.
Due to the work of the glomerular renal apparatus, the reverse process of reabsorption of all elements of blood cells is carried out. If a large number of red blood cells are observed in the sediment, this indicates a violation of the filtration functions of the kidneys.
Cylinders are normal in children
Cylinders are compounds consisting of protein molecules. If dangerous damage to the kidneys occurs, they accumulate in the tubules of these organs. The nature of the lesions can be infectious or tumor.
The norm in children is no more than 20 cylinders per 1 ml. If there are more of them, this indicates that there is kidney dysfunction.
What do deviations from the norm indicate?
The doctor can decipher the results and understand what pathologies are indicated by deviations from normal values.
Leukocytes
An increased number indicates that the cause of the pathology is an infection. In this case, it is worth suspecting the presence of the following pathologies:
- inflammation in the kidneys (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis);
- inflammation in the bladder;
- urolithiasis disease.
Red blood cells
If the interpretation of the result showed their increased level, this may indicate the following pathologies: tumor, chronic kidney pathology that developed due to diabetes mellitus.
Cylinders
Granular casts should be absent in healthy children. They appear due to the death of the mucosal cells of the inner walls of the renal tubules. Waxy ones are observed in the urine of children suffering from renal amyloidosis.
Red blood cell casts indicate the presence of terminal vein thrombosis. The presence of epithelial ones indicates dangerous pathologies. This could be a viral infection, toxicosis caused by salicylate poisoning.
Increased indicators of cylinders in infants indicate the presence of renal failure and autoimmune diseases.
A poor analysis may indicate not only the presence of pathology, but also that the urine collection algorithm was violated.
We recommend that you read:
Possible distortion of results
If the material was taken incorrectly, the data will be distorted. Here are the factors that influence the result:
- Long-term storage of material. In an alkaline environment, red blood cells can be destroyed.
- Physical strain and trauma to the urethra. They cause hematuria, which shows an increased number of red blood cells. The same situation can occur if urine was collected during menstruation.
- Insufficient genital hygiene before giving urine. As a result, the study may show a large number of leukocytes.
- Proteinuria. Because of this, cylinders may be missing.
- Taking certain medications.
Collection of analysis from infants
Many parents are perplexed about how to collect a urine test from a child who is less than a year old. After all, it is difficult to do this. To take urine from a baby, you should use a urinal. It consists of an oilcloth with a hole and a surface with a sticky layer. The sticky side will stay on your baby's skin until he urinates. Before collecting urine from a child, you should wash it.
The baby should be placed on the changing table and calmed down. You need to place a container between its legs. After this, the baby will need to be lifted and waited until he goes down in a small way. After this, the urine bag can be peeled off from its legs, and the collected urine can be poured into a separate container.
The method of collecting urine using a urine bag is suitable for both little boys and girls. It can be used for both newborns and one-year-old children.
Conclusion
Urinalysis using the Nechiporenko method is a study that allows you to identify the presence of pathologies of the urinary tract and kidneys and begin treatment in a timely manner. During this study, the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and casts in 1 ml of urine is counted.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko in children has its own standards; the results must be deciphered by a doctor. If the results show higher than normal levels of certain components, this indicates the presence of a disease.
A similar situation can also occur if the rules for collecting urine have been violated.
Clinical significance
This method of research makes it possible to detect unexpressed leukocyturia, which is often observed with gloerulonephritis of a chronic, latent or sluggish form and cannot be detected by picroscopy of sediments.
The method is used in diagnosing kidney diseases. Elevated red blood cells confirm the development of arteriosclerosis or glomerulonephritis, an increase in leukocytes is inherent in pyelonephritis. It should be remembered that calculous pyelonephritis is confirmed by red blood cells found in sediments.
Numerous studies using Nechiporenko’s method make it possible to confidently state that this method is very adequate when prescribing a therapeutic course and helps to correct the treatment process.
During medical examination, the technique will help to track the progress of the disease and immediately prescribe additional medications if deviations from the norm are detected.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko in a baby: how to take it correctly, norm based on the results
Various tests are used to diagnose diseases. One of the specific research methods is urine analysis according to Nechiporenko. It is prescribed to adults and children, including infants.
Analysis of urine
What does the analysis according to Nechiporenko indicate?
Using the Nechiporenko test, infectious and other diseases of the kidneys and urinary organs are determined. It is carried out as an in-depth study in the following cases:
- When examining a general urine test, discrepancies with the norm were revealed;
- the baby has signs of disease of the urinary organs, but in the general analysis the indicators are normal;
- fever without other symptoms of any disease;
- pathologies of the kidneys and urinary organs in acute or chronic form were detected;
- infectious diseases of the kidneys and urinary organs have ever been diagnosed before;
- the child has a systemic pathology, with a high probability of kidney damage;
- medical examinations for preventive purposes.
Advantages of the Nechiporenko method
- technically simple, convenient, accessible;
- not burdensome for the examinee and the staff, since it does not require additional preparation of the patient or urine collection for a strictly defined time;
- for the study, the average portion of urine can be used (which eliminates the need for catheterization of the bladder) and urine obtained from the kidneys during separate catheterization of the ureters to clarify topical diagnostics;
- does not require a large amount of urine - determination of leukocyturia can be carried out in a small amount of urine obtained from the kidney;
- in terms of quantitative indicators it is not inferior to other methods;
- easy to perform in dynamics;
- is a unified method.
Urine analysis according to Sulkovich: norms and interpretation in children
The norm for urine analysis in children according to Nechiporenko
The Nechiporenko analysis is one of the studies of a child’s urine that helps in clarifying the diagnosis and treating diseases of the excretory system. Why is it prescribed to a child, how to properly prepare for such an analysis and what will its results tell you?
While a general examination of a child’s urine can be called a screening analysis, the Nechiporenko test has a different purpose. This analysis helps to verify the presence of inflammation and clarify its location.
Detection of blood cells in a general analysis involves counting in the field of view of a microscope. And for analysis according to Nechiporenko, the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes is counted per unit volume.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko is prescribed if an inflammatory process in the kidneys is suspected. Most often, such an analysis is carried out after a general urine test, which shows an increased number of leukocytes or red blood cells. This test is also performed to monitor the treatment being given to a child with kidney disease.
A day or two before the test, you should consume plant and meat products in moderation so that the diet does not change the acidity of the urine, which can affect the number of cylinders.
Before such a study, the child should not take medications with a diuretic effect, since frequent urination distorts the results of this test. Physical and emotional overload should also be excluded.
Before collecting urine, the child’s genitals should be toileted to prevent additional leukocytes from entering the urine sample. In order for kidney function to be shown most reliably in the analysis, an average portion of excreted urine is collected.
The child is told to start urinating into the toilet, then some of the urine is collected into a container, after which the child finishes urinating back into the toilet.
If the child is too small, it is possible to collect all the urine excreted, but the doctor who will interpret the test results should be informed about this. The collected material should be brought to the laboratory within 1-2 hours after urination.
Peculiarities of interpretation of results in children
There are certain deviations from the norm that indicate certain diseases and damage to the kidney tissue. Thus, high levels of leukocytes may indicate the infectious nature of the lesion.
It is important to suspect problems such as pyelonephritis (microbial inflammation of the calyces and pelvis of the kidneys) or glomerulonephritis (damage to the interstitium and kidney tissue). An increase in the level of leukocytes may be evidence of damage to the urinary tract or bladder walls, as well as a manifestation of urolithiasis
An increase in the number of red blood cells is often evidence of damage to the urinary tract by a stone or a tumor process; in addition, it can be a marker of kidney damage against the background of autoimmune, metabolic or other pathologies, glomerulonephritis.
The cylinders, depending on their type in the detected sample, can indicate the level of damage and certain diseases.
Important
Children should not have granular casts at all; they are formed due to dying epithelial cells lining the urinary tract.
Waxy casts in the urine of children are typical of amyloid kidney disease.
Red blood cell casts arise due to the sticking of red blood cells in the tubules; they appear with thrombosis of the renal veins.
Epithelial casts are typical for various serious pathologies, these can be viral infections of the urinary tract, toxicoses that occur against the background of drug poisoning. An increase in the level of cylinders in the urine indicates the presence of renal failure and manifestations of autoimmune pathology.
Important
Unsatisfactory urine tests may be due to collection defects if the sample contains materials from the genitals or anus.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko is the norm in children
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko in children is carried out to accurately count the number of red blood cells and white blood cells. This is necessary for the diagnosis of latent pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. For analysis, take 1 ml of an average portion of urine.
Indications for Nechiporenko analysis in children
Using a urine test according to Nechiporenko, latent leukocyturia can be detected in a child. It is characteristic of chronic, sluggish forms of glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis. In this course of the disease, leukocytes and red blood cells are not detected in a routine urine test. Identifying the predominance of erythrocyturia or leukocyturia helps to accurately diagnose the baby.
The Nechiporenko test is prescribed for suspected kidney disease, which includes the following symptoms:
- change in the color or smell of urine;
- frequent or infrequent, painful urination;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- swelling on the face;
- poor appetite;
- prolonged elevated temperature.
The analysis is carried out for children with chronic kidney disease to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. The study is not indicated for healthy children.
Preparing children to take a urine test according to Nechiporenko
You need to prepare for a urine test 24 hours in advance. Preparation rules:
- exclude beets, carrots, and protein foods from the diet;
- If possible, stop taking medications;
- limit physical activity.
It is not advisable to take the Nechiporenko test against the background of acute respiratory infections. Teenage girls should not have the test during their periods.
Formula-fed babies are fed as usual. New complementary foods should not be introduced on the eve of the study. If the child is breastfed, the mother should follow the diet. She needs to exclude protein foods, spices, colored vegetables and fruits from her diet.
Rules for collecting urine in children
Urine is collected from the middle portion. The baby releases the first portion into the potty or toilet, then the parent places a sterile container under the stream of urine and collects a little liquid.
If the baby does not yet know how to voluntarily hold urination, let him urinate as usual.
The parent should place the container a few seconds after the start of urination, draw some liquid and remove the container.
Before collecting urine, the child should be washed with clean water. The girls are washed from front to back. A sample is taken in the morning, immediately after waking up. The container with the collected urine is delivered to laboratory technicians no later than two hours after the sample is taken. Urine should be warm and should not be stored in the refrigerator.
What does urine analysis according to Nechiporenko show in children?
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko in children shows the number of red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders in 1 ml of urine. By the predominance of one or another indicator, one can judge the child’s illness.
If, as a result of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko, leukocytes predominate, this indicates a bacterial infection, most often pyelonephritis. The predominance of red blood cells indicates damage to the renal glomeruli - glomerulonephritis.
The interpretation of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko in children is carried out by a doctor, taking into account the data of other examinations. If deviations occur, additional examination is prescribed:
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
The doctor may prescribe tests for infections and autoimmune diseases.
Interpretation of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko in children
Parents can independently evaluate the result of a urine test by comparing it with the norm. The table shows the norms for urine analysis according to Nechiporenko in children.
Indicator Norm for children per 1 ml of urine
| Leukocyte | Until 2000 |
| Red blood cells | Up to 1000 |
| Cylinders | Up to 20 |
The decision on diagnosis and subsequent treatment is made only by the doctor. Deviations from the norm are not always pathological. To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to compare the existing symptoms and the data of all examinations.
The norm of leukocytes in the analysis according to Nechiporenko in children
Leukocytes are white blood cells that are responsible for the functioning of the immune system. When inflammation occurs in any part of the body, they accumulate there and destroy microbes. The main part of them is in the blood. The norm of leukocytes per 1 ml of urine in children is up to 2000.
Norm of red blood cells in urine analysis according to Nechiporenko
Red blood cells are red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen. They enter the urine from the blood vessels of the kidneys. Their quantity per 1 ml should not exceed 1000 pieces. Most healthy children normally do not have red blood cells in their urine.
Norm of cylinders in analysis according to Nechiporenko
The casts are protein casts of the renal tubules. They consist of protein and exfoliated epithelial cells. The normal number of cylinders should not be more than 20 per 1 ml of urine.
What do deviations from the norm indicate in urine analysis according to Nechiporenko?
Deviations from the norm in urine tests according to Nechiporenko in children indicate the development of the disease or are associated with violations of sample collection. Only a doctor can correctly determine what the analysis shows, evaluate the norm and give an interpretation of the result.
Leukocytes
An increase in leukocytes in the urine of a child indicates the development of an inflammatory process. Most often it is of bacterial origin. If you receive such a result, you should think about pyelonephritis or a complication of urolithiasis. Purulent inflammation of the kidneys with the formation of abscesses is rare in children.
White blood cells may appear when there is a disease of the bladder or urethra. Common causes of increase are cystitis, urethritis, chlamydial infection.
Red blood cells
A high level of red blood cells in the urine indicates excessive permeability of the blood vessels of the kidneys. This happens with autoimmune inflammation - glomerulonephritis. Red blood cells increase with kidney injuries and urolithiasis.
Cylinders
Elevated cylinders are rare in children. They talk about damage to the renal tubules, when their epithelium is quickly exfoliated. This happens with inflammation, injury, cysts and kidney tumors, and poisoning with drugs or heavy metals.
Red blood cell casts contain red blood cells. They are formed during vein thrombosis or destruction of kidney tissue. Granular casts contain a lot of desquamated epithelium. They appear with severe glomerulonephritis. Waxy casts are dense protein casts. Formed during amyloidosis and renal failure.
Possible distortions of the results of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko in children
Inflated test results according to Nechiporenko do not always indicate a disease. Distortions are possible if urine is collected incorrectly according to Nechiporenko, the sample is stored for a long time, or lack of preparation before taking the test. The result is influenced by:
- intense physical activity on the eve of the procedure;
- eating large amounts of protein foods;
- trauma to the urethra;
- menstruation in girls;
- insufficient hygiene procedures before collecting urine;
- long-term storage of the sample container.
In this case, the results are at the upper limit of the norm or slightly exceed it. The doctor will recommend retaking the test, following the rules for preparing and collecting urine.
Collection of analysis from infants
It is difficult to collect a urine test from infants, because they do not yet know how to urinate in a potty. For the Nechiporenko study, a medium portion is needed, and this makes urine collection even more difficult.
You can use a urine bag to collect urine from an infant. This is a plastic container that is glued to the crotch. First, the child is washed, then a urinal is placed so that it covers the urethra. When the baby urinates, the container is peeled off and the urine is poured into a container. This method can only collect all the urine without dividing it into portions.
What does analysis using the Nechiporenko method show?
The presence of a high number of red blood cells, casts, and leukocytes in the Nechiporenko test will indicate a pathology occurring in the genitourinary system.
Leukocytes are cells that protect against the penetration of infectious agents from the external environment, so if the number of such particles in urine is increased, this means that an inflammatory process is occurring in the body.
An increased number of leukocytes indicates the onset of an inflammatory process concentrated in the urinary tract.
It is important to know that not all patients can be prescribed a similar collection to determine elements in urine. In order for a doctor to give a referral for such an analysis, the following reasons must be present:
- the presence of an inflammatory process concentrated in the genitourinary system;
- assessment of ongoing drug treatment;
- if there is a possibility of bleeding;
- if the patient is in childhood and has suspicions of diseases of the urinary organs and kidney function.
The presence of many red blood cells in urine means that normal substances (red blood cells) have penetrated the glomerular apparatus in the kidney area.
If a single amount of these substances is found in the biological material being studied, this is not a significant deviation in the overall functional system of the body.
An excessive number of red blood cells in urine can often be determined by the color of the liquid. If there is a sharp jump in the red blood cell ratio, then the attending physician may assume that the person has:
- Bleeding that occurred in the genitourinary system.
- Severe complication associated with kidney function. The glomerular apparatus located in the body is almost unable to contain the elements entering it.
- The presence of processes associated with oncology.
- The onset of an inflammatory process localized in the area of the bladder and urethra.
- The process of urolithiasis exacerbation of the disease. This may be due to damage to the walls of the ureter when the stone moves.
- Casts of protein origin located in the renal tubules. This means that a certain amount of protein has passed through the kidneys, which should not normally be present there.
Read our article on how to remove protein from urine.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko in children: norm and interpretation of results, collection of biomaterial
Along with instrumental diagnostic methods, various studies of biological fluids of the body are of great importance in recognizing diseases of various organs and systems.
General clinical and biochemical blood tests, stool examination, cerebrospinal fluid puncture, sputum microscopy, pleural fluid washout, and, of course, urine samples often play a decisive role in verifying the diagnosis.
Primary importance in identifying diseases of the genitourinary system in children is given to changes in urine tests. Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko complements the general study, bringing clarity to the differential diagnosis of the manifestations of various diseases of the urinary system.
READ ALSO: decoding the results of a biochemical blood test in children Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko allows the doctor to accurately diagnose and prescribe the correct treatment for the patient
Why is the study being conducted and what does it show?
A routine general clinical analysis of urine determines its physical properties (color, transparency, acidity, specific gravity), chemical composition, absence or presence of low molecular weight organic substances (sugar, protein) (we recommend reading: protein in the urine of a child: the norm and reasons for the increase). Sediment microscopy can detect impurities in the form of squamous epithelium, crystals, mucus or bacteria. The results of the Nechiporenko analysis, when collected correctly, show the quantitative composition of blood cellular elements in urine, their proportional ratio in 1 ml of urine sediment.
READ ALSO: Normal blood sugar levels in children: table
This study is prescribed if the doctor suspects chronic diseases of the urinary system with a latent course, or urinary tract infections. For example, if a general analysis showed a high level of white blood cells, pathological casts, bacteria or mucus were detected.
Assessment of the proportional ratio of cellular elements allows us to determine the degree and location of organ damage. Depending on the value, we can talk about dysfunction and damage to the kidneys, bladder or urethra.
Preparation and collection of urine for analysis
It is important to follow the following technique when a child is scheduled to take this test:
- It is unacceptable for teenage girls to submit urine for any analysis during menstruation;
- 1-2 days before the appointed day, it is not recommended to eat foods, drinks or medicines containing dyes, or take antibacterial or diuretic medications;
- refrain from physical and emotional overload;
- prepare a container for collecting biological material in advance; it is better to buy a special sterile jar at the pharmacy;
- before collecting urine, it is necessary to perform a thorough hygienic toilet of the external genitalia without soap or antiseptics;
- the first part of morning urine is skipped, the middle portion of 30–50 ml is collected for analysis in a prepared container;
- an hour to an hour and a half after collection, the sample should be delivered to the laboratory.
When such a urine sample is prescribed for an infant or child under one year of age, it is important to correctly collect the biological fluid. In order not to disrupt the algorithm of correct urine collection, it is worth using a special device - a pediatric urinal.
A children's urinal is a plastic bag with a hole and Velcro fasteners around it. The Velcro is absolutely safe for the baby’s delicate skin and is easy to stick on and remove.
Three types of urinals are available: for boys, girls and universal. The child's external genitalia is washed without detergents, and the skin is dried with a soft towel.
READ ALSO: how to collect urine from a baby boy with a urinal?
The urinal is then secured to the baby's skin so that the anus remains outside the opening of the urinal.
The excreted urine is collected in a bag.
After collecting a sufficient amount of liquid, a corner of the bag is cut off, the contents are poured into a previously prepared container, and the sample is sent to the laboratory.
Table with norms for children
When studying according to Nechiporenko, the amount of the following blood elements in the urine is calculated:
- leukocytes - white blood cells responsible for specific and nonspecific defense of the body, having the ability to penetrate the wall of the renal capillaries, absorb and destroy foreign agents, dying and forming an accumulation of dead red blood cells (pus);
- erythrocytes - red blood cells that transport oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and reverse transport of carbon dioxide from internal organs to the lungs;
- hyaline casts - microscopic protein casts of the kidney tubules.
Normal indicators for the number of formed elements in 1 ml of urine sediment are presented in the table:
| Shaped elements | Normal amount in 1 ml of urine sediment |
| Leukocytes | Until 2000 |
| Red blood cells | Up to 1000 |
| Hyaline casts | Up to 20 |
| Ratio of cellular elements leukocytes/erythrocytes | 2/1 |
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko should be carried out in the laboratory by experienced specialists
Explanation: what diseases does the analysis reveal?
Only the attending physician can correctly and competently decipher and interpret urine test results according to Nechiporenko. However, the presence of any disease can be assumed immediately upon receipt of laboratory results.
An excess of the normal number of leukocytes (leukocyturia) indicates an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system (we recommend reading: norms and elevated levels of leukocytes in the urine in children).
Depending on the level of excess of the norm, pyelonephritis, kidney infarction, urolithiasis, cystitis, urethritis can be suspected.
In addition to the above, leukocyturia in infants indicates ureteropelvic or vesicoureteral reflux.
High levels of red blood cells in the urine are called erythrocyturia (otherwise known as hematuria). Depending on the number of red blood cells, they speak of acute or chronic glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, kidney tumor, high level of general intoxication, kidney or bladder stones, hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney, cystitis, chronic renal failure.
READ ALSO: what do unchanged red blood cells in a child’s urine mean?
The detection of hyaline casts in an amount of more than 2 dozen indicates the beginning of inflammation of the renal pelvis - pyelitis. When combined with leukocyturia, one can judge the bacterial origin of the inflammation; with hematuria, one can judge about glomerulonephritis.
Sometimes the analysis determines the presence of cylinders of a different origin and structure (granular, waxy, erythrocyte). This indicates the possible progression of serious chronic kidney diseases - glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, the onset of kidney stones, and various nephropathies.
Decoding Nechiporenko's analysis
In the laboratory, urine is examined and leukocytes and red blood cells are counted. All interpretation of the results is noted in the direction. Decoding of the analysis in 1 milliliter of collection:
Analysis rate:
- Protein - no.
- Cylinders – maximum 20.
- Leukocytes – maximum 2000.
- Red blood cells – 1000.
- Bacteria - no.
This is the result of tests on healthy children. If there are deviations from the norm, then the children have a genitourinary or kidney disease.
If elevated leukocytes are found in children, then the genitourinary area is suffering in children, the doctor discovers:
- Cystitis.
- Stones in the kidneys.
- Pyelonephritis.
When the red blood cell count is elevated, the following disease is detected:
- Pyelocystitis.
- Kidney failure, tumor processes.
If the cylinders in the urine increase, it means a kidney tumor, or nephrosis, or pyelonephritis. As a rule, if elevated values are detected, doctors send for repeated collection of tests.